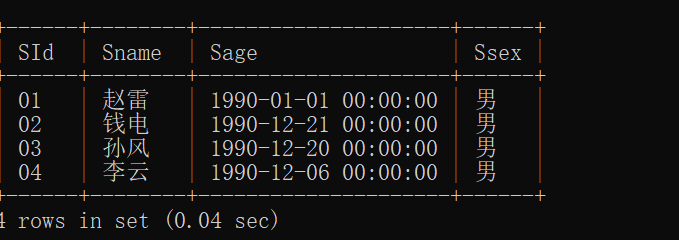
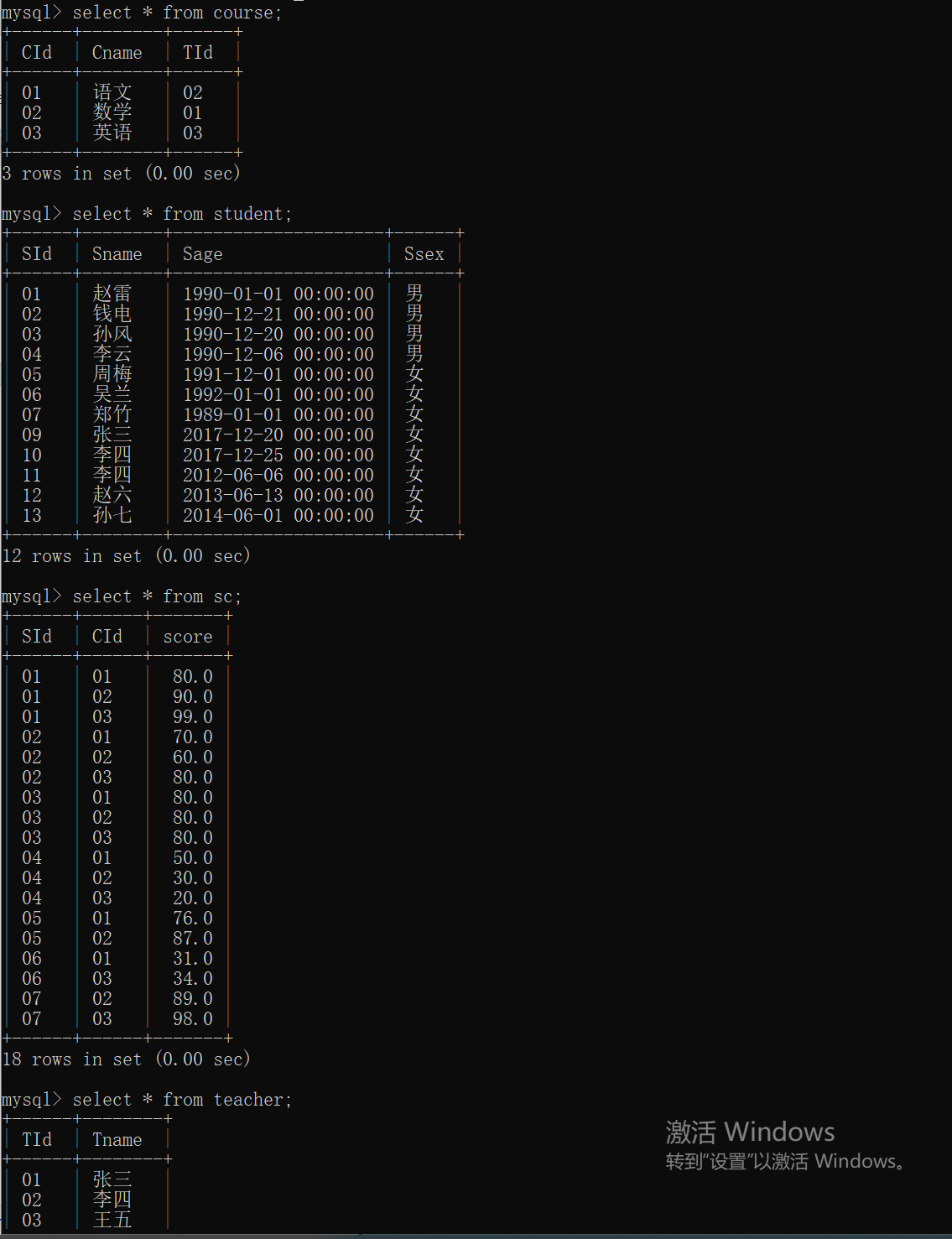
准备工作,创建三个四个表:sc student course teacher
以下50个题:
1.查询" 01 "课程比" 02 "课程成绩高的学生的信息及课程分数
数据库原理中的内外链接分别指的是内连接(INNER JOIN)和外连接(OUTER JOIN),它们用于合并来自两个或多个表的数据。在内连接中,只返回两个表中匹配的行,而外连接则包括了匹配和不匹配的行。
内连接适用于需要获取两个表中共有数据的场景;它用于从两个或多个表中返回匹配的行。如果两个表中的某一列匹配,内连接将会显示这些匹配的行。
而外连接则适用于需要保留一个或两个表中所有数据的场景。外连接用于返回两个表中的所有行,无论它们是否匹配。
内连接的常见用法是通过主键和外键的匹配来获取相关联的数据,而外连接可以进一步分为左外连接(LEFT JOIN)、右外连接(RIGHT JOIN)和全外连接(FULL JOIN),分别包括了左表的所有行、右表的所有行,以及两个表的所有行。
左外连接返回左表中的所有行,即使右表中没有匹配的行。它包括了匹配和不匹配的行,右表中没有匹配的行将显示为NULL。
RIGHT JOIN(右连接)
作用:以右表(
RIGHT JOIN右侧的表)为基础,返回右表的所有记录,即使左表中没有匹配的记录。匹配规则:
如果右表的某行在左表中有匹配,则合并左右表的数据。
如果右表的某行在左表中无匹配,左表字段以
NULL填充。
mysql> select * from student right join(
-> select t1.sid,subject1,subject2 from
-> (select sid,score as subject1 from sc where sc.cid='01') as t1,
-> (select sid,score as subject2 from sc where sc.cid='02') as t2
-> where t1.sid = t2.sid and t1.subject1 > t2.subject2)r
-> on student.sid = r.sid;
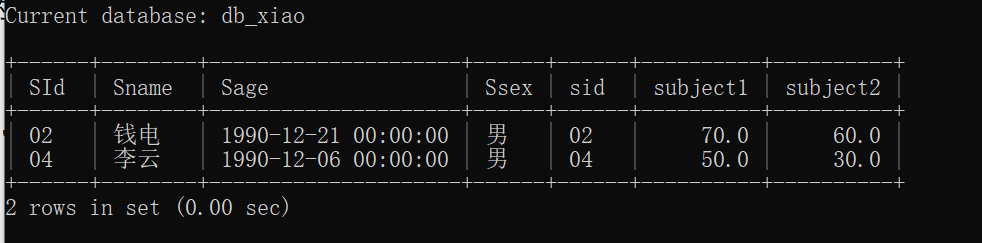
注意:
ON Student.SId = r.SId;是将将Student表与子查询结果r通过SId关联,补充学生的详细信息(如姓名、年龄等)。
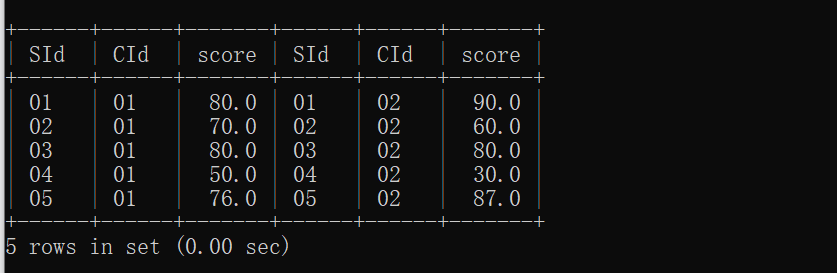
2.查询同时存在" 01 "课程和" 02 "课程的情况
mysql> select * from (select * from sc where sc.cid="01") as t1,
-> (select * from sc where sc.cid="02") as t2
-> where t1.sid = t2.sid;
3.查询存在" 01 "课程但可能不存在" 02 "课程的情况(不存在时显示为 null
