1. 图的数据表示
1.1 邻接矩阵法
若存在点 i i i到点 j j j的边, 则矩阵A中 A [ i , j ] A[i, j] A[i,j]等于1,否则等于0
# 1.图的数据表示法:邻接矩阵法
# data里面每个列表存的是一个边的起点和终点
data = [[1,2], [2,1], [1,5], [5,1], [2,3], [3,2], [2,4], [4,2], [3,4], [4,3]]
arr = [[0]*6 for i in range(6)]
# 构建邻接矩阵
for i in range(len(data)):
tempi = data[i][0]
tempj = data[i][1]
arr[tempi][tempj] = 1
# 输出邻接矩阵
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
for j in range(1, len(arr[0])):
print(arr[i][j], end=" ")
print()
输出
0 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 1 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
1.2 邻接表法
若有n条边,则用n个链表来表示,每个链表以一个顶点开始
# 2. 图的数据表示法:邻接表法
class list_node:
def __init__(self):
self.val = 0
self.next = None
data = [[1,2], [2,1], [1,5], [5,1], [2,3], [3,2], [2,4], [4,2], [3,4], [4,3]]
head = [list_node]*6
# 起点
for i in range(1, 6):
head[i] = list_node()
head[i].val = i
head[i].next = None
print("顶点%d=>"%i, end=" ")
ptr = head[i]
# 遍历所有数据
for j in range(len(data)):
if data[j][0] == i:
newnode = list_node()
newnode.val = data[j][1]
newnode.next = None
ptr.next = newnode
ptr = ptr.next
print(ptr.val, end=" ")
print()
输出:
顶点1=> 2 5
顶点2=> 1 3 4
顶点3=> 2 4
顶点4=> 2 3
顶点5=> 1
2. 图的遍历
2.1 深度优先
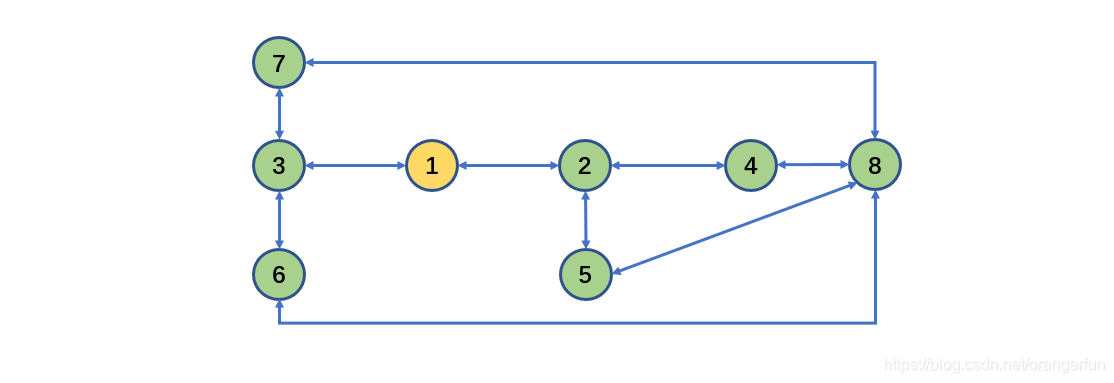
# 使用深度优先遍历
class list_node:
def __init__(self):
self.val = 0
self.next = None
data = [[1,2], [2,1], [1,3], [3,1], [2,4], [4,2], [2,5], [5,2],\
[3,6], [6,3], [3,7], [7,3], [4,8], [8,4], [5,8], [8,5],\
[6,8], [8,6], [8,7], [7,8]]
# 构建邻接表
head = [list_node]*9
for i in range(1, 9):
head[i] = list_node()
head[i].val = i
head[i].next = None
ptr = head[i]
for j in range(len(data)):
if data[j][0] == i:
newnode = list_node()
newnode.val = data[j][1]
newnode.next = None
ptr.next = newnode
ptr = ptr.next
# 打印邻接表
print("图的邻接表内容为:")
for i in range(1, len(head)):
ptr = head[i]
while ptr != None:
print(ptr.val, end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print()
# 深度遍历/递归
run = [0]*9
def dfs(current):
# run记录当前节点是否被遍历过
run[current] = 1
print(current, end=" ")
ptr = head[current].next
while ptr!=None:
if run[ptr.val] == 0:
dfs(ptr.val)
ptr = ptr.next
print("深度优先遍历顶点:")
dfs(1)
输出:
图的邻接表内容为:
1 2 3
2 1 4 5
3 1 6 7
4 2 8
5 2 8
6 3 8
7 3 8
8 4 5 6 7
深度优先遍历顶点:
1 2 4 8 5 6 3 7
2.2 广度优先
方法1:推荐此种方法
class node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
data = [[1,2], [2,1], [1,3], [3,1], [2,4], [4,2], [2,5], [5,2],\
[3,6], [6,3], [3,7], [7,3], [4,8], [8,4], [5,8], [8,5],\
