文章目录
CS-Notes
相交链表
#160
设 两条链表分别为A,B;
若两条链表有交点,
A的长度为a+c,B的长度为b+c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
当访问 A 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,下一个结点为null,令它从链表 B 的头部开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问 B 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
如果不存在交点,那么 a + b = b + a,以下实现代码中 l1 和 l2 会同时为 null,从而退出循环。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode l1 = headA,l2 = headB;
while(l1 != l2){
//写法一
l1 = (l1 == null) ? headB : l1.next;
l2 = (l2 == null) ? headA : l2.next;
//写法二
if(l1 == null){
l1 = headB;
}else{
l1 = l1.next;//尾结点后为null
}
if(l2 == null){
l2 = headA;
}else{
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
return l1;
}
}
反转整个链表
#206
Reverse a singly linked list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
法一:用栈
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;//不加这句,执行可以,提交不行,应该是没考虑到特殊情况
Stack<ListNode> s = new Stack<>();
while(head.next != null){
s.push(head);
head = head.next;
}//head此时指向尾结点,入栈尾结点之前的所有结点
ListNode l = head;//需要返回链表头结点
while(!s.empty()){
head.next = s.pop();
head = head.next;
}
head.next = null;// 别忘了链表末尾要指向null
return l;
}
}
法二:迭代法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode next = null;//下一个结点,用来让head迭代
ListNode prev = null;//前一个结点
while(head != null){
next = head.next;
head.next = prev;
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;//最后next和head都是null
}
}
法三:递归法
知乎参考讲解
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//空链表或单个结点,反转它自己
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}//base case
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
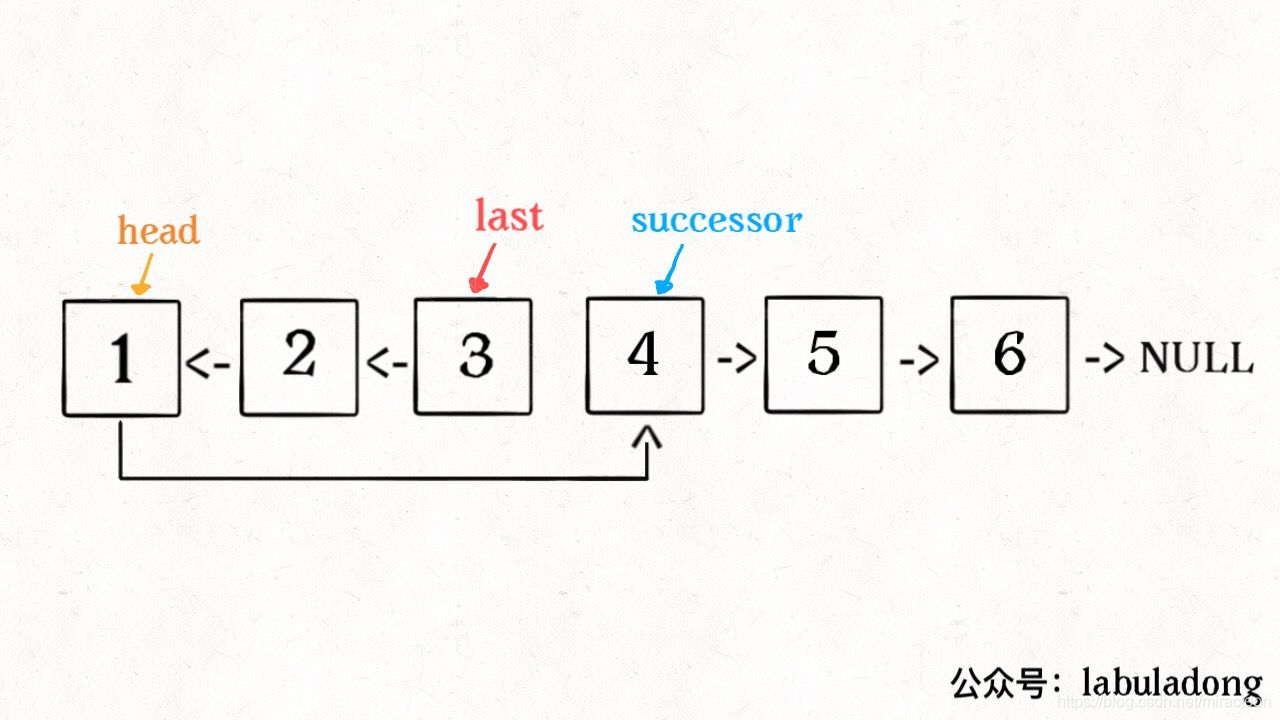
反转链表前N个结点
比如说对于下图链表,执行 reverseN(head, 3):

class Solution {
ListNode successor = null;
public ListNode reverseListN(ListNode head,int n) {
// 记录第 n + 1 个节点
if(n == 1){
successor = head.next;
return head;
}
// 以 head.next 为起点,需要反转前 n - 1 个节点
ListNode last = reverseListN(head.next,n-1);
head.next.next = head;
// 让反转之后的 head 节点和后面的节点连起来
head.next = successor;
return last;
}
反转链表一部分
#92
给一个索引区间 [m,n](索引从 1 开始),仅仅反转区间中的链表元素。
ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n)
如果 m != 1 怎么办?如果我们把 head 的索引视为 1,那么我们是想从第 m 个元素开始反转对吧;如果把 head.next 的索引视为 1 呢?那么相对于 head.next,反转的区间应该是从第 m - 1 个元素开始的;那么对于 head.next.next 呢……
- 递归法
ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
// base case
if (m == 1) {
return reverseN(head, n);
}
// 前进到反转的起点触发 base case
head.next = reverseBetween(head.next, m - 1, n - 1);
return head;
}
- python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
# successor = None
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, left: int, right: int) -> ListNode:
self.successor = None
if left == 1:
return self.reverseN(head, right)
head.next = self.reverseBetween(head.next, left - 1, right - 1)
return head
def reverseN(self, node, n):
if n == 1:
self.successor = node.next
return node
last = self.reverseN(node.next, n - 1)
node.next.next = node
node.next = self.successor
return last
- 迭代法
- 添加一个哑结点作为辅助,该结点位于列表头部。哑结点用来简化某些极端情况,例如列表中只含有一个结点,或需要删除列表的头部。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;// 用来返回头结点
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
//遍历到m-1位置
for(int k = 1;k < m;k++){
pre = pre.next;
}
//套用反转整个链表模板
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = pre.next;
for(int i = m; i <= n; i++){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
//修改m和n-m位置处的结点的指向
pre.next.next = cur;
pre.next = prev;
return dummyHead.next;//返回链表头结点
}
}
25 k个一组翻转链表
# @lc code=start
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
if not head:
return None
lNode = rNode = head
# base case 不足 k 个结点,保持原样
for i in range(k):
if not rNode:
return head
rNode = rNode.next
newHead = self.reverse(lNode, rNode)
lNode.next = self.reverseKGroup(rNode, k)
return newHead
# [left, right) 左闭右开区间
# self 不能缺少
def reverse(self, left, right):
pre = ListNode()
cur = left
pre.next = cur
while cur != right:
nextNode = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nextNode
return pre
# @lc code=end
合并两个有序链表
Example:
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
- 迭代法
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
cur.next = l1;
cur = cur.next;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
cur.next = l2;
cur = cur.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
// 任一为空,直接连接另一条链表
if(l1 == null){
cur.next = l2;
}else{
cur.next = l1;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
- 递归法
两个链表头部值较小的一个节点与剩下元素的 merge 操作结果合并
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1 == null){
return l2;
}
if(l2 == null){
return l1;
}
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素
- 普通法
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null && cur.next != null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
if(cur.val == next.val){
cur.next = next.next;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
- 递归
递归套路解决链表问题:- 找终止条件:当head指向链表只剩一个元素的时候,自然是不可能重复的,因此return
- 想想应该返回什么值:应该返回的自然是已经去重的链表的头节点
- 每一步要做什么:宏观上考虑,此时head.next已经指向一个去重的链表了,而根据第二步,我应该返回一个去重的链表的头节点。因此这一步应该做的是判断当前的head和head.next是否相等,如果相等则说明重了,返回head.next,否则返回head
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
if(head.val == head.next.val){
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}
或者
class Solution {
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
if (head.val == head.next.val)
head = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
else
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head;
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素II
力扣82
题目描述:给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
1. 1——>1——>1——>2(null)
2. 1——>2——>2——>3——>3——>4(null)
递归法
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
if (head.val == head.next.val){
//情况1 移动 head 直到出现值不相等的情况
while (head.next != null && head.val == head.next.val){
head.next = head.next.next;
}
//此时 head 依然是重复的值,向右再移动一次
head = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
}else {
//2
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
}
return head;
}
}
非递归
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);
pre.next = head;
ListNode cur = pre;//哑结点,可以合并一开始就有重复元素的情况
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null){
if (fast.next != null && fast.val == fast.next.val){
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.val == fast.val){
fast = fast.next;
}
//此时 fast 指向的依然是重复元素,往后再移一位
cur.next = fast.next;
fast = fast.next;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
}
return pre.next;
}
}
删除链表的倒数N个结点
- 双指针法

class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
//相隔n+1个结点
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;//有些情况会把head删掉,所以不能返回head
}
}
- 两次遍历算法
删除从列表开头数起的第 (L - n + 1)个结点,其中 LL是列表的长度。只要我们找到列表的长度 L,这个问题就很容易解决。
我们把第 (L - n) 个结点的 next 指针重新链接至第 (L - n + 2) 个结点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode first = head;
int length = 0;
while(first != null){
length++;
first = first.next;
}
length -= n;
first = dummy;
while(length > 0){
length--;
first = first.next;
}
first.next = first.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
两两交换链表中的结点
leetcode#24
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
