1. Spring简介
是作为Java EE开发的一个框架,可以实现对象的注入、事务管理、面向切面编程等很多功能。
就好比是武林盟主,有自己的生态圈,地位非常高,所有大家必须精通掌握它。
2. 创建一个Spring项目
简单方法:用已经配置好的,复制一份,就不用一步步去手工创建
如从mavendemo项目中去复制
找到mavendemo的位置

复制一份mavendemo项目,并修改项目名


点击进springdemo项目

修改pom.xml文件

进入idea的操作




接下来部署jetty服务器



测试访问结果

至此,一个springdemo项目就创建成功!
根据需求,可导入到不同的工作空间中
先在D盘创建一个工作空间spring_course,并将刚创建好的springdemo项目复制到此工作空间中


打开idea




新的工作空间创建好后,导入springdemo项目





至此,新空间下的springdemo项目创建完毕!
还需要在pom.xml文件的dependencies中添加依赖:spring-context 和spring-core

3. 用Spring IOC创建对象
Java中创建对象方法
(1)new
(2)clone:实体类实现Cloneable接口,重写clone()方法,并且权限改为public
(3)反射
(4)对象反序列化:实体类实现Serializable接口
除了以上四种外,也可以用Spring IOC容器创建
(5)使用spring ioc 容器注入了一个对象。没有使用new,内部也是通过反射+xml文档的解析来实现的
代码测试(实现上述五种方法):
- 首先在java文件夹下创建一个实体类Student
package com.zz.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private String birthday;
private String major;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, String gender, String birthday, String major) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.major = major;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getMajor() {
return major;
}
public void setMajor(String major) {
this.major = major;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
", major='" + major + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 在java文件夹下创建一个测试类IocDemo(测试前四种)
package com.zz.test;
import com.zz.domain.Student;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class IocDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("dest.data");
//new
Student s1 = new Student(01,"刘一","男","1998-05-11","通信");
System.out.println(s1);
//clone()
Student s2 = (Student) s1.clone();
System.out.println(s2);
//反射
Class aClass = s1.getClass(); //创建类对象
//反射构造方法,返回构造方法对象
Constructor constructor = aClass.getConstructor(int.class, String.class, String.class, String.class, String.class);
Student s3 = (Student) constructor.newInstance(new Object[]{02, "王二", "男", "1999-12-01", "英语"});
System.out.println(s3);
//对象反序列化
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
out.writeObject(s1); //把刘一对象写入到文件中。
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Student s4 = (Student) in.readObject();
System.out.println(s4);
}
}
- 运行结果

