基于MySQL8.0版本
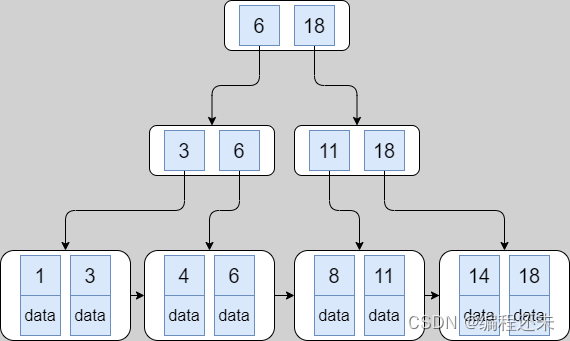
1.聚集索引简介
每个表都有一个称为聚集索引的特殊索引,用于存储行数据。通常,聚集索引与主键同义。
注意:
- 创建表的时候应该设置一个索引,使用唯一非空的列或列集,或使用自动递增列;
- 未设置主键,则使用第一个索引作,并将所有键列定义为聚集索引;
- 没有索引或适合做索引的列,则生成一个隐藏的聚集索引。以包含行ID值的综合列命名,行ID是一个6字节的字段,自增,按插入顺序排序。
2.聚集索引如何加快查询速度
- 索引搜索直接指向包含行数据的页面;
- 表很大的时候,使用聚集索引通常会节省磁盘I/O操作。
3.二级索引
聚集索引以外的索引称为二级索引。二级索引的每条记录都包含行的主键列,以及为二级索引指定的列。使用此主键值在聚集索引中搜索行。
主键很长,则二级索引会占用更多空间,推荐使用短主键。
4.MySQL如何使用索引
索引用于快速查找列。
没有索引的话,则需要从第一行开始遍历整个表。表越大,成本越高。
大多数MySQL索引存储在B-Tree(其实是B+树,B+Tree也是B-Tree的一种,B-Tree=B Tree)中。
空间数据类型的索引使用R树;表还支持hash索引;
MySQL使用索引进行以下操作:
-
快速查找与where子句匹配的行。
-
如果需要在多个索引之间选择,通常使用查找最小行数的索引(最具选择性的索引)。
-
多列索引,使用最左前缀来查找。举个栗子:
# 创建多列索引 create index user_name_no_age_index on user (name, no, age);验证
-
生效的三种情况,最左匹配
#生效 mysql> explain select * from user where name='张三'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 43 | const | 3 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+#生效 mysql> explain select * from user where name='张三' and no='1'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 48 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+#生效 mysql> explain select * from user where name='张三' and no='1' and age=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 53 | const,const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ -
部分生效,最左匹配中间断了
#部分生效 mysql> explain select * from user where name='张三' and age=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 43 | const | 3 | 10.00 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ -
不生效的三种情况
#不生效 mysql> explain select * from user where no='1' and age=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 28 | 3.57 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+#不生效 mysql> explain select * from user where no='张三'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 28 | 10.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+#不生效 mysql> explain select * from user where age=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 28 | 10.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
-
join查询时,从其他表中检索。如果讲列声明为相同的类型和大小,会更有效的使用列上的索引。对于该条,VARCHAR和CHAR声明相同的的大小,会被认为是相同的。
非二进制字符串列之间,两列应该使用相同的字符集,否则索引会失效。
不进行转换无法直接比较的值,比较的时候会使索引失效。例如字符列和数字列比较,数字列可能和字符串中的任意数量的值比较。
#week_price是int(11),name是varchar(50) mysql> select d.week_price, a.name from abcd d join abc a on d.week_price = a.name where d.week_price = 11; +------------+------+ | week_price | name | +------------+------+ | 11 | 11 | | 11 | 0011 | +------------+------+ -
查找索引列的MIN()或MAX()值,预处理器会优化,如果表达式为常量,则查询会立即返回。
SELECT MIN(key_part2),MAX(key_part2) FROM tbl_name WHERE key_part1=10; -
order by 或 group by可以按最左前缀使用索引。如果是降序索引,按正向顺序取值;升序索引反之。
-
某些情况下,可以优化查询检索值,不需要查询数据行。(为查询提供所有必要结果的索引称为索引覆盖,在select的数据列只用从索引中就能获取到,换言之,查询列被所建的索引覆盖了。)。如果索引覆盖,会提升查询速度。减少一次回表的IO。(回表,指在二级索引中查到主键,再回到主键索引、聚集索引再查数据行)
# 创建多列索引 create index user_name_no_age_index on user (name, no, age);索引覆盖查询
mysql> explain select name,no,age from user where name='张三' and no='1'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 48 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------------+非索引覆盖
mysql> explain select name,no,age,time from user where name='张三' and no='1'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 48 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+mysql> explain select * from user where name='张三' and no='1' and age=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_name_no_age_index | user_name_no_age_index | 53 | const,const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+
对于小表上的查询;报表查询处理大部分或全部行的大表,索引不太重要。需要查询大多数行的时候,按顺序读取比索引查询更快,顺序读取可以减少硬盘检索。
关注公众号- 编程highway - 获取更多好文和学习资料























 1万+
1万+












