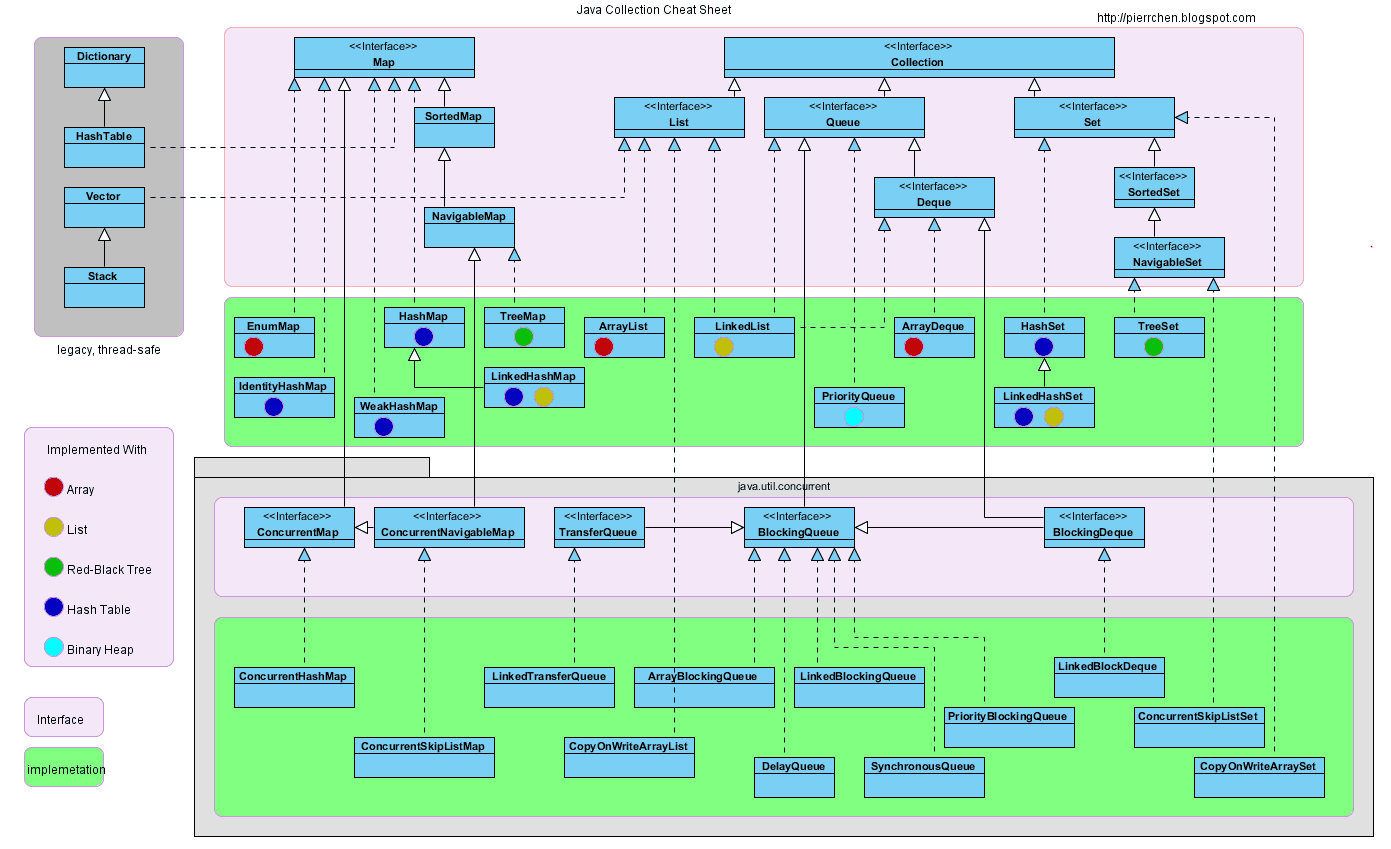
Collection 类关系图
容器,就是可以容纳 Java 对象的容器
优点:
- 降低编程难度
- 提高程序性能
- 提高 API 之间的互操作性
- 降低学习难度
- 降低设计和实现相关 API 的难度
- 增加程序的可复用性
一、Collection
容器主要包括 Collection 和 Map 两种 ,Collection 存储着对象的集合,而 Map 存储着键值对(两个对象)的映射表。
Set
TreeSet
基于红黑树实现,支持有序性操作,例如根据一个范围查找元素的操作。但是查找效率不如 HashSet,HashSet 查找的时间复杂度为 O(1),TreeSet 则为 O(logN)。
HashSet
基于哈希表实现,支持快速查找,但不支持有序性操作。并且失去了元素的插入顺序信息,也就是说使用 Iterator 遍历 HashSet 得到的结果是不确定的。
LinkedHashSet
具有 HashSet 的查找效率,且内部使用双向链表维护元素的插入顺序。
List
ArrayList
基于动态数组实现,支持随机访问。
Vector
和 ArrayList 类似,但它是线程安全的。
LinkedList
基于双向链表实现,只能顺序访问,但是可以快速地在链表中间插入和删除元素。不仅如此,LinkedList 还可以用作栈、队列和双向队列。
Queue
LinkedList
可以用它来实现双向队列。
PriorityQueue
基于堆结构实现,可以用它来实现优先队列。
二、Map
TreeMap
基于红黑树实现。
HashMap
基于哈希表实现。
HashTable
和 HashMap 类似,但它是线程安全的,这意味着同一时刻多个线程可以同时写入 HashTable 并且不会导致数据不一致。它是遗留类,不应该去使用它。现在可以使用 ConcurrentHashMap 来支持线程安全,并且 ConcurrentHashMap 的效率会更高,因为 ConcurrentHashMap 引入了分段锁。
LinkedHashMap
使用双向链表来维护元素的顺序,顺序为插入顺序或者最近最少使用(LRU)顺序。
三、Collection——ArrayList
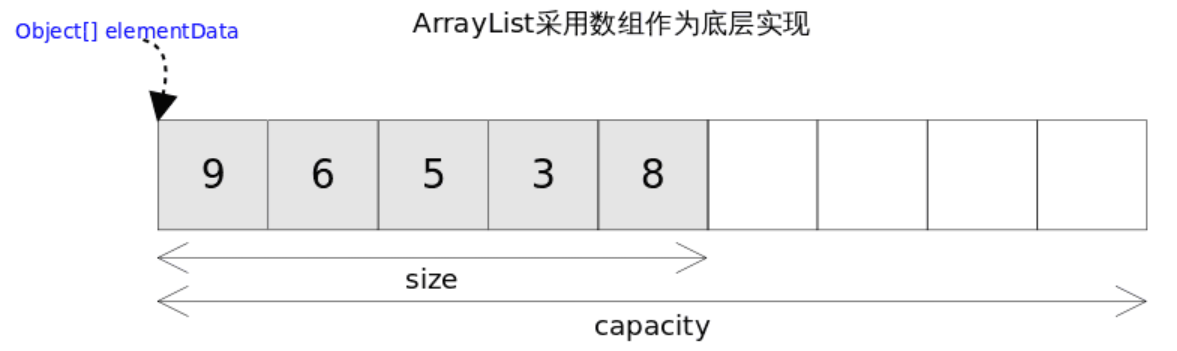
概述
-
实现了list接口、顺序容器
-
元素存放的数据和与放进去的顺序相同
-
允许有 null
-
底层通过数组实现(Object数组)、可以容纳任何类型
-
有一定的 capacity,容量不足的时候会自动扩大底层数组的大小
-
方法
-
- size(), isEmpty(), get(), set()方法均能在常数时间内完成
- add()方法的时间开销跟插入位置有关,addAll()方法的时间开销跟添加元素的个数成正比
