目录
一、前提
是学习 Efficient string matching: an aid to bibliographic search 1975年的论文,看了很久,但是很多内容还是没看懂。
这里就其中的一些算法java版本实现及自己的理解记录下。
这个算法是用于文本匹配的,这在搜索中很常用,比如有词根:he、his,输入she,可以解析出he。
二、java实现(版本1)
节点类:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class ApNode {
private int state;
private Map<Character, ApNode> go;
private ApNode fail;
/**
* output函数,仅root节点有
*/
private Map<ApNode, List<String>> output;
public ApNode() {
go = new TreeMap<>();
}
public int getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(int state) {
this.state = state;
}
public Map<Character, ApNode> getGo() {
return go;
}
public void setGo(Map<Character, ApNode> go) {
this.go = go;
}
public ApNode getFail() {
return fail;
}
public void setFail(ApNode fail) {
this.fail = fail;
}
public Map<ApNode, List<String>> getOutput() {
return output;
}
public void setOutput(Map<ApNode, List<String>> output) {
this.output = output;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder bld = new StringBuilder();
bld.append(state);
if (go.size() > 0) {
bld.append("->");
}
for (Map.Entry<Character, ApNode> entry : go.entrySet()) {
bld.append("\n\t");
bld.append(entry.getKey());
bld.append(":");
String value = entry.getValue().toString();
for (int i = 0; i < value.length(); i++) {
char c = value.charAt(i);
bld.append(c);
if (i != 0 && value.charAt(i - 1) == '\n' && c == '\t') {
bld.append('\t');
}
}
}
return bld.toString();
}
}节点帮助类:
import java.util.*;
public class ApNodeHelper {
public static ApNode goFunc(ApNode root, ApNode state, char a, boolean isCreating) {
if (state.getGo().containsKey(a)) {
return state.getGo().get(a);
}
if (isCreating) {
//代表没有通路
return null;
}
//如果是root没有路径的,全部赋值root
return root == state ? root : null;
}
public static String outputFail(ApNode node) {
StringBuilder noBld = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder failBld = new StringBuilder();
if (node.getState() != 0) {
noBld.append(node.getState()).append(" ");
failBld.append(node.getFail().getState()).append(" ");
}
LinkedList<ApNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (ApNode goNode : node.getGo().values()) {
queue.offer(goNode);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ApNode currentNode = queue.poll();
noBld.append(currentNode.getState()).append(" ");
failBld.append(currentNode.getFail().getState()).append(" ");
for (ApNode goNode : currentNode.getGo().values()) {
queue.offer(goNode);
}
}
noBld.append('\n');
noBld.append(failBld);
return noBld.toString();
}
public static void output(ApNode root) {
for (Map.Entry<ApNode, List<String>> entry : root.getOutput().entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey().getState() + ":" + Arrays.toString(entry.getValue().toArray()));
}
}
public static void addOutput(Map<ApNode, List<String>> output, ApNode c, List<String> keywords) {
if (keywords == null || keywords.size() == 0) {
return;
}
List<String> emits = output.get(c);
if (emits == null) {
ArrayList<String> newEmits = new ArrayList<>();
newEmits.addAll(keywords);
output.put(c, newEmits);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < keywords.size(); i++) {