该题涉及到两门课程,所以要用到join,可以用left join 也可以用right join;
mysql> select * from (select * from sc where sc.cid = "01") as t1
-> right join (select * from sc where sc.cid = "02") as t2
-> on t1.sid = t2.sid;
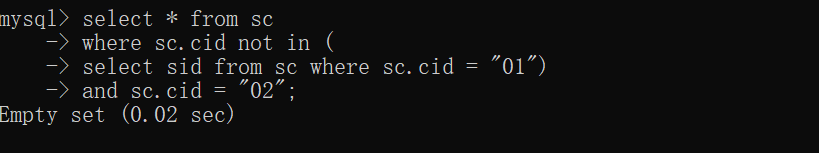
4.查询不存在" 01 "课程但存在" 02 "课程的情况
mysql> select * from sc
-> where sc.cid not in (
-> select sid from sc where sc.cid = "01")
-> and sc.cid = "02";
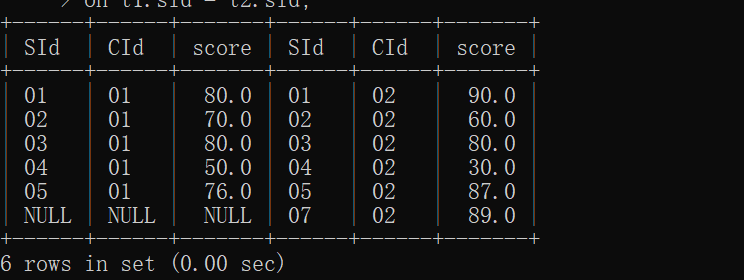
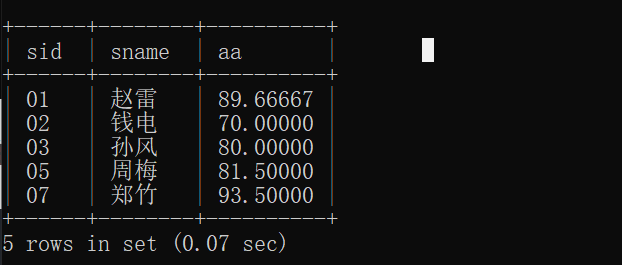
5.查询平均成绩大于等于 60 分的同学的学生编号和学生姓名和平均成绩
该题与第一题类似,都用到主查询和子查询;
注意:在sc表中查询的是sid和score,通过sid进行分组,对分组中的score求平均值,最后在选取结果中AVG大于60的即可;但是需要对avg结果进行取别名;
select student.sid,student.sname,r.aa from student right join(
select sid,avg(score) as aa from sc
group by sid having avg(score) > 60) as r
on student.sid = r.sid;
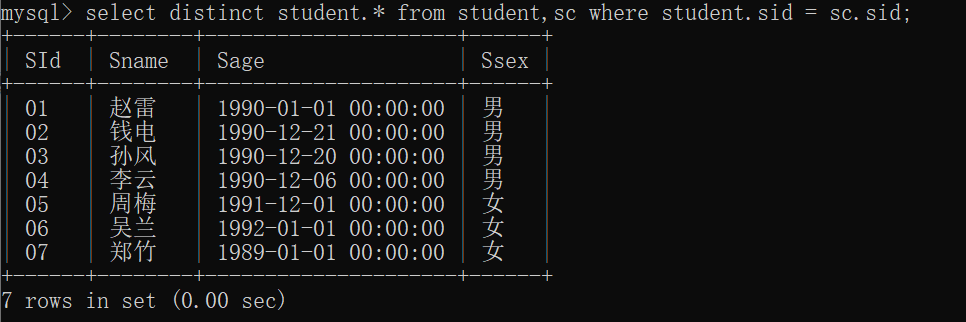
6.查询在 SC 表存在成绩的学生信息
mysql> select distinct student.* from student,sc where student.sid = sc.sid;
7.查询所有同学的学生编号、学生姓名、选课总数、所有课程的总成绩(没成绩的显示为 null )
INNER JOIN(内连接)
- 仅返回两个表中 完全匹配的行。如果左表的某行在右表中没有对应记录,或右表的某行在左表中没有对应记录,这些行会被丢弃。
LEFT JOIN(左外连接)
返回 左表的所有行,即使右表中没有匹配的行。若右表无匹配,右表字段以
NULL填充。
mysql> SELECT student.sid, student.sname, r.coursenumber, r.scoresum
-> FROM student
-> left JOIN (
-> SELECT sid, SUM(score) AS scoresum, COUNT(cid) AS coursenumber
-> FROM sc
-> GROUP BY sid
-> ) r
-> ON student.sid = r.sid
-> ;
8. 查有成绩的学生信息
注意:exists和in的区别。
结论:
IN()适合B表比A表数据小的情况;
EXISTS()适合B表比A表数据大的情况;
