6. 字符串z字形变换
string convert(string s, int numRows) {
if (numRows < 2)
return s;
vector<string> rows(numRows, "");
string zString_;
int curRow = 0;
// 由于数组以0指标开始的访问方式,对numRows做减1操作
numRows--;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
curRow = ((i / numRows) % 2) == 0 ? i % numRows :
((i / numRows) % 2) * numRows - i % numRows;
rows[curRow] += s[i];
}
for (auto str : rows)
zString_ += str;
return zString_;
}
8. 字符串转换整数atoi
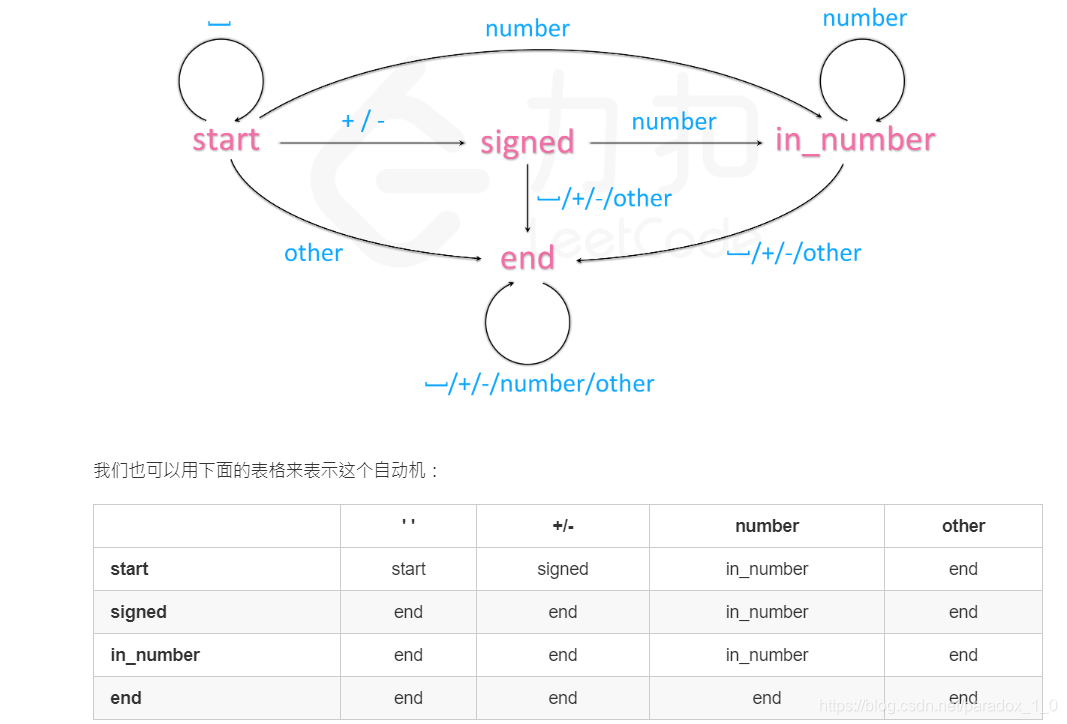
这里实现了一个非常标准的状态机,也算是一种复习,状态转换图这里是使用了官网的思路。
状态转换图:
实现代码:
class Solution {
public:
enum class STATE {
Start,
Signed,
In_Number,
End,
};
enum class END_STATE {
Error,
Overflow,
Normal,
};
/* if true when s2 > s1*/
bool stringCmp(const string& s1, const string& s2) {
if (s2.length() > s1.length())
return true;
if (s2.length() == s1.length())
return s1 < s2;
return false;
}
int mypow(int n, int e) {
int count_ = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++)
count_ *= n;
return count_;
}
int myAtoi(string str) {
for (int i = 0; i <= str.length(); ) {
switch (m_state_)
{
case STATE::Start:
{
if (str[i] == ' ') {
i++; continue;
}
else if (str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+') {
m_state_ = STATE::Signed;
}
else if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') {
m_state_ = STATE::In_Number;
m_signed_ = 1;
}
else {
m_state_ = STATE::End;
m_end_state_ = END_STATE::Error;
}
}
break;
case STATE::Signed:
{
m_signed_ = str[i] == '-' ? -1 : 1;
m_state_ = STATE::In_Number;
i++;
}
break;
case STATE::In_Number:
{
// 去除首部 0
while (i < str.length()) {
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') {
if (str[i] != '0')
break;
i++;
}
else
break;
}
while (i <= str.length()) {
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') {
m_number_str_ += str[i];
i++;
}
else {
m_state_ = STATE::End;
break;
}
if ((m_signed_ == 1 && !stringCmp(m_number_str_, m_int_max_str_)) ||
(m_signed_ == -1 && !stringCmp(m_number_str_, m_int_min_str_))) {
m_state_ = STATE::End;
m_end_state_ = END_STATE::Overflow;
}
}
}
break;
case STATE::End:
{
switch (m_end_state_)
{
case END_STATE::Error:
return 0;
case END_STATE::Overflow:
return m_signed_ == -1 ? INT_MIN : INT_MAX;
case END_STATE::Normal:
{
int val_ = 0;
int length_ = m_number_str_.length();
for (int j = length_ - 1; j >= 0; j--)
val_ += (m_number_str_[j] - '0') * mypow(10, length_ - j - 1);
return m_signed_ == -1 ? -val_ : val_;
}
default:
break;
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
private:
// 状态
STATE m_state_{ STATE::Start };
// 最终子状态
END_STATE m_end_state_{ END_STATE::Normal };
// 符号
int m_signed_{ 1 };
// 当前数字字符串
string m_number_str_{ "" };
// 最大int和最小int的字符串形式
const string m_int_min_str_ = "2147483648";
const string m_int_max_str_ = "2147483647";
};
执行结果:

13. 罗马数字转整数
int romanToInt(string s) {
int cout_ = 0;
unordered_map<char, int> map_{ {'I', 1},
{'V', 5},
{'X', 10},
{'L', 50},
{'C', 100},
{'D', 500},
{'M', 1000} };
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0;) {
int unitCount_ = map_.find(s[i--])->second;
while (i >= 0 && map_.find(s[i])->second < map_.find(s[i + 1])->second) {
unitCount_ -= map_.find(s[i])->second;
i--;
}
cout_ += unitCount_;
}
return cout_;
}







 本文深入探讨了字符串处理的高级技巧,包括Z字形变换算法和状态机实现的字符串转换整数功能,以及罗马数字到整数的转换方法。通过具体代码示例,详细解析了每种算法的工作原理和实现细节。
本文深入探讨了字符串处理的高级技巧,包括Z字形变换算法和状态机实现的字符串转换整数功能,以及罗马数字到整数的转换方法。通过具体代码示例,详细解析了每种算法的工作原理和实现细节。
















 487
487

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