if (!emits.contains(keywords.get(i))) {
emits.add(keywords.get(i));
}
}
}
}
public static void addOutput(Map<ApNode, List<String>> output, ApNode c, String keyword) {
List<String> emits = output.get(c);
if (emits == null) {
ArrayList<String> newEmits = new ArrayList<>();
newEmits.add(keyword);
output.put(c, newEmits);
} else if (!emits.contains(keyword)) {
emits.add(keyword);
}
}
}
算法实现类:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AhoPaper {
public static ApNode gotoFunc(ApNode root, AtomicInteger newStateNo, String keyword) {
if (keyword == null || keyword.length() == 0) {
return root;
}
char[] text = keyword.toCharArray();
ApNode state = root;
int j = 0;
char a;
while (true) {
a = text[j];
ApNode goState = ApNodeHelper.goFunc(root, state, a, true);
if (goState == null) {
break;
}
state = goState;
j++;
}
for (int p = j; p < text.length; p++) {
a = text[p];
ApNode newState = new ApNode();
newState.setState(newStateNo.incrementAndGet());
state.getGo().put(a, newState);
state = newState;
}
ApNodeHelper.addOutput(root.getOutput(), state, keyword);
return state;
}
public static void failFunc(ApNode root) {
LinkedList<ApNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//第一层
for (ApNode node : root.getGo().values()) {
node.setFail(root);
queue.offer(node);
}
//剩余层
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ApNode parentNode = queue.poll();
for (Map.Entry<Character, ApNode> entry : parentNode.getGo().entrySet()) {
char a = entry.getKey();
ApNode currentNode = entry.getValue();
queue.offer(currentNode);
ApNode state = parentNode.getFail();
while (true) {
ApNode goState = ApNodeHelper.goFunc(root, state, a, false);
if (goState != null) {
currentNode.setFail(goState);
ApNodeHelper.addOutput(root.getOutput(), currentNode, root.getOutput().get(goState));
break;
}
state = state.getFail();
}
}
}
}
public static List<String> findFunc(ApNode root, String x) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (x == null || x.length() == 0) {
return result;
}
ApNode state = root;
for (int i = 0; i < x.length(); i++) {
char a = x.charAt(i);
ApNode matchNode;
while ((matchNode = ApNodeHelper.goFunc(root, state, a, false)) == null) {
state = state.getFail();
}
state = matchNode;
if (root.getOutput().containsKey(state)) {
result.addAll(root.getOutput().get(state));
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] keywords = {"he", "she", "his", "hers"};
ApNode root = new ApNode();
root.setState(0);
root.setOutput(new LinkedHashMap<>());
AtomicInteger newStateNo = new AtomicInteger(0);
ApNode finalState = root;
for (int i = 0; i < keywords.length; i++) {
finalState = gotoFunc(root, newStateNo, keywords[i]);
System.out.println("-----------" + i + ":" + keywords[i] + "-----------");
System.out.println(root);
}
failFunc(root);
System.out.println("---------fail--------");
System.out.println(ApNodeHelper.outputFail(root));
System.out.println("---------output--------");
ApNodeHelper.output(root);
System.out.println("---------find--------");
String text = "ushers";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text).toArray()));