mysql> select * from student
-> where student.sid in (select sc.sid from sc);
mysql> select * from student
-> where student.sid in (select sc.sid from sc);
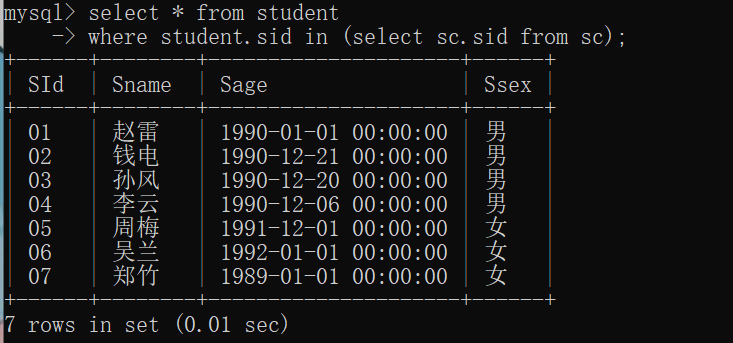
9.查询「李」姓老师的数量
select count(*) from teacher where tname like "李%";
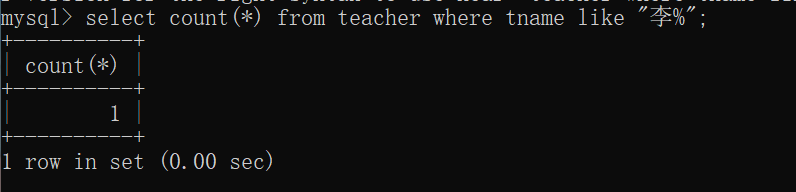
10.查询学过「张三」老师授课的同学的信息
连接路径
学生 → 选课
student.sid = sc.sid
(筛选有选课记录的学生)选课 → 课程
sc.cid = course.cid
(定位学生选修的课程)课程 → 教师
course.tid = teacher.tid
(找到课程的授课教师)筛选教师
teacher.tname = '张三'
(仅保留教师姓名为“张三”的记录)
mysql> select student.* from student,teacher,course,sc
-> where student.sid = sc.sid
-> and course.cid = sc.cid
-> and course.tid = teacher.tid
-> and tname = "张三";
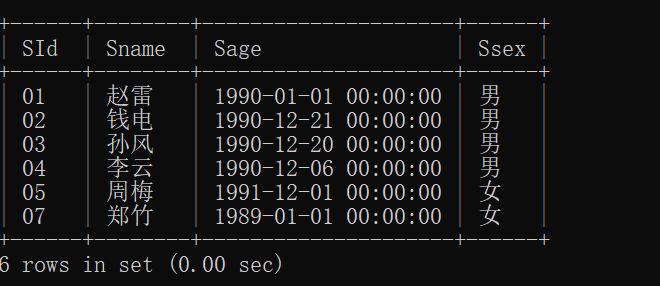
11.查询没有学全所有课程的同学的信息
having count(sc.cid)= (select count(cid) from course) ----- 是指筛选出选课数量等于总课程数的学生(即选修了所有课程的学生)
反向思维,找出不相等的。
mysql> select * from student
-> where student.sid not in (
-> select sc.sid from sc
-> group by sc.sid
-> having count(sc.cid)= (select count(cid) from course)
-> );
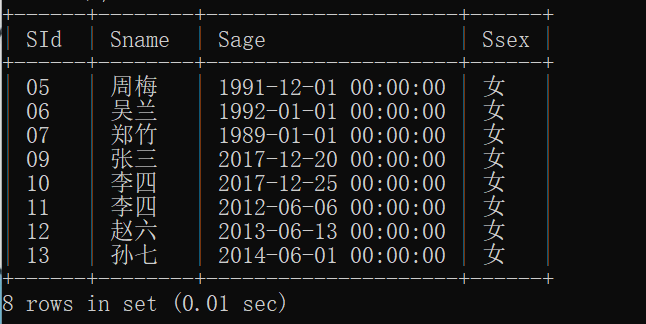
12.查询至少有一门课与学号为" 01 "的同学所学相同的同学的信息
思维:先查找到学号为“01”学生的所有课程cid,再通过cid筛选出对应的sid,最后看studen.sid只要在这个sid里面就能筛选出我们想要的信息;
select * from student
where student.sid in (
select sc.sid from sc
where sc.cid in(
select sc.cid from sc
where sc.sid = '01'
)
);
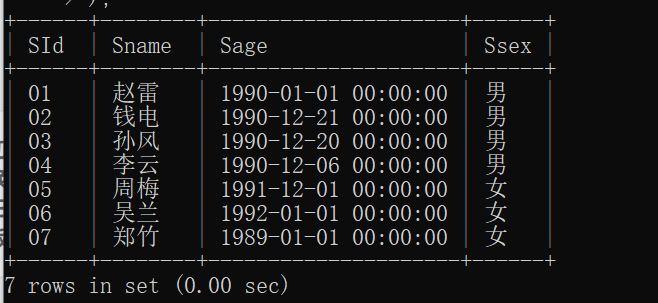
13.查询和" 01 "号的同学学习的课程 完全相同的其他同学的信息
GROUP_CONCAT 方法:
将每个学生的课程按
