文章目录
CUDA 编程总汇
这些库的基本说明-cuda的相关库和基本使用
TODO
1. CUDA 基本写法
1.1 CUDA常用官方doc的链接
方便日常使用查看,有的文档需要点击跳转多次才能找到,比较麻烦
- nsight system工具官方文档
- CUDA的toolkit doc: 流处理等一些都可以在这个网页查询
- CUDA C++ Best Practices Guide
- CUDA C++ Programming Guide
- CUDA Math API
- CUDA Documents Hub包含nvidia所有文档
- CUDA API sync behavior的文档
1.2 基本用法
- [CUDA] pin_memory的理解
- CUDA编程实战: TODO 待整理
- launch_bounds的使用
- 基础函数
- reduce: - reduce问题探究, cuda 进阶编程
- shared memory sync_fence
- [CUDA] warp_shfl等线程间交换函数的使用
- 指令集
如何设置block size和grid size ?
-
应该设置:block_size > 96:也就是说 block 调度到 SM 的过程是原子的。SM 允许多于一个 block 在其上并发执行,如果一个 SM 空闲的资源满足一个 block 的执行,那么这个 block 就可以被立即调度到该 SM 上执行。显然,一个 kernel 的 block_size 应大于 SM 上最大线程数和最大 block 数量的比值,否则就无法达到 100% 的 Occupancy,对应不同的架构,这个比值不相同,对于 V100 、 A100、 GTX 1080 Ti 是 2048 / 32 = 64,对于 RTX 3090 是 1536 / 16 = 96,所以为了适配主流架构,如果静态设置 block_size 不应小于 96。考虑到 block 调度的原子性,那么 block_size 应为 SM 最大线程数的约数,否则也无法达到 100% 的 Occupancy,主流架构的 GPU 的 SM 最大线程数的公约是 512,96 以上的约数还包括 128 和 256,也就是到目前为止,block_size 的可选值仅剩下 128 / 256 / 512 三个值
-
tail effect问题:GPU 一次可以调度 SM 数量 * 每个 SM 最大 block 数个 block,因为每个 block 的计算量相等,所以所有 SM 应几乎同时完成这些 block 的计算,然后处理下一批,这其中的每一批被称之为一个 wave。想象如果 grid_size 恰好比一个 wave 多出一个 block,因为 stream 上的下个 kernel 要等这个 kernel 完全执行完成后才能开始执行,所以第一个 wave 完成后,GPU 上将只有一个 block 在执行,GPU 的实际利用率会很低,这种情况被称之为 tail effect。
- 如何缓解tail effect 问题:尽量将gride size 设置大一些。 我们应尽量避免这种情况,将 grid_size 设置为精确的一个 wave 可能也无法避免 tail effect,因为 GPU 可能不是被当前 stream 独占的,常见的如 NCCL 执行时会占用一些 SM。所以无特殊情况,可以将 grid_size 设置为数量足够多的整数个 wave,往往会取得比较理想的结果,如果数量足够多,不是整数个 wave 往往影响也不大。普通的 elementwise kernel 或者近似的情形中,block_size 设置为 128,grid_size 设置为可以满足足够大的 wave【SM同时计算一批block为一个wave】 就可以得到一个比较好的结果了。
1.2 CUDA C++ Programming Guide 学习笔记
1.2.1 基本优化策略
