目录
网络 编程的三要素: 1.IP地址 :网络设备在网络中的唯一标识
2.端口: 应用程序在计算机中的唯一标识
3. 协议:通讯双方必须遵守的
IP地址:
分类:
IPV4 :由32位组成 4个字节
IPV6:由128位组成 16个字节
类型:
内网IP:192.168.xx.xx
公网IP:互联网上存在的IP
特殊IP:127.0.0.1 localhost
域名:
在DNS服务器上记录的IP和一个字符串的对应关系e.g(baidu.com)
使用浏览器访问,如果使用域名访问 首先访问DNS服务器 得到域名对应的IP地址 才能访问真正的服务器
端口:
周知端口:1 - 1023
注册端口:
动态端口:
协议:
UDP协议 :

无链接 可能丢包 不安全 效率高 数据包大小限制不能64KB
TCP协议:

连接 可靠 效率低 数据包大小没有限制
三次握手: 为了确保通信双方都能收发消息
四次挥手: 为了确保数据完整的处理
UDP编程:


空参构造为随机分配端口号
一个对象只能绑定一个端口号
port为指定端口号
DatagramSocket类中提供的方法为:


获取adderss 地址用方法 InetAddress.getByName()
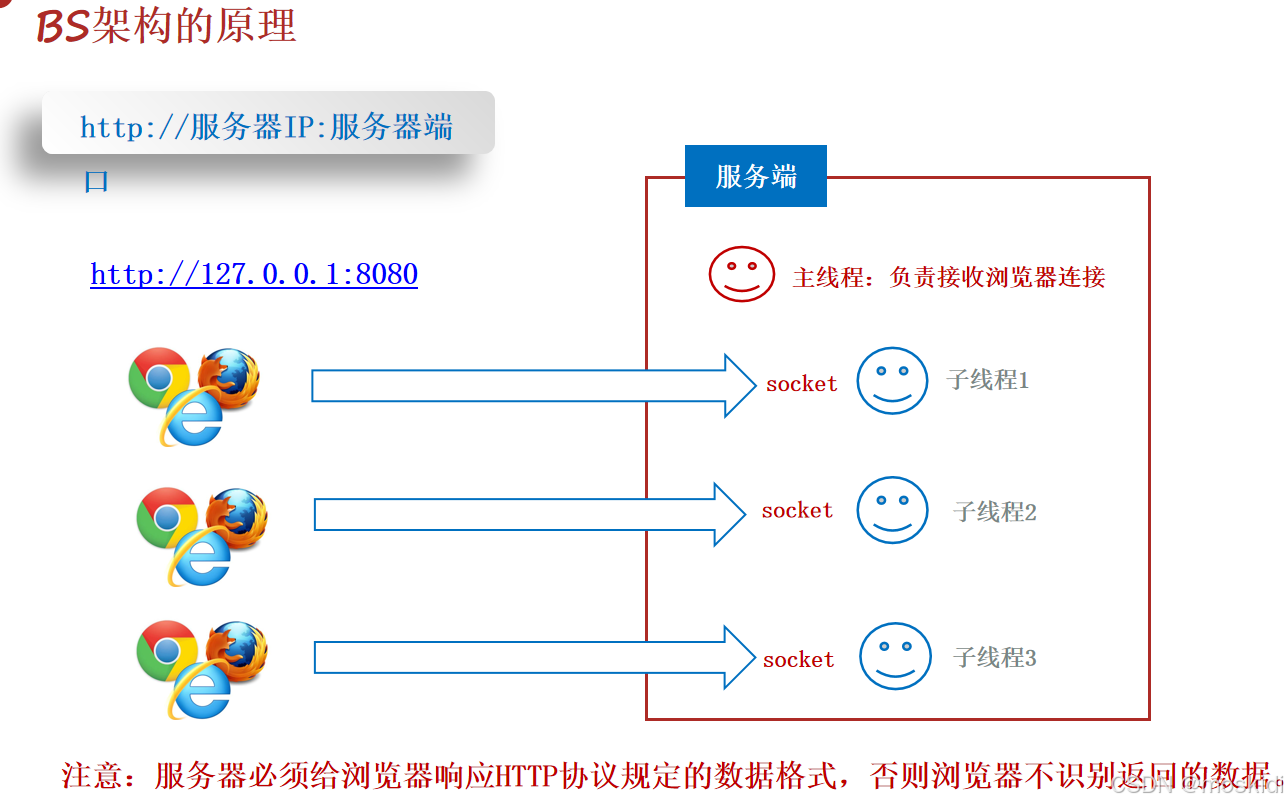
CS Clint-Server架构
BS browser Server架构
客户端:

服务器端:


重试机制 一直提交直到submit成功
TCP编程:



模拟CS架构:
客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建对象,代表客户端
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 9999);
//2.获取一个网络字节输出流
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
//3.发送数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
if ("886".equals(line)){
break;
}
byte[] bys = line.getBytes();
os.write(bys);
os.write("\r\n".getBytes());
}
//4.释放资源
s.close();//释放网络资源的时候, 由于字节输出流是通过socket获取的,所以在释放socket资源时,流资源会自动释放
}服务端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建ServerSocket对象,用于绑定端口,等待客户链接
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9999);
while (true) {
//2.调用Socket accept()方法, 等待客户端连接, 如果没有客户链接,会阻塞,如果有客户连了, 会返回一个Socket对象,用于与客户端通信
Socket s = ss.accept();
//开启子线程, 完成与客户端的通信
new Thread(() -> {
try {
//3.获取网络字节输入流
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
//4.读取数据
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
//5.释放资源
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}).start();
}
//ss.close();此服务端为用多线程解决了多个客户端同时向服务端发送数据 每来一个客户就开启一个线程(此处可以用线程池进行优化)
ctrl+alt+t 可以全选中一块代码选择让什么方式包裹
模拟BS架构:

public class LiuYanServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 创建一个服务器对象
//ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8080);
//HTTP协议默认端口是80
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(80);
//创建线程池对象
ThreadPoolExecutor tp = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
8,
8,
0,
TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
while (true) {
//2. 监听浏览器的连接
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//3. 开启子线程与浏览器进行通信, 发送一个字符串: 柳岩是我的, 别跟我抢
Runnable r = new CommunicationRunnable(socket);
//new Thread(r).start();
tp.submit(r);
}
}
}
public class CommunicationRunnable implements Runnable {
//记录通信使用的socket对象
private Socket socket;
public CommunicationRunnable(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
//public void run() throws IOException { //如果父类或者接口中的方法没有抛异常, 重写的时候也不能抛
public void run() {
// 发送一个字符串: 柳岩是我的, 别跟我抢
try {
//获取输出流,并包装
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
//写出数据
bw.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("Content-Type:text/html; charset=UTF-8");
bw.newLine();
bw.newLine();//单独换行
bw.write("<h1 style='color:red'>柳岩</h1> 是我的,别跟我抢!");
//把数据刷入到网络中去
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放资源
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}时间获取的相关方案:

public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取当前日期
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(ld);
//获取当前时间
LocalTime lt = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println(lt);
//获取当期日期时间
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(ldt);
//获取指定的日期
LocalDate ld2 = LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 1);
System.out.println(ld2);
//获取指定的时间
LocalTime lt2 = LocalTime.of(12, 50, 33);
System.out.println(lt2);
//获取指定的日期时间
LocalDateTime ldt2 = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 5, 5, 12, 12, 12);
System.out.println(ldt2);
}时间的格式化与解析:

LocalDate.parse()为静态方法 返回一个时间对象 有两个构造方法 自己给出的时间格式 需要给出格式对象 注意格式对象类为 DataTimeFormatter静态方法为ofPattern (y M d H m s)其中月和小时需要大写
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 字符串到日期时间对象的转换
//默认认识的格式:2021-01-12
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2021-01-12");//只有写成这样的格式才能被识别
System.out.println(ld);
//日期格式化器: 日期格式组成
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日");
LocalDate ld2 = LocalDate.parse("2021年01月12日",dtf);
System.out.println(ld2);
DateTimeFormatter dtf2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.parse("2021-01-01 11:11:12",dtf2);
System.out.println(ldt);
//演示从日期时间对象到字符串
LocalDate ld3 = LocalDate.now();
String dateStr = ld3.format(dtf);
System.out.println(dateStr);
LocalDateTime ltd3 = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter dtf3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm");
String datetimeStr = ltd3.format(dtf3);
System.out.println(datetimeStr);
}
StringBuilder:
应为字符串长度是不可变的 如果用+拼接字符串 每次都要在堆上产生空间 频繁拼接会很消耗内存
所以用StringBuilder 拼接字符串

public static void main(String[] args) {
//构建空白的StringBuilder
//StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//构建好的StringBuilder中初始化有内容
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("123");
//append(任意类型的数据): 把参数的内容拼接到SringBuilder的末尾
sb.append("456");
sb.append("abc");
sb.append("我爱你");
sb.append(true);
sb.append(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("-------");
}
});
//reverse(): 反转StringBuilder的内容
//sb.reverse();
//toString(): 把StringBuilder转换为String
String str = sb.toString();
System.out.println(str);//123456abc我爱你truecom.itheima.api.Test04$1@3b07d329
}BigDecimal:
由于浮点数无法进行精确计算 bigdicimal可以进行精确计算

bigdicimal本质把数字转化成字符串进行计算所以 不用构造器double val
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal b1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3.0);
BigDecimal b2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(1.3);
//add(BigDecimal b) 求和
System.out.println(b1.add(b2));
//subtract(BigDecimal b) 减法
System.out.println(b1.subtract(b2));
//multiply(BigDecimal b) 乘法
System.out.println(b1.multiply(b2));
//divide(BigDecimal b) 除法
//System.out.println(b1.divide(b2));
//divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, RoundingMode roundingMode), scale:保留几位小数, roundingMode:按照什么方式保留
System.out.println(b1.divide(b2, 3, RoundingMode.FLOOR));//向下取整
System.out.println(b1.divide(b2, 3, RoundingMode.CEILING));//向上取整
System.out.println(b1.divide(b2, 3, RoundingMode.HALF_UP));//四舍五入
BigDecimal result = b1.add(b2);
System.out.println(result.doubleValue());
}如果用divide无法整除 需要指定 精确几位和 舍入模式
RoundingMode.FLOOR 向下取整
RoundingMode.CEILING 向上取整
RoundingMode.HALF_UP 四舍五入

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








