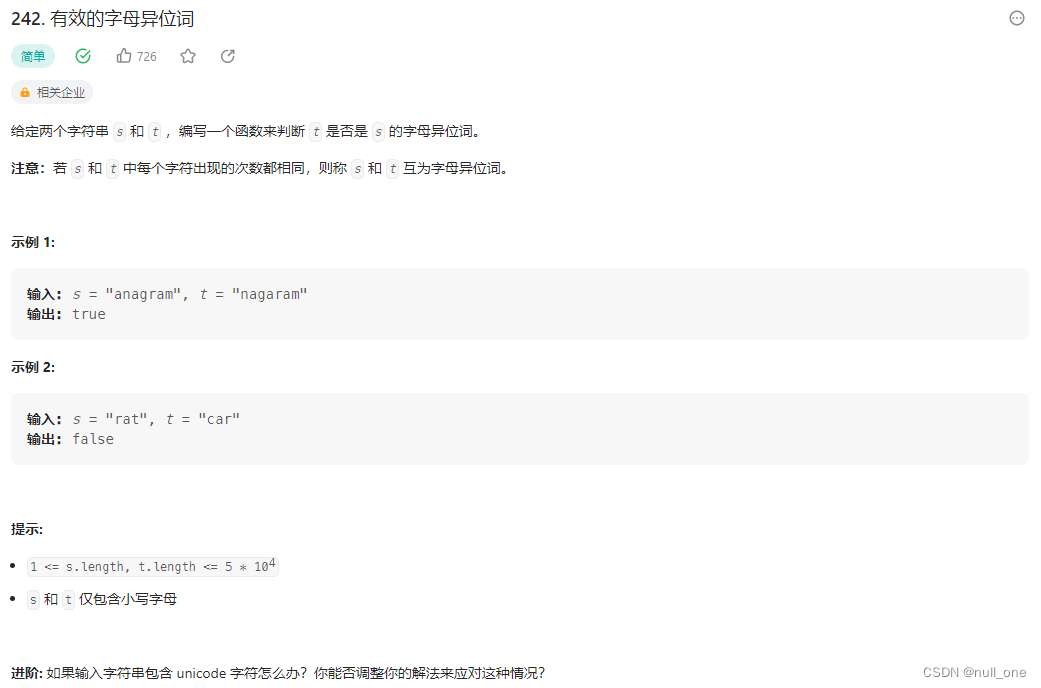
242 有效的字母异位词
题目描述
解决方法
使用vector充当哈希表
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
vector<int> flag(26,0);
for(char a :s)
{
flag[a-'a']++;
}
for(char a:t)
{
flag[a-'a']--;
}
for(int i = 0;i<26;i++)
{
if(flag[i]!=0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
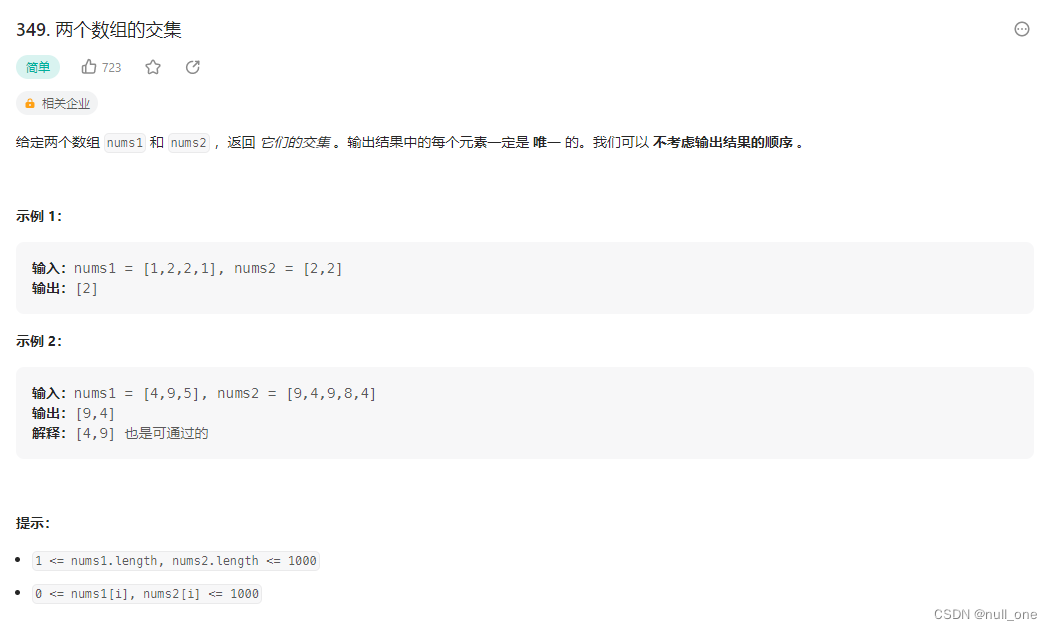
349 两个数组的交集
题目描述
- 两个数组的交集
解决方法
采用三个哈希表(均是vector)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int>hash1(1001,0);
vector<int>hash2(1001,0);
vector<int>hash3(1001,0);
for(auto i : nums1)
{
hash1[i]++;
}
for(auto j: nums2)
{
hash2[j]++;
}
vector<int> ans;
for(int i = 0;i<1000;i++)
{
if((hash1[i]>0)&&(hash2[i]>0)){
hash3[i] = min(hash1[i],hash2[i]);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<1000;i++)
{
if(hash3[i]>0)
ans.push_back(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
通过set作为哈希表来解决哈希问题
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_set<int> result_set;
unordered_set<int> nums1_set(nums1.begin(),nums1.end());
for(int i:nums2)
{
if(nums1_set.find(i)!=nums1_set.end())
{
result_set.insert(i);
}
}