- APOD: assess评估可能存在的运算瓶颈, Parallel 并行化将一些操作并行化, optimization 针对性优化一些并行kernel,Deploy部署
- cuda代码编写过程中要有代码检查, 如CUDA_CHECK这样的,保证程序的错误暴露准确。
- 注意数据传输的消耗,尽量将操作放在一种设备上进行操作,比如在GPU上的多个操作要连续,而不是在host-device之间来回传输进行操作。
- 加速比计算方式:强扩展,弱扩展;
- 弱扩展指的是一些应用如果更大的并行,那么他只会更加准确而不是更快,也就是是深度上的扩展(比如一些复杂方程式的解算或者RANSAC这样迭代次数不确定的算法解算就是一种弱扩展);
- 强扩展是增加并行性会极大增加执行的效率。
- host device 描述函数可能更能保证正确性,尤其在CPU能测试其正确性;然后其可以用到gpu上,从而确定正确。
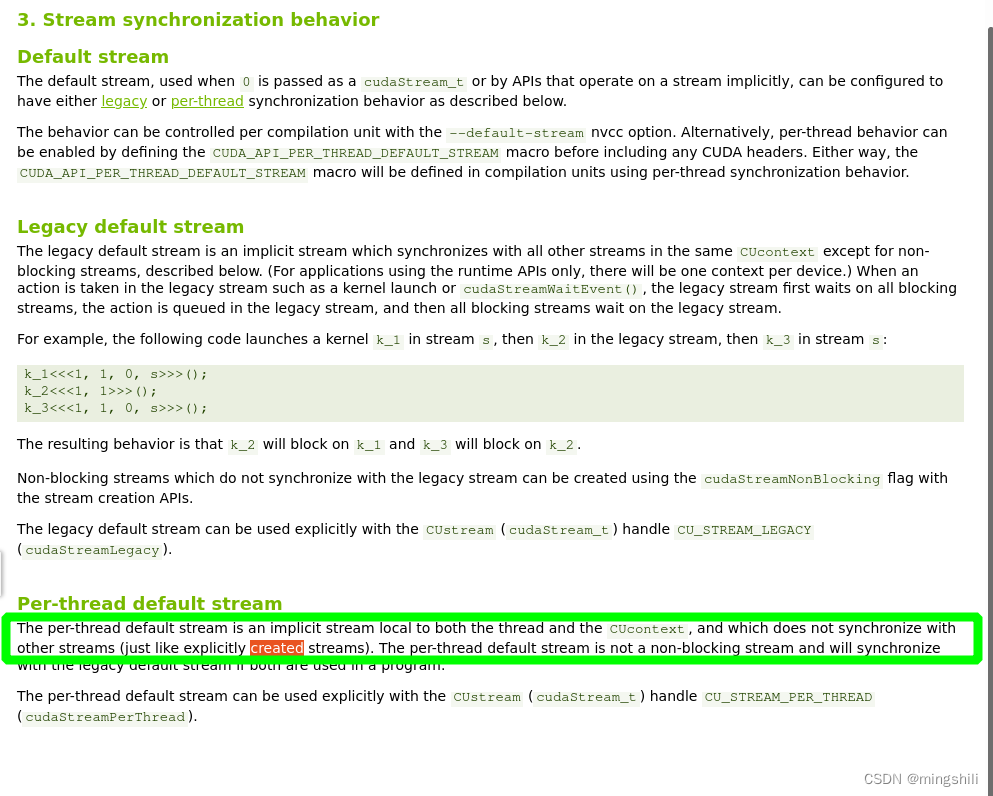
- 注意default stream的使用有两种类型,一种是per-thread default stream,这个不会像default stream那样阻塞cpu线程,而是会存在一定的异步性,所以需要用同步stream的方式使用自定义流而不是默认流和自定义流之间来回切换。
-在实现lidar preprocess中一个函数时,使用了默认流 cudaMemcpy方式copy数据(改为异步流并且和其他操作保持一致的流就没有闪现问题),这个cudaMemcpy操作错误地认为成是具有同步特性的,但是刚才查了官方文档的描述(如下图所示),发现在device to device的时候 不与host同步;也就是这个操作虽然在默认流上 但是实际上不具有同步性【也就是与cpu的同步只作用于和host之间数据传输上】,且因为是per-thread default stream,所以也不与其他流保持同步;所以数据正在或还没拷贝时,下面在其他流上的操作就使用了,所以导致最终输入到engine的数据不正确;【从保存的错误数据上看,也是这样的表现,因为没有使用正确的indices,所以错误的数据中存在大量为零的点;也是从这个现象出发才发现这段代码问题】, 另外,为什么会存在其他GPU模块影响 当前GPU preprocess的的情况,应该是通过影响cuda 流的底层调度来影响这个操作的时效性产生的(也就是cuda流队列中有操作,那么这个操作使用的默认流就会堵塞去等待legacy default stream,从而没有及时执行,而这个preprocess后续操作又被很快执行,所以产生了不一致)。

- 使用pinned memory 有更好的带宽传递; 如果内存分配的时候没有使用cudaHostMalloc直接创建pinned memory,那么可以用cudaHostRegister()对已经分配的内存进行pin操作。但是注意不要多用,否则会导致系统内存资源过少,从而性能降低。The asynchronous transfer version requires pinned host memory。
- GPU的一些函数指令启示是很快返回到CPU控制端的。就算是使用默认stream。
cudaMemcpyAsync(a_d, a_h, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, 0);
kernel<<<grid, block>>>(a_d);
cpuFunction();
// 也就是虽然使用的是默认流,但是因为这两个函数都是直接返回到host,所以cpuFunction和上面两个是并行的。
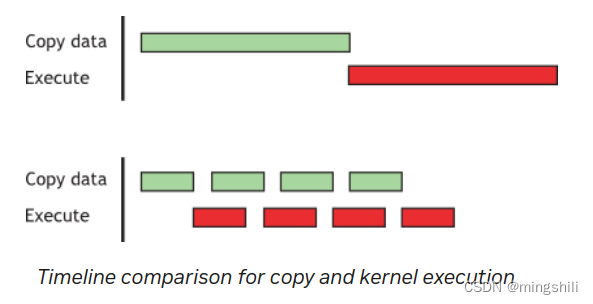
Because the memory copy and the kernel both return control to the host immediately, the host function cpuFunction() overlaps their execution.