text = "";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text).toArray()));
text = "u";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text).toArray()));
text = "she";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text).toArray()));
text = "he";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text).toArray()));
}
}运行输出:
-----------0:he-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2
-----------1:she-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2
s:3->
h:4->
e:5
-----------2:his-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2
i:6->
s:7
s:3->
h:4->
e:5
-----------3:hers-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2->
r:8->
s:9
i:6->
s:7
s:3->
h:4->
e:5
---------fail--------
1 3 2 6 4 8 7 5 9
0 0 0 0 1 0 3 2 3
---------output--------
2:[he]
5:[she, he]
7:[his]
9:[hers]
---------find--------
ushers:[she, he, hers]
:[]
u:[]
she:[she, he]
he:[he]可以看到已正确解析出模式串。
1、节点类-ApNode
节点有如下属性和功能:
| 编号 | 字段 | 备注 | root | other |
| 1 | int state | 编号,从0开始 | 0 | 1开始递增 |
| 2 | Map<Character, ApNode> go | 下一层路径,比如sh,节点s的go字段为<h, nodeH> | √ | √ |
| 3 | fail | fail节点,用于匹配失败跳转 | × | √ |
| 4 | Map<ApNode, List<String>> output | 当前节点匹配的完整文本,仅有root有值 | √ | × |
主要存储当前数字码及下级路径,并且存储了一个output内容。
2、节点帮助类-ApNodeHelper
帮助类,具有如下方法:
| 编号 | 方法 | 方法描述 | 参数描述 |
| 1 | ApNode goFunc(ApNode root, ApNode state, char a, boolean isCreating) | 原生go方法,判断是否真实有路径 | isCreating表示是否在构建trie树过程中 true:state节点到a字符无通路则返回null; false:如果state是root,如无通路则返回root |
| 2 | String outputFail(ApNode node) | 向下追溯节点的fail | node:一般传入root节点,输出整个trie树逐个节点对应的fail节点编码 |
| 3 | void output(ApNode root) | 输出整个trie树的output | root:取root节点的output字段输出 |
| 4 | void addOutput(Map<ApNode, List<String>> output, ApNode c, List<String> keywords) void addOutput(Map<ApNode, List<String>> output, ApNode c, String keyword) | 在构建自动机过程中,构建root节点output字段 |
3、算法类-AhoPaper
提示:可以配合论文查看,基本按照论文描述实现,输入keywords:{he, she, his, hers}
3.1、goto函数-gotoFunc
构建trie树,编码从root节点(赋值为0)依次递增,并且实现部分output函数,完成后如图示:
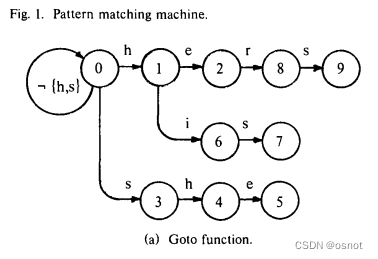
算法分成3部分,第一部分针对输入keyword(比如his)是找当前trie已存在的节点(h节点已存在):
while (true) {
a = text[j];
ApNode goState = ApNodeHelper.goFunc(root, state, a, true);
if (goState == null) {
break;
}
state = goState;
j++;
}
则这里state会是节点1,接续算法下一部分,添加i、s节点:
for (int p = j; p < text.length; p++) {
a = text[p];
ApNode newState = new ApNode();
newState.setState(newStateNo.incrementAndGet());
state.getGo().put(a, newState);
state = newState;
}
这里添加新节点到state节点的go字段中,并且继续遍历keyword剩余部分。
最后整个keyword添加完成后,添加到root节点的output字段中:
ApNodeHelper.addOutput(root.getOutput(), state, keyword);
完成后整个trie树如上图。
3.2、fail函数-failFunc
fail概念及解决的问题讲解
fail概念可能来自KMP算法的失败函数。此算法fail函数的概念是指,当根据trie树路径依次遍历输入文本时,如果下一字符无法匹配时,应该怎么处理。
举例:上图trie树完成图,当输入shers时:
从第一个字符s开始:从root-0节点出发找到一条s路径通向节点3,然后s-3节点通过h路径找到h-4节点,进而e-5节点,但e-5节点没有r路径,故这条路径匹配失败,此时需要从第二个字符从头匹配一遍:
从第二个字符h开始:从root-0节点出发找到一条h路径通向节点1,然后h-1节点通过e路径找到e-2节点,进而找到r-8节点、s-9节点,此时完整路径匹配:hers keyword,故匹配成功。
然后从第三个字符e开始,继续从root-0匹配......
直到最后一个字符s为止。
这里可以看到有2个问题:
1、整体次数过多,需要输入文本每个字符从root-0匹配一遍。
2、第一、二作为起始字符匹配过程,h->e 这个状态转移执行了2遍,是否可以减少匹配次数?
第1个问题后续再专门讲下,先看第2个问题,是否可以第二个字符h匹配时不从root-0开始,而是从e-2节点开始?
