在上一章《Shiro步步为营--Springboot开启身份验证》中,我们并未编写任何关于密码校验的代码,却实现了用户登录身份验证。很显然,密码的比对工作是由Shiro来帮我们实现了,接下来,我们就先来看看Shiro是如何完成密码比对的。
密码比对过程分析
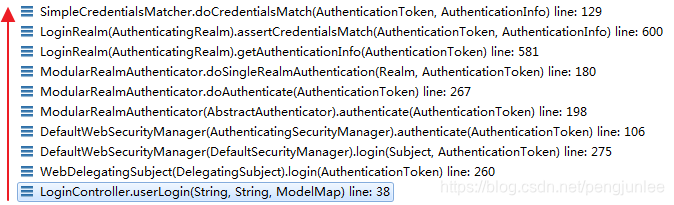
在调用 subject.login(token) 方法后,其内部会通过 LoginRealm 调用父类 AuthenticatingRealm 的 assertCredentialsMatch() 方法来进行密码比对。代码如下:
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info)
throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取 Realm 实例中的 CredentialsMatcher 属性
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();
if (cm != null) {
// 调用 CredentialsMatcher 实例的 doCredentialsMatch() 方法对 Token 和 Info
// 中的密码进行比对
if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {
// not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:
String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);
}
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify "
+ "credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you "
+ "can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");
}
}最终是调用的 CredentialsMatcher 实例的 doCredentialsMatch() 方法对 Token 和 Info 中的密码进行比对。在本例中, LoginRealm 的 redentialsMatcher 属性并未设置,默认使用 SimpleCredentialsMatcher。比对代码如下:
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
// 取 AuthenticationToken 中的密码
Object tokenCredentials = getCredentials(token);
// 取 AuthenticationInfo 中的密码
Object accountCredentials = getCredentials(info);
// 判断二者是否相同
return equals(tokenCredentials, accountCredentials);
}设置加密算法
在实际项目中,将密码明文保存到数据库中存在极大的安全隐患,推荐的做法是:将密码使用不可逆算法加密,并将加密后的密文保存到数据库中。身份验证时,将用户输入的密码使用相同的算法加密,再将获得的密文与数据库中保存的密文做比较,判断密码是否正确。
AuthenticatingRealm 默认的 SimpleCredentialsMatcher 不使用任何的加密算法,获取到 AuthenticationToken 和 AuthenticationInfo 中的密码后直接进行比对。
为 Realm 设置加密算法非常简单,使用 HashedCredentialsMatcher 替换掉默认的 SimpleCredentialsMatcher 即可。
/**
* Realm配置,需实现 Realm 接口
*/
@Bean
LoginRealm loginRealm() {
LoginRealm loginRealm = new LoginRealm();
// 设置加密算法
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher("SHA-1");
// 设置加密次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(16);
loginRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return loginRealm;
}HashedCredentialsMatcher 支持的加密算法有如下几个:
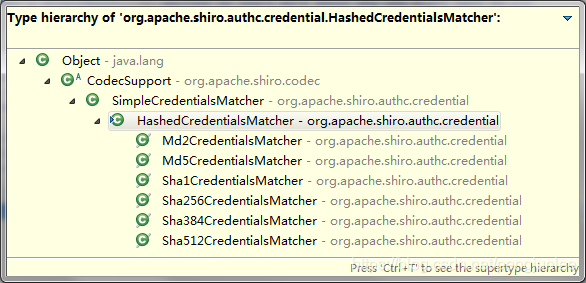
HashedCredentialsMatcher 的 doCredentialsMatch() 方法代码如下:
@Override
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
// 取 AuthenticationToken 中的密码经算法加密后的结果
Object tokenHashedCredentials = hashProvidedCredentials(token, info);
// 取 AuthenticationInfo 中的密码
Object accountCredentials = getCredentials(info);
// 判断二者是否相同
return equals(tokenHashedCredentials, accountCredentials);
}设置盐值加密
盐值加密可以实现:即使是密码相同的不同用户,保存到数据库中的密文也应不同。关于 “盐值” 有如下两个要求:盐值必须唯一、盐值不可改变。
在 LoginRealm 中为 SimpleAuthenticationInfo 加入盐值。
// 使用用户名作为盐值
ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username);
/**
* 将获取到的用户数据封装成 AuthenticationInfo 对象返回,此处封装为 SimpleAuthenticationInfo 对象。
* 参数1. 认证的实体信息,可以是从数据库中获取到的用户实体类对象或者用户名
* 参数2. 查询获取到的登录密码
* 参数3. 盐值
* 参数4. 当前 Realm 对象的名称,直接调用父类的 getName() 方法即可
*/
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPassword(), credentialsSalt,
getName());
return info; /**
* 可以使用如下方法获取某一字符串加密后的密文
* algorithmName 算法类型 例:SHA-1
* source 要加密的字符串
* salt 盐值
* hashIterations 加密次数
*/
