基础知识
存储
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
新建一个结点
node * newnode(int v)
{
node * newn = new node;
newn->data = v;
newn->lchild = newn->rchild = NULL;
return newn;
}
查找并修改一个或多个
void search(node* root, int x, int newdata)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
if(root->data == x)
root->data = newdata;
search(root->lchild, x, newdata);
search(root->rchild, x, newdata);
}
插入一个节点
void insert(node *&root, int x)
{
if( root == NULL)
{
root = newnode(x);
return;
}
else if (x<root->data)
insert(root->lchild, x);
else
insert(root->rchild, x);
}
创建二叉树
node* create(int data[], int n)
{
node * root = NULL;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
insert(root, data[i]);
return root;
}
四种遍历
void preorder(node* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
printf("%d ", root->data);
preorder(root->lchild);
preorder(root->rchild);
}
void inorder(node* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inorder(root->rchild);
}
void postorder(node* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
postorder(root->lchild);
postorder(root->rchild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
void layerorder(node*root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
queue<node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
node* now = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%d ", now->data);
if(now->lchild != NULL) q.push(now->lchild);
if(now->rchild != NULL) q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {1,4,2,3,6};
int n = 5;
node * root = create(a, n);
cout << "先序遍历:";
preorder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "中序遍历:";
inorder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "后序遍历:";
postorder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "层次遍历:";
layerorder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
利用遍历重建二叉树
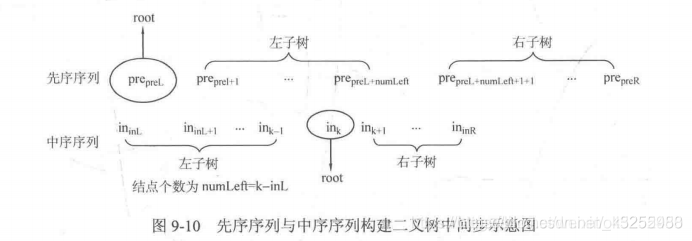
node * cre(int pre[], int prel, int prer, int in[], int inl, int inr)
{
if(prel > prer)
return NULL;
node * root = new node;
root->data = pre[prel];
int k;
for(k = inl; k<=inr;k++)
{
if(in[k] == pre[prel])
break;
}
int numl = k - inl;
root->lchild = cre(pre, prel + 1, prel + numl, in, inl, k - 1);
root->rchild = cre(pre, prel+numl+1, prer, in, k+1, inr);
return root;
}
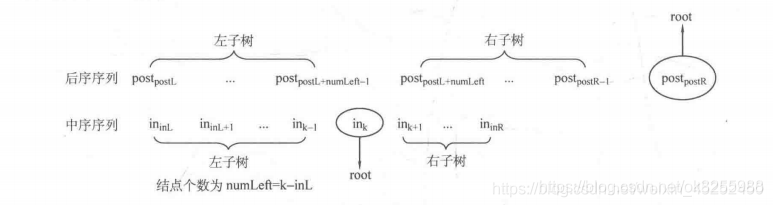
root->lchild = cre(post, postl, postl+ numl -1, in, inl, k - 1);
root->rchild = cre(post, postl + numl, postr-1, in, k+1, inr);




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