CId排序并拼接成字符串(如'01,02,03')。直接比较字符串是否与01同学的课程字符串完全一致。
步骤解析:
获取01同学的课程集合:先查出学号01选修的所有课程。
匹配其他同学的课程集合:确保其他同学的课程集合与01同学的完全相同(数量一致且内容完全一致)。
mysql> select * from student
-> where sid in (
-> select sid from sc
-> where sid != "01"
-> group by sid
-> having group_concat(distinct cid order by cid) = (
-> select group_concat(distinct cid order by cid)
-> from sc
-> where sid = "01"
-> )
-> );
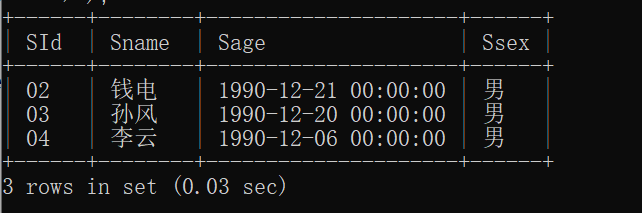
14.查询没学过"张三"老师讲授的任一门课程的学生姓名
子查询逻辑:
通过隐式连接(
FROM sc, course, teacher)关联三张表。筛选条件:
sc.cid = course.cid:选课表与课程表关联。
course.tid = teacher.tid:课程表与教师表关联。
teacher.tname = "张三":教师姓名为“张三”。获取所有选修了“张三”老师课程的学生ID(
sc.sid)
主查询逻辑:
从学生表(
student)中选择所有字段。使用
NOT IN排除子查询结果中的学生ID,即未选修“张三”课程的学生
mysql> select * from student
-> where student.sid not in(
-> select sc.sid from sc,course,teacher
-> where
-> sc.cid = course.cid
-> and course.tid = teacher.tid
-> and teacher.tname= "张三"
-> );
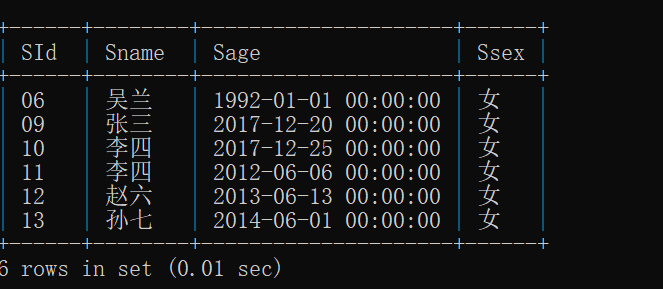
15.查询两门及其以上不及格课程的同学的学号,姓名及其平均成绩
最内层子查询:筛选出至少有两门课程不及格的学生ID(
sid)
HAVING COUNT(score) > 1:统计每个学生不及格的课程数量,保留数量大于1的学生。中间层子查询(别名为a):计算符合条件(至少两门不及格)的学生所有课程的平均成绩。
mysql> select student.sid,student.sname,a.avg
-> from student right join
-> (select sid,avg(score) as avg from sc
-> where sid in (
-> select sid from sc
-> where score < 60
-> group by sid
-> having count(score) > 1)
-> group by sid) as a
-> on student.sid = a.sid;
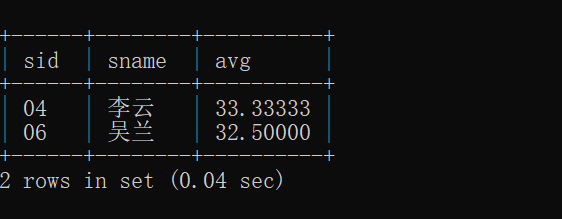