new SimpleHash(String algorithmName, Object source, Object salt, int hashIterations)设置多Realm
对于一些比较大型的项目,存储用户的数据源可能会有多个,这在 Shiro 中就意味着需要创建多个 Realm ,各 Realm 所使用的加密算法可以不同。例如,下面这两个 Realm 。
/**
* Realm1 配置,需实现 Realm 接口
*/
@Bean
LoginRealm loginRealm() {
LoginRealm loginRealm = new LoginRealm();
// 设置加密算法
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher("SHA-1");
// 设置加密次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(16);
loginRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return loginRealm;
}
/**
* Realm2 配置,需实现 Realm 接口
*/
@Bean
UserRealm userRealm() {
UserRealm userRealm = new UserRealm();
// 设置加密算法
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher("MD5");
// 设置加密次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(16);
userRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return userRealm;
}在 Shiro 配置多Realm 可以通过如下两种方式:
- 方式一 在 ModularRealmAuthenticator 中配置多个Realm
- 方式一 在 SecurityManager 中配置多个Realm
方式一
/**
* 配置 SecurityManager
*/
@Bean
public SecurityManager securityManager() {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
// 将 Authenticator 设置给 SecurityManager
securityManager.setAuthenticator(authenticator());
return securityManager;
}
/**
* 配置 ModularRealmAuthenticator
*/
@Bean
public ModularRealmAuthenticator authenticator() {
ModularRealmAuthenticator authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
List<Realm> realms = new ArrayList<Realm>(16);
realms.add(loginRealm());
realms.add(userRealm());
// 设置多 Realm
authenticator.setRealms(realms);
// 设置多 Realm 的认证策略,默认 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy
AuthenticationStrategy strategy = new FirstSuccessfulStrategy();
authenticator.setAuthenticationStrategy(strategy);
return authenticator;
}
方式二
/**
* 配置 SecurityManager
*/
@Bean
public SecurityManager securityManager() {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
// 先将 Authenticator 设置给 SecurityManager
securityManager.setAuthenticator(authenticator());
// 再将多个 Realm 设置给 SecurityManager
List<Realm> realms = new ArrayList<Realm>(16);
realms.add(loginRealm());
realms.add(userRealm());
securityManager.setRealms(realms);
return securityManager;
}
/**
* 配置 ModularRealmAuthenticator
*/
@Bean
public ModularRealmAuthenticator authenticator() {
ModularRealmAuthenticator authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
// 设置多 Realm的认证策略,默认 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy
AuthenticationStrategy strategy = new AllSuccessfulStrategy();
authenticator.setAuthenticationStrategy(strategy);
return authenticator;
}此时,需要注意必须先设置 Authenticator 再设置 Realms ,否则登录认证时会出现如下错误:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Configuration error: No realms have been configured! One or more realms must be present to execute an authentication attempt.认证策略
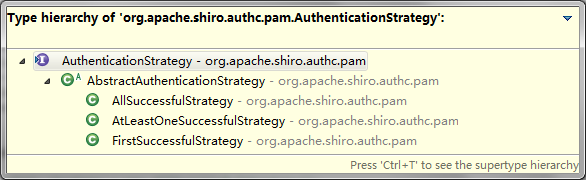
ModularRealmAuthenticator 可选的认证策略有下面几个:





 本文深入解析Shiro框架中的密码比对机制,包括默认的SimpleCredentialsMatcher及如何通过HashedCredentialsMatcher实现密码加密比对。同时,介绍了如何在多数据源环境下配置多个Realm并设置不同的加密算法。
本文深入解析Shiro框架中的密码比对机制,包括默认的SimpleCredentialsMatcher及如何通过HashedCredentialsMatcher实现密码加密比对。同时,介绍了如何在多数据源环境下配置多个Realm并设置不同的加密算法。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