- 其余方法大都是线性时间
-
为了实现效率 ArrayList 没有实现同步 synchronized
-
- 如果需要多个线程进行访问,用户可以手动同步,也可以用 Vector 来代替
ArrayList的实现
底层数据结构
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
//关键字表示这个成员变量不会被序列化
//即在对象序列化时,它不会被写入到输出流中。这样做是为了节省空间和提高性能。
/**1
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
构造函数
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
这个构造函数用于创建一个初始容量为10的空列表。
它使用了一个预定义的空Object数组DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA。
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
这个构造函数用于创建一个包含指定集合元素的列表。
它首先将集合转换为一个Object数组,然后检查数组的类型是否为Object[]。
如果不是,它会创建一个新的Object[]数组并复制元素。
如果集合为空,它将使用一个空的Object数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA。
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
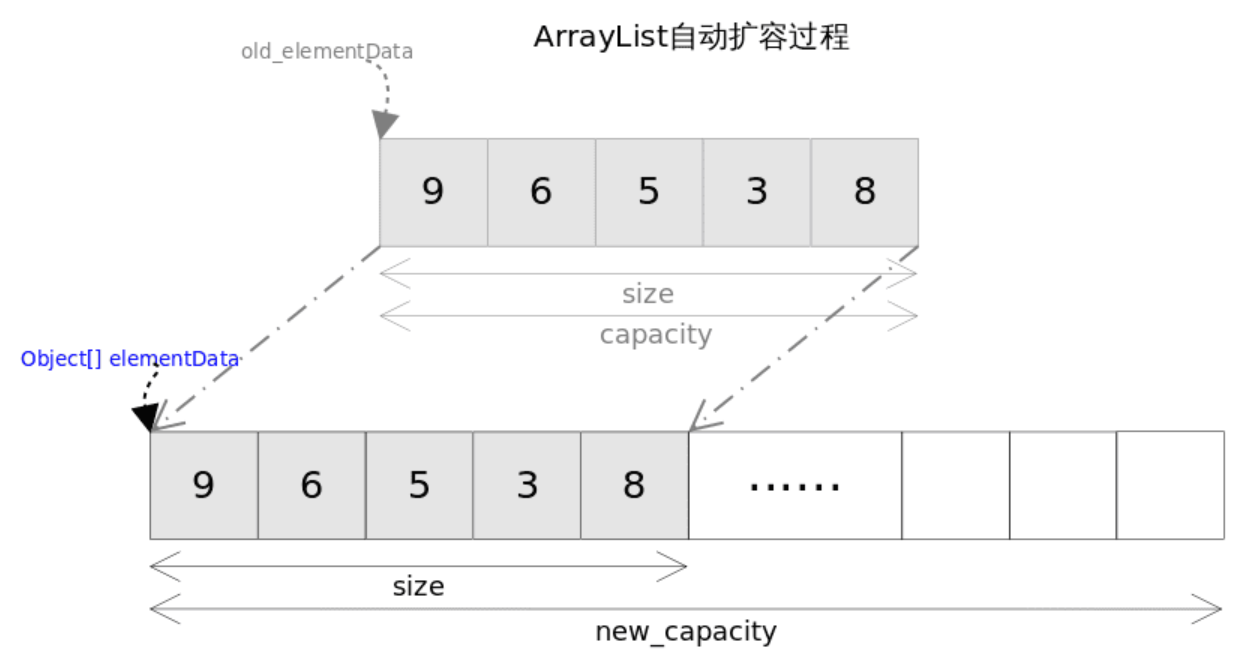
自动扩容
每当向数组中添加元素时,都要去检查添加后元素的个数是否会超出当前数组的长度
如果超出,数组将会进行扩容,以满足添加数据的需求。
数组扩容通过一个公开的方法ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)来实现。
在实际添加大量元素前,我也可以使用ensureCapacity来手动增加ArrayList实例的容量,以减少递增式再分配的数量。
数组进行扩容时,会将老数组中的元素重新拷贝一份到新的数组中,每次数组容量的增长大约是其原容量的1.5倍。
这种操作的代价是很高的,因此在实际使用时,我们应该尽量避免数组容量的扩张。当我们可预知要保存的元素的多少时,要在构造 ArrayList 实例时,就指定其容量,以避免数组扩容的发生。或者根据实际需求,通过调用ensureCapacity 方法来手动增加 ArrayList 实例的容量。
/**
