须知:在尖括号中定义你容器里的元素类型 map<string,int> people
使用前提,#include<map>
1.特征
map元素存储在键值对中
Map 映射通常实现为二叉搜索树
2.映射中的元素包括:
- 可通过键(而不是索引)访问,并且每个键都是唯一的。
- 按其键自动按升序排序。
map<keytype, valuetype> mapName,也就是说上面的string是key,int是value。
3.声明时赋值方式;
eg:map<string, int> people = { {"John", 32}, {"Adele", 45}, {"Bo", 29} };
4.访问方式
,无法通过索引访问,需要通过key访问对应的value值,也可以通过.at()来访问
eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Create a map that will store the name and age of different people
map<string, int> people = { {"John", 32}, {"Adele", 45}, {"Bo", 29} };
// Get the value associated with the key "John"
cout << "John is: " << people["John"] << "\n";
// Get the value associated with the key "Adele"
cout << "Adele is: " << people.at("Adele") << "\n";
return 0;
}
运行结果:

更改值
可以people["John"] = value,也可以people.at("John") = value
添加值:
eg:people[key] = value
也可以使用.insert({key,value})
map中不能出现key相同的元素,但是value是可以相等的
5.删除元素
用.erase(),只用删除Key值,全删可以用.clear
eg:.erase("John")
6.查看地图大小
.size()
7.查询是否为空
.empty()
8..count()
还可以使用该函数检查是否存在特定元素。.count(key)
如果元素存在,则返回 (true),如果元素不存在,则返回 (false)
eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> people = { {"John", 32}, {"Adele", 45}, {"Bo", 29} };
cout << people.count("John")<<endl;
cout<< people.count("chen");
return 0;
}
运行结果: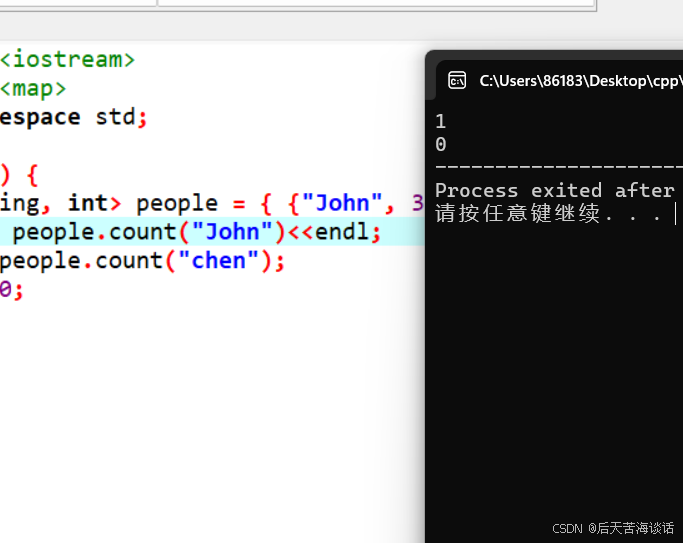
9.遍历map
map不同于前几个(vector,stack,set,queue,list)只储存一种类型的元素,map存储一组元素,可能相同也可能不同,所以遍历方式也不同于其他。我们需要用auto关键字,这个关键字可以自动识别元素的类型,在循环中每次访问需要用.first和.second访问每个元素的key和value。、
eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> people = { {"John", 32}, {"Adele", 45}, {"Bo", 29} };
for (auto pair : people) {
cout << pair.first << " is: " << pair.second << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
输出结果:
通过输出结果我们可以发现,map自动把key给排序了,默认是升序。若想在遍历输出时是按照key的降序输出可以这样定义map<string, int, greater<string>> people = { {"John", 32}, {"Adele", 45}, {"Bo", 29} };
10.swap()函数
将 map 的内容与 map x 的内容交换
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
map<char, int> m1 = {
{'a', 1},
{'b', 2},
{'c', 3},
{'d', 4},
{'e', 5},
};
map<char, int> m2;
m2.swap(m1);
cout << "Map2 contains following elements" << endl;
for (auto it = m2.begin(); it != m2.end(); ++it)
cout << it->first << " = " << it->second << endl;
cout << "Map1 contains following elements" << endl;
for (auto it = m1.begin(); it != m1.end(); ++it)
cout << it->first << " = " << it->second << endl;
cout<<m1.size();
return 0;
}运行结果:

unordered_map
无序映射是像字典一样的数据结构。 它是(键,值)对的序列,其中只有单个值与每个唯一键相关联。 它通常被称为关联数组。它可以根据它们的键快速检索单个元素。 它还实现了直接访问运算符(下标运算符[]),它允许使用其键值作为参数直接访问映射值。他不会按照键的值来进行排序,而是根据其哈希值组织成桶,以允许直接通过键值快速访问各个元素。
在通过键访问单个元素时,无序映射比映射执行得更好。 但是对于范围迭代,它们的性能相当低。
大家根据需求来选取map还是unordered_map
























 1155
1155

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










