可验证延迟函数(Verifiable Delay Function, VDF):
VDF 这个概念最初由斯坦福大学密码学教授 Dan Boneh 等人在2018年论文《Verifiable Delay Functions》中给出。该篇文章于 2018 年发表在密码学顶级会议之一的 CRYPTO 上。
目前的VDF算法复杂度较高,离实用仍有差距。
https://github.com/Chia-Network/vdf-competition/中有对VDF的实现进行了竞赛。
[研究]可验证延迟函数(VDF)(一)一文搞懂VDF中有很详细的介绍。
https://github.com/cambrian/accumulator/blob/master/src/group/class.rs中有对https://github.com/Chia-Network/vdf-competition/blob/master/classgroups.pdf的class group 做实现。
VDF是串行运算算法,执行时间可预知,且无法通过并行来加速。通过VDF生成的证明可被快速verify。
目前知名的不可并行的串行运算为:对未知order的group进行repeated squaring。
The unknown order requirement is due to the divisibility of the order of a finite group by the order of any element in the group; if the group order is known then the repeated squaring operation could be reduced modulo the order of the group, shortcutting the computation.
在VDF中:
- 若使用RSA group,则需要trusted setup,并保证生成后的有毒垃圾被即时清理,否则VDF的sequentiality requirement将broken。
- 若使用class group of binary quadratic form将不需要trusted setup。因为其order为一个负素数判别式 d d d,当 ∣ d ∣ ≡ 3 m o d 4 |d|\equiv 3\ mod\ 4 ∣d∣≡3 mod 4时,is believed to be difficult to compute when d d d is sufficiently large, making the order of the class group effectively unknown. Therefore, a suitable discriminant ——and its associated class group —— can be chosen without the need for a trusted setup, which is a major advantage for using class groups in applications requiring groups of unknown order.
1. Binary quadratic form
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
a
x
2
+
b
x
y
+
c
y
2
f(x,y)=ax^2+bxy+cy^2
f(x,y)=ax2+bxy+cy2, where
a
,
b
,
c
∈
R
a,b,c\in R
a,b,c∈R and
a
!
=
0
,
b
!
=
0
,
c
!
=
0
a!=0, b!=0,c!=0
a!=0,b!=0,c!=0。
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f=(a,b,c)
f=(a,b,c)可称为a form。
若
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f=(a,b,c)
f=(a,b,c), where
a
,
b
,
c
∈
Z
a,b,c\in Z
a,b,c∈Z and
a
!
=
0
,
b
!
=
0
,
c
!
=
0
a!=0, b!=0,c!=0
a!=0,b!=0,c!=0,则 f 称为integral form。
c
o
n
f
(
f
)
=
g
c
d
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
conf(f)=gcd(a,b,c)
conf(f)=gcd(a,b,c)称为content of a form。
若
c
o
n
f
(
f
)
=
1
conf(f)=1
conf(f)=1,则form f称为primitive。
discriminant of form f为:
Δ
(
f
)
=
b
2
−
4
a
c
\Delta(f)=b^2-4ac
Δ(f)=b2−4ac。
若
−
a
<
b
≤
a
-a<b\leq a
−a<b≤a,则form
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f=(a,b,c)