- 注意查询可以异步的stream的个数或者引擎数,. The number of copy engines on a GPU is given by the asyncEngineCount field of the cudaDeviceProp structure, which is also listed in the output of the deviceQuery CUDA Sample
- High Priority: To maximize developer productivity, profile the application to determine hotspots and bottlenecks.
- High Priority: To get the maximum benefit from CUDA, focus first on finding ways to parallelize sequential code.
- High Priority: Use the effective bandwidth of your computation as a metric when measuring performance and optimization benefits.
- High Priority: Minimize data transfer between the host and the device, even if it means running some kernels on the device that do not show performance gains when compared with running them on the host CPU。
1.2.2 存储优化
- Low Priority: Use zero-copy operations on integrated GPUs for CUDA Toolkit version 2.2 and later.使用零copy就是让kernel直接访问pinned memory从而实现0 copy,但是效率怎么样需要看实际情况。【低优先级策略】
float *a_h, *a_map;
...
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, 0);
if (!prop.canMapHostMemory)
exit(0);
cudaSetDeviceFlags(cudaDeviceMapHost);
cudaHostAlloc(&a_h, nBytes, cudaHostAllocMapped);
cudaHostGetDevicePointer(&a_map, a_h, 0);
kernel<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(a_map);
- Zero copy 的使用注意事项:Mapped pinned host memory allows you to overlap CPU-GPU memory transfers with computation while avoiding the use of CUDA streams. But since any repeated access to such memory areas causes repeated CPU-GPU transfers, consider creating a second area in device memory to manually cache the previously read host memory data.