16.检索" 01 "课程分数小于 60,按分数降序排列的学生信息
mysql> select student.* ,sc.score from student,sc
-> where student.sid = sc.cid
-> and sc.score < 60
-> and cid = "01"
-> order by sc.score desc;
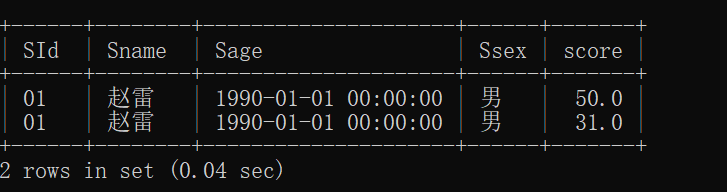
17.按平均成绩从高到低显示所有学生的所有课程的成绩以及平均成绩
首先在sc表通过sid分组筛选出sid和平均成绩;
其次与sc表做一个连接
最后结果以平均成绩做一个降序排列;
mysql> select * from sc
-> left join (
-> select sid,avg(score) as average from sc
-> group by sid
-> )r
-> on sc.sid = r.sid
-> order by average desc;
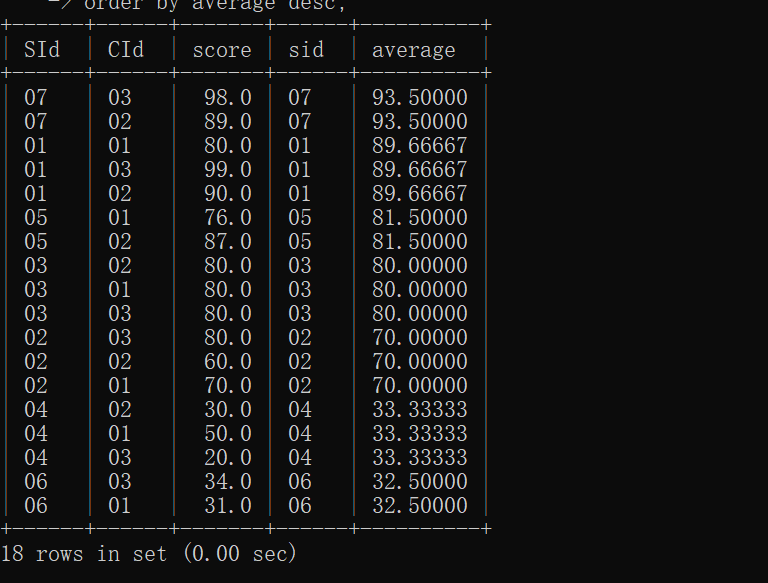
18.查询各科成绩最高分、最低分和平均分:
以如下形式显示:课程 ID,课程 name,最高分,最低分,平均分,及格率,中等率,优良率,优秀率
及格为>=60,中等为:70-80,优良为:80-90,优秀为:>=90
要求输出课程号和选修人数,查询结果按人数降序排列,若人数相同,按课程号升序排列
mysql> select
-> sc.CId ,
-> max(sc.score)as 最高分,
-> min(sc.score)as 最低分,
-> AVG(sc.score)as 平均分,
-> count(*)as 选修人数,
-> sum(case when sc.score>=60 then 1 else 0 end )/count(*)as 及格率,
-> sum(case when sc.score>=70 and sc.score<80 then 1 else 0 end )/count(*)as 中等率,
-> sum(case when sc.score>=80 and sc.score<90 then 1 else 0 end )/count(*)as 优良率,
-> sum(case when sc.score>=90 then 1 else 0 end )/count(*)as 优秀率
-> from sc
-> GROUP BY sc.CId
-> ORDER BY count(*)DESC, sc.CId ASC
-> ;
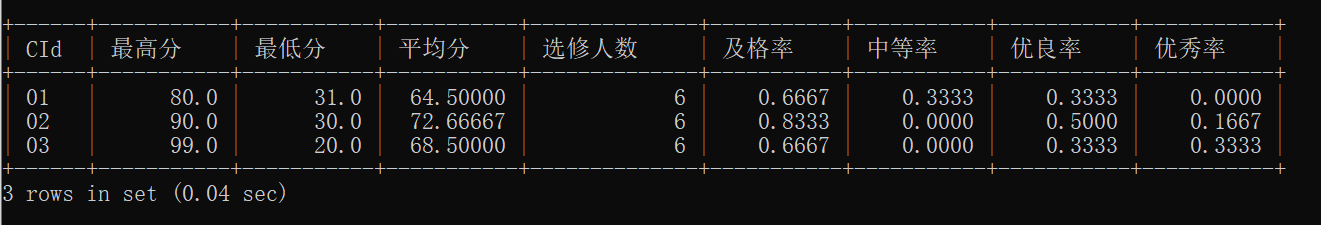
19.按各科成绩进行排序,并显示排名, Score 重复时保留名次空缺
关键函数对比
函数 行为 适用场景 ROW_NUMBER()唯一递增序号(无并列) 需严格唯一排名时使用 RANK()并列跳过名次(如 1,1,3) 竞赛排名(本题需求) DENSE_RANK()并列不跳名次(如 1,1,2) 连续排名场景
自连接逻辑:
将
sc表自连接为a(主表)和b(从表)。连接条件:
a.cid = b.cid:确保比较同一课程的成绩。
a.score < b.score:筛选出比当前学生(a)成绩更高的其他学生(b)。统计高分段人数:
对每个学生(
a表的每条记录),统计同一课程中成绩更高的人数(COUNT(b.score))。最终排名为
COUNT(b.score) + 1:例如,若有 2 人成绩更高,则当前学生排名第 3。分组与排序:
GROUP BY a.cid, a.sid, a.score:按课程、学生、成绩分组,确保唯一性。
ORDER BY a.cid, rank ASC:按课程升序、排名升序展示结果;
mysql> select a.cid, a.sid, a.score, count(b.score)+1 as rank
-> from sc as a
-> left join sc as b
-> on a.score<b.score and a.cid = b.cid
-> group by a.cid, a.sid,a.score
-> order by a.cid, rank ASC;
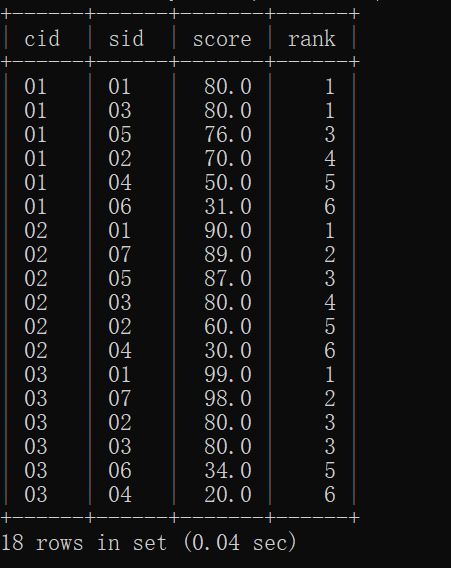
20.按各科成绩进行排序,并显示排名, Score 重复时合并名次
mysql> select a.cid,a.sid,a.score,count(b.score)+1 as rank
-> from sc as a
-> left join sc as b
-> on a.score < b.score and a.cid = b.cid
-> group by a.cid,a.sid,a.score
-> order by a.cid,rank asc;
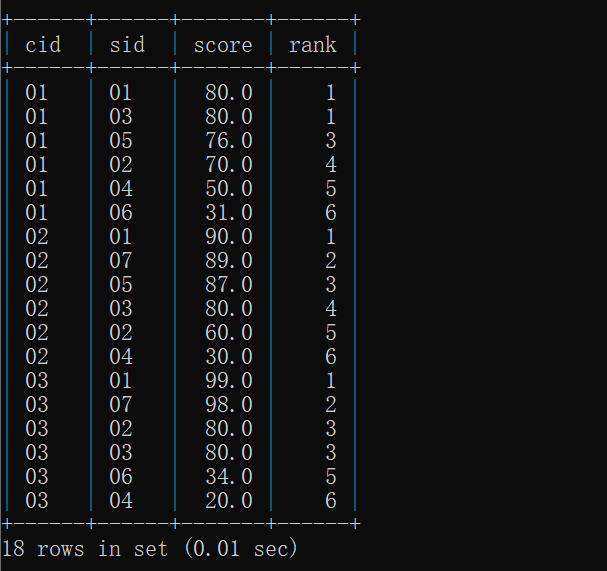
21.查询学生的总成绩,并进行排名,总分重复时保留名次空缺
主要学习一下使用变量。在SQL里面变量用@来标识。
外层查询作用:从子查询结果中读取每个学生的
sid和total,并通过@crank := @crank + 1逐行递增生成排名。
mysql> select q.sid, total, @crank := @crank +1 as rank from(
-> select sc.sid, sum(sc.score) as total from sc
-> group by sc.sid
-> order by total desc)q;
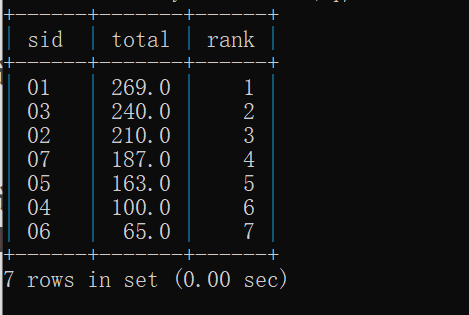
22.查询学生的总成绩,并进行排名,总分重复时不保留名次空缺
set @crank=0;
select q.sid, total, @crank := @crank +1 as rank from(
select sc.sid, sum(sc.score) as total from sc
group by sc.sid
order by total desc)q;
23.统计各科成绩各分数段人数:课程编号,课程名称,[100-85],[85-70],[70-60],[60-0] 及所占百分比