f=(a,b,c)称为normal。
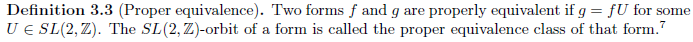
1.1 Normalization操作
Normalization操作(当
−
a
<
b
≤
a
-a<b\leq a
−a<b≤a时,需要进行此操作, Normalization操作不会影响discriminant值,即
b
2
−
4
a
c
b^2-4ac
b2−4ac保持不变。):
η
(
f
)
=
η
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
=
(
a
,
b
+
2
r
a
,
a
r
2
+
b
r
+
c
)
\eta(f)=\eta(a,b,c)=(a,b+2ra,ar^2+br+c)
η(f)=η(a,b,c)=(a,b+2ra,ar2+br+c),其中
r
=
⌊
a
−
b
2
a
⌋
r=\left \lfloor \frac{a-b}{2a} \right \rfloor
r=⌊2aa−b⌋。
若
f
n
o
r
m
=
(
a
′
,
b
′
,
c
′
)
=
η
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f_{norm}=(a',b',c')=\eta(a,b,c)
fnorm=(a′,b′,c′)=η(a,b,c),
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f=(a,b,c)
f=(a,b,c),则
f
n
o
r
m
∼
f
f_{norm}\sim f
fnorm∼f两者等价:
U
=
(
1
r
0
1
)
U=\begin{pmatrix} 1&r \\ 0&1 \end{pmatrix}
U=(10r1),
(
f
U
)
(
x
,
y
)
=
f
n
o
r
m
(fU)(x,y)=f_{norm}
(fU)(x,y)=fnorm。
1.2 Reduced form
在Chia VDF中频繁地reduce
f
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f(a,b,c)
f(a,b,c)非常重要,可保证在做平方运算时,a,b,c的值不会增长过大。
若
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f=(a,b,c)
f=(a,b,c)已为normal,且
a
<
c
a<c
a<c或者当
a
=
c
时
,
b
≥
0
a=c时,b\geq0
a=c时,b≥0,则称 f 为Reduced form。
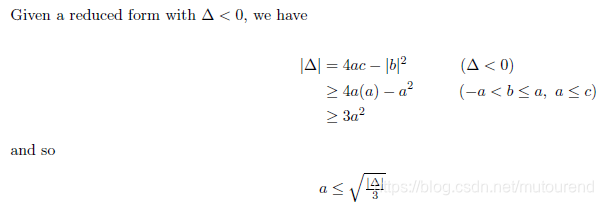
1.3 Reduction操作
在reduction操作之前应先进行normalization操作。
Reduction操作为(当
a
>
c
a>c
a>c时或
a
=
c
a
n
d
b
<
0
a=c\ and\ b<0
a=c and b<0,需要进行此操作, Reduction操作不会影响discriminant值,即
b
2
−
4
a
c
b^2-4ac
b2−4ac保持不变。):
对于
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f=(a,b,c)
f=(a,b,c),有reduction操作
ρ
(
f
)
=
ρ
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
=
(
c
,
−
b
+
2
s
c
,
c
s
2
−
b
s
+
a
)
\rho(f)=\rho(a,b,c)=(c,-b+2sc,cs^2-bs+a)
ρ(f)=ρ(a,b,c)=(c,−b+2sc,cs2−bs+a),其中
r
=
⌊
c
+
b
2
c
⌋
r=\left \lfloor \frac{c+b}{2c} \right \rfloor
r=⌊2cc+b⌋
ρ
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
∼
η
(
c
,
−
b
,
a
)
\rho(a,b,c)\sim \eta(c,-b,a)
ρ(a,b,c)∼η(c,−b,a)两者等价。
若
f
r
e
d
=
(
a
′
,
b
′
,
c
′
)
=
ρ
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
f_{red}=(a',b',c')=\rho(a,b,c)
fred=(a′,b′,c′)=ρ(a,b,c),则
f
=
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
∼
f
r
e
d
f=(a,b,c)\sim f_{red}
f=(a,b,c)∼fred两者等价,其中的
U
=
(
0
−
1
1
r
)
U=\begin{pmatrix} 0&-1 \\ 1&r \end{pmatrix}
U=(01−1r),
(
f
U
)
(
x
,
y
)
=
f
r
e
d
(fU)(x,y)=f_{red}
(fU)(x,y)=fred。

