前言
在一篇文章中我们对红黑树进行了简单的模拟实现
map和set的底层都是红黑树,而map和set中存储的键不同(map是键值对<K,V>;set是键K),那么如何用一棵红黑树来封装出map和set这两种容器呢?
为适应不同的类型(键/键值对),也就是泛型编程,之前的红黑树是RBTree<class K,class V>,额现在的红黑树RBTree<class K,class T>,当set调用红黑树时这个T会是K,当map调用时T则是pair<K,V>,是不是挺眼熟的(实际上就是之前学的模板)

一、红黑树模板(封装)
1.1参数模板以及红黑树节点修改
事不宜迟,先上代码
红黑树
template<class K,class T>
class RBTreemap
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
private:
RBTree<K,pair<K,V>> _t;
};set
template<class K>
class set
{
private:
RBTree<K, const K> _t;
};_t用红黑树模板类构造的对象,到时候可以调用红黑树里面的内容
既然红黑树的模板参数改了,那么红黑树节点的代码自然也要改
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
Color _col;
T _data;
RBTreeNode(const T& data = T())
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED)
, _data(data)
{}
};节点中存数据的对象相比之前的pair<K,V> _kv改成T _data,其它成员函数中new节点或者调用数据时也要记得修改为 data(data的类型)哦
1.2面对不同类型的比较
既然我们对参数模板修改了,且红黑树又是二叉搜索树(比根小的往左走,比根大的往右走),不同的模板参数要对应不同的比较原则,对于set而言节点之间的比较只需要对比K就行了,那么map其节点之间的比较呢?map里面的pair是如何比较的?
我们不妨看一下库里面是怎么比较的

first小就小,若first相等则second小就小
这明显不符合我们泛型编程的思路,如果按照这种写法,那么每传一次不同的模板参数,都要根据这个模板参数去实现一个新的比较大小的重载函数
我们可以面对不同的调用(比如map和set),对其取出不同的值(map中pair里面的first,set中的K)然后再进行比较,具体的怎么取出不同的值可以在要调用红黑树的类中实现(map和set中)
红黑树
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
//...
}map
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)//取出map中pair的first
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>,MapKeyOfT> _t;
};set
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)//取出set中的key
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};在红黑树的成员函数中所有需要用到比较,或者需要取到所需要的"key"时可以调用对应的方法
可以通过KeyOfT实例化出对象,然后就可以调用所需要的取出"key"的方法,以Find为例吧(比较短)