[6,8], [8,6], [8,7], [7,8]]
# 构建邻接表
head = [node]*9
for i in range(1, 9):
head[i] = node(i)
ptr = head[i]
for j in range(len(data)):
if data[j][0] == i:
newnode = node(data[j][1])
ptr.next = newnode
ptr = ptr.next
# 广度优先
def bfs(current, nodes, run):
nodes.append(current)
while nodes:
node = nodes.pop(0)
if run[node] == 0:
print(node, end=" ")
run[node] = 1
ptr = head[node].next
while ptr != None:
nodes.append(ptr.val)
ptr = ptr.next
run = [0]*9
bfs(1, [], run)
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
方法2
# 队列最大容量
MaxSize = 10
front = -1
rear = -1
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.x = x
self.next = None
# 构建邻接表
class GranphLink:
def __init__(self):
self.first = None # 记录表头
self.last = None # 记录表尾位置
# 打印表
def my_print(self):
current = self.first
while current != None:
print(current.x, end=" ")
current = current.next
print()
# 在表尾加入节点
def insert(self, x):
newnode = Node(x)
if self.first == None:
self.first = newnode
self.last = newnode
else:
self.last.next = newnode
self.last = self.last.next
# 队列数据存入
def enqueue(value):
global MaxSize
global rear
global queue
if rear>=MaxSize:
return
rear += 1
queue[rear]=value
# 队列数据取出
def dequeue():
global front
global queue
if front == rear:
return -1
front += 1
return queue[front]
def bfs(current):
global front
global rear
global Head
global run
enqueue(current) # 将第一个数加入队列
run[current] = 1 # 遍历过的数做上标记
print(current, end=" ")
while front!=rear:
current = dequeue()
tempNode = Head[current].first
while tempNode != None:
if run[tempNode.x] == 0:
enqueue(tempNode.x)
run[tempNode.x] = 1
print(tempNode.x, end=" ")
tempNode = tempNode.next
data = [[1,2], [2,1], [1,3], [3,1], [2,4], [4,2], [2,5], [5,2],\
[3,6], [6,3], [3,7], [7,3], [4,8], [8,4], [5,8], [8,5],\
[6,8], [8,6], [8,7], [7,8]]
run = [0]*9
queue = [0]*MaxSize
Head = [GranphLink]*9
print("图的邻接表内容:")
for i in range(1, 9):
print(i, end=" ")
Head[i] = GranphLink()
for j in range(len(data)):
if data[j][0] == i:
dataNum = data[j][1]
Head[i].insert(dataNum)
Head[i].my_print()
print("广度优先遍历节点:")
bfs(1)
print()
输出
图的邻接表内容:
1 2 3
2 1 4 5
3 1 6 7
4 2 8
5 2 8
6 3 8
7 3 8
8 4 5 6 7
广度优先遍历节点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
4. 图中的最短距离
4.1 单点对全部顶点(Dijkstra)
思路流程
(1)计算起点到能够到达的顶点的距离, 不能到达的设置为无穷,记录再distance数组中
(2)从distance中找出最短距离D,假设对应的顶点为 x
(3)更新distance,起点到每个顶点的i的距离distance[i]=min(distance[i], distance[x]+matrix[x][i])