- Unified Virtual Addressing: 在 UVA 下,使用 cudaHostAlloc() 分配的固定主机内存将具有相同的主机和设备指针
- device memory space: Reading from a texture while writing to its underlying global memory array in the same kernel launch should be avoided because the texture caches are read-only and are not invalidated when the associated global memory is modified.
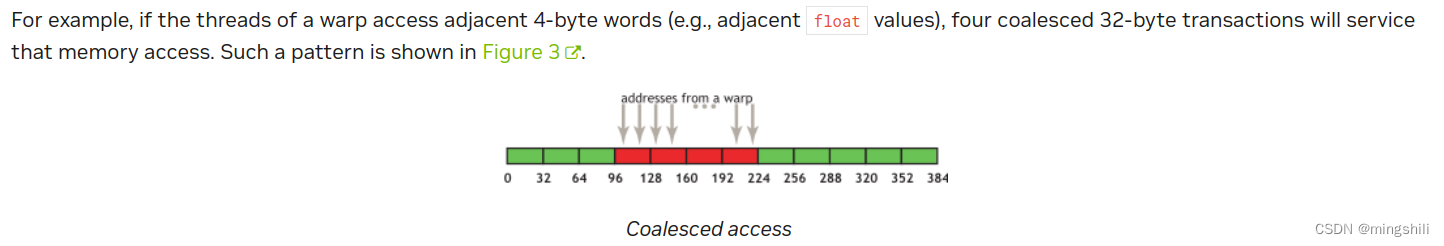
- High Priority: Ensure global memory accesses are coalesced whenever possible. 比如多使用int4, float4这种复合类型来增加合并访存的比例。Global memory的访存 - 32B:On devices of compute capability 6.0 or higher, L1-caching is the default, however the data access unit is 32-byte regardless of whether global loads are cached in L1 or not. 如果一个kernel要获取一个float值,那么每个warp需要4个32B的访存事务【32(warp size)*4B(float)】。
- Misalignment: If sequential threads in a warp access memory that is sequential but not aligned with a 32-byte segment, five 32-byte segments will be requested, 所以内存地址对齐很重要。 当然有些情况会导致没有这么大的差距4/5; 而是9/10, 因为与缓存行的存在,会导致差距没那么低。
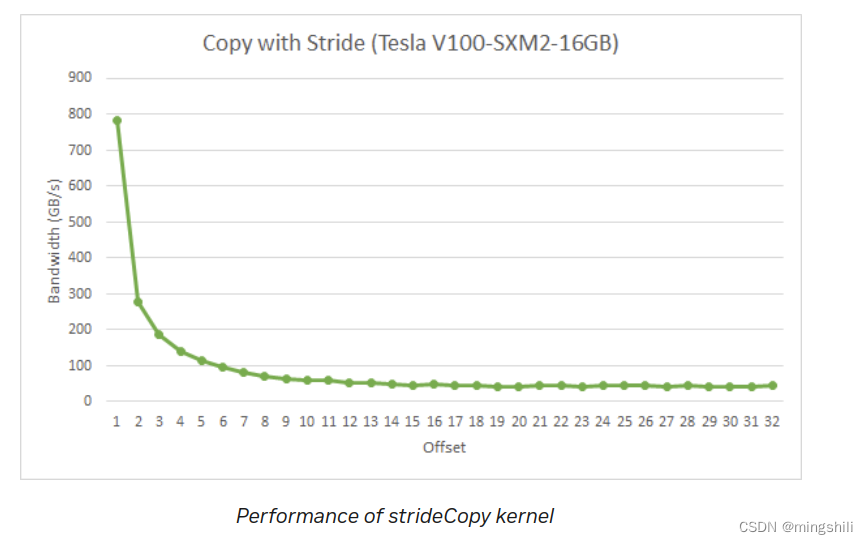
- Strided Accesses: 可能需要8个访存事务,甚至更多;所以访存合并需要考虑一下,能极大提升效率。stride的读取耗时情况,下降很严重,offset代表stride的布场。
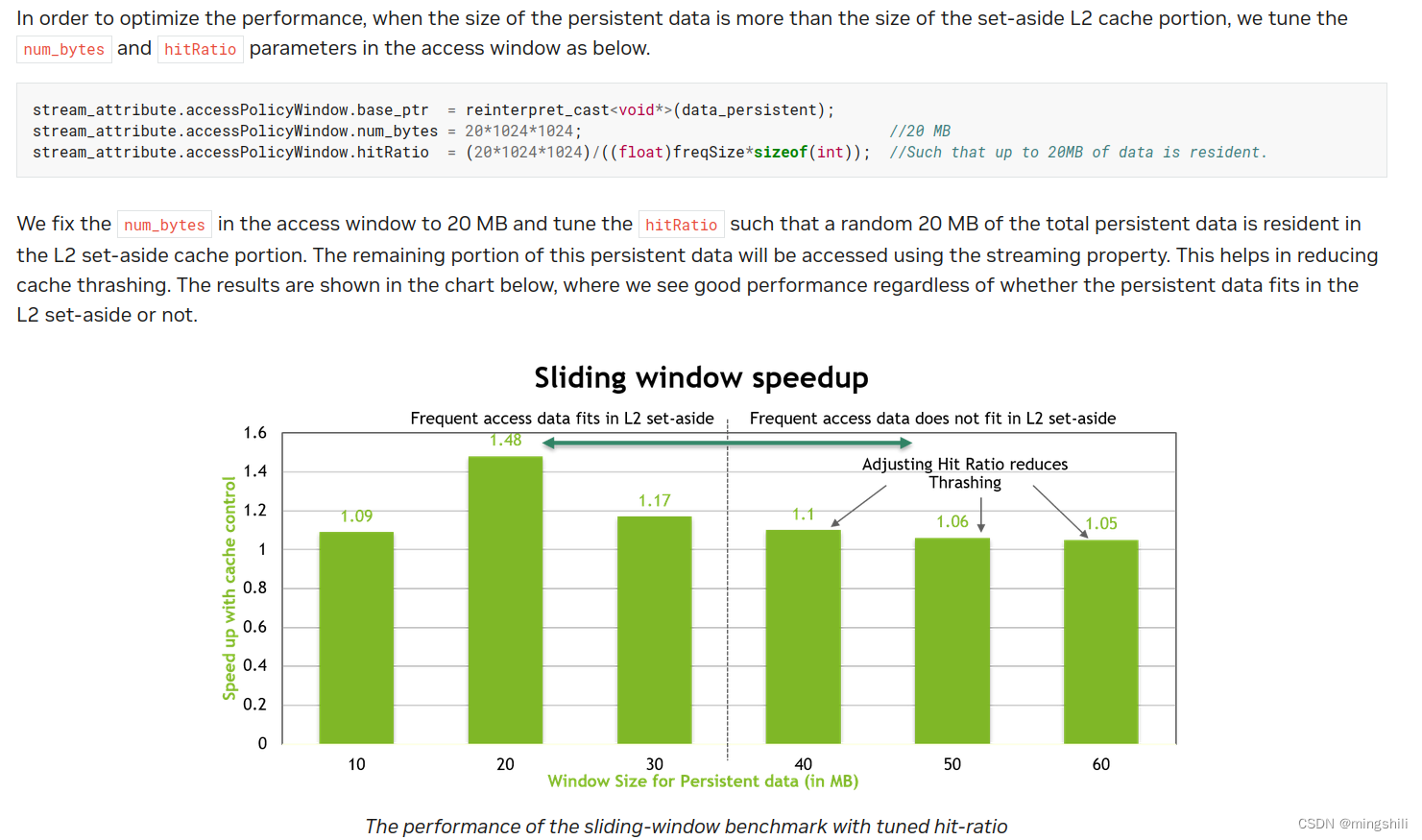
- L2的使用方式和使用L2时需要注意 设置hiRate的大小,来提升L2的命中率
- Medium Priority: Use shared memory to avoid redundant transfers from global memory.
