1、基本概念
channel :数据通道
msg:数据通道中流动的数据,最开始是ByteBuf 之后经过多个handler 的处理 变成java对象 最后又变成 ByteBuf输出到管道中。
Handler: 一道道处理工序
handler 可以对数据进行处理 ,多个handler 就是pipeline,pipeline 负责事件的发送(读写…)给下一个handler,然后handler对感兴趣的handler处理。 handler可分为Inbound 和outbound
EventLoop:工人
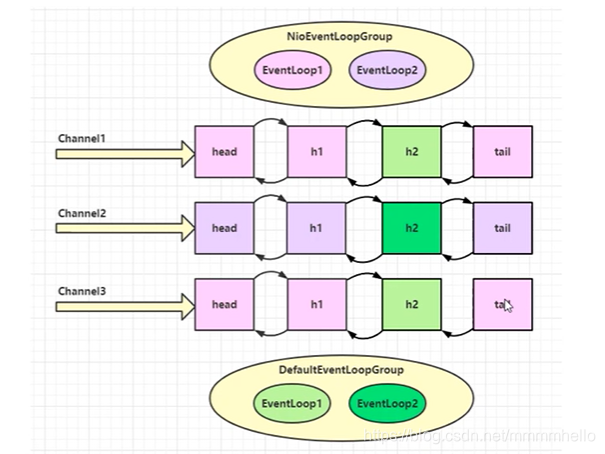
eventloop 可以对多个channel进行操作,但是一旦一个channel被eventloop接收,那么他就会负责到底。
eventloop 既可以执行io操作,也可以执行普通或者定时任务,其维护一个任务队列,存放待完成的任务。
eventloop 按照 pipeline 的顺序按顺序处理一道道工序。当然 handler可以指定其他工人完成。
2、channelfuture 的关闭问题
NioEventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建启动器
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//处理io线程组设置
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)
//建立的channel 设置
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//channel 初始化处理器的设置
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
//异步非阻塞 建立连接
}).connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",9999));
//nio线程执行回调任务 即完成channel 的建立之后 才进行读写
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
future.channel().writeAndFlush("gaojl hello world");
}
});
netty 异步化的理解
假设4个医生看病 每天每个医生工作8小时,每个病人花费20分钟,则 4个医生同时工作的时候处理能力是4 再多来的看病任务就就需要等待。那么能不能有什么方法使得处理大量任务的时候不要使得那么多人等待呢?
假设可以将看病分为4个步骤 挂号(5min) 看病(5min) 缴费(5min) 取药(5min) ,那么可以使得每个医生只干一件事。这时候吞吐量就上来了,每小时可以进12个病人,即同时可以有12个人在被操作(走看病流程)。
netty EmbeddedChannel
EmbeddeChannel 可以方便的测试我们编写的各种入站 出站 channelHandler.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChannelHandler h1 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("1");
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
};
ChannelHandler h2 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("2");
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
};
ChannelHandler h3 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("3");
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
};
ChannelHandler h4 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("4");
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
};
EmbeddedChannel embeddedChannel = new EmbeddedChannel(h1,h2,h3,h4);
embeddedChannel.writeInbound("gaojl");
embeddedChannel.writeOutbound("gaojl");
}
Nio 和Netty 的零拷贝
Nio 可以将一个文件的内容 读到FileChannel 中之后,直接传给另一个FileChannel,不用经过用户空间的拷贝。相当于只需要3次拷贝
FileChannel srcChannel = new
FileInputStream("D:\\worksapce\\nettyLearn\\helloNetty\\src\\main\\resources\\log4j.properties").getChannel();
FileChannel desChannel = new
FileOutputStream("D:\\worksapce\\nettyLearn\\helloNetty\\src\\main\\resources\\log4j2.properties").getChannel();
srcChannel.transferTo(0,srcChannel.size(),desChannel);
Zero-Copy has two means in the netty’s world.
First,if your platform support zero-memory-copy,you can write a
DefaultFileRegion to the Channel, ChannelHandlerContrext, or
ChannelPipeline.Second, CompositeByteBuf is a virtual buffer which shows multiple
buffers as a single merged buffer. So you can composite some byteBufs
to one CompositeByteBuf, and it doesn’t need copy.Netty提供了CompositeByteBuf类,它可以将多个ByteBuf合并为一个逻辑上的ByteBuf,避免了各个ByteBuf之间的拷贝。通过wrap操作,我们可以将byte[]数组、ByteBuf、
ByteBuffer 等包装成一个 Netty ByteBuf对象,进而避免了拷贝操作。ByteBuf支持slice
操作,因此可以将ByteBuf分解为多个共享同一个存储区域的ByteBuf,避免了内存的拷贝。通过FileRegion包装的FileChannel.tranferTo实现文件传输,可以直接将文件缓冲区的数据发送到目标Channel,避免了传统通过循环write方式导致的内存拷贝问题。
slice 体现了 Netty 层面的零拷贝 这里并不是说减少了cpu copy ,而是减少了对原始ByteBuf 的重复复制 使用,而是直接在原ByteBuf 上使用。
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(512,1024);
buf.writeInt(12);
ByteBuf b = buf.slice();
b.retain();//创建之后 ref++
b.release();//使用完之后
ByteBuf s1 = buf.slice(0,2);
s1.retain();//创建之后 ref++
//使用完之后
s1.release();
duplicate 同样是 复用同一个物理内存,来减少拷贝。
Netty中的池化与非池化技术
我们知道对于创建销毁很耗时的资源,比如数据库连接 、线程的创建都可以将其复用 即 不用的时候不要销毁 ,而是在需要的时候重用数据库连接或者 线程。Netty 中由于直接内存的创建和销毁同样昂贵,所以也采用了池化技术对Bytebuf 进行了复用。
这样在高并发下 减少了内存溢出的可能。
Netty 中的ByteBuf 和Nio中的ByteBuffer 有什么区别?
