文章目录
一、Devtools
Devtools 是一个用来调试 Vue 程序的谷歌浏览器插件
安装到谷歌浏览器
1) Github 中下载
① 在 Devtools Github 下载 devtools 源码,注意不要选择 beta 分支,例中版本是 v5.3.4

② 选择 Zip 下载

2) 拉取 Devtools 需要的依赖
① 将下载的 Zip 解压后,进入 Devtools 的根目录,如下图:

② 在根目录打开 CMD 窗口,运行 npm install ,安装 devtools 需要的依赖包,本地需要有 node.js 环境

3) 构建 Devtools
① 下载完依赖后,继续运行命令,npm run build 来构建 devtools

4) 修改 Devtools 配置文件
② 将 devtools-5.3.4\packages\shell-chrome\manifest.json 中的 persistent 属性改为 true

5) 将插件安装到谷歌浏览器
① 打开谷歌浏览器的 更多工具-> 扩展程序

② 打开谷歌浏览器的扩展程序后会出现下图画面,先选择开发者模式、在点击加载已解压的扩展程序,最后选中我们的 devtools,v5.3.4 版本的路径为 devtools-5.3.4\packages\shell-chrome

③ 添加成功后,会像下图一样,显示出 Vue.js devtools 插件

6) 验证插件是否安装成功
用 Vue-CLI 脚手架创建一个 Vue 项目,然后浏览器运行项目,按 F12,看看是否像下图一样多出 vue 选择项

二、变量的共享
1. 创建共享变量文件的方式
当我们想在多个组件中使用同一变量时,可以用共享变量文件的方式解决,简单说就是单独创建一个 JS 文件,并将所有要共享的变量都定义在该文件中,最后使用模块化导出的方式将这些变量导出
用例子演示一下共享变量文件的具体实现方式,假设需求:
有一个计数器和两个组件,两个组件分别要实现计数器递增和递减的操作,在一个组件中操作计数器后,计数器最新的值会影响另一个组件,另一个组件对计数器的所有操作,都要基于最新值,很显然我们只需要把计数器变量共享出来,然后让两个组件都使用该变量就可以了
1) 创建项目
使用脚手架命令 vue init webpack vuex-study,创建一个单页面的 Vue 项目

2) 创建共享变量文件
在项目中创建文件夹 src/js,然后在文件夹内创建文件 src/js/common.js,文件中定义一个计数器并将其导出 :
export default {
count: 0
}
3) 创建两个组件
① 创建组件A, 目录:src/components/A.vue, 内容如下:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件A 当前计数为:{{ count }}</div>
<div><button @click="getCount">获取最新计数</button></div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button
><button @click="decrement">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import COMMON from '../js/common'
export default {
data() {
return {
count: COMMON.count
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
COMMON.count++
this.count = COMMON.count
},
decrement() {
COMMON.count--
this.count = COMMON.count
},
getCount() {
this.count = COMMON.count
}
}
}
</script>
② 创建组件B, 目录:src/components/B.vue, 内容如下:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件B 当前计数为:{{ count }}</div>
<div><button @click="getCount">获取最新计数</button></div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button
><button @click="decrement">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import COMMON from '../js/common'
export default {
data() {
return {
count: COMMON.count
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
COMMON.count++
this.count = COMMON.count
},
decrement() {
COMMON.count--
this.count = COMMON.count
},
getCount() {
this.count = COMMON.count
}
}
}
</script>
4) 修改入口组件
修改入口组件 src/App.vue 文件,在组件内使用组件A和组件B:
<template>
<div id="app">
<A></A>
<br />
<B></B>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import A from './components/A'
import B from './components/B'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
A,
B
}
}
</script>
5) 运行查看效果
① 此时项目结构如下:

② 使用 npm run dev 运行后查看效果:
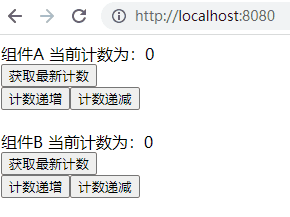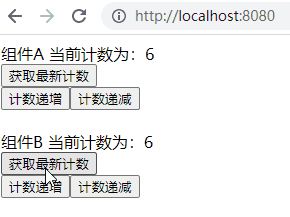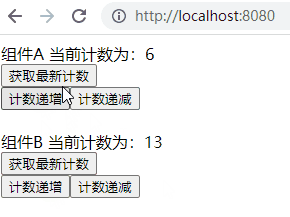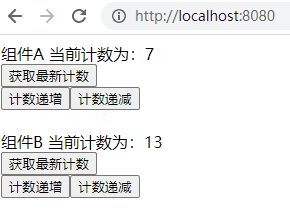
运行结果很明显,不管操作哪个组件改变了计数器的值,其都会对另一个组件产生影响
2. 使用 Vuex 的方式共享变量
Vuex 是 Vue 的一个插件,其本质也为了解决共享变量问题的,可能会好奇,既然都是解决共享变量问题,为什么要选择 Vuex 呢,其实细心琢磨共享变量文件的方式,我们能发现一个弊端,当共享变量进行多次修改时,我们只能看见最后一次结果,中间其他次修改的过程我们很难统计,这就导致有时候调试很不方便
使用 Vuex 的方式,每次修改共享变量的时候都会记录修改信息,并可以搭配 Devtools 对修改记录进行查看,所以使用 Vuex 可以更好的帮助我们调试项目,使用 Vuex 还有一个优点,就是用它定义的共享变量是响应式的
接下来将记录如何使用 Vuex 实现前面的需求,更多详细的 Vuex 的使用方式建议参照 Vuex 中文官网
1. Vuex 的安装
1) 下载 Vuex 模块
在项目的根路径使用 CMD 来运行命令 npm install vuex@3.0.0 --save ,如果我们项目中使用的是 Vue 2.x ,尽量不要使用 Vuex 4.x 以上版本,最好指定版本来安装 Vuex

