目录
1.1. Spring AOP 和 CGLIB 是什么关系?
一. 前言
CGLIB 是一个强大的高性能的代码生成包。它广泛的被许多 AOP 的框架使用,例如 Spring AOP 和 dynaop,为他们提供方法的 interception(拦截)。CGLIB 包的底层是通过使用一个小而快的字节码处理框架 ASM,来转换字节码并生成新的类。除了 CGLIB 包,脚本语言例如 Groovy和 BeanShell,也是使用 ASM 来生成 Java 的字节码。当然不鼓励直接使用 ASM,因为它要求你必须对 JVM 内部结构包括 class 文件的格式和指令集都很熟悉。
1.1. Spring AOP 和 CGLIB 是什么关系?
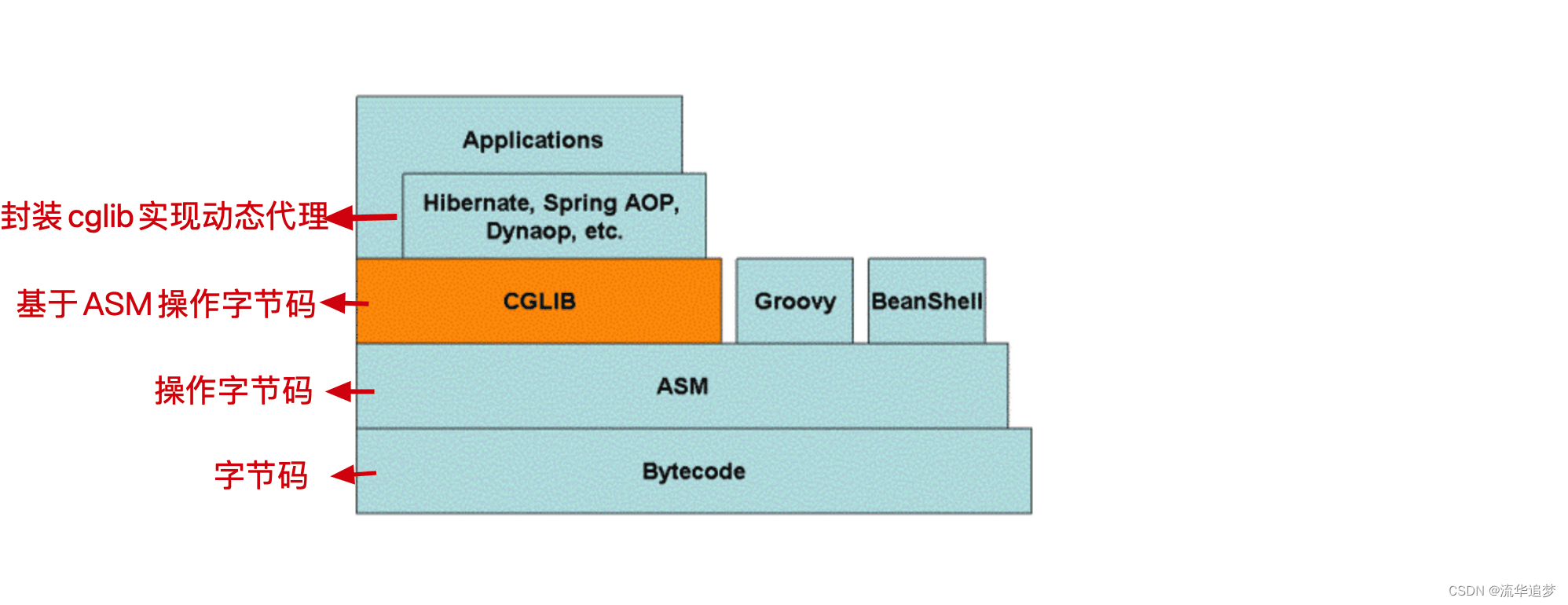
- 最底层是字节码,字节码相关的知识请参见《JVM 之 class文件详解》。
- ASM是操作字节码的工具。
- CGLIB 基于 ASM 字节码工具操作字节码(即动态生成代理,对方法进行增强)。
- Spring AOP 基于 CGLIB 进行封装,实现 CGLIB 方式的动态代理 。
二. CGLIB 代理示例
2.1. pom 包依赖
引入 CGLIB 的依赖包:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>com.lm.it</groupId>
<artifactId>lm-spring-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>06-lm-spring-demo-aop-proxy-cglib</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/cglib/cglib -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>2.2. 定义实体
User 类:
package com.lm.it.springframework.entity;
/**
* User
*/
public class User {
/**
* user's name.