其实看一眼图,人脑就判断出在s->h->e 到 r匹配失败时,可以直接跳到e-2节点,也就是h->e->r继续匹配,这就是fail函数要解决的问题(最终fail函数要配合find函数使用)。
算法讲解
每个节点的fail跳转值是按照动态规划思路进行的,ApNode节点fail值代表当匹配失败时,可以跳转到fail节点继续匹配,比如s->h->e 到 r匹配失败,此时代表e-5节点匹配失败,则e可以跳转到e-2节点继续匹配r。
1、root没有fail,因为goto函数root出发的所有路径均有通路,如果trie树没有实际路径会指向root本身,所以不会出现匹配失败的情况。
2、trie树-1层节点(h、s)的fail指向root;
3、依次计算-2层节点(e-2、i、h)、-3层节点(r、s-6、e-5)、-4层(s-9)节点;
3.1、针对要计算fail的节点,比如e-2,首先找到节点对应的父节点(h-1)的fail节点(root-0),查找其有无当前节点字符(e)的通路:
- 如有找到下一个节点(root)并赋值给当前节点fail:e-2的fail=root-0;
- 如果没有,则继续追溯fail节点(root-0)的fail节点;
- 循环上2步,直到追溯到root(root不会匹配失败),则root作为当前节点fail值。
详细代码
第一层节点fail统一赋值为root,并放置到队列中:
LinkedList<ApNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//第一层
for (ApNode node : root.getGo().values()) {
node.setFail(root);
queue.offer(node);
}
广度遍历trie树,先将下一层的节点加入到队列中,而后开始逐个处理队列中节点:
//剩余层
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ApNode parentNode = queue.poll();
for (Map.Entry<Character, ApNode> entry : parentNode.getGo().entrySet()) {
char a = entry.getKey();
ApNode currentNode = entry.getValue();
queue.offer(currentNode);
......
}
}
查找当前节点currentNode的fail:
ApNode state = parentNode.getFail();
while (true) {
ApNode goState = ApNodeHelper.goFunc(root, state, a, false);
if (goState != null) {
currentNode.setFail(goState);
ApNodeHelper.addOutput(root.getOutput(), currentNode, root.getOutput().get(goState));
break;
}
state = state.getFail();
}
首先查找父节点(parentNode)的fail节点是否有到当前节点字符(a) 的通路,如果有则fail直接赋值为通路节点;
否则继续追溯父节点的fail节点,看是否有到当前节点字符(a) 的通路,直到root。
其中还有部分代码涉及output值生成:当找到fail节点后,也将fail节点对应的keywords加入到当前节点output值中,比如she的e-5节点fail为e-2节点,则e-2节点的keywords{he}也加入到e-5节点的keywords中:{he, she}
ApNodeHelper.addOutput(root.getOutput(), currentNode, root.getOutput().get(goState));
疑问-为何fail节点只查找上层?
比如待解析文本shers,算法目的是解析出{he, she, his, hers}中的keyword:{he, she, hers};
此时找到一条路径:s->h->e,此时 r 没有匹配,如果跳转到 e-5 的同级或者 下级节点,说明跳转到的链路,比如:
- n1->n2->e->*,此时n1 n2 3一定要匹配she,也就是trie树存在两条前缀为she的路径,这种情况在goto函数构建trie的过程中是不会发生的;
- n1->n2->n3->e->*,此时n1 n2 n3 e一定要匹配she,比如ushe,这种情况是不存在的,因为起始的n1(u字符)并没有在待解析文本中;
所以she这条路径一定是待解析文本shers,在trie树中的最长前缀,也就是没有任何keyword匹配节点数大于等于3(she字符数),所以如果要接续解析剩余待解析文本(rs),一定要在e-5节点的上N层去查找。
小结
fail函数生成每个节点的失配跳转节点,在当前节点匹配失败后,可以快速跳转到上层(跳跃层级可能不止1层)节点,避免每次从root节点开始匹配,减少匹配次数;
fail生成的原理可以认为是keywords之间最大重叠,比如只看{he, she},he的前缀(h、he)和she的后缀(she、he、e)之间相同部分{he},其中字符数最多就是最大重叠,这种she的e节点fail跳转就是he的e节点。
上面{he, she, hers}trie树的fail节点对应是:
![]()
3.3、output生成
output“函数”其实是一个当前节点对应的keywords值,其存储在root节点(这个实现和论文不同,论文是一个单独函数,这里没有做的这么复杂)。
其分别在goto、fail函数中生成,最终为:

可以看到e-5节点对应的是{she, he},说明当匹配走到keyword {she} 的e-5节点时,其一定同时匹配了keyword {he},这样就避免了每次移动待解析文本的字符从头(root-0)开始逐个匹配,即3.2中提到的第一个问题(1、整体次数过多,需要输入文本每个字符从root-0匹配一遍)。
生成的逻辑分成2部分:
1、生成tire树时,每个keyword添加(到trie树)完成时,最后一个节点output值设置为该keyword;
2、生成fail函数时,当前节点的fail节点,后者output值也加入到当前节前的keyword中。
第1部分好理解,第2部分还是和fail函数逻辑有关:从root算起,到当前节点的路径一定包含到fail节点的路径,所以当匹配走到当前节点时:
- 如果失配则跳转,当前节点和fail节点的output值都不会输出;
- 如果可以匹配结束或者继续匹配,此时说明已解析到keyword,会将当前节点和fail节点的output值都输出。