2) Vue 项目中安装 Vuex 模块
① 我们需要使用 Vuex.Store 对象来管理共享变量,一般习惯将这个对象创建在一个专门管理 Vuex 信息的文件中,所以我们先创建用来管理 Vuex 的目录和文件 src/store/index.js,下面代码就是一个 Vuex 的最基本配置:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
② 修改入口文件,将我们的 Vuex 配置模块传入,重点在第 6 行和第 11 行:
// 导入 Vue 模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入项目入口模块
import App from './App'
// 导入我们创建的 Vuex 配置模块
import store from './store/index.js'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 此处 store 必须小写
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
2. Vuex 核心属性 - state
state 对象是 Vuex.Store 对象的一个核心属性,它用来真正的定义共享变量
1) 添加 Vuex.Store 中的核心属性 - state
在 src/store/index.js 文件中添加 state 属性,定义计数器共享变量,重点代码在 第12 ~ 14 行:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
2) 重写 组件A 和 组件B
重写两个组件,在组件内我们可以使用 Vue 的全局属性 $store.state.共享变量名 来访问我们定义的共享变量,如果在函数内访问 Vue 全局属性,不要忘了需要加上 this,如 this.$store.state.共享变量名
① 组件A src/components/A.vue:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件A 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="$store.state.count++">计数递增</button>
<button @click="$store.state.count--">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
② 组件B src/components/B.vue:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件B 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="$store.state.count++">计数递增</button>
<button @click="$store.state.count--">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
3) 查看运行效果
运行项目查看功能实现效果,并使用 Devtools 来观察共享变量的变更记录
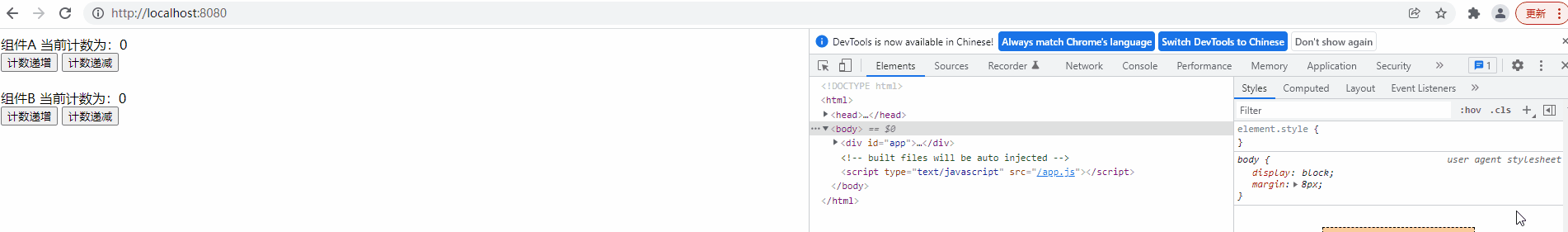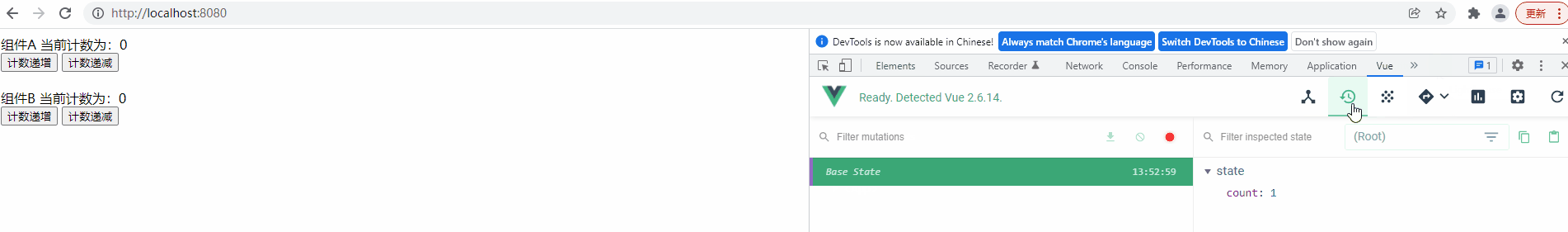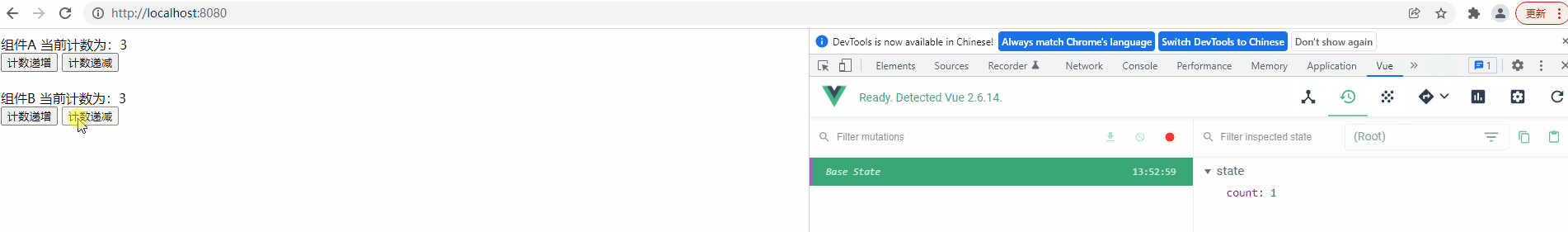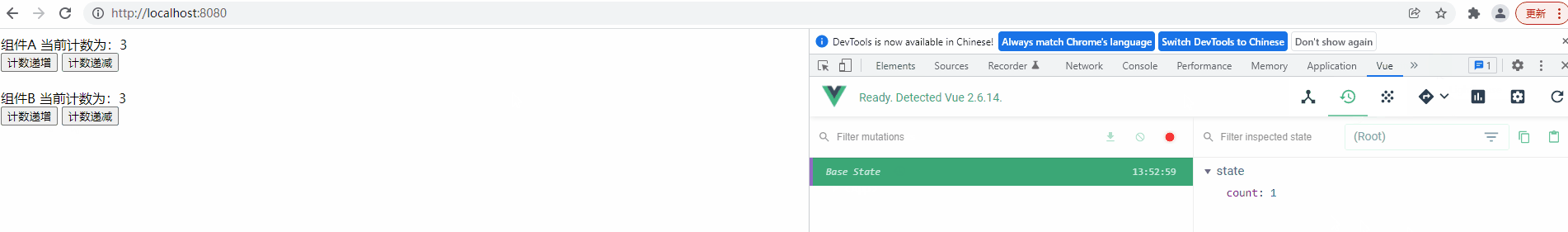
测试后发现,程序能满足任意组件操作计数器后会影响另一个组件的效果,而且可以看出 Vuex 中定义的变量是响应式的,当一个组件改变计数器值后,另一个组件会马上显示出最新结果
