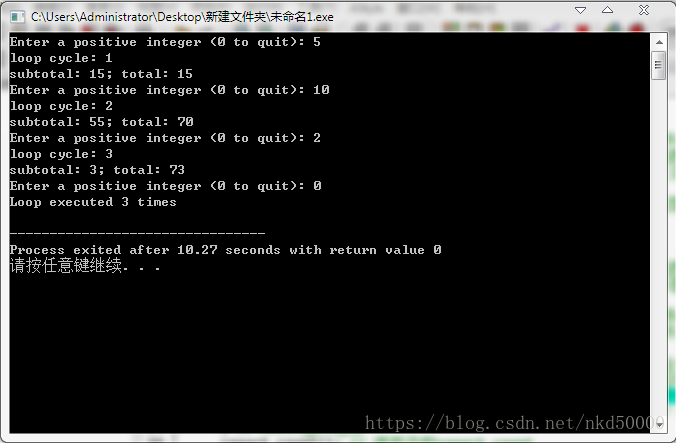
// parta.c --- various storage classes
#include <stdio.h> // 包含头文件stdio.h,后面需要用到这个文件中的东西
void report_count(); // 函数原型声明,可以保证后面使用这个函数的时候不需要考虑它所定义的
// 位置,如果没有这条语句,则只能在定义这个函数之后才能使用它。
void accumulate(int k); // 同上,也是另一个函数的原型声明
int count = 0; // file scope, external linkage // 定义一个整型的全局常量,名称为count,初始值为0
int main(void) // 主函数的入口,程序从这里开始执行
{
int value; // automatic variable // 定义一个作用域为本函数的局部整型变量value,未初始化
register int i; // register variable // 定义一个整型寄存器变量i(存储到CPU的寄存器中),未初始化
printf("Enter a positive integer (0 to quit): "); // 调用stdio.h头文件中的函数printf输出一串字符串
while (scanf("%d", &value) == 1 && value > 0) // 循环条件:使用一个循环,强制输入一个整数,且值必须大于0
{ // while循环开始
++count; // use file scope variable // 每循环一次,全局变量count的值加1
for (i = value; i >= 0; i--) // 使用输入的正值作为循环的起始值,让循环每执行一次i减1,当i>=0就一直循环
accumulate(i); // 每循环一次就把i的当前值作为参数传入函数accumulate,并调用它
printf("Enter a positive integer (0 to quit): "); // for循环结束,输出一串字符串
} // while循环结束
report_count(); // 调用函数report_count
return 0; // 返回本函数,返回值为0(本函数由操作系统调用,返回0一般表示成功执行结束)
}
void report_count() // 定义函数report_count,无返回值,不需要参数
{
printf("Loop executed %d times\n", count); // 输入全局变量count的当前值
}
// partb.c -- rest of the program
#include <stdio.h> // 包含头文件 stdio.h
extern int count; // reference declaration, external linkage // 声明全局整型变量count为外部变量,即这个变量在
// 其它文件中已经定义了,此处只是声明一下,并不是
// 定义,声明的原因是,可能后面的代码要用到这个其
// 它文件中声明的变量
static int total = 0; // static definition, internal linkage // 定义一个全局整型变量total,初始值为0
void accumulate(int k); // prototype // 原型声明,声明的原因是让使用这个函数的代码不用考虑这个函数定义的位置
void accumulate(int k) // k has block scope, no linkage // 函数accumulate定义,无返回值,需要一个整型参数传给k
{
static int subtotal = 0; // static, no linkage // 定义一个作用域为本函数的局部静态整型变量subtotal,初始值为0
if (k <= 0) // 当k<=0则执行大括号中的代码
{
printf("loop cycle: %d\n", count); // 输出引用到的其它文件中定义的外部变量count的值
printf("subtotal: %d; total: %d\n", subtotal, total); // 输出subtotal,total两个变量的值
subtotal = 0; // 给subtotal赋值为0
}
else // 当 k<=0 不满足时执行后面大括号中的代码
{
subtotal += k; // 让subtotal的值加上k,再赋给subtotal本身,即让subtotal自己增大k, 相当
// 于subtotal = subtotal + k;注意=不是指相等的意思,而是赋值运算符
total += k; // 让total自增k,同上
}
}




 本文详细解析C语言中的存储类别,包括自动变量、寄存器变量、静态变量及外部变量的使用,通过具体代码示例展示了不同作用域变量的生命周期与链接属性。同时,介绍了如何在多个源文件间共享全局变量。
本文详细解析C语言中的存储类别,包括自动变量、寄存器变量、静态变量及外部变量的使用,通过具体代码示例展示了不同作用域变量的生命周期与链接属性。同时,介绍了如何在多个源文件间共享全局变量。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