- 迭代
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
while(pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null){
ListNode l1 = pre.next;
ListNode l2 = pre.next.next;
ListNode next = l2.next;
//交换
l1.next = next;
l2.next = l1;
pre.next = l2;
//迭代
pre = l1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
- 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = head.next;
l1.next = swapPairs(l2.next);
l2.next = l1;
//此时l2变成了头结点
return l2;
}
}
关于递归的题: 判断平衡二叉树
a binary tree in which the left and right subtrees of every node
differ in height by no more than 1.
- 自顶向下(暴力法): 先序遍历 + 判断深度
class Solution {
private int height(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right)) + 1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) < 2
&& isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
}
针对满二叉树,设共有 n 层,第 i 层有 2i-1个结点,全部结点个数为 2n- 1,设总结点个数为 N,则最后一层结点个数为 2n-1=(N+1)/2

- 自底向上:后序遍历 + 剪枝
class Solution {
private boolean isB = true;
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
height(root);
return isB;
}
private int height(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = height(root.left);
int right = height(root.right);
if(Math.abs(left - right) > 1) isB = false;
return Math.max(left,right) + 1;//返回结点深度
}
}
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N): N为树的节点数;最差情况下,需要递归遍历树的所有节点。
空间复杂度 O(N): 最差情况下(树退化为链表时),系统递归需要使用 O(N)的栈空间。
两数相加II(两条链表相加)
leetcode445
示例:
输入:(7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
- 法一:利用两个栈存储两条链表每个结点的值
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
int carry = 0;
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
while(l1 != null){
s1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while(l2 != null){
s2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
//链表头结点值相加可能产生进位
while(!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty() || carry != 0){
int x = s1.isEmpty() ? 0 : s1.pop();
int y = s2.isEmpty() ? 0 : s2.pop();
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;//进位
ListNode node = new ListNode(sum % 10);
node.next = head.next;//若声明head = null,这里出错
head.next = node;
}
return head.next;
}
}
- 法二: 尝试反转链表
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode n1 = reverse(l1);
ListNode n2 = reverse(l2);
int carry = 0;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode pre = dummy;
while(n1 != null || n2 != null || carry != 0){
int x = n1 == null ? 0 : n1.val;
int y = n2 == null ? 0 : n2.val;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(sum % 10);
pre.next = n3;
pre = pre.next;
n1 = n1 == null ? null : n1.next;
n2 = n2 == null ? null : n2.next;
}
return reverse(dummy.next);
}
//反转链表
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
- 法三:递归
- 如果len1与len2都为1,那么当前的值应为
(l1.val+l2.val)%10,进位更新为(l1.val+l2.val)/10; - 如果len1大于len2,递归计算
(l1.next,l2),当前的值应为(l1.val+进位)%10,进位更新为(l1.val+进位)/10; - 如果len1等于len2,递归计算
(l1.next,l2.next),当前的值应为(l1.val+进位+l2.val)%10,进位更新为(l1.val+进位+l2.val)/10; - 返回当前节点的指针
- 递归结束
- 如果len1与len2都为1,那么当前的值应为
为方便递归,递归开始前我们保证len1>=len2,另外递归结束后若进位为1,需要新建值为1的头节点
class Solution {
private int carry = 0;
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode n1 = l1,n2 = l2;
int len1 = 0,len2 = 0;
while(l1 != null){
l1 = l1.next;
len1++;
}
while(l2 != null){
l2 = l2.next;
len2++;
}
ListNode node = (len1 > len2) ? add(n1,n2,len1,len2) : add(n2,n1,len2,len1);
if(carry != 0){
ListNode pre = new ListNode(1);
pre.next = node;
return pre;
}
return node;
}
private ListNode add(ListNode l1,ListNode l2,int len1,int len2){
int temp = 0;
if(len1 == 1 && len2 == 1){
temp = l1.val;