*/
private String name;
/**
* user's age.
*/
private int age;
/**
* init.
*
* @param name name
* @param age age
*/
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}2.3. 被代理的类
即目标类,对被代理的类中的方法进行增强:
package com.lm.it.springframework.service;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User;
/**
* UserService
*/
public class UserServiceImpl {
/**
* find user list.
*
* @return user list
*/
public List<User> findUserList() {
return Collections.singletonList(new User("流华追梦", 18));
}
/**
* add user
*/
public void addUser() {
// do something
}
}2.4. CGLIB 代理
CGLIB 代理类,需要实现 MethodInterceptor 接口,并指定代理目标类 target:
package com.lm.it.springframework.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
/**
* This class is for proxy demo.
*/
public class UserLogProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
/**
* 业务类对象,供代理方法中进行真正的业务方法调用
*/
private Object target;
public Object getUserLogProxy(Object target) {
// 给业务对象赋值
this.target = target;
// 创建加强器,用来创建动态代理类
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 为加强器指定要代理的业务类(即:为下面生成的代理类指定父类)
enhancer.setSuperclass(this.target.getClass());
// 设置回调:对于代理类上所有方法的调用,都会调用CallBack,而Callback则需要实现intercept()方法进行拦
enhancer.setCallback(this);
// 创建动态代理类对象并返回
return enhancer.create();
}
// 实现回调方法
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
// log - before method
System.out.println("[before] execute method: " + method.getName());
// call method
Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
// log - after method
System.out.println("[after] execute method: " + method.getName() + ", return value: " + result);
return null;
}
}2.5. 使用代理
启动类中指定代理目标并执行:
package com.lm.it.springframework;
import com.lm.it.springframework.proxy.UserLogProxy;
import com.lm.it.springframework.service.UserServiceImpl;
/**
* Cglib proxy demo.
*/
public class App {
/**
* main interface.
*
* @param args args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// proxy