3.4、find函数-findFunc
有了goto函数、fail函数和output后,就可以生成find查找函数了。
首先是待解析文本x的空检查,为空直接返回:
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (x == null || x.length() == 0) {
return result;
}
而后逐个字符遍历x,如果存在路径匹配则继续,否则进行失配跳转;失配跳转到存在路径则继续,否则继续失配跳转,直到root(再次提示root不会匹配失败):
ApNode state = root;
for (int i = 0; i < x.length(); i++) {
char a = x.charAt(i);
ApNode matchNode;
while ((matchNode = ApNodeHelper.goFunc(root, state, a, false)) == null) {
state = state.getFail();
}
state = matchNode;
if (root.getOutput().containsKey(state)) {
result.addAll(root.getOutput().get(state));
}
}
return result;
上面有一块代码用到了output值,当匹配到state时,分成3种情况:
- root:其没有output值;
- his:只输出s-7节点goto函数产生的output值{his};
- she:输出e-5节点goto函数产生的output值{she},和fail函数(指向e-2)产生的output值{he},故整体输出{she, he};
三、java实现(版本2)有限确定自动机
第一个版本中当匹配失败时,会走到fail路径,如果没有匹配则会一直走到root,这些追溯其实可以避免掉,如下新增一个新版的fail函数:movenext。
import com.kite.www.ac_paper.AhoPaper;
import com.kite.www.ac_paper.ApNode;
import com.kite.www.ac_paper.ApNodeHelper;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* eliminating failure transitions
*/
public class AhoPaper2 {
/**
* 确定有限自动机
*/
public static Map<Character, ApNode>[] dfaFunc(ApNode root, ApNode finalState) {
//[下标:Map<字符,跳转>]
Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove = new TreeMap[finalState.getState() + 1];
nextMove[0] = root.getGo();
LinkedList<ApNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (ApNode goNode : root.getGo().values()) {
queue.offer(goNode);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ApNode node = queue.poll();
Map<Character, ApNode> nmMap = new TreeMap<>(node.getGo());
Map<Character, ApNode> failNodeNM = nextMove[node.getFail().getState()];
for (Character c : failNodeNM.keySet()) {
if (!nmMap.containsKey(c)) {
nmMap.put(c, failNodeNM.get(c));
}
}
nextMove[node.getState()] = nmMap;
for (ApNode goNode : node.getGo().values()) {
queue.offer(goNode);
}
}
return nextMove;
}
public static List<String> findFunc(ApNode root, String x, Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (x == null || x.length() == 0) {
return result;
}
ApNode state = root;
for (int i = 0; i < x.length(); i++) {
state = moveNext(state, x.charAt(i), nextMove, root);
if (root.getOutput().containsKey(state)) {
result.addAll(root.getOutput().get(state));
}
}
return result;
}
public static ApNode moveNext(ApNode apNode, char c, Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove, ApNode root) {
ApNode nextNode = nextMove[apNode.getState()].get(c);
if (nextNode == null) {
return root;
}
return nextNode;
}
public static void outputMoveNext(Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove) {
for (int i = 0; i < nextMove.length; i++) {
System.out.println("state " + i + ":");
Map<Character, ApNode> map = nextMove[i];
for (Map.Entry<Character, ApNode> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("\t" + entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue().getState());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] keywords = {"he", "she", "his", "hers"};