当然其它的成员函数insert、erase啥的也要
Node* Find(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}二、迭代器的实现
2.1迭代器的定义及其构造函数
跟实现过程跟链表差不多,都是节点封装迭代器
template<class T>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T> Self;
Node* _pNode;
RBTreeIterator(Node* pNode)
: _pNode(pNode)
{}
}2.2解引用操作符*和箭头操作符->的重载
// 让迭代器具有类似指针的行为
T& operator*()
{
return _pNode->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_data;
}2.3重载==和!=
// 让迭代器可以比较
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _pNode != s._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)const
{
return _pNode == s._pNode; ;
}2.4重载++和--
跟链表不同的是++和--,毕竟链表和红黑树的结构不同,往前/后走的方法也就不同
红黑树该怎么往前/后走呢?首先我们要先知道一个点:红黑树中序打印是有序的
中序:左子树、根、右子树
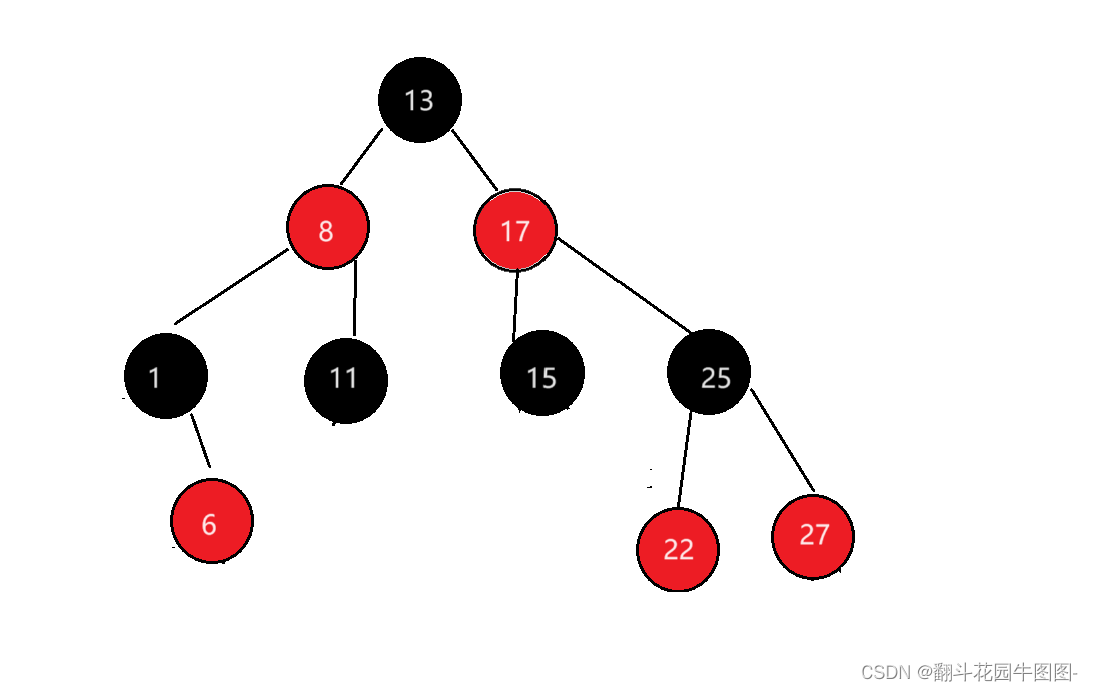
以++为例
假设it是用来遍历的一个节点, it指向的节点右子树不为空,下一个(也就是++后)就是右子树的最左节点
it指向的节点右子树为空,意味着这个节点的子树中序已经访问完了,下一个节点找祖先里面孩子等于父亲左的那个(以上图为例:6的下一个是8;15的下一个是17)
Self& operator++()
{
if (_pNode->_right)//右不为空
{
//右子树的最左节点
Node* subLeft = _pNode->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_pNode = subLeft;
}
else
{
//右为空
//祖先里面孩子是父亲左的那个
Node* cur = _pNode;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent&&cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_pNode = parent;
}
return *this;
}当然--和++类似
如果当前节点(it)的左子树不为空,那么上一个节点(--后)应该找到左子树的最右节点
如果it的左子树为空,则上一个节点应该在祖先节点中孩子等于父亲右的那个
Self& operator--()
{
if (_pNode->_parent==_pNode&&_pNode->_col==RED)//如果是头节点--那返回
{
_pNode = _pNode->_right;
}
else if (_pNode->_left)//左不为空
{
Node* subRight = _pNode->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_pNode = subRight;
}
else//左为空
{
Node* cur = _pNode;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//往上找
while (parent&&cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_pNode = parent;
}
return *this;
}
三、全部代码
myset.h
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace xxx
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_set1()
{
set<int> s;
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
mymap.h
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace xxx
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K,V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
bool insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K,pair<K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_map1()
{
map<int, int> m;
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
for (auto e : a)
{
m.insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}myRBTree.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace xxx
{
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
Color _col;
T _data;
RBTreeNode(const T& data = T())
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED)
, _data(data)
{}
};
//迭代器
template<class T>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T> Self;
Node* _pNode;
RBTreeIterator(Node* pNode)
: _pNode(pNode)
{}
// 让迭代器具有类似指针的行为
T& operator*()
{
return _pNode->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_pNode->_right)//右不为空
{
//右子树的最左节点
Node* subLeft = _pNode->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_pNode = subLeft;
}
else
{
//右为空
//祖先里面孩子是父亲的那个
Node* cur = _pNode;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent&&cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_pNode = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_pNode->_parent==_pNode&&_pNode->_col==RED)//如果是头节点--那返回
{
_pNode = _pNode->_right;
}
else if (_pNode->_left)//左不为空
{
Node* subRight = _pNode->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_pNode = subRight;
}
else//左为空
{
Node* cur = _pNode;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//往上找
while (parent&&cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_pNode = parent;
}
return *this;
}
// 让迭代器可以比较
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _pNode != s._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)const
{
return _pNode == s._pNode; ;
}
};
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef RBTreeIterator<T> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* subLeft = _root;
while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
return iterator(subLeft);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
// 在红黑树中插入值为data的节点,插入成功返回true,否则返回false
// 注意:为了简单起见,本次实现红黑树不存储重复性元素
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点为黑色
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
//找可以插入的节点
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//开始插入
cur = new Node(data);//新增节点为红色
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//判断要不要旋转
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)//父节点在左边,uncle在右边
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情况一:uncle存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//情况二:uncle不存在或存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_left) // g
{ // p u
RotateR(parent); // c
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
//双旋
RotateL(parent); // g
RotateR(grandfather); // p u
cur->_col = BLACK; // c
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
}
}
else//父节点在右边,uncle在左边
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情况一
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//不存在或者存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather); // g
parent->_col = BLACK; //u p
grandfather->_col = RED; // c
}
else
{
RotateR(parent); // g
RotateL(grandfather); // u p
cur->_col = BLACK; // c
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
// 检测红黑树中是否存在值为data的节点,存在返回该节点的地址,否则返回nullptr
Node* Find(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
/*获取红黑树最左侧节点*/
Node* LeftMost()
{
Node* cur = _root;
if (cur == nullptr)
{
return _root;
}
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return cur;
}
// 获取红黑树最右侧节点
Node* RightMost()
{
Node* cur = _root;
if (nullptr == cur)
{
return _root;
}
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
return cur;
}
// 检测红黑树是否为有效的红黑树,注意:其内部主要依靠_IsValidRBTRee函数检测
bool IsValidRBTRee()
{
if (_root && _root->_col == RED)
{
return false;
}
int refBlackNum = 0;//黑节点参考值
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
refBlackNum++;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _IsValidRBTRee(_root, 0, refBlackNum);
}
private:
bool _IsValidRBTRee(Node* cur, size_t blackCount, size_t refBlack)
{
if (cur == nullptr)
{
if (refBlack != blackCount)
{
cout << "黑色节点不相等" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (cur->_col == RED && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "存在连续红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
blackCount++;
return _IsValidRBTRee(cur->_left, blackCount, refBlack)
&& _IsValidRBTRee(cur->_right, blackCount, refBlack);
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
subL->_right = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








