- 可以发现,每个Java文件中,若都要连接数据库,那么,都要写一些死命令(连接数据库的固定代码),这些会影响代码的书写效率,而且数据库的用户名和密码都会显式的出现在代码中,因此,我们可以将其封装到一个文件中,制作一个工具类来使用,这样每次连接数据库都只需调用工具类就好了
- 先创建一个db.properties文件并将连接数据库的固定代码写入
如下图: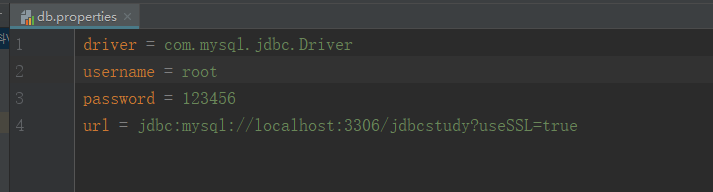
URL格式为:协议 + 子协议 + 主机:端口 + 数据库 + 参数
这是上一篇博客中用到的url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy
是没有加参数的,这里加到的 ?useSSL=true为将数据库连接设置为安全连接,一些新版本的数据库会有此要求,建议加上
- 制作JDBC工具类JDBCUtils,java
package com.kuang.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
//编写一个工具类简化开发 , 创建连接数据库都是死代码 , 每次写及其不方便 , 还有关闭连接;
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String driver=null;
private static String username=null;
private static String password=null;
private static String url=null;
static{
try {
//加载配置文件
InputStream is = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
//读取配置文件
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
//加载数据库驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取数据库连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
//释放资源
public static void closeAll(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,Connection connection){
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
解释:
- 将加载配置文件、读取配置文件、加载数据库驱动的操作放入static静态代码块中,只需加载一次
- 获取数据库连接对象也写成了一个getConnection()方法,调用直接连接。
- 释放资源也为一个closeAll()方法,需要将使用的ResultSet,Statement,connection作为参数传入进去即可
工具类到这里就制作完成了,接下来我们使用工具类来测试数据库的增删改查(这里用到了Junit测试,没有main函数)
import com.studycode.utils.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo1{
//增
@Test
public void insert(){
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
try{
//1.连接数据库
connection =JDDCUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建statement对象
statement=connection.createStatement();
//3.编写sql语句
String sql="insert into users(id,name,password,email,birthday) values(5,'wangwu','123456','wangwu@sina.com,'1998-09-09)";
//执行sql语句
int i =statement.executeUpdate(sql);//返回受影响的行数
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5.释放资源
JDBCUtils.closeAll(null,statement,connection);
}
}
//删
@Test
public void delete() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建statement对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.编写Sql语句
String sql = "delete from users where id = 5";
//4.执行sql语句
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql); //返回受影响的行数
if (i>0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5.释放资源
JDBCUtils.closeAll(null,statement,connection);
}
}
//改
@Test
public void update() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建statement对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.编写Sql语句
String sql = "update users set name = 'qinjiang' where id = 4";
//4.执行sql语句
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql); //返回受影响的行数
if (i>0){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5.释放资源
JDBCUtils.closeAll(null,statement,connection);
}
}
//查
@Test
public void query() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建statement对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.编写Sql语句
String sql = "select * from users";
//4.执行sql语句
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("name"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("password"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("email"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getDate("birthday"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5.释放资源
JDBCUtils.closeAll(resultSet,statement,connection);
}
}
}
使用工具类来连接数据库,方便了很多,并且把释放资源加入到try-catch代码后面的finally代码块中,使之无论如何都会释放资源





















 1449
1449

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