(4)重复第2步, 但是注意要在将前面找出的最短距离去掉后,再找最短距离
举例
找出顶点5到各顶点的距离

找到顶点5到各顶点的最小距离,不能到达的以无穷表示
(1)D[0] =
∞
\infty
∞, D[1] = 12, D[2] =
∞
\infty
∞, D[3] = 20, D[4] = 14;最小点为D[1] = 12, 然后根据最小点更新到所有顶点的最小值distance[i]=min(distance[i], distance[x]+matrix[x][i])
(2)重复步骤1, 第二次得到的结果为:D[0] =
∞
\infty
∞, D[1] = 12 , D[2] = 18, D[3] = 20, D[4] = 14;注意第二次选最小值要把第一次选过的D[1]去掉,最小值为D[4]
(3)和第2步一样,得到结果为:D[0] = 26, D[1] = 12 , D[2] = 18, D[3] = 20, D[4] = 14 ;最小值为D[2]
(4)D[0] = 26, D[1] = 12 , D[2] = 18 , D[3] = 20, D[4] = 14 ;最小值为D[3]
(5)D[0] = 26, D[1] = 12 , D[2] = 18 , D[3] = 20 , D[4] = 14 ;最小值为D[0], 所有顶点更新完毕
到每个顶点的最小值存在D数组中,遍历数组即可得到结果
程序
# func: 图中某个单点对所有顶点的最短距离
# 顶点是1-6, size定为7
size = 7
# 顶点数目
NUMBER = 6
GraphMatrix = [[0]*size for _ in range(size)]
distance = [0]*size
# 构建一个矩阵,存入图的边
def BuildGraphMatrix(pathCost):
# 初始化对角线为0,其他为无穷
for i in range(1, size):
for j in range(1, size):
if i == j:
GraphMatrix[i][j] = 0
else:
GraphMatrix[i][j] = float("inf")
# 存入图的边
i = 0
while i < size:
start_Point = pathCost[i][0]
end_Point = pathCost[i][1]
GraphMatrix[start_Point][end_Point] = pathCost[i][2]
i += 1
# 求start顶点到各个顶点的最短距离
def shortestPath(start, nums):
shortestPoint = 1
goal = [0]*size
for i in range(1, nums+1):
# 起点到各点的距离
distance[i] = GraphMatrix[start][i]
goal[start] = 1
distance[start] = 0
# 重复nums-1次,每次去掉已经使用过的最小值,用goal记录
for i in range(1, nums):
shortestDistance = float("inf")
# 获取当前最小距离
for j in range(1, nums+1):
if goal[j] == 0 and shortestDistance > distance[j]:
shortestDistance = distance[j]
shortestPoint = j
goal[shortestPoint] = 1
# 对每个点更新最小距离
for j in range(nums+1):
if goal[j] == 0 and distance[shortestPoint]+GraphMatrix[shortestPoint][j] < distance[j]:
distance[j] = distance[shortestPoint]+GraphMatrix[shortestPoint][j]
if __name__ == "__main__":
pathCost = [[1, 2, 29], [2, 3, 30], [2, 4, 35], [3, 5, 28], [3, 6, 87], [4, 5, 42], [4, 6, 75], [5, 6, 97]]
BuildGraphMatrix(pathCost)
shortestPath(1, NUMBER)
for i in range(1, size):
print("顶点1到顶点%d最短距离"%i, distance[i])
输出:
顶点1到顶点1最短距离 0
顶点1到顶点2最短距离 29
顶点1到顶点3最短距离 59
顶点1到顶点4最短距离 64
顶点1到顶点5最短距离 87
顶点1到顶点6最短距离 139
从上可知,一个有n各顶点的图,需要重复n-1次,即代码中for i in range(1, nums):








 本文深入解析图数据结构的表示方法,包括邻接矩阵和邻接表,并详细阐述图的遍历算法,如深度优先和广度优先搜索。此外,还介绍了Dijkstra算法,用于寻找图中两点间的最短路径。
本文深入解析图数据结构的表示方法,包括邻接矩阵和邻接表,并详细阐述图的遍历算法,如深度优先和广度优先搜索。此外,还介绍了Dijkstra算法,用于寻找图中两点间的最短路径。
















 3837
3837

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