最后在 Devtools 的 Vuex Tab 中也能看见我们定义的变量,但有一个问题,操作变量后并没有将变量的最新值同步到Devtools 中,而且 Devtools 中也没显示操作记录,这是因为我们操作共享变量的方式不正确,需要使用特殊的方式
3. Vuex 核心属性 - mutations
前面我们已经知道了,在组件里操作 Vuex 定义的共享变量,可以使用 $store.变量名 的方式,但是这种写法只适合访问变量,不适合修改变量,虽然这种方式确实可以将变量修改成功,但是修改后的值却不能同步到 Devtools 中,我们接下来要记录另外一种修改共享变量并可以同步到 Devtools 中的方式,它也是 Vuex.Store 对象的核心属性 mutations
1) 添加 Vuex.Store 中的核心属性 - mutations
在 src/store/index.js 文件中添加 mutations 属性,定义操作共享变量的函数,重点代码在 第15 ~ 23 行:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义共享变量的修改方式
mutations: {
increment(state, params) {
state.count += params
},
decrement(state, params) {
state.count -= params.step
}
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
在 mutations 中定义的函数,被调用时会被传入两个参数,第一个参数是 Vuex.Store 中定义的state 对象,第二个参数是我们调用该方法时传进来的任意类型
2) 修改 组件A 和 组件B
修改两个组件,通过 $store.commit 调用 mutations 中定义的操作共享变量的函数,$store.commit 调用函数时传参两种方式,第一种是传入 mutations 中定义的方法名,第二种是传入一个对象,对象的 type 属性是 mutations 中定义的方法名,payload 属性是想传给 mutations 中定义的函数的任意数据,既上面代码 increment(state, params) 中params 的实参
① 组件A src/components/A.vue,重点在第 11 ~ 22 行:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件A 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('increment', 1)
},
decreament(){
this.$store.commit({type:'decrement', step:1})
}
}
}
</script>
② 组件B src/components/B.vue,重点在第 11 ~ 22 行:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件B 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('increment', 1)
},
decreament(){
this.$store.commit({type:'decrement', step:1})
}
}
}
</script>
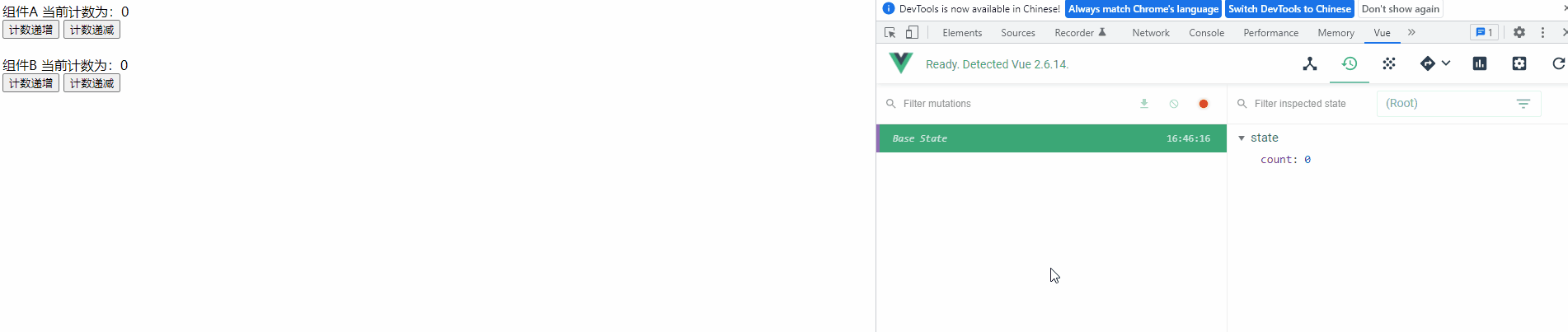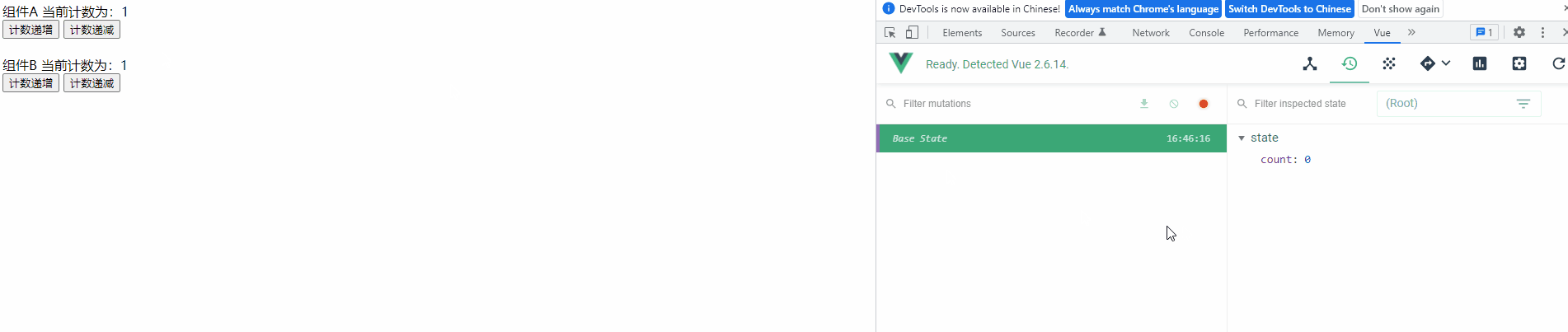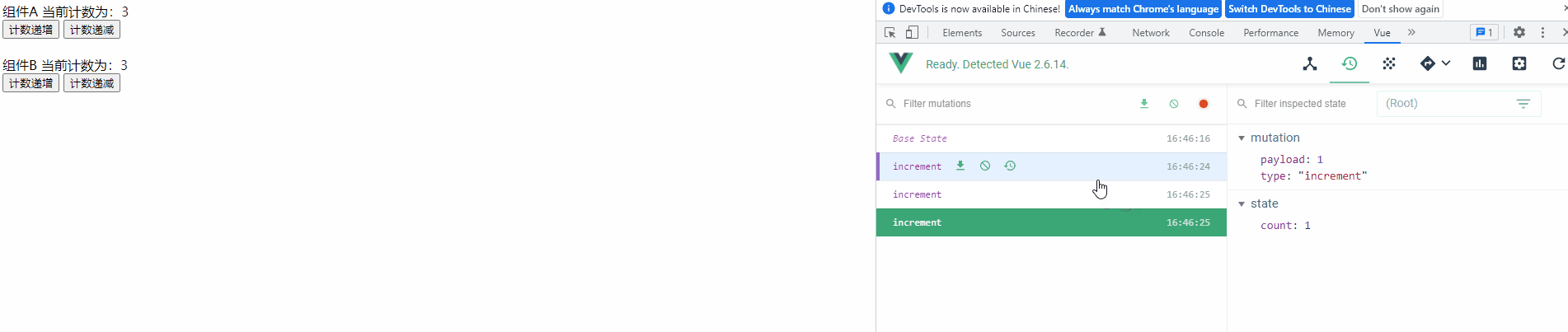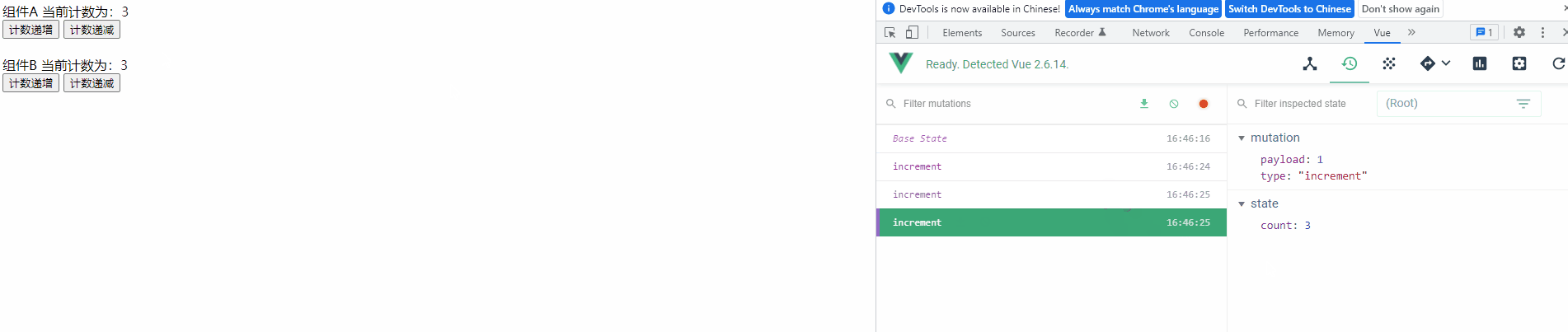