ApNode root = new ApNode();
root.setState(0);
root.setOutput(new LinkedHashMap<>());
AtomicInteger newStateNo = new AtomicInteger(0);
ApNode finalState = root;
for (int i = 0; i < keywords.length; i++) {
finalState = AhoPaper.gotoFunc(root, newStateNo, keywords[i]);
System.out.println("-----------" + i + ":" + keywords[i] + "-----------");
System.out.println(root);
}
AhoPaper.failFunc(root);
Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove = dfaFunc(root, finalState);
System.out.println("---------nextmove--------");
outputMoveNext(nextMove);
System.out.println("---------fail--------");
System.out.println(ApNodeHelper.outputFail(root));
System.out.println("---------output--------");
ApNodeHelper.output(root);
System.out.println("---------find--------");
String text = "ushers";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text, nextMove).toArray()));
text = "";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text, nextMove).toArray()));
text = "u";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text, nextMove).toArray()));
text = "she";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text, nextMove).toArray()));
text = "he";
System.out.println(text + ":" + Arrays.toString(findFunc(root, text, nextMove).toArray()));
}
}输出:
-----------0:he-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2
-----------1:she-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2
s:3->
h:4->
e:5
-----------2:his-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2
i:6->
s:7
s:3->
h:4->
e:5
-----------3:hers-----------
0->
h:1->
e:2->
r:8->
s:9
i:6->
s:7
s:3->
h:4->
e:5
---------nextmove--------
state 0:
h:1
s:3
state 1:
e:2
h:1
i:6
s:3
state 2:
h:1
r:8
s:3
state 3:
h:4
s:3
state 4:
e:5
h:1
i:6
s:3
state 5:
h:1
r:8
s:3
state 6:
h:1
s:7
state 7:
h:4
s:3
state 8:
h:1
s:9
state 9:
h:4
s:3
---------fail--------
1 3 2 6 4 8 7 5 9
0 0 0 0 1 0 3 2 3
---------output--------
2:[he]
5:[she, he]
7:[his]
9:[hers]
---------find--------
ushers:[she, he, hers]
:[]
u:[]
she:[she, he]
he:[he]
Process finished with exit code 0
下面分块讲解。
1、moveNext概念
moveNext就是为了避免fail追溯的,比如keywords:{he, she, his, hers},待解析文本ushers:
u:root匹配结果为root,终止;
s:root匹配s-3;
h:匹配h-4;
e:匹配e-5;
r:不匹配,追溯e-5的fail到e-2,继续匹配r-8;
s:匹配s-9;
可以看到r有一次fail追溯,如何避免这一次追溯?
如果e-5节点有支持(不一定有实际路径,即goto函数不一定支持)的所有节点列表,其中包含r-8,此时就可以直接匹配到r-8,而不是走失配逻辑了。
所以我们要构建一个moveNext列表,其结果如下:
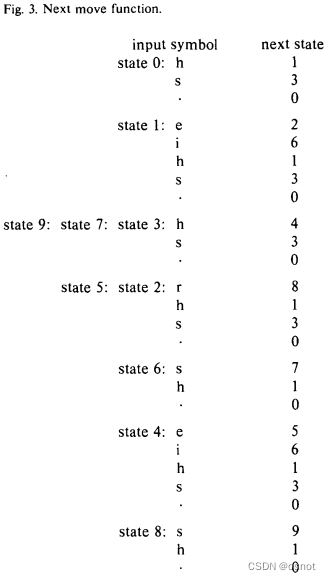
其中.表示除上面列举的字符之外的所有字符。
2、构建moveNext-dfaFunc及相关函数
函数入参是第一个节点root和最后一个节点finalState,该函数执行是在goto、fail函数之后。
首先根据最后一个节点的编号构建nextMove字典数组,下标就是节点编码值,数组值是可以支持的字符及对应节点;
构建队列广度遍历所有节点,首先处理节点0即root节点,将go值直接赋值到nextMove(因为root没有fail):
//[下标:Map<字符,跳转>]
Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove = new TreeMap[finalState.getState() + 1];
nextMove[0] = root.getGo();