__global__ void coalescedMultiply(float *a, float *c, int M)
{
// TILE_DIM = 32;
// transposedTile[threadIdx.x][threadIdx.y] 正好是一个warp中访问相同的threadidx.y 从而一个warp访问同一个blank,从而导致blank冲突。
// transposedTile[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM + 1]; 通过修改为加一就可以了,避免blank冲突了。
__shared__ float aTile[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM],
transposedTile[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM];
int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
int col = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
float sum = 0.0f;
aTile[threadIdx.y][threadIdx.x] = a[row*TILE_DIM+threadIdx.x];
transposedTile[threadIdx.x][threadIdx.y] =
a[(blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.y)*TILE_DIM +
threadIdx.x];
__syncthreads();
for (int i = 0; i < TILE_DIM; i++) {
sum += aTile[threadIdx.y][i]* transposedTile[i][threadIdx.x];
}
c[row*M+col] = sum;
}
-
shared memory的使用会降低kernel的occupancy,这个有好处就是对于占用不敏感,可以更好地和其他程序并行;但是如果没有其他程序并行,那么可以考虑occupancy更加饱满为好。
-
Asynchronous Copy from Global Memory to Shared Memory: CUDA 11.0 introduces an async-copy feature that can be used within device code to explicitly manage the asynchronous copying of data from global memory to shared memory. This feature enables CUDA kernels to overlap copying data from global to shared memory with computation. It also avoids an intermediary register file access traditionally present between the global memory read and the shared memory write. The synchronous version for the kernel loads an element from global memory to an intermediate register and then stores the intermediate register value to shared memory.. In the asynchronous version of the kernel, instructions to load from global memory and store directly into shared memory are issued as soon as __pipeline_memcpy_async() function is called., 对于复杂的kernel计算,可以考虑一下,隐藏shared上的计算和shared 到Global的延迟。
- Data copied from global memory to shared memory using asynchronous copy instructions can be cached in the L1 cache or the L1 cache can be optionally bypassed(绕过L1). If individual CUDA threads are copying elements of 16 bytes, the L1 cache can be bypassed.
From the performance chart, the following observations can be made for this experiment.
Best performance with synchronous copy is achieved when the copy_count parameter is a multiple of 4 for all three element sizes. The compiler can optimize groups of 4 load and store instructions. This is evident from the saw tooth curves.
Asynchronous copy achieves better performance in nearly all cases.
The async-copy does not require the copy_count parameter to be a multiple of 4, to maximize performance through compiler optimizations.
Overall, best performance is achieved when using asynchronous copies with an element of size 8 or 16 bytes.