3) 查看运行效果
运行项目,可以发现变量的每次修改都记录在Devtools 中
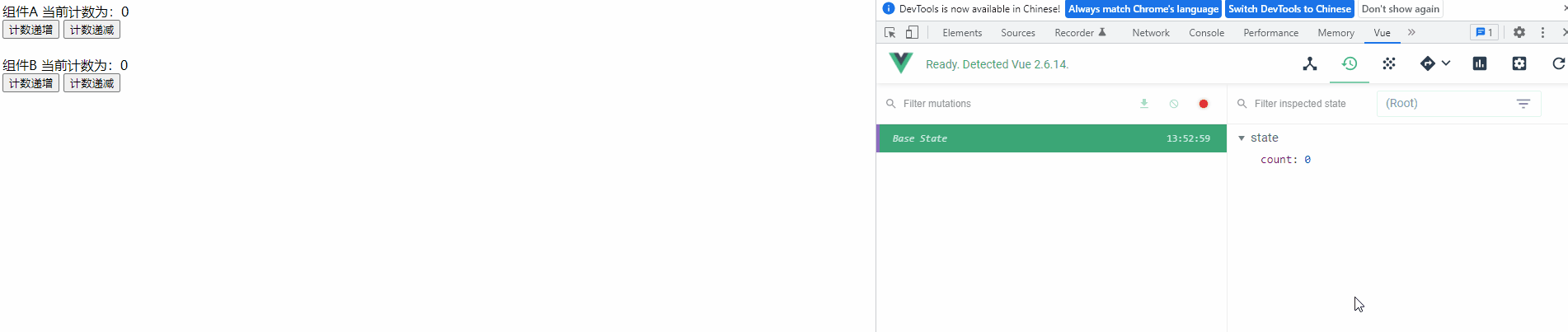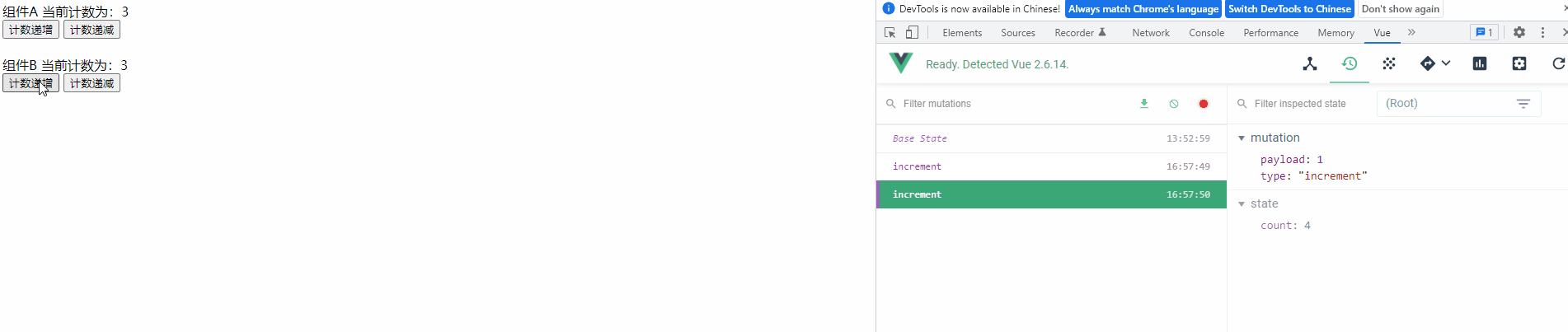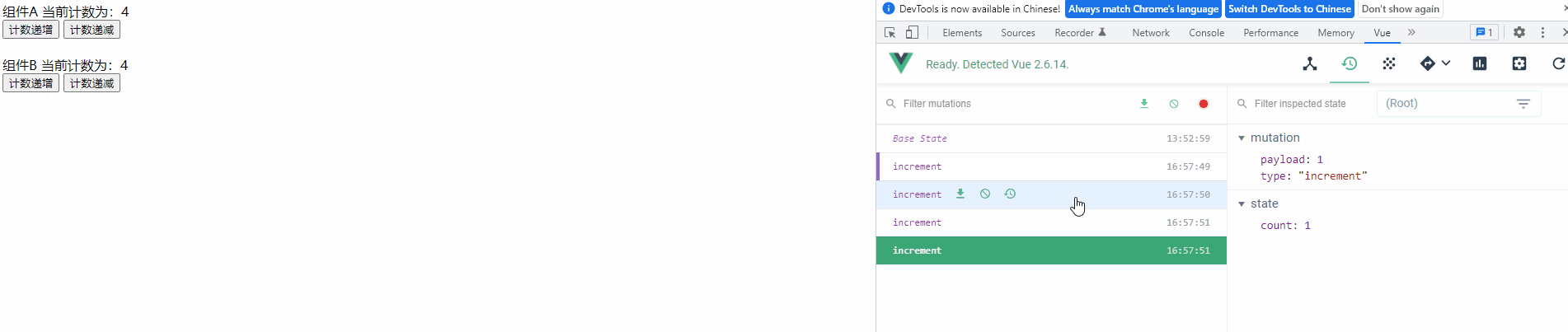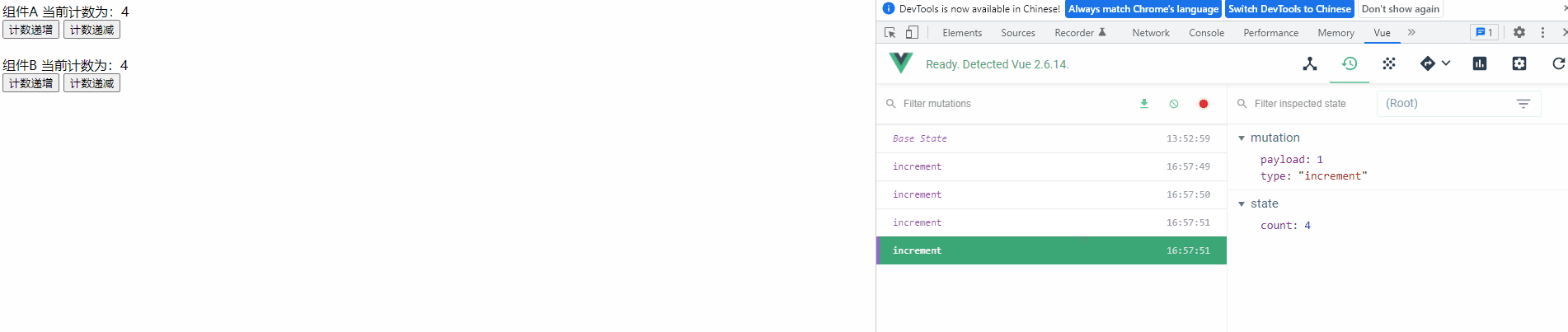
4) 定义常量文件
我们使用 $store.commit 调用 mutations 中定义的方法时,需要向 commit 函数传入要调用的方法名,这时候很容易出现名字拼错的情况,所以一般在实际开发的时候,会创建一个文件专门定义方法名
① 创建定义方法名的文件, src/store/storeConstants.js, 内容如下:
// 定义函数名 increment
export const INCREMENT = 'increment'
// 定义函数名 decrement
export const DECREMENT = 'decrement'
② 修改 src/store/index.js 文件,重点代码在第 6 、19、22 行:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from './storeConstants'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义共享变量的修改方式
mutations: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT](state, params) {
state.count += params
},
[STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT](state, params) {
state.count -= params.step
}
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
③ 修改组件A,src/components/A.vue 文件,重点在第 13、18、21 行:
<template>A
<div>
<div>组件A 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from '../store/storeConstants'
export default {
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit(STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT, 1)
},
decreament(){
this.$store.commit({ type: STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT, step: 1 })
}
}
}
</script>
修改后,不管是 mutations 中定义函数的地方,还是组件A 中调用函数的地方,都统一使用了方法名常量模块,这样可以很好的避免我们编码时手误写错方法名
4. Vuex 核心属性 - actions
当我们在 mutations 定义的方法中,对共享变量进行异步操作时,修改后的值是不会同步到 Devtools 中的,或者显示的也不准,这种对共享变量进行异步修改的情况,推荐使用 Vuex 的另一个核心属性 actions
actions 中用来定义异步操作共享变量的方法,但是一定要注意的是,在这些方法中不能直接操作共享变量,而是要通过调用 mutations 中的方法才可以
假设我们将需求改为,组件A 对计数器递增的时候要延迟 2 秒,我们就可以向下面这样做