注意:用case when 返回1 以后的统计不是用count而是sum
步骤:
连接课程和成绩表,按课程分组,使用条件聚合统计各分数段人数,计算百分比,最后排序输出。确保所有条件正确,并且处理了可能的边界情况,比如分数正好是85、70、60的情况,应该归属于哪个区间。例如,85分属于[85-70]还是[100-85],需要明确。根据用户的示例,可能包含等于的情况,比如85分属于[100-85],70分属于[85-70],60分属于[70-60],而60以下属于[60-0]。
SELECT
c.cid AS 课程编号,
c.cname AS 课程名称,
-- [100-85] 分数段
SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score BETWEEN 85 AND 100 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS '[100-85]人数',
CONCAT(ROUND(SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score BETWEEN 85 AND 100 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) / COUNT(sc.score) * 100, 2), '%') AS '[100-85]占比',
-- [85-70] 分数段
SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score >=70 AND sc.score <85 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS '[85-70]人数',
CONCAT(ROUND(SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score >=70 AND sc.score <85 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) / COUNT(sc.score) * 100, 2), '%') AS '[85-70]占比',
-- [70-60] 分数段
SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score >=60 AND sc.score <70 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS '[70-60]人数',
CONCAT(ROUND(SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score >=60 AND sc.score <70 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) / COUNT(sc.score) * 100, 2), '%') AS '[70-60]占比',
-- [60-0] 分数段
SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score <60 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS '[60-0]人数',
CONCAT(ROUND(SUM(CASE WHEN sc.score <60 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) / COUNT(sc.score) * 100, 2), '%') AS '[60-0]占比'
FROM
sc
INNER JOIN
course c ON sc.cid = c.cid
GROUP BY
c.cid, c.cname
ORDER BY
c.cid;

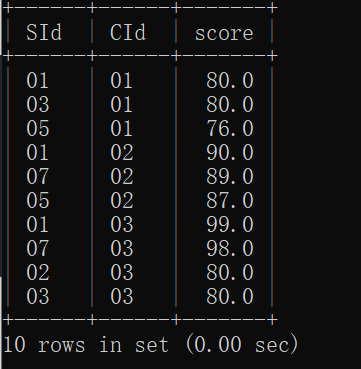
24.查询各科成绩前三名的记录
select * from sc
where (
select count(*) from sc as a
where sc.cid = a.cid and sc.score<a.score
)< 3
order by cid asc, sc.score desc;
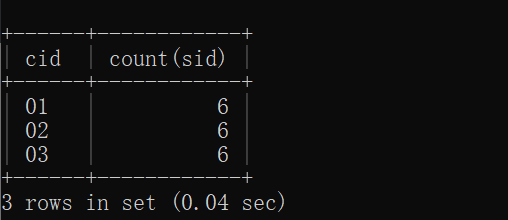
25.查询每门课程被选修的学生数
select cid, count(sid) from sc
group by cid;
26.查询出只选修两门课程的学生学号和姓名
mysql> select student.sid,student.sname from student
-> where student.sid in
-> (select sc.sid from sc group by sc.sid
-> having count(sc.cid) = 2);
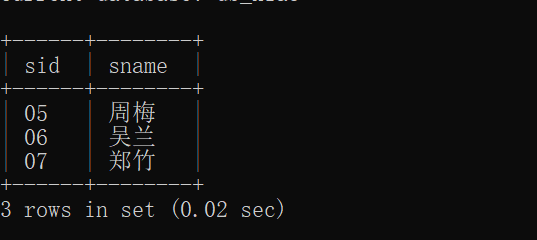
27.查询男生、女生人数
select ssex,count(*) from student group by ssex;
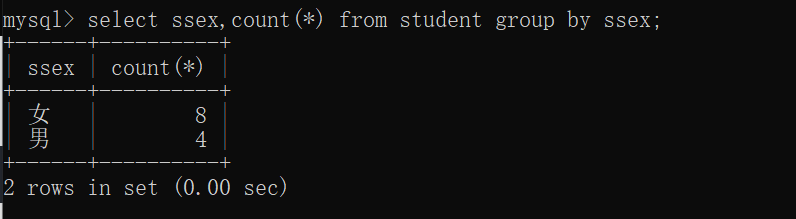
28.查询名字中含有「风」字的学生信息
select * from student where student.sname like "%风%";
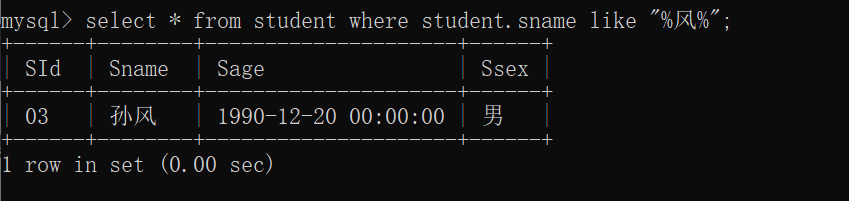
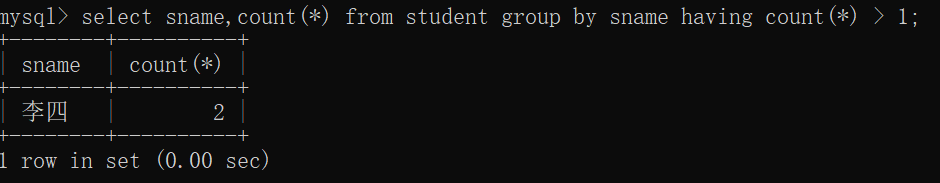
29.查询同名同性学生名单,并统计同名人数
select sname,count(*) from student group by sname having count(*) > 1;
30查询 1990 年出生的学生名单
select * from student where year(student.sage) = 1990;























 2905
2905

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