UserServiceImpl userService = (UserServiceImpl) new UserLogProxy().getUserLogProxy(new UserServiceImpl());
// call methods
userService.findUserList();
userService.addUser();
}
}启动上述类 main() 函数,运行结果如下:
[before] execute method: findUserList
[after] execute method: findUserList, return value: [User{name='流华追梦', age=18}]
[before] execute method: addUser
[after] execute method: addUser, return value: null三. CGLIB 代理的流程
我们把上述 Demo 的主要流程画出来,以便能很快理解:
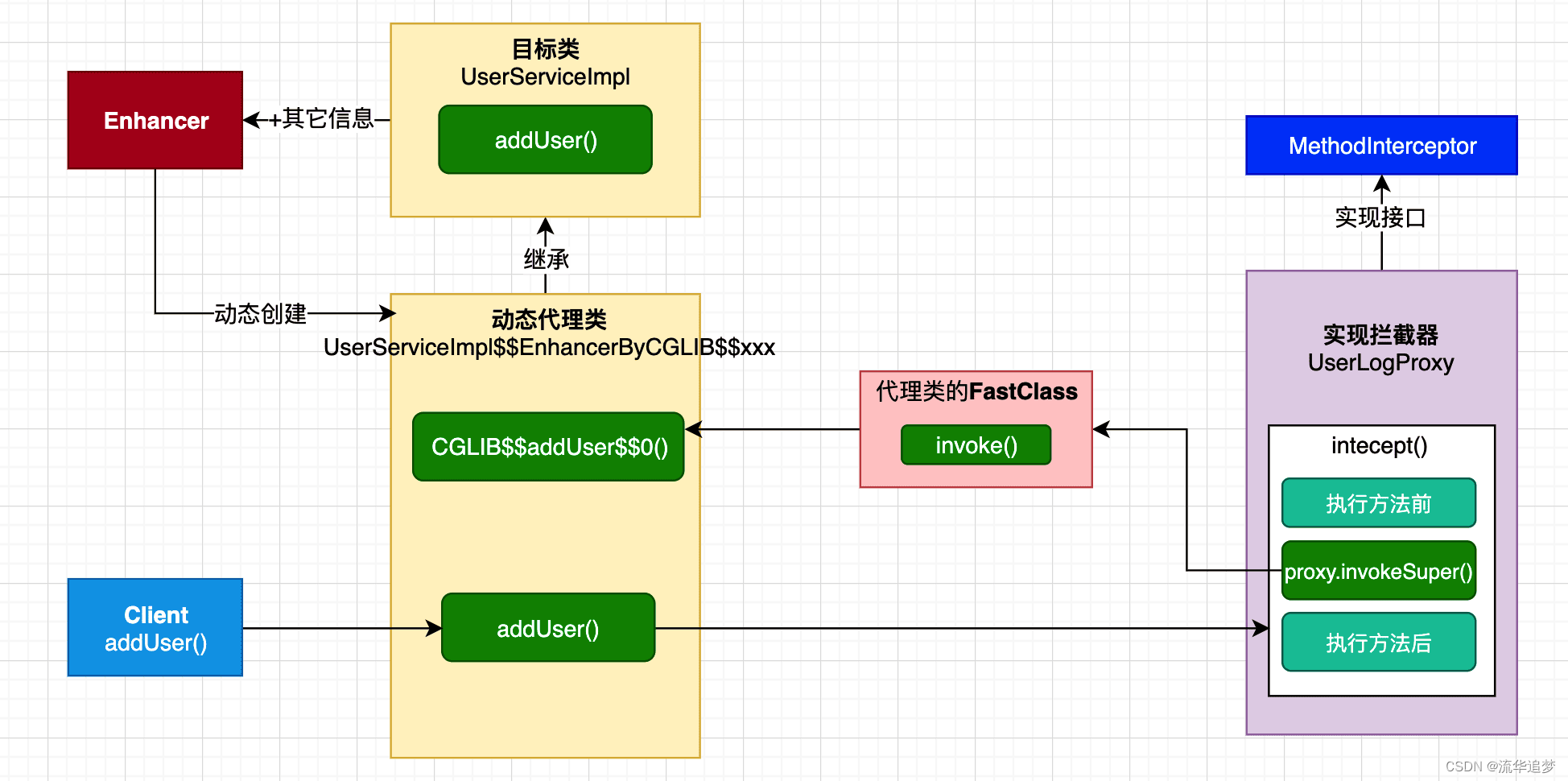
更多细节:
- 在上图中,我们可以通过在 Enhancer 中配置更多的参数来控制代理的行为,比如如果只希望增强这个类中的一个方法而不是所有方法,那就增加 callbackFilter 来对目标类中方法进行过滤。Enhancer 可以有更多的参数类配置其行为,不过我们在学习上述主要的流程就够了。
- final 方法为什么不能被代理?很显然 final 方法没法被子类覆盖,当然不能代理了。
- Mockito 为什么不能 mock 静态方法?因为 mockito 也是基于 CGLIB 动态代理来实现的,static 方法也不能被子类覆盖,所以显然不能 mock。但 PowerMock 可以 mock 静态方法,因为它直接在 bytecode 上工作,更多可以看 Mockito 单元测试。
四. Spring AOP 中 CGLIB 代理的实现
Spring AOP封装了 CGLIB,通过其进行动态代理的创建。
我们看下 CglibAopProxy 的 getProxy() 方法:
@Override
public Object getProxy() {
return getProxy(null);
}
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
// 上面流程图中的目标类
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// 重点看这里,就是上图的enhancer,设置各种参数来构建
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// 设置callback回调接口,即方法的增强点
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// 上节说到的filter
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// 重点:创建proxy和其实例
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
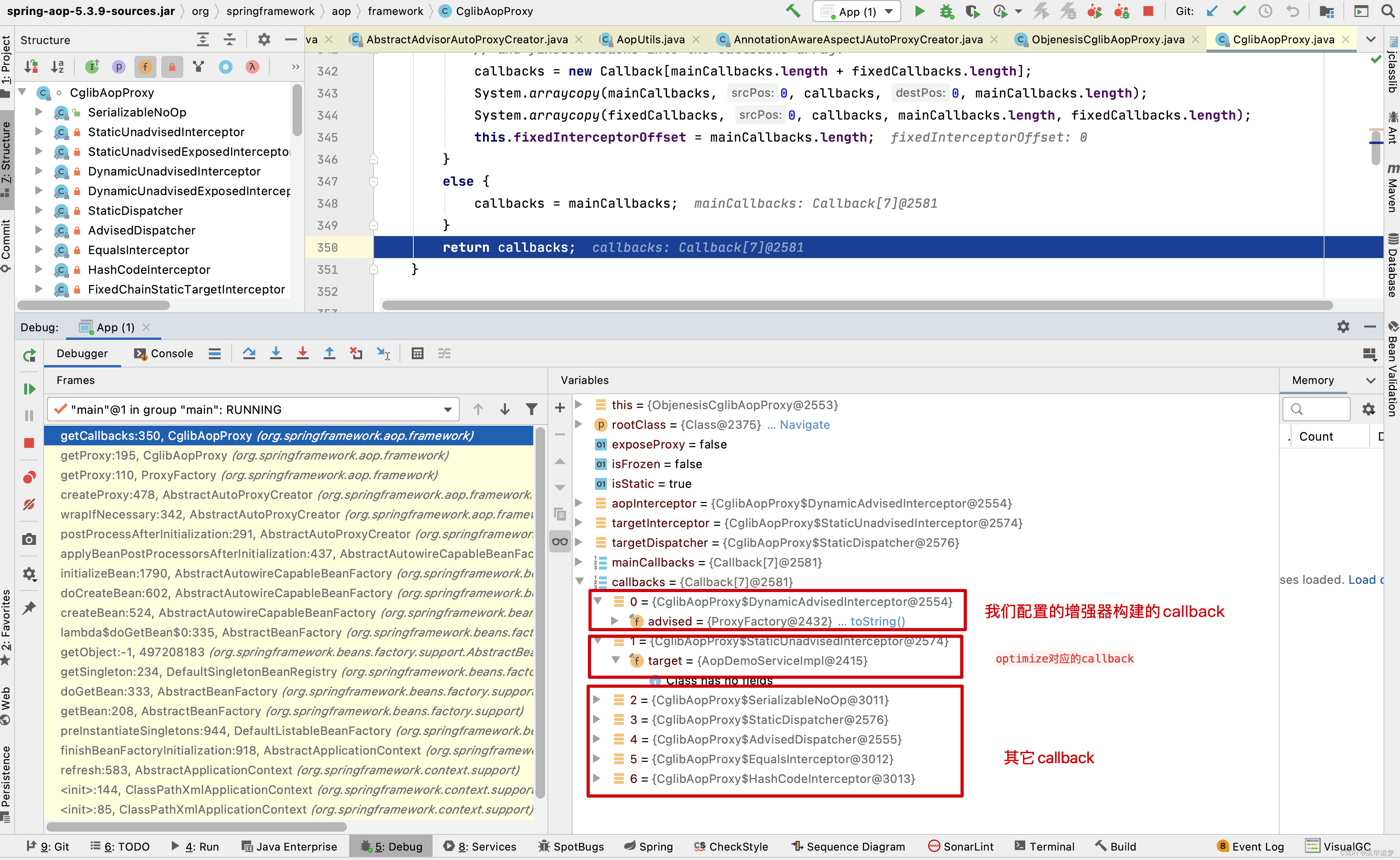
}获取 callback 的方法如下,提几个理解的要点:
- rootClass:即目标代理类。
- advised:包含上文中我们获取到的 advisor 增强器的集合。
- exposeProxy:在 xml 配置文件中配置的,背景就是如果在事务 A 中使用了代理,事务 A 调用了目标类的的方法 a,在方法 a 中又调用目标类的方法 b,方法 a、b 同时都是要被增强的方法,如果不配置 exposeProxy 属性,方法 b 的增强将会失效,如果配置 exposeProxy,方法 b 在方法 a 的执行中也会被增强了
- DynamicAdvisedInterceptor:拦截器将 advised(包含上文中我们获取到的 advisor 增强器)构建配置的 AOP 的 callback(第一个 callback)。
- targetInterceptor:xml 配置的 optimize 属性使用的(第二个 callback)。
- 最后连同其它5个默认的 Interceptor 返回作为 CGLIB 的拦截器链,之后通过 CallbackFilter 的accpet() 方法返回的索引从这个集合中返回对应的拦截增强器执行增强操作。
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
// Parameters used for optimization choices...
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are
// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.
Callback targetInterceptor;
if (exposeProxy) {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
else {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for
// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).
Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ?
new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
aopInterceptor, //
targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,
// then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls
// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();
Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];
this.fixedInterceptorMap = CollectionUtils.newHashMap(methods.length);
// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)
for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {
Method method = methods[x];
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, rootClass);
fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(
chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());
this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(method, x);
}
// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks
// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.
callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];
System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);
System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);
this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;
}
else {
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}可以结合调试,方便理解:





 本文详细介绍了CGLIB库在SpringAOP中的应用,包括CGLIB代理的示例、流程以及SpringAOP中CGLIB代理的实现机制,涵盖了字节码操作、代理类创建和方法增强等内容。
本文详细介绍了CGLIB库在SpringAOP中的应用,包括CGLIB代理的示例、流程以及SpringAOP中CGLIB代理的实现机制,涵盖了字节码操作、代理类创建和方法增强等内容。



















 2957
2957

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










