Nearest Excluded Points(1900)
题意:
给定n个独特的二维坐标点,找出距离每个点最近汉明距离的不在这些n个独特二维坐标点的整数坐标二维格点。
数据范围:

题解:
没有找到对每个点在Log复杂度内的算法。
事实上,对于距离相邻的点或者说挨在一起的点可以增量更新。
首先距离最近汉明距离为1的点。
再遍历这些点的邻接顶点,一定可以加入一些距离为2的点。
以此类推。每次都可以加入新格点。
迭代到所有点都加入完毕即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
set<pair<int,int>> m;
map<pair<int,int>,int> mapp;
pair<int,int> ans[n];
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)
{
int x,y; cin >> x >> y;
m.insert({x,y});
mapp[{x,y}]=i;
}
set<pair<int,int>> m_;
for(auto& p : m)
{
int x = p.first; int y = p.second;
if(m.find({x+1,y})==m.end()){
m_.insert({x,y});ans[mapp[{x,y}]] = {x+1,y};
}
else if(m.find({x-1,y})==m.end())
{
m_.insert({x,y});ans[mapp[{x,y}]] = {x-1,y};
}
else if(m.find({x,y-1})==m.end())
{
m_.insert({x,y});ans[mapp[{x,y}]] = {x,y-1};
}
else if(m.find({x,y+1})==m.end())
{
m_.insert({x,y});ans[mapp[{x,y}]] = {x,y+1};
}
}
for(auto &p : m_) m.erase(p.first);
int dis = 1;
while(!m.empty())
{
set<pair<int,int>> newadd;
dis++;
for(auto &p:m_)
{
int x = p.first.first,y = p.first.second;
int ind= mapp[{x,y}];
int nx = ans[ind].first,ny = ans[ind].second;
if(m.find({x-1,y})!=m.end()) {newadd.insert({x-1,y});ans[mapp[{x-1,y}]] = {nx,ny};
}
if(m.find({x,y-1})!=m.end()) {newadd.insert({x,y-1});ans[mapp[{x,y-1}]] = {nx,ny};
}
if(m.find({x+1,y})!=m.end()) {newadd.insert({x+1,y});ans[mapp[{x+1,y}]] = {nx,ny};
}
if(m.find({x,y+1})!=m.end()) {newadd.insert({x,y+1});ans[mapp[{x,y+1}]] = {nx,ny};
}
}
m_.clear();
for(auto p : newadd)
{
m.erase(p);
m_.add(newadd);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) printf("%d")
}
反思:这道题最初想法是看距离相同距离汉明距离上是否有点,但均不能在log复杂度内求解。但注意这里有多个点,看输出看能否增量更新,相邻点间的汉明距离有何关系。
Expand the Path(1900)
题意: 给定n*n网格。你初始处于(1,1)位置,给定字符串初始s只包含D和R字符,分别表示向下和向右移动一个单位。你可以任意选择字符将其在原始位置重复任意多次。对所有结果字符串对应的路径(不能走出网格),求所有能够抵达的网格数。
注意:len(s)在1e5,n在1e8
题解:划分解空间。
如果s中第i个字符前既有D又有R,考察处理完s第i个字符时(所有解中),可能走到的网格点。显然为一个长方形。处理完s第i+1个字符后,该长方形向下或向右平移一个单位,新增范围就是该长方形的长或宽。再注意一些边界条件即s中全是D或R即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
int t;scanf("%d",&t);
for(int i = 0;i<t;i++){
ll n;cin>>n;
string s;cin>>s;
ll countD = 0,countR = 0;
char first = s[0];
for(int v = 0;v<s.size();v++) if(s[v]=='D') countD++; else countR++;
if(countD == 0 || countR == 0) cout<<n<<endl;
else
{
ll ans = n - (first=='R'?countR:countD) + 1;int v = 0;
int t1 = countR,t2 = countD;
v++;
if(first=='R') countR--;else countD--;
while(s[v]==first) {v++;ans++;if(first=='R')countR--;else countD--;}
if(s[v] == 'D') countD--; else countR--;
ll w = n - t1; ll h = n - t2;
