1. 两数之和
题目
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个
整数,并返回它们的数组下标。你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] ==
9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6 输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-109 <= target <= 109 只会存在一个有效答案 进阶:你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 O(n2) 的算法吗?
解法
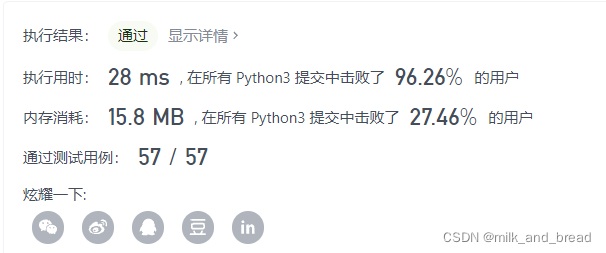
既然要求时间复杂度小于O(n^2 ),采用字典,底层为哈希表结构,是线性表的改进版,时间复杂度O(1),内容为键,下标为值。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
hashmap = dict()
for i,n in enumerate(nums):
if target - n in hashmap:
return [hashmap[target -n],i]
hashmap[n] = i
return []
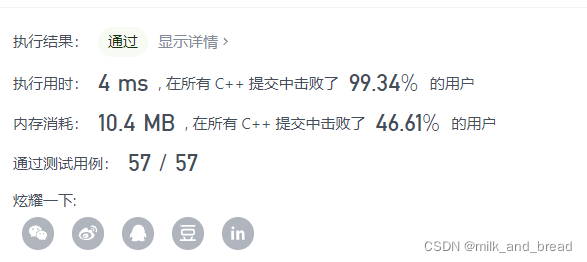
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int,int> hashmap ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size(); i++){
auto it = hashmap.find(target- nums[i]);
if(it != hashmap.end()){
return {it->second, i};
//return {hashmap[target- nums[i]],i};
}
hashmap[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {};
}
};





















 1411
1411

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