接下来通过第五种方法Spring 创建:
- 首先在rescourse文件夹里创建一个配置文档applicationContext.xml,并在里面定义一个学生对象
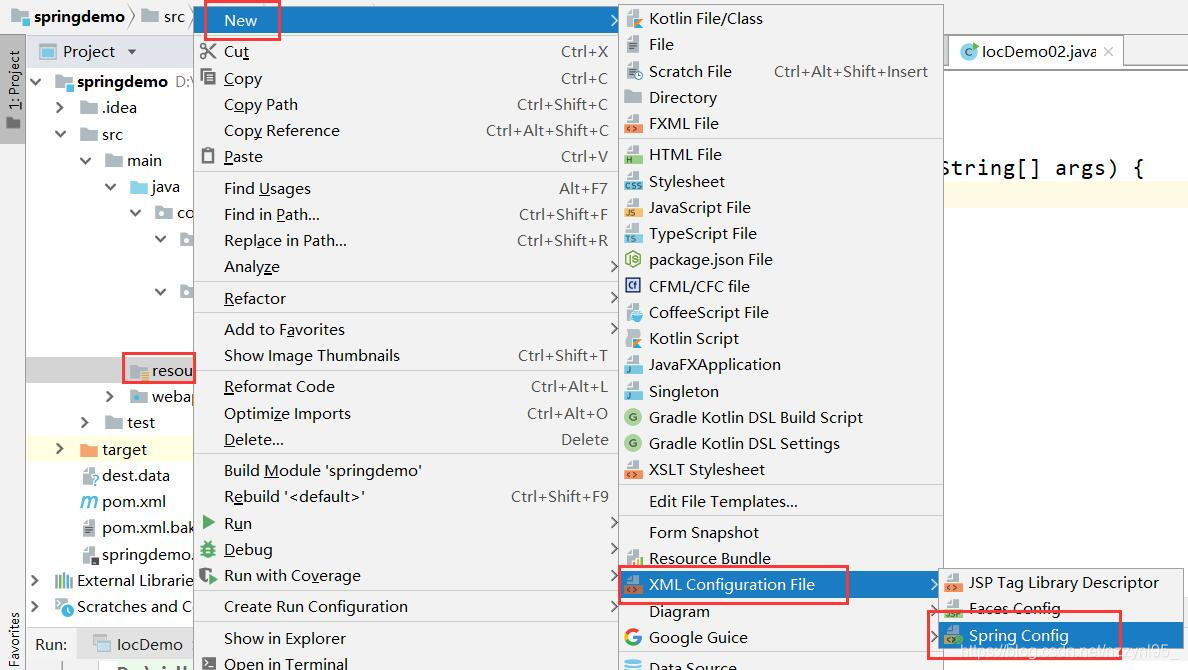
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--定义一个学生对象-->
<bean id="s1" class="com.zz.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="088"/>
<property name="name" value="王思聪"/>
<property name="gender" value="男"/>
<property name="birthday" value="1988-07-18"/>
<property name="major" value="谈恋爱"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 然后在java文件夹下创建一个测试类IocDemo02
package com.zz.test;
import com.zz.domain.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class IocDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用了spring ioc 容器注入了一个对象。没有使用new.内部也是通过反射+xml文档的解析来实现的。
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student s1 = (Student) context.getBean("s1");
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
- 运行结果
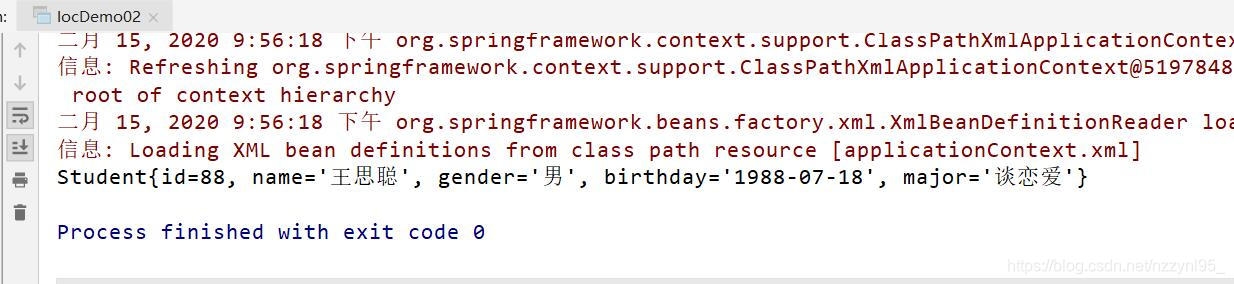
Spring IOC 执行顺序:
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student s1 = (Student) context.getBean("s1");
(1)首先到resources下加载applicationContext.xml 文档
(2)解析这个文档
(3)getBean(‘s1’),从文档中解析到s1对象。使用java的反射机制,反射出一个对象出来并返回
简单一句:Spring IOC 内部实现的原理就是xml解析+反射
注意:属性的初始化是通过调用setXXX来实现的,对象创建通过调用默认的无参构造方法去实现的,那么要求必须保留那个默认的无参构造方法,否则spring ico容器也无法实例化对象。
总结IOC对象初始化的步骤:
(1)加载applicationContext.xml
(2)解析对应的id对象
(3)通过反射调用默认的无参构造方法,实例化对象
(4)通过调用setXXX,初始化属性








 本文介绍了Spring框架的基本概念,展示了如何快速创建一个Spring项目,详细讲解了使用Spring IOC容器创建对象的步骤,包括Java中创建对象的五种方法,并探讨了Spring IOC的内部实现原理和对象初始化过程。
本文介绍了Spring框架的基本概念,展示了如何快速创建一个Spring项目,详细讲解了使用Spring IOC容器创建对象的步骤,包括Java中创建对象的五种方法,并探讨了Spring IOC的内部实现原理和对象初始化过程。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