ans += w*h;
ans = ans + h * countR + w * countD;
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
反思:最初的想法不成熟。只考虑了处理到第一次s出现D和R时能够走到的范围,想当然地认为其能够覆盖所有,并没有考虑再处理后面可能新增的范围。为何要在每个末尾处理,是因为s中初始的D和R必须存在。
Required Length(1700)
题意: 给定两个整数n,x。每次操作选取整数x的某位将x乘以它。问将x变为n位数的最小操作次数。
题解:
实验表明计算结点数不会很多。理论证明:
乘的每一位数分解质因数都是2,3,5,72,3,5,72,3,5,7的幂次
因此中间每个结果必可以表示为
x⋅2a⋅3b⋅5c⋅7dx \cdot 2^a \cdot 3^b \cdot 5^c \cdot 7^dx⋅2a⋅3b⋅5c⋅7d的形式
由数据范围的限制,中间结果数不会很多。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 998244353;
ll dfs(ll x,ll n,map<ll,ll>& m)
{
auto it = m.find(x);
if(it!=m.end()) return it->second;
bool occ[10]; memset(occ,0,sizeof(occ));
int c = 0;
ll t = (ll)x;
while(x > 0)
{
occ[x%10]=true; x/=10; c++;
}
if((ll)c == n) {m[t]=0;return 0;}
ll ans = LONG_LONG_MAX;
for(ll i = 2;i<=9;i++)
{
ll a = dfs(t*i,n,m);
if(occ[i] && a!=LONG_LONG_MAX)
ans = min(dfs(t*i,n,m) + 1,ans);
}
m[t] = ans;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ll n,x;
cin >> n >> x;
map<ll,ll> m;
ll ans = dfs(x,n,m);
if(ans == LONG_LONG_MAX) cout << -1 <<endl; else cout << ans <<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
反思:走投无路时反思暴力做法是否可行。
Not Adding(1900 GOOD)
题意:给定n个整数组成的数组a1,a2⋯ana_1,a_2 \cdots a_na1,a2⋯an.(不同整数)。每次操作选取i,ji,ji,j,如果数组中不存在gcd(ai,aj)gcd(a_i,a_j)gcd(ai,aj)则将其加入。问最多可以执行多少次这样的操作。
数据范围:
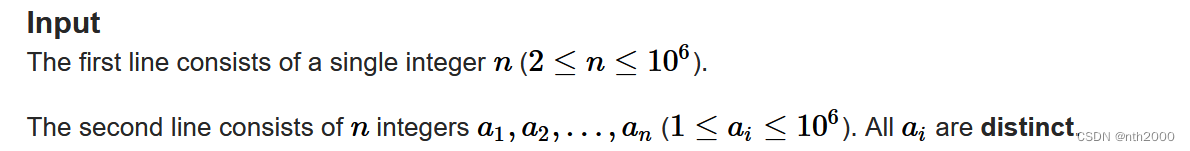
题解:解空间中至多有1∼max(a)1 \sim max(a)1∼max(a)种可能。暴力枚举每个数看其是否可以被加入。每个数只可由原数组中是其倍数的数生成,如果这些数的gcd等于该数,则由生成过程该数必须加入。否则一定不能加入(因为这些数的gcd大于该数,后续生成的gcd都大于该数,该数一定不能存在于最终数组)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define RG register int
#define LL long long
#define N 200001
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b == 0?a:gcd(b,a%b);}
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
ll a[n]; ll maximal = - 1;set<ll> a_;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){cin>>a[i];maximal = max(maximal,a[i]);}
bool has[maximal+1]; memset(has,0,sizeof(has));
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) {has[a[i]]=true;}
for(int i = 1;i<=maximal;i++) a_.insert(i);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) {a_.erase(a[i]);}
vector<ll> r;for(ll v : a_) r.push_back(v);
ll ans = 0;
for(ll v:r)
{
ll g = 0;
for(ll s = v;s<=maximal;s+=v) if(has[s]) g=gcd(s,g);
if(g==v) ans++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
反思:看看数据范围,反思暴力是否可行(考察每一个解是否可以被加入)。
 算法解析:二维坐标点的汉明距离与路径规划
算法解析:二维坐标点的汉明距离与路径规划




















 375
375

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