如上图所示,reduction算法会循环执行步骤2,以保证最终获得reduced form。执行步骤2的次数为:


1.4 composition计算
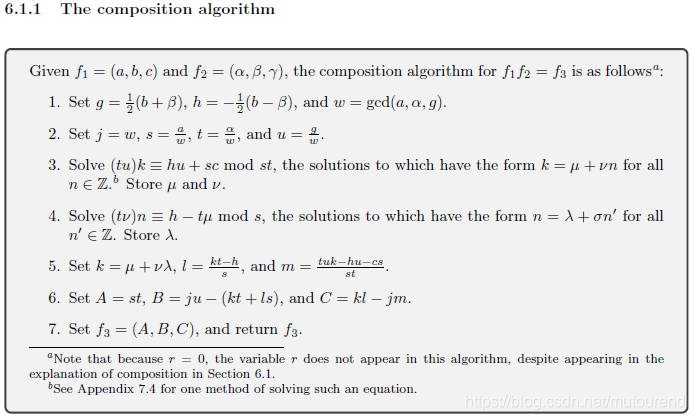
1.4.1 squaring算法
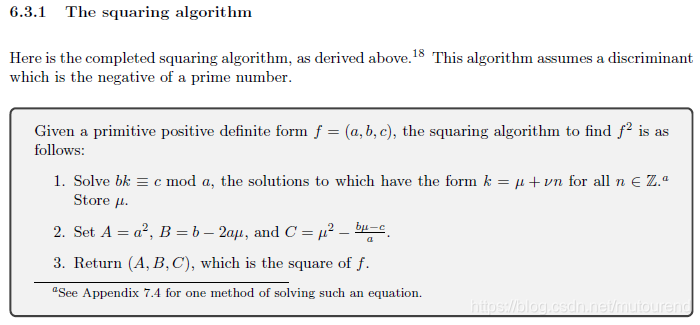
1.4.2 linear congruence算法
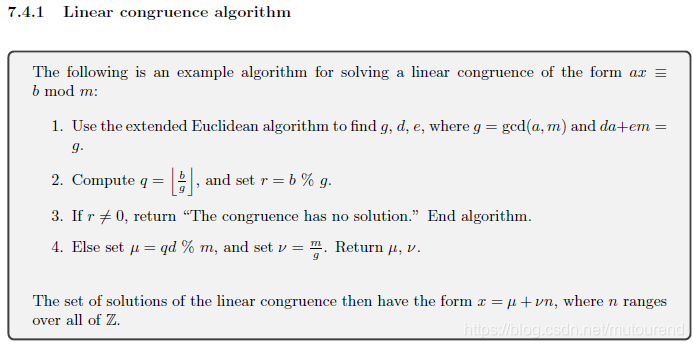
2. Matrix表示a form
M
(
f
)
=
(
a
b
/
2
b
/
2
c
)
M(f)=\begin{pmatrix} a&b/2 \\ b/2&c \end{pmatrix}
M(f)=(ab/2b/2c),其中
d
e
t
(
M
(
f
)
)
=
a
c
−
b
2
4
det(M(f))=ac-\frac{b^2}{4}
det(M(f))=ac−4b2
若
X
=
(
x
y
)
X=\begin{pmatrix} x&y \end{pmatrix}
X=(xy),则有:
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
a
x
2
+
b
x
y
+
c
y
2
=
X
M
(
f
)
X
T
=
(
x
y
)
(
a
b
/
2
b
/
2
c
)
(
x
y
)
f(x,y)=ax^2+bxy+cy^2=X\ M(f)\ X^T =\begin{pmatrix} x&y \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix} a&b/2 \\ b/2&c \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix}
f(x,y)=ax2+bxy+cy2=X M(f) XT=(xy)(ab/2b/2c)(xy)
如上有:
Δ
(
f
)
=
−
4
∗
d
e
t
(
M
(
f
)
)
=
b
2
−
4
a
c
\Delta(f)=-4*det(M(f))=b^2-4ac
Δ(f)=−4∗det(M(f))=b2−4ac

参考资料:
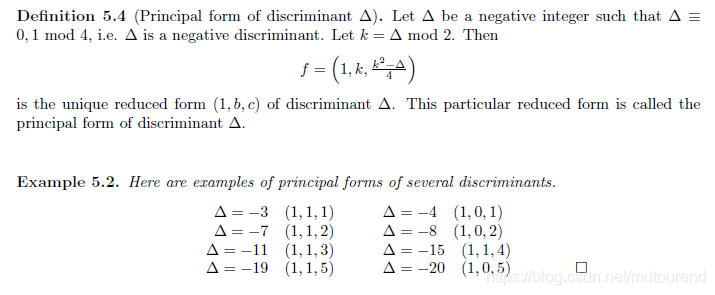
[1] [研究]可验证延迟函数(VDF)(一)一文搞懂VDF
[2] https://github.com/Chia-Network/vdf-competition/
[3] 2018年论文《Verifiable Delay Functions》
[4] class group论文《Binary quadratic forms》





















 1147
1147

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