1) 修改常量文件
修改 src/store/storeConstants.js,新增常量,代码在第 5、6 行:
// 定义函数名 increment
export const INCREMENT = 'increment'
// 定义函数名 decrement
export const DECREMENT = 'decrement'
// 定义函数名 incrementAction
export const INCREMENT_ACTION = 'incrementAction'
2) 添加 Vuex.Store 中的核心属性 - actions
在 actions 中定义的函数,被调用时会被传入两个参数,第一个参数是 Vuex.Store 对象,第二个参数是我们调用该方法时传进来的任意类型
在 src/store/index.js 文件中添加 actions 属性,定义延迟操作共享变量的函数,重点代码在 第 26 ~ 31 行:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from './storeConstants'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义共享变量的修改方式
mutations: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT](state, params) {
state.count += params
},
[STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT](state, params) {
state.count -= params.step
}
},
// 定义异步操作共享变量的方法
actions: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT_ACTION](context, params) {
setTimeout(() => context.commit(STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT, params), 2000)
}
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
3) 修改组件A
通过使用 $store.dispatch 来调用 actions 中的方法,dispatch 的用法及参数与 $store.commit 一样
修改组件A,src/components/A.vue 文件,重点在第 18 行:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件A 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from '../store/storeConstants'
export default {
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.dispatch(STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT_ACTION, 1)
},
decreament() {
this.$store.commit({ type: STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT, step: 1 })
}
}
}
</script>
4) 查看运行效果
运行项目,可以发现变量在延迟修改后,可以成功的同步到 Devtools 中
5. Vuex 核心属性 - getters