-
Local Memory:如果寄存器不够用,那么编译器会给kernel分配本地存储,这个耗时不一定比global快,有可能一样耗时。所以减少寄存器使用也是个很好的优化方向。
- profile中占有率低一方面是kernel个数少,另一个方面kernel使用寄存器导致并行性小。
- 寄存器使用: use the -maxrregcount=N 通过这个compiler command-line option控制每个线程的寄存器数目。
-
NUMA(Non Uniform Memory Access)技术可以使众多服务器像单一系统那样运转,同时保留小系统便于编程和管理的优点: 最好关闭NUMA的使用,否则可能会降低cuda的性能。
1.2.3 配置优化
- launch_bounds的设置用处,也就是由于某些kernel逻辑导致,我们希望每个block中thread的个数不能超过多少,比如对shared memory的使用就需要限制一个block不能太大,否则会导致问题
- Medium Priority: To hide latency arising from register dependencies, maintain sufficient numbers of active threads per multiprocessor (i.e., sufficient occupancy). 但是寄存器的使用和occ之间没有直接的关系,因为不同的blocksize 粒度和kernel使用的register个数以及shared memory的资源都会影响occ的值。 【cudaOccupancyMaxActiveBlocksPerMultiprocessor, --ptxas options=v option】
- Medium Priority: The number of threads per block should be a multiple of 32 threads, because this provides optimal computing efficiency and facilitates coalescing.
There are many such factors involved in selecting block size, and inevitably some experimentation is required. However, a few rules of thumb should be followed:
▶ Threads per block should be a multiple of warp size to avoid wasting computation on underpopulated warps and to facilitate coalescing.
▶ A minimum of 64 threads per block should be used, and only if there are multiple concurrent blocks per multiprocessor.
▶ Between 128 and 256 threads per block is a good initial range for experimentation with different block sizes.
▶ Use several smaller thread blocks rather than one large thread block per multiprocessor if latency affects performance. This is particularly beneficial to kernels that frequently call __syncthreads().
Note that when a thread block allocates more registers than are available on a multiprocessor, the kernel launch fails, as it will when too much shared memory or too many threads are requested. 所以有些kernel出现问题,可以考虑是这个原因;
- gpu会存在多个context切换情况,可以考虑用
∕∕ When initializing the program∕library
CUcontext ctx;
cuDevicePrimaryCtxRetain(&ctx, dev);
∕∕ When the program∕library launches work
cuCtxPushCurrent(ctx);
kernel<<<...>>>(...);
cuCtxPopCurrent(&ctx);
cuDevicePrimaryCtxRelease(dev);
1.2.4 指令集优化都是低优先级优化
- Single-precision floats provide the best performance, and their use is highly encouraged
- Note: Low Priority: Use shift operations to avoid expensive division and modulo calculations.
- If n is a power of 2, ( i/n ) is equivalent to ( i ≫ log2(n) ) and (i%n ) is equivalent to ( i& (n − 1) ).
- Note: Low Medium Priority: Use signed integers rather than unsigned integers as loop counters.
- The reciprocal square root should always be invoked explicitly as rsqrtf() for single precision andrsqrt() for double precision; 倒数平方根
- Note: Low Priority: Avoid automatic conversion of doubles to floats. The latter case can be avoided by using single-precision floating-point constants, defined with an fsuffix such as 3.141592653589793f, 1.0f, 0.5f.
- 幂次计算是需要使用cuda原声一些math函数,而不是用pow等。
- Note: Medium Priority: Use the fast math library whenever speed trumps precision.
- Two types of runtime math operations are supported. They can be distinguished by their names: some have names with prepended underscores, whereas others do not (e.g., __functionName() versus functionName()). Functions following the __functionName() naming convention map directly to the hardware level. __functionName函数更加快,但是精度低。一般对float单精度有效。
- Note: Medium Priority: Prefer faster, more specialized math functions over slower, more general ones when possible. 用更快的专用函数,而不是一些一般函数。
- For exponentiation using base 2 or 10, use the functions exp2() or expf2() and exp10() orexpf10() rather than the functions pow() or powf().
- For exponentiation with an exponent of 1/3, use the cbrt() or cbrtf() function rather than the generic exponentiation functions pow() or powf(), as the former are significantly faster than the latter
- Replace sin(π*) with sinpi(), cos(π*) with cospi(), and sincos(π*) with sincospi().
通过编译器选项来控制计算的速度和精确度之间的trade off
▶ -ftz=true (denormalized numbers are flushed to zero)
▶ -prec-div=false (less precise division)
▶ -prec-sqrt=false (less precise square root)
-
Note: High Priority: Minimize the use of global memory. Prefer shared memory access where possible.
-
Note: High Priority: Avoid different execution paths within the same warp. Flow control instructions (if, switch, do, for, while) can significantly affect the instruction throughput by causing threads of the same warp to diverge; that is, to follow different execution paths. 尽量减少kernel分支。
-
如果有分支情况,可考虑使用显式 __syncwarp() 可用于保证warp重新收敛。
-
对于只包含少数指令的分支,warp发散通常会导致边际性能损失
- Note: Low Priority: Make it easy for the compiler to use branch predication in lieu of loops or control statements. 用它
#pragma unroll去unroll loop
- Note: Low Priority: Make it easy for the compiler to use branch predication in lieu of loops or control statements. 用它
▶ A C-style function interface (cuda_runtime_api.h).