return vector<int>(result_set.begin(),result_set.end());
}
};
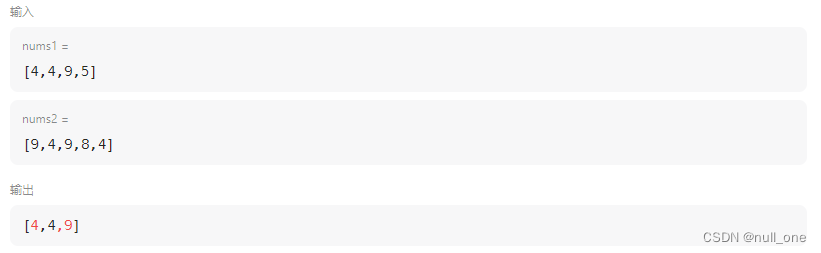
思考, 如果题目中的每个元素一定是唯一的 改为可以重复
解决方法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int>hash1(1001,0);
vector<int>hash2(1001,0);
vector<int>hash3(1001,0);
for(auto i : nums1)
{
hash1[i]++;
}
for(auto j: nums2)
{
hash2[j]++;
}
vector<int> ans;
for(int i = 0;i<1000;i++)
{
if((hash1[i]>0)&&(hash2[i]>0)){
hash3[i] = min(hash1[i],hash2[i]);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<1000;i++)
{
while(hash3[i])
{
ans.push_back(i);
hash3[i]--;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
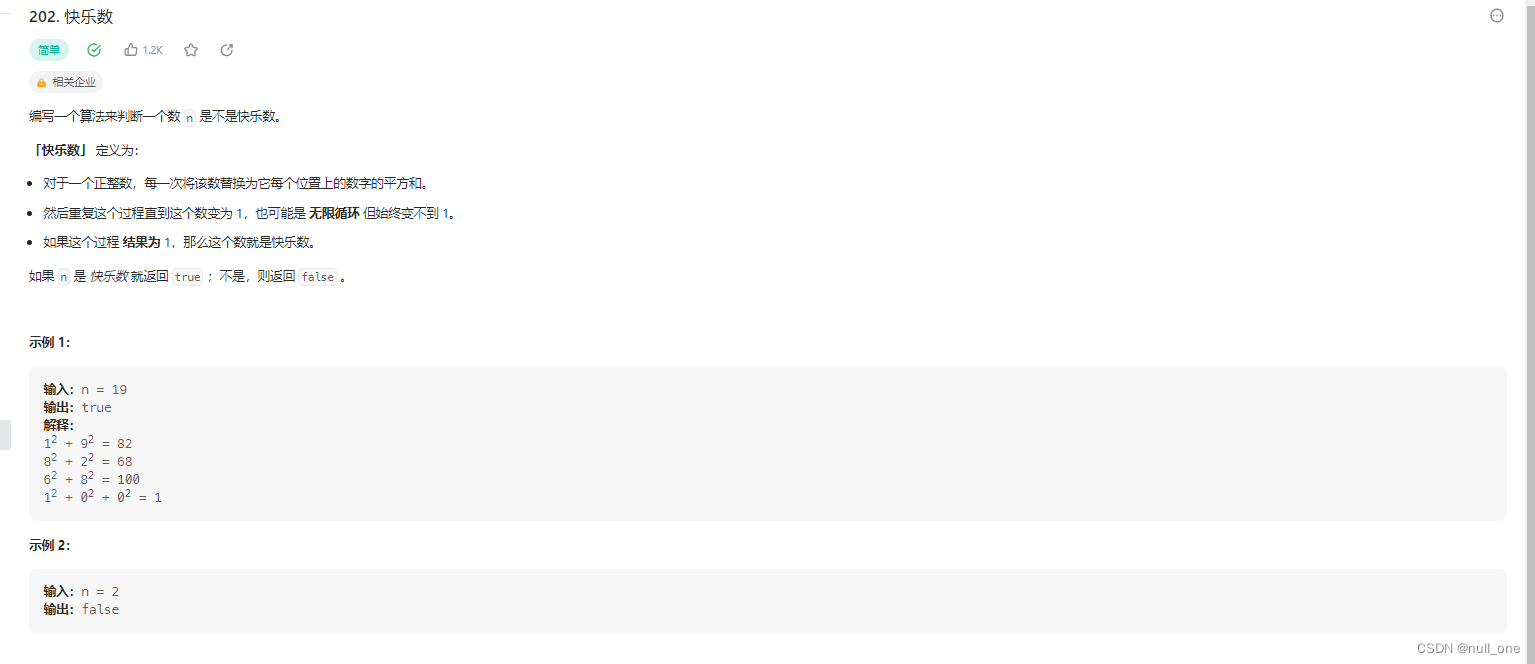
202. 快乐数
题目描述
方法1 暴力求解
class Solution {
public:
int bitSquareSum(int n) {
int sum = 0;
while(n > 0)
{
int bit = n % 10;
sum += bit * bit;
n = n / 10;
}
return sum;
}
bool isHappy(int n) {
int slow = n, fast = n;
do{
slow = bitSquareSum(slow);
fast = bitSquareSum(fast);
fast = bitSquareSum(fast);
}while(slow != fast);
return slow == 1;
}
};
哈希解法
class Solution {
public:
// 取数值各个位上的单数之和
int getSum(int n) {
int sum = 0;
while (n) {
sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