我们之前都是通过 $store.state.变量名 的方式来访问共享变量,但是有时候我们不想直接展示这个变量的值,而是要对其进行计算或包装后显示,所以需要在各个组件内编写计算逻辑方法,如果多个组件的计算逻辑都相同,会造成很多重复代码,而且修改时工作量也会变大
这种情况时,可以通过 getters 属性,对相同的计算逻辑进行统一定义,这可以很好的避免代码重复,使用 getters 还有一个优点, getters 中定义的计算逻辑执行后会对结果进行缓存来提升访问性能,直到共享变量变化了才会重新执行
1) 添加 Vuex.Store 中的核心属性 - getters
在 getters 中定义的函数,被调用时会被传入两个参数,第一个参数是 Vuex.Store 对象的 state 属性,第二个参数是 Vuex.Store 对象的 getters 属性,说白了就是在方法里还可以调用其他 getters
在 src/store/index.js 文件中添加 getters 属性,让访问共享变量时增加一些话术,重点代码在 第 32 ~ 37 行:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from './storeConstants'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义共享变量的修改方式
mutations: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT](state, params) {
state.count += params
},
[STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT](state, params) {
state.count -= params.step
}
},
// 定义异步操作共享变量的方法
actions: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT_ACTION](context, params) {
setTimeout(() => context.commit(STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT, params), 2000)
}
},
// 定义共享变量的计算方法
getters: {
getCount(state, getters) {
return '共享变量递增后的值是: ' + state.count
}
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
3) 修改组件B
修改 src/components/B.vue 文件,使用 $store.getters.方法名 来调用 getters 中的方法,,重点在第 3 行:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件B 当前计数为:{{ $store.getters.getCount }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('increment', 1)
},
decreament(){
this.$store.commit({type:'decrement', step:1})
}
}
}
</script>
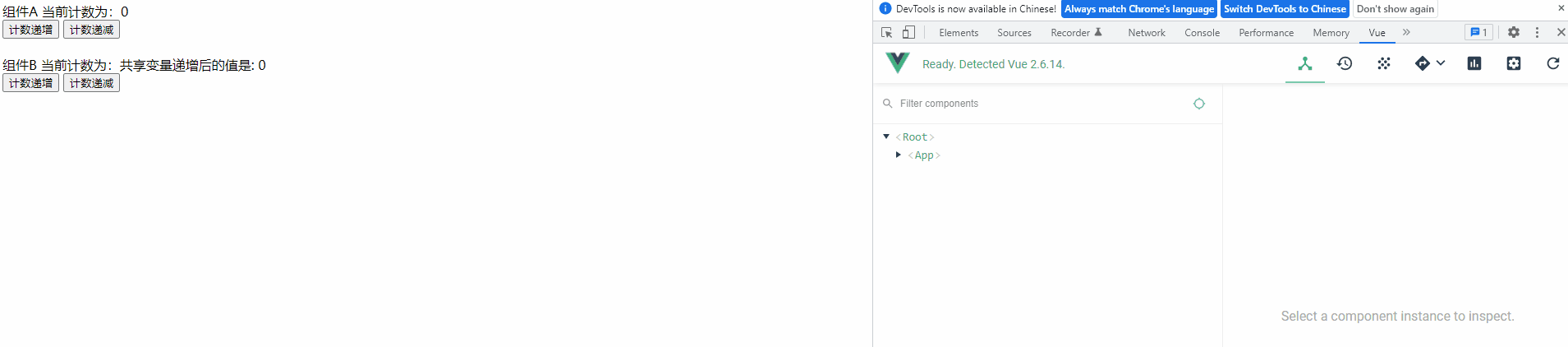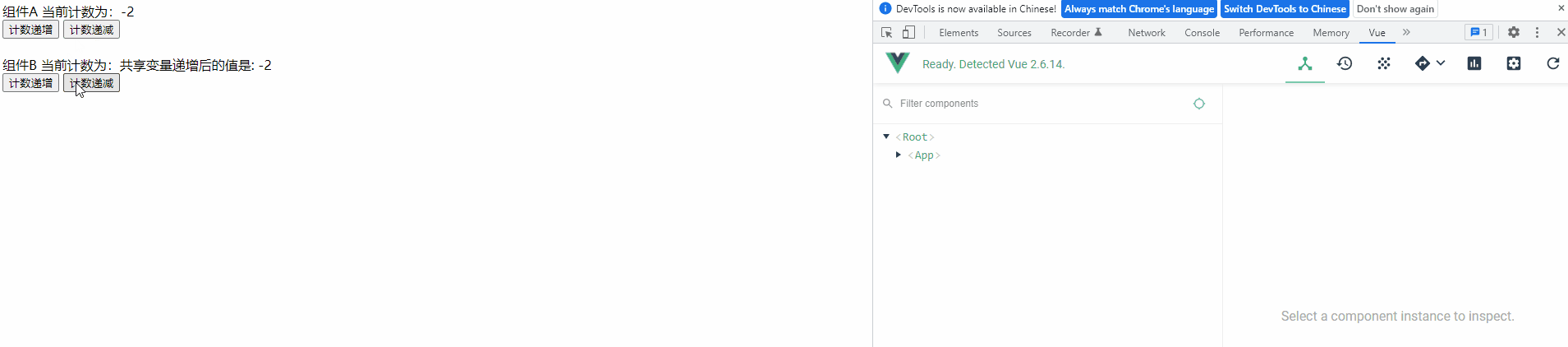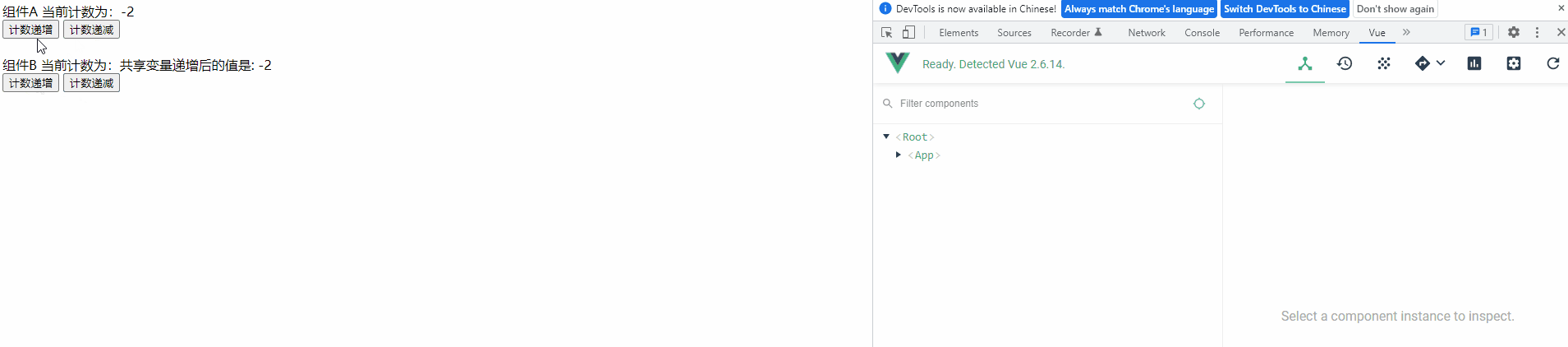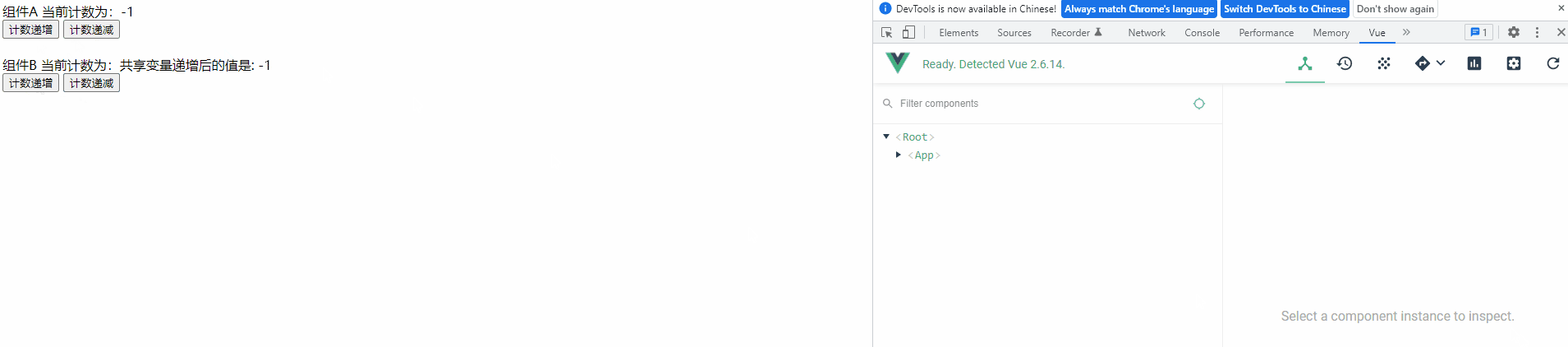
4) 查看运行效果

