我们现在介绍的是sort函数的第三个参数,以支持自定义比较。这个函数的名字你可以随便起,但是一般喜欢用cmp这个名字。
通常情况下这个函数的类型是bool型,有两个参数,返回值为true或者false。当你认为第一个参数小于(注意这里不能有等于)第二个参数时,应该返回true,而当第一个参数大于第二个参数时,应该返回false。之所以说没有等于,是因为使用sort时需要遵循严格弱序,永远让等于的情况返回false。具体可见STL 深入理解 sort 函数 和 严格弱序比较
其实cmp的排序规则可以理解为:a是排序后前面的数,b是排序后后面的数,你想让a和b怎么排就就返回什么为true。比如你想让前面的数大于后面的数就return a>b;你想让前面的数小于后面的数就return a<b;
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct person
{
string name;
int number;
};
bool cmp(person a, person b)
{
if (a.number > b.number)//按照升序排列
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
// return a.number > b.number;//这一行代码的作用与上面的整块if else 的作用一样,可以等价替换
}
int main()
{
freopen("test.in", "r", stdin); // 重定向读取待排序数列:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 9 1
person a[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
a[i].number = t;
a[i].name = 'a' + i; // 给它个名方便看看排序是否稳定
}
sort(a, a + 10, cmp); // stable_sort(a,a+10,cmp)是稳定排序,我也不清楚这里用sort为什么结果也稳定了
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << "name:" << a[i].name << " "
<< "number:" << a[i].number << endl;
}
return 0;
}
排序结果
name:i number:9
name:g number:7
name:e number:5
name:d number:4
name:c number:3
name:b number:2
name:f number:2
name:a number:1
name:h number:1
name:j number:1但是严格弱序并不代表if语句里不能出现等于号,我们需要探究为什么需要严格弱序?是因为如果a==b,那么用"cmp(a,b)==false && cmp(b,a)==false"会返回false,将无法判断相等的情况。只要我们在使用的时候能够避免掉这种情况就好。比如下面这个例子:
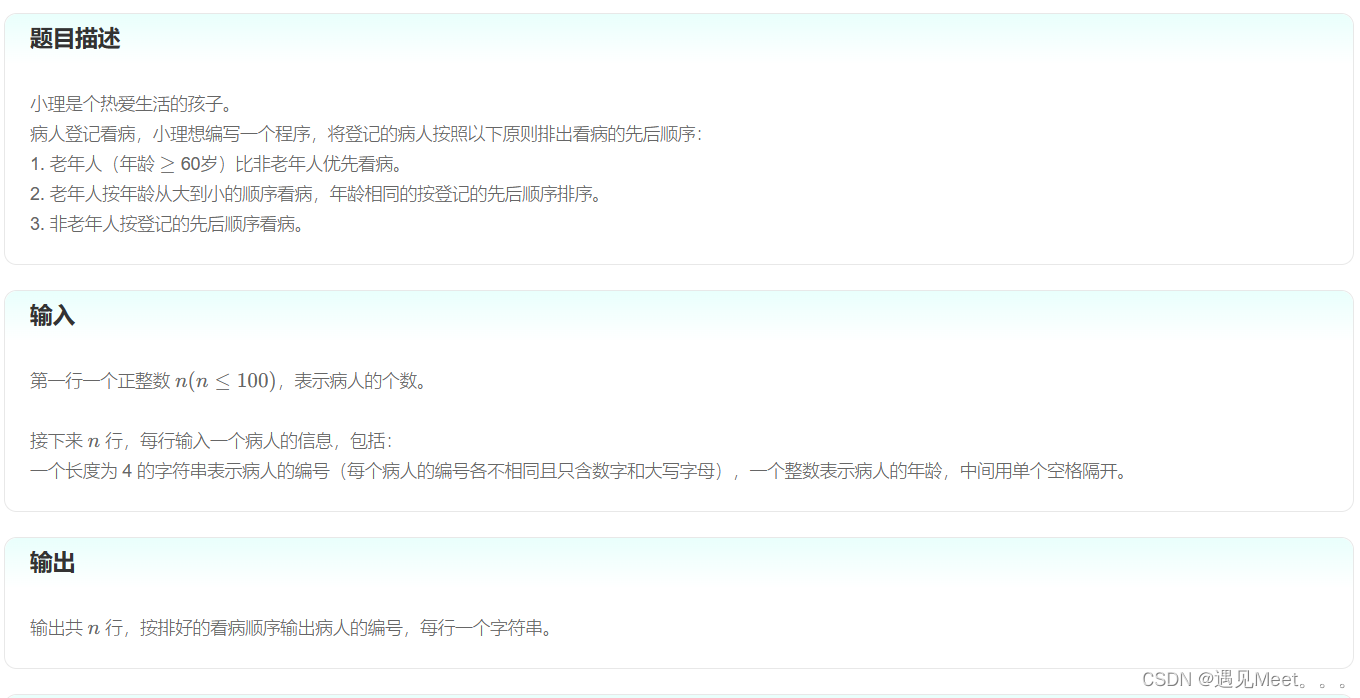
样例输入
5
1075 40
4003 15
01B8 65
1GC3 75
201A 30样例输出
1GC3
01B8
1075
4003
201AAC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct patient
{
string name;
int age;
};
// 但是这并不代表if语句里不能出现等于号,我们需要探究为什么需要严格弱序?是因为如果a==b,
// 那么用"cmp(a,b)==false && cmp(b,a)==false"会返回false,将无法判断相等的情况。只要我们在使用的时候能够避免掉这种情况就好。比如下面这个例子
// 举个例子,当a.age=b.age=60时,会return a.age > b.age,严格弱序;当a.age=b.age=40时,return false,严格弱序
bool cmp(patient a, patient b)
{
if (a.age >= 60 && b.age < 60)
{
return true;
}
if (a.age < 60 && b.age >= 60)
{
return false;
}
if (a.age >= 60 && b.age >= 60)
{
return a.age > b.age;
}
return false;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// freopen("text.in", "r", stdin);
int n;
cin >> n;
patient p[100];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> p[i].name >> p[i].age;
}
stable_sort(p, p + n, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << p[i].name << endl;
}
return 0;
}




 文章介绍了在C++中使用sort函数进行自定义排序时,如何使用cmp函数进行比较操作。cmp函数需要遵循严格弱序原则,即相等的情况应返回false,以确保排序的稳定性。示例代码展示了如何根据成员变量进行升序排序,并解释了在cmp函数中避免等于情况的原因。
文章介绍了在C++中使用sort函数进行自定义排序时,如何使用cmp函数进行比较操作。cmp函数需要遵循严格弱序原则,即相等的情况应返回false,以确保排序的稳定性。示例代码展示了如何根据成员变量进行升序排序,并解释了在cmp函数中避免等于情况的原因。
















 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