▶ C+±style convenience wrappers (cuda_runtime.h) built on top of the C-style functions.
Note: The CUDA Toolkit Samples provide several helper functions for error checking with the various CUDA APIs; these helper functions are located in the samples∕common∕inc∕helper_cuda.h file in the CUDA Toolkit.
The NVIDIA Management Library (NVML) is a C-based interface that provides direct access to the queries and commands exposed via nvidia-smi intended as a platform for building 3rd-party system management applications. NVIDIA 管理库 (NVML) 是一个基于 C 的界面,它提供了直接访问通过 nvidia-smi 暴露的查询和命令,旨在作为构建第三方系统管理应用程序的平台。
也就是可以用NVML的API来实现nvidia-smi的功能。
PTX 定义了一个虚拟机和 ISA,用于通用并行线程执行。PTX程序通过JIT编译器在load时间转换为目标硬件指令集,该编译器是CUDA驱动程序的一部分, PTX- 即时编译(JIT) 增加了应用程序加载时间,但允许应用程序受益于最新的编译器改进;
及时编译PTX 是能够将字符串指令编译为硬件指令进行执行的;可能在编译器加载时间内起作用的, 所以在写汇编的时候,一般用PTX方式将汇编语言转化为有效指令
1.2 shared memory什么时候用有效
当进行atomicAdd等操作是,这个地址用shared memory会更加有效,应为每个kernel都进行加法操作,而且Global memory带宽又高,所以使用shared memory更有优势。
- cuda graph: cuda graph的使用心得

https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/685842177
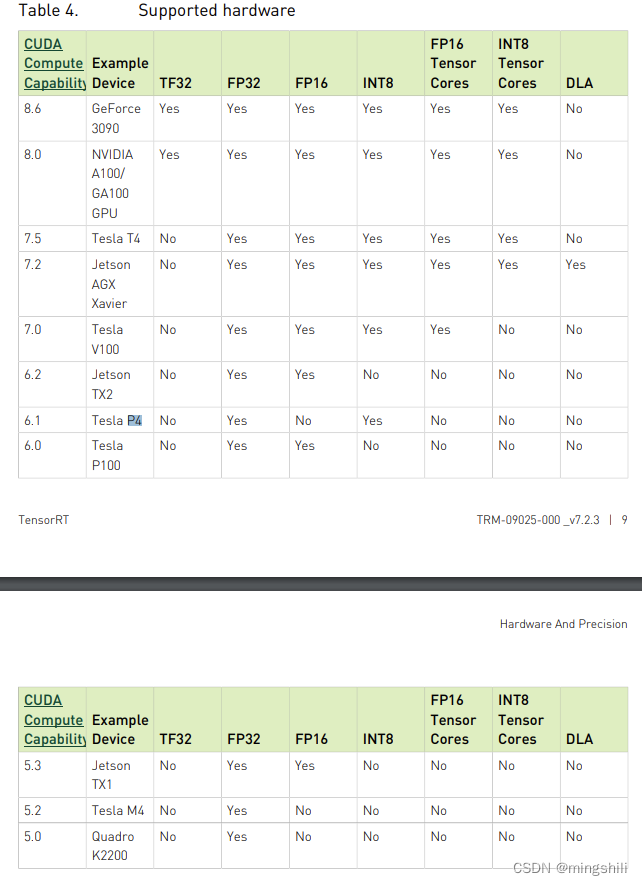
1.3 DLA 支持
- 只有一些嵌入式GPU支持DLA
- https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/archives/tensorrt-723/pdf/TensorRT-Support-Matrix-Guide.pdf
2. CUBLAS
- cublas Segmm 是列优先排序:将数据按照行放置的时候,要再按照列优先排布的方式将shape重新梳理一遍,然后再使用(基本上就是将输入的两个matrix先后顺序颠倒,传入Segmm),这样避免错误;
cublasStatus_t cublasSgemm(cublasHandle_t handle,
cublasOperation_t transa, cublasOperation_t transb,
int m, int n, int k,
const float *alpha,
const float *A, int lda,
const float *B, int ldb,
const float *beta,
float *C, int ldc)
// for example
/// if Segmm works for input_a(A) and input_b(B);
// input_a: row-major (N, 4):[[0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]...] in memory is: [0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2....]