6. Vuex 核心属性 - modules
当我们的共享变量特别多时,我们可以使用 modules 属性对共享变量进行分模块管理,modules 中声明的每个对象又分别可以使用 state、mutations、actions、getters 属性
我们现在将组件A 和 组件B 当成一个模块,使用 mutations 进行管理,
1) 添加 Vuex.Store 中的核心属性 - modules
修改 src/store/index.js 文件, 在 modules 中配置模块信息,实际项目中可能会有多个模块,如果全都写在Vuex.store 中会显的很乱,所以我们在第 11 ~ 41 行将配置模块的代码提取成一个对象变量,并在第 46 行 modules 中引用
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from './storeConstants'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
const moduleFirst = {
// 让该 module 使用命名空间,防止多个 module 中
// 的 state、mutations、actions、getters 中定义的方法重名
namespaced: true,
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义共享变量的修改方式
mutations: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT](state, params) {
state.count += params
},
[STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT](state, params) {
state.count -= params.step
}
},
// 定义异步操作共享变量的方法
actions: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT_ACTION](context, params) {
setTimeout(() => context.commit(STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT, params), 2000)
}
},
// 定义共享变量的计算方法
getters: {
getCount(state, getters) {
return '共享变量递增后的值是: ' + state.count
}
}
}
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
moduleFirst: moduleFirst
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
有两点要注意一下:
① 第 14 行的 namespaced: true,这段代码的作用是,当我们有多个模块时,模块间的 state、mutations、actions、getters 中定义的方法名字很有可能会重复,这可能会影响我们的调用结果,当加上这个属性后,我们调用模块中state、mutations、actions、getters 定义的方法时,强制要求加上命名空间名(既第 46 行的模块名),这样能帮助我们保证方法名唯一性,以免命名重复造成的歧义性
② modules、state、mutations、actions、getters 它们是可以同时定义在 Vuex.store 的同一级的,定义在Vuex.store 第一层的 state、mutations、actions、getters 属性是全局注册,而 modules 内定义的是局部作用域
2) 修改常量文件
修改 src/store/storeConstants.js,新增模块的命名空间前缀常量,调用 state、mutations、actions、getters 中的方法时会使用,代码在第 7、8 行:
// 定义函数名 increment
export const INCREMENT = 'increment'
// 定义函数名 decrement
export const DECREMENT = 'decrement'
// 定义函数名 incrementAction
export const INCREMENT_ACTION = 'incrementAction'
// 模块内方法调用时的命名空间前缀
export const MODULE_FIRST_PREFIX = 'moduleFirst/'
3) 修改组件
因为我们使用了命名空间,所以调用 Vuex 的方法时需要加上命名空间前缀,格式如下:
| 未使用命名空间的调用方式(普通方式) | 使用命名空间的调用方式 |
|---|---|
| this.$store.commit( mutations中的方法名, 参数) | this.$store.commit( 模块命名空间名/mutations中的方法名, 参数) |
| this.$store.dispatch( actions中的方法名, 参数) | this.$store.commit( 模块命名空间名/actions中的方法名, 参数) |
| this.$store.getters.getters中的方法名 | this.$store.getters[模块命名空间名/getters中的方法名] |
| this.$store.state.共享变量名 | this.$store.state.模块命名空间名.共享变量名 |
学习了调用方式,我们将修改组件A 和组件B,并分别使用 Vuex.store 的这些属性
① 修改 src/components/A.vue 文件,重点在第 3、18、21 行:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件A 当前计数为:{{ $store.state.moduleFirst.count }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from '../store/storeConstants'
