Handler作为android入门来讲是相当重要的,感觉自己快忘光了,在学习Spring的时候同时来复习一下。
执行流程其实很简单:
首先,当Handler被创建的时候就发送了一个新消息
发送至MessageQueue,Looper这个类就开始进行遍历MessageQueue,并从中取出Message,执行Runnable方法。这里面可以看出Looper是一直在进行循环遍历的,也就是死循环,但是它并不会卡死,这与它的执行机制有关。
Linux pipe/epoll机制:在主线程MQ没有消息的时候,使阻塞在loop的queue.next()
中的nativePollOnce()方法里,此时主线程会释放CPU资源进入休眠状态,直到下个消息到达或者有事务发生,通过往pipe管道写端写入数据来唤醒主线程的工作。
这种 呼之即来 挥之即去的方式 避免了的死循环。

此处脑内过一遍,接下来看下主要代码。。。。
mLooper = Looper.myLooper() 即创建了Looper
Handler类中:
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
***mLooper = Looper.myLooper();***
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread " + Thread.currentThread()
+ " that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
创建了MessageQueue,消息队列
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
***mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);***
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
*****final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;*****
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
从ThreadLocalPool中取出线程
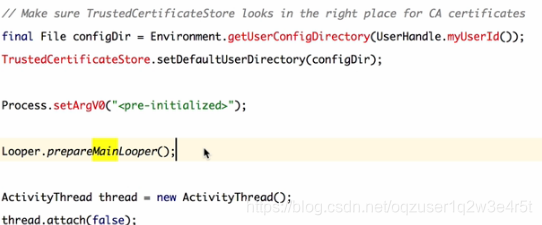
looper取出的线程被统一放置在TLP中,说到TLP,就必须要说一下APP的程序入口,ActivityThread这个类
Handler和Message,Runnable间的关系
这条代码中,Handler中runnable被封装成了一个Msg
通过执行handler.post()…方法时,会传递一个Runnable参数,Handler会将runnable
封装成Message来进行处理,所以,一直在进行传递的Message,其实就是runnable的封装体。
public final boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis)
{
return **sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), delayMillis);**
}
总结一下,Handler执行的代码原理:
Handler被创建的时候就**发送了一个被封装成Message形式的Runnable信息至MessageQueue,而这时,随着程序一启动就被创建的Looper接收到了新消息并从ThreadPool中将其取出来,当MessageQueue中没有消息到来的时候,Looper不会进行循环,所以不会引发卡死问题。Looper取出的Message 通过dispatchMessage方法进行回调,即而流程开始走通。
二、了解一下ActivityThread
程序一开始的时候 Handler
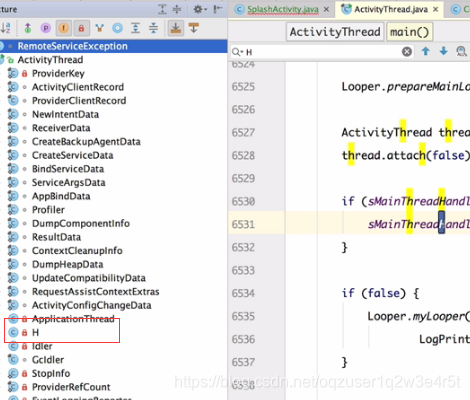
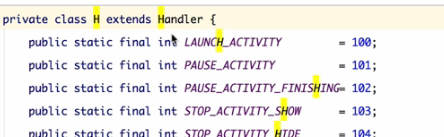
**
H这个类会处理类似activity的启动。。。。。。等等的执行。 所以,Activity的生命周期其实就是通过ActivityThread发送一些消息,处理不同消息 类型来回调的,所以handler的复习还是很必要的,用处很多。
**

Handler的复习暂时告一段落。
有写的不对的地方,希望有人指出,ThankYou/n





 本文是Handler的复习笔记,详细解析了Handler、MessageQueue和Looper的工作流程。Handler在创建时发送Runnable到MessageQueue,Looper循环读取消息并执行。通过Looper的Linux pipe/epoll机制避免了死循环,确保系统资源的有效利用。此外,Handler与ActivityThread的关系也得以阐述,说明Handler在处理Activity生命周期中的关键作用。
本文是Handler的复习笔记,详细解析了Handler、MessageQueue和Looper的工作流程。Handler在创建时发送Runnable到MessageQueue,Looper循环读取消息并执行。通过Looper的Linux pipe/epoll机制避免了死循环,确保系统资源的有效利用。此外,Handler与ActivityThread的关系也得以阐述,说明Handler在处理Activity生命周期中的关键作用。

















 977
977

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










