一、IO流标准的异常处理
JDK7版本之前,异常处理、关闭字节流的标准操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a.txt");
fos.write("hello world".getBytes());
fos.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
// 判断字节流对象是否为空,避免空指针异常
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JDK7版本之后,异常处理、关闭字节流的标准操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
// try () 中对象自动调用close()方法,有异常也会执行
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a.txt")){
fos.write("hello world".getBytes());
fos.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
注:try () 中的对象需要实现过 AutoCloseable 接口
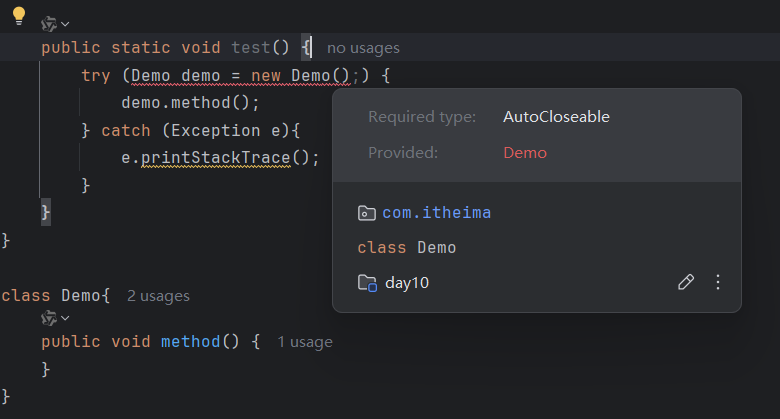
try () 中创建的自定义类对象,没有实现AutoCloseable接口时,如下图:
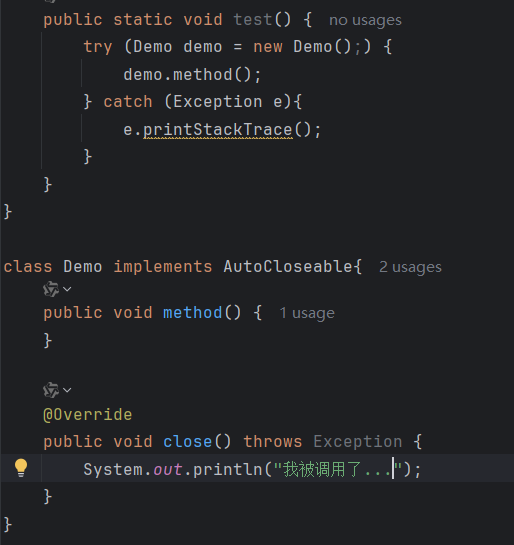
try () 中创建的自定义类对象,实现了AutoCloseable接口,并重写了close()方法,如下图:
 Java IO流异常处理及AutoCloseable接口
Java IO流异常处理及AutoCloseable接口




















 2640
2640

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