* Increases the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
/**
这个方法首先检查当前数组是否为默认的空数组,如果不是,则将最小扩展容量设置为 0;
如果是,则将其设置为默认容量。然后,如果指定的最小容量大于最小扩展容量
就调用 ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) 方法来确保有足够的空间容纳新的元素。
*/
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// 表示ArrayList结构修改次数的计数器
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
/**
根据当前数组的长度计算新的容量,新容量等于旧容量加上旧容量的一半。
然后,它会检查新容量是否小于所需的最小容量,如果是,则将新容量设置为所需的最小容量。
接下来,它会检查新容量是否超过了最大数组大小
(MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 如果超过了,就调用 hugeCapacity(int minCapacity)方法来确定合适的新容量。
最后,它会使用 Arrays.copyOf() 方法将旧数组的内容复制到新的更大的数组中。
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
/**
用于处理特殊情况,当所需的最小容量超过最大数组大小时,它会抛出一个OutOfMemoryError异常,
或者返回Integer.MAX_VALUE或MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,取决于所需的最小容量是否大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE。
*/
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
add()、addAll()
和 C++ 的 vector 不一样,ArrayList 没有 push_back() 方法,,对应的方法是 add(E e) , ArrayList 也没有insert()方法,对应的方法是 add(int index, E e)。
这两个方法都是向容器中添加新元素,这可能会导致capacity不足,因此在添加元素








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 2033
2033

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