// input_b: row-major (4, 2): [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5]] in memory is: [1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5]
// because the segmm is colum-major; So input_a's shape 应该视为 (4,N); input_b's shape 应为视为 (2,4)
// 所以Segmm应该是input_b(2,4) 作为第一个输入, input_a(4,N)作为第二个输入; 输出C则是(2,N)因为是列优先排列,则实际作为行优先输入的话是(N,2);所以也就不用转换,在memory中排布就是row-major方式的(N,2); 因此使用Segmm唯一需要注意的就是将row-major的输入颠倒一下传入Segmm。
2.1 cublas_v2
2.2 cublas_Lt
3. CUTLASS library
CUTLASS是一个 CUDA C++ 模板库,用于在 CUDA 中 实现 所有等级的 高性能矩阵乘法 (GEMM)。CUTLASS 本身是一个 头文件模板库,使用的话只需要 包含头文件,无需链接操作。如果需要和 vcpkg管理的库方便的集成,可以自定义 vcpkg库安装文件。
作者:uiemUI
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/097756147535
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
然而凭借人力手工优化算子的方式已经没有办法应对如此多的数据类型,因此对于 DL 应用的优化渐渐地越来越依赖一些自动化的工具,例如面向深度学习领域的编译器。在这样的趋势下, Nvidia 开发了线性代数模板库 CUTLASS ,抽象了一系列高性能的基本组件,可以用于生成各种数据类型,各种计算单元的卷积、矩阵乘算子。MegEngine 在 CUTLASS 的基础上进行了二次开发,可以高效地开发新的高性能的算子,快速地迁移到新的 GPU 架构
4. THRUST (thrust)
- thrust 制定stream: reference from oneflow repo in github
// Create two vectors of {0, 1, ..., N-1} on CUDA device
thrust::device_vector<int> order1(N), order2(N);
thrust::sequence(
thrust::cuda::par.on(context_.cuda_stream()),
order1.begin(),
order1.end());
thrust::sort_by_key(
thrust::cuda::par.on(context_.cuda_stream()),
buffer,
buffer + N,
order1.begin());
5. CUB
官方教程链接: 很多好的示例代码,可以好好研读和学习,需要的时候可以在这里面找自己可能用到的代码。
cub使用笔记,含以下示例:
-
NonZero的实现: cub_v1.16.0, 参考oneflow源码
-
How is CUB different than Thrust and Modern GPU? CUB更加底层(block-wise, warp-wise),专门为CUDA设计,可以作为thrust 后端。然而thrust后端不仅仅只有cuda,还有其他硬件需要的库,所以对CUDA的细节没有太开放,比如stream就无法传递到thrust底层的cuda中。
CUB and Thrust share some similarities in that they both provide similar device-wide primitives for CUDA. However, they target different abstraction layers for parallel computing. Thrust abstractions are agnostic of any particular parallel framework (e.g., CUDA, TBB, OpenMP, sequential CPU, etc.). While Thrust has a “backend” for CUDA devices, Thrust interfaces themselves are not CUDA-specific and do not explicitly expose CUDA-specific details (e.g., cudaStream_t parameters).
CUB, on the other hand, is slightly lower-level than Thrust. CUB is specific to CUDA C++ and its interfaces explicitly accommodate CUDA-specific features. Furthermore, CUB is also a library of SIMT collective primitives for block-wide and warp-wide kernel programming.
CUB and Thrust are complementary and can be used together. In fact, the CUB project arose out of a maintenance need to achieve better performance-portability within Thrust by using reusable block-wide primitives to reduce maintenance and tuning effort.
6. CUDNN
7. Modern GPU
- moderngpu is a productivity library for general-purpose computing on GPUs. It is a header-only C++ library written for CUDA. The unique value of the library is in its accelerated primitives for solving irregularly parallel problems.
8. CUDA编程的一些实用工具
- [CUDA] cuda的一些实用工具
- 打印gpu数据
- nsight system工具的使用
- 性能分析工具
- cuda-gdb使用
- nsight compute的使用
9. 开源参考库
可看这些层的源码,来查阅自己需要写的功能是否有参考代码和参考示例,从而学习一些高级写法
- caffe
- pytorch/caffe2
- oneflow
- tensorRT/plugins
- NVIDIA toolkit / samples
10. 工具库
- gdrcopy: A low-latency GPU memory copy library based on NVIDIA GPUDirect RDMA technology. 可用于直接copy camera数据到gpu。
- cudaSift: 尺度不变特征转换库





















 767
767

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