bool isHappy(int n) {
unordered_set<int> set;
while(1) {
int sum = getSum(n);
if (sum == 1) {
return true;
}
// 如果这个sum曾经出现过,说明已经陷入了无限循环了,立刻return false
if (set.find(sum) != set.end()) {
return false;
} else {
set.insert(sum);
}
n = sum;
}
}
};
1.两数之和
题目描述
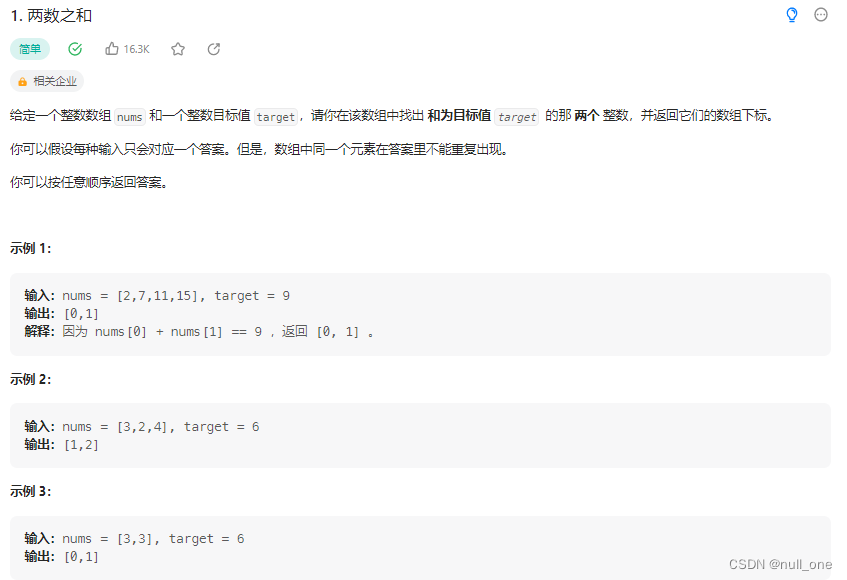
解决方法
1 暴力求解
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i<n;i++)
{
for( int j = i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(nums[i]+nums[j] == target)
return {i,j};
}
}
return {};
}
};
2 哈希表
本题其实有四个重点:
为什么会想到用哈希表
哈希表为什么用map
本题map是用来存什么的
map中的key和value用来存什么的
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
std::unordered_map <int,int> map;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
auto iter = map.find(target - nums[i]);
if(iter != map.end()) {
return {iter->second, i};
}
map.insert(pair<int, int>(nums[i], i));
}
return {};
}
};





 文章介绍了如何使用哈希表解决编程问题,包括判断字母异位词、找出两个数组的交集、处理重复元素的交集以及判断快乐数。同时,对比了暴力求解和哈希表解法的效率差异。
文章介绍了如何使用哈希表解决编程问题,包括判断字母异位词、找出两个数组的交集、处理重复元素的交集以及判断快乐数。同时,对比了暴力求解和哈希表解法的效率差异。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