l1.val = (temp + l2.val) % 10;
carry = (temp + l2.val) / 10;
return l1;
}
if(len1 > len2){
l1.next = add(l1.next,l2,len1 - 1,len2);
temp = l1.val;
l1.val = (temp + carry)% 10;
carry = (temp + carry) / 10;
return l1;
}
l1.next = add(l1.next,l2.next,len1 - 1,len2 - 1);
temp = l1.val;
l1.val = (temp + l2.val + carry) % 10;
carry = (temp + l2.val + carry) / 10;
return l1;
}
}
回文链表
Example 1:
Input: 1->2
Output: false
Example 2:
Input: 1->2->2->1
Output: true
Example 3:
Input:1->2->1
Output: true
- 法一:暴力法(不推荐)
反转整个链表,观察反转的链表和原链表是否完全相同
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = head;
ListNode cur = copy(head);
ListNode last = reverse(head);
while(cur != null && last != null){
if(cur.val != last.val) return false;
cur = cur.next;
last = last.next;
}
return true;
}
//递归实现复制单链表
private ListNode copy(ListNode head){
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(head.val);
newNode.next = copy(head.next);
return newNode;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
- 法二:快慢指针(推荐)


class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return true;
ListNode slow = head,fast = head;
ListNode cur = null,prev = null;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
cur = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
}
if(fast != null){
slow = slow.next;
}
while(cur != null && slow != null){
if(cur.val != slow.val) return false;
cur = cur.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}
分隔链表
Input:
root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], k = 5
Output: [[1,2], [3,4], [5],[6],[7]]
Explanation:
The input has been split into consecutive parts with size difference at most 1, and earlier parts are a larger size than the later parts.
以上面的例子为例,mod = 7 % 5 = 2,size = 7 / 5 = 1,让前面两个数组元素储存的结点个数为1 + 1,剩下三个储存结点个数为1,
注:迭代时要让每一段的尾结点后连接NULL
class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
ListNode[] list = new ListNode[k];
// int length = count(root);
int length = 0;
ListNode cur = root;
while(cur != null){
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
int mod = length % k;
int size = length / k;
for( int i = 0; root != null && i < k; i++){
list[i] = root;
int curSize = size + (mod-- > 0 ? 1 : 0);//实际每段长度
for(int j = 1; j < curSize; j++){
root = root.next;
}
//让每一段的尾结点后接NULL
ListNode temp = root.next;
root.next = null;
root = temp;
}
return list;
}
//递归计算链表长度
// private int count(ListNode root){
// return root==null?0:count(root.next)+1;
// }
}
链表元素按奇偶聚集
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
Example 2:
Input: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
Output: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode odd = head,even = head.next,node = even;
while(even != null && even.next != null){
ListNode n1 = odd.next.next;
ListNode n2 = even.next.next;
odd.next = n1;
even.next = n2;
odd = n1;
even = n2;
}
odd.next = node;
return head;
}
}
旋转链表
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Example 2:
Input: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
Output: 2->0->1->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 1->2->0->NULL
rotate 3 steps to the right: 0->1->2->NULL
rotate 4 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
int length = 0;
while(head != null){
head = head.next;
pre = pre.next;
length++;
}
//首尾相连
pre.next = dummy.next;
int n = k / length + 1;
int N = n * length - k;//新的头结点位置,也可以看作倒数第k % length个结点,倒数第0个是原头结点,倒数第一个是原尾结点
while(N-- > 0){
pre = pre.next;
}
head = pre.next;
pre.next = null;
return head;
}
}
























 2418
2418

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