ByteBuf 中有读写指针、capacity 、maxCapcity 等指针把ByteBuf 分为 discard 区 、readable 区、writeable区、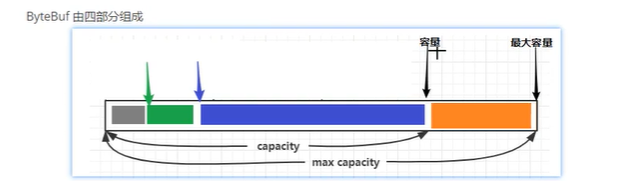
扩容规则:以512 为分界点,小于512 则16 的整数倍调整,大于512 则 直接容量加倍。比如一开始为由16 变为17时容量不够了,则容量会加16。当由512 变为513 容量不够时 容量变为1024。
ByteBuffer 是Nio中的存储容器 中有 position mark limit capacity ; position 代表读写位置 limit 代表数据有效位置 capacity代表容量一般是ByteBuffer 先put /read 写入数据 然后 flip 读数据或者compact 之后 再写入数据 read /put。
put 会使得position++ flip 会使得limit = position position = 0; compact 会将未处理完的内容移到ByteBuffer 然后position = offset(未处理完的长度)
limit = capacity;
当position 大于limit 时会抛出异常。
区别:池化技术 减少了创建和释放带来的开销 可以重复利用资源 在高并发下减少了内存溢出的可能性
读写指针分离 不必切换读写模式(flip compact ).
零拷贝技术 减少复制 slice duplicate compositeByteBuf
自动扩容 不会轻易发生越界异常。
netty 设计协议的基本要素?
魔数 + 版本号 + 指令类别 +序列化方法+序列号+ 长度+内容
netty 如果一段时间未收到数据 可以 断开连接。避免长时间占用服务器资源同时应该在客户端有心跳机制。
使用 IdleStateHandler(60,0,0,TimeUnit.Seconds) 代表60秒未收到数据就会出发一个用户事件。
下一个Handler应该捕获这个事件做断开连接的处理。
pipeline.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler(){
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent)evt;
if(event.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE){
log.debug("一段时间未收到写数据了");
//关闭
ctx.Channel().close();
}
}
});
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0,3,0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler(){
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if(event.state() == IdleState.WRITER_IDLE){
ByteBuf message = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
message.writeBytes("this is a pingpong message".getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}
});
NioEventLoop串行化设计理念?
NioEventLoop 是netty 重要的一个类,可以接收连接请求,创建NioSocketChannel,同时在wokergroup 中的EventLoop 注册 selector 并 初始化其感兴趣的事件。对于一个channel 仅由一个EventLoop来负责其io输入输出。减少了线程切换,NioEventLoopGroup默认创建的线程数是2*cpu处理器数。所以 EventLoop的设计 既考虑了并发 又考虑了串行化。
Netty 是如何做到高性能的?
1、io多路复用大大减少了服务线程创建带来的线程创建销毁与切换。
2、可配置的EventLoopGroop线程数和TCP参数 可以更适应各种场景
3、使用直接内存避免了堆内内存向堆外内存的拷贝带来损耗。‘
4、使用池化技术减少频繁创建堆外内存的带来的开销。
5、使用引用计数及时释放不再被引用的对象,降低GC频率。
netty 源码理解
java Nio 服务器端网络编程的步骤是:创建ServerSocketChannel 创建 Selector ServerSocketChannel注册到selector上,并注册感兴趣的事件。之后便可以接收客户端的请求 selector.select() 便可以阻塞到监听事件上面。
netty 同样是由类似的步骤,在创建ServerBootstrap之后,bind时会完成下面的操作:
1、创建NioServerSocketChannel,并在其pipeline上面注册一个初始化handler,这个handler的主要作用是为NioserverSocketChannel增加一个acceptor Handler
2、在Nio线程中注册ServerSocketChannel.register(eventloop().selector,0,Nssc),即NSSC对应的ssc会向EventLoop的selector注册,selectionkey 并未设置感兴趣的事件。注册完成之后会调用Nssc的初始化handler,此时nssc就有了一个handler链head->acceptor->tail从而具备accept的能力。
3、注册完成后会调用回调函数进行bind绑定,主要是设置端口号和连接队列的大小,之后会用channel发送一个ChannelActive请求,HeadContext中的ChannelActive事件触发之后会向NioServerSocketChannel的SelectionKey注册感兴趣事件。
之后当有感兴趣的事件比如op_accept到来时候,会使得selector.select()返回SelectedKeys,然后遍历拿到accept事件,从而调用selectionKey的channel 进行accept,生成ServerSocketChannel、注册到eventloop的selector中,然后设置NioSocketChannel感兴趣事件。





















 1100
1100

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