export default {
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.dispatch(STORE_CONSTANTS.MODULE_FIRST_PREFIX + STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT_ACTION, 1)
},
decreament() {
this.$store.commit({ type: STORE_CONSTANTS.MODULE_FIRST_PREFIX + STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT, step: 1 })
}
}
}
</script>
② 修改 src/components/B.vue 文件,重点在第 3 行:
<template>
<div>
<div>组件B 当前计数为:{{ $store.getters['moduleFirst/getCount'] }}</div>
<div>
<button @click="increment">计数递增</button>
<button @click="decreament">计数递减</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as AA from '../store/storeConstants'
export default {
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('moduleFirst/increment', 1)
},
decreament(){
this.$store.commit({type:'moduleFirst/decrement', step:1})
}
}
}
</script>
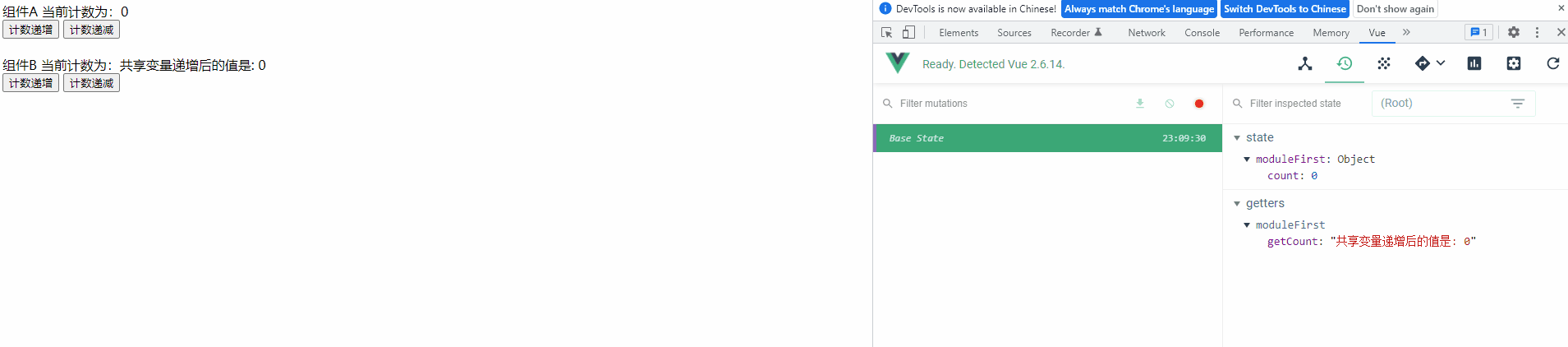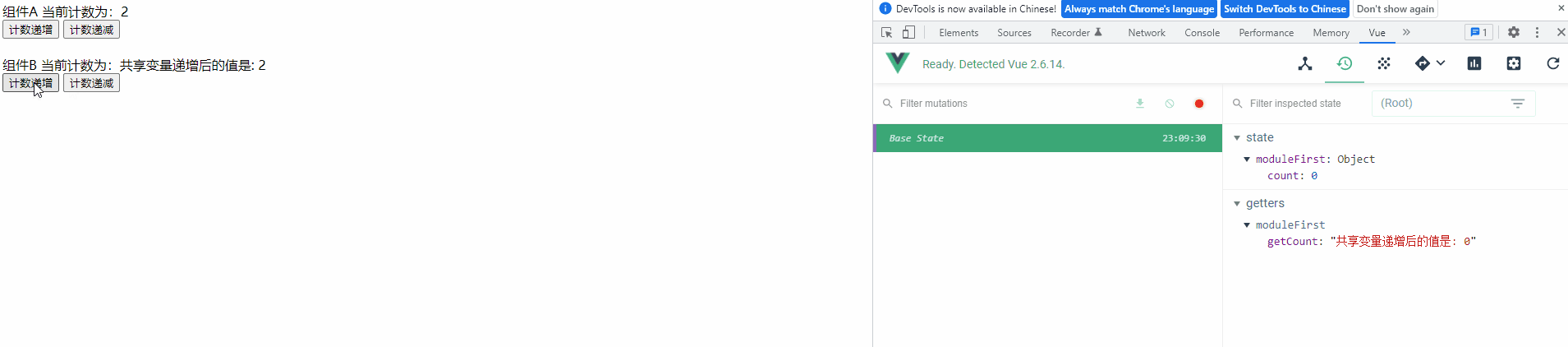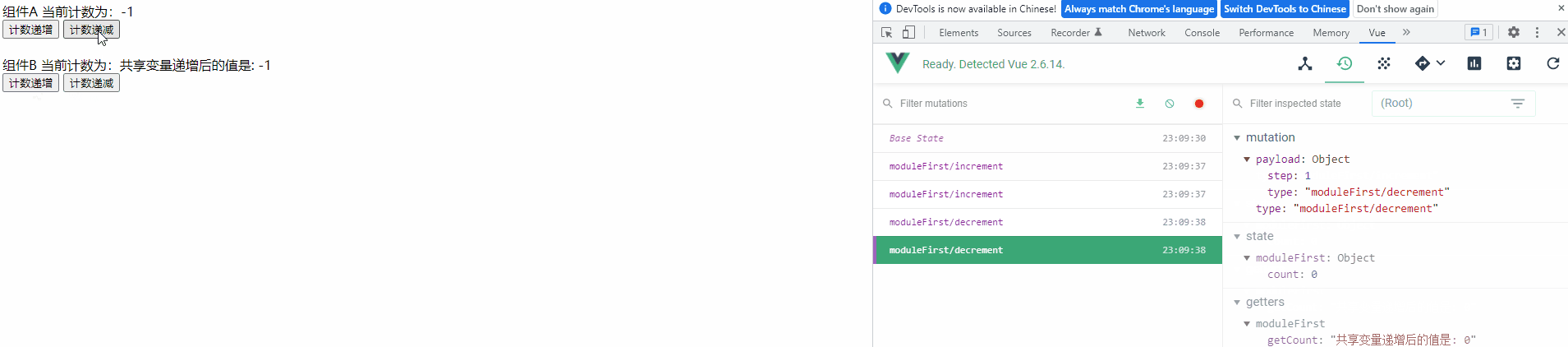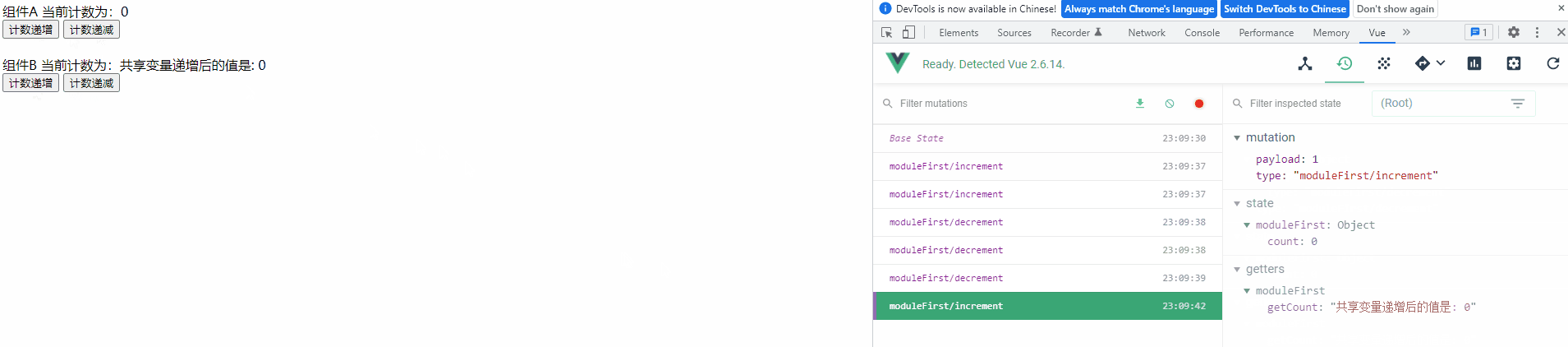
4) 查看运行效果
功能与之前一样,未受影响
5) 将 Vuex.store 的模块定义,抽离到文件
我们在 src/store/index.js 文件中,为了防止 Vuex.store 中定义的模块内容过多,所以将模块抽取成对象变量,而实际项目中往往习惯分别创建专门管理各个模块配置信息的文件,然后将模块信息抽离到该文件中
① 创建专门管理 moduleFirst 模块的文件夹和文件 src/store/moduleFirst/moduleFirst.js,将原来 src/store/index.js 中
moduleFirst 的模块信息,复制到该文件中,注意第 2 行代码路径变了:
// 导入方法名常量模块
import * as STORE_CONSTANTS from '../storeConstants'
// Vuex 中 moduleFirst 模块的配置信息
export default {
// 让该 module 使用命名空间,防止多个 module 中
// 的 state、mutations、actions、getters 中定义的方法重名
namespaced: true,
// 定义共享变量
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义共享变量的修改方式
mutations: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT](state, params) {
state.count += params
},
[STORE_CONSTANTS.DECREMENT](state, params) {
state.count -= params.step
}
},
// 定义异步操作共享变量的方法
actions: {
[STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT_ACTION](context, params) {
setTimeout(() => context.commit(STORE_CONSTANTS.INCREMENT, params), 2000)
}
},
// 定义共享变量的计算方法
getters: {
getCount(state, getters) {
return '共享变量递增后的值是: ' + state.count
}
}
}
② 修改 src/store/index.js 文件,删除原 moduleFirst 的模块信息,导入其专门的配置模块,第 6 行:
// 导入 Vue模块
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 Vuex模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 导入 moduleFirst 模块的配置信息
import moduleFirst from './moduleFirst/moduleFirst.js'
// 将 Vuex插件 安装到 Vue 中
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Vuex 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
moduleFirst: moduleFirst
}
})
// 导出 Vuex 对象
export default store
③ 确认目录结构

④ 查看运行效果是否受影响
这种方式是实际项目中使用 Vuex 时常用的目录结构,模块信息分开管理,易于阅读和维护

























 531
531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