LinkedList<ApNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (ApNode goNode : root.getGo().values()) {
queue.offer(goNode);
}
开始遍历队列,首先将该节点本身goto路径节点加入nextMove,而后加入fail节点的nextMove,也是基于动态规划思想,最终将该节点的下一层节点加入到队列:
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ApNode node = queue.poll();
Map<Character, ApNode> nmMap = new TreeMap<>(node.getGo());
Map<Character, ApNode> failNodeNM = nextMove[node.getFail().getState()];
for (Character c : failNodeNM.keySet()) {
if (!nmMap.containsKey(c)) {
nmMap.put(c, failNodeNM.get(c));
}
}
nextMove[node.getState()] = nmMap;
for (ApNode goNode : node.getGo().values()) {
queue.offer(goNode);
}
}
return nextMove;
当前节点匹配失败时跳转到fail节点,那fail节点支持的所有下一层节点,都可认为当前节点也支持,所以最终moveNext输出见上图,对应输出函数:
public static void outputMoveNext(Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove) {
for (int i = 0; i < nextMove.length; i++) {
System.out.println("state " + i + ":");
Map<Character, ApNode> map = nextMove[i];
for (Map.Entry<Character, ApNode> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("\t" + entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue().getState());
}
}
}
产生文本输出:
state 0:
h:1
s:3
state 1:
e:2
h:1
i:6
s:3
state 2:
h:1
r:8
s:3
state 3:
h:4
s:3
state 4:
e:5
h:1
i:6
s:3
state 5:
h:1
r:8
s:3
state 6:
h:1
s:7
state 7:
h:4
s:3
state 8:
h:1
s:9
state 9:
h:4
s:3
除列出值外,其他字符匹配均跳转到root:
public static ApNode moveNext(ApNode apNode, char c, Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove, ApNode root) {
ApNode nextNode = nextMove[apNode.getState()].get(c);
if (nextNode == null) {
return root;
}
return nextNode;
}
3、加入moveNext的find函数
最终find函数就很简单了,去掉了fail追溯:
public static List<String> findFunc(ApNode root, String x, Map<Character, ApNode>[] nextMove) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (x == null || x.length() == 0) {
return result;
}
ApNode state = root;
for (int i = 0; i < x.length(); i++) {
state = moveNext(state, x.charAt(i), nextMove, root);
if (root.getOutput().containsKey(state)) {
result.addAll(root.getOutput().get(state));
}
}
return result;
}
首先仍是判空,然后从root节点开始遍历待解析文本x,每个字符直接从nextMove中进行匹配,下标寻址+字典匹配,避免了fail追溯,最终根据output值加入到匹配结果中,完成了优化目标。
四、总结
1、算法总结
整体而言,该算法相对将keyword存储到map,然后将待解析文本从第1位开始逐层解析(
第一遍:第1次:1-N,第2次:1-N-1 ...... 第N次:1
第二遍:第1次:2-N,第2次:2-N-1 ...... 第N-1次:2
...
第N遍:N
)的粗暴匹配算法而言,有如下优点:
- 构建trie树,可以减少字符存储,匹配速度也优于字典匹配;
- 加入fail失配跳转,可减少文本匹配次数,加速查找过程;
- 优化fail失配为moveNext,减少fail追溯,再一次加速查找过程;
其中失配表的加入对算法效率提升很多,赞叹算法的思想!
2、阅读论文总结
论文中的证明过程及效率计算等,没有看懂。
这是1974年的论文,而现在2023年还在学习,足以证明有用的知识永不过时。
3、勘误
如本人有错误或者描述不清楚、不恰当之处,敬请留言,会加以改正。





 本文介绍了Aho-Corasick算法,用于文本匹配。通过学习1975年的论文,作者实现了该算法的Java版本,包括节点类、节点帮助类和算法类。在Java实现中,详细讲解了goto、fail函数以及输出生成,同时提供了有限确定自动机的优化版本,减少匹配次数。最后进行了算法总结和论文阅读心得分享。
本文介绍了Aho-Corasick算法,用于文本匹配。通过学习1975年的论文,作者实现了该算法的Java版本,包括节点类、节点帮助类和算法类。在Java实现中,详细讲解了goto、fail函数以及输出生成,同时提供了有限确定自动机的优化版本,减少匹配次数。最后进行了算法总结和论文阅读心得分享。
















 5990
5990

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








