首先我们要知道,HashMap中是不允许存在两个相同的key的,即相同的键会覆盖值。
那么hashmap是如何判断键是否相同呢?
步骤 1:使用 hashCode() 判断键是否可能相同
步骤 2:使用 equals() 方法进一步判断键是否相同
即hashcode相同且equals返回true,hashmap才会认为是同一个key,进行覆盖。
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Person,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Person p1 = new Person("John", 30);
Person p2 = new Person("John", 30);
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
map.put(p1, 1);
map.put(p2, 2);
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}
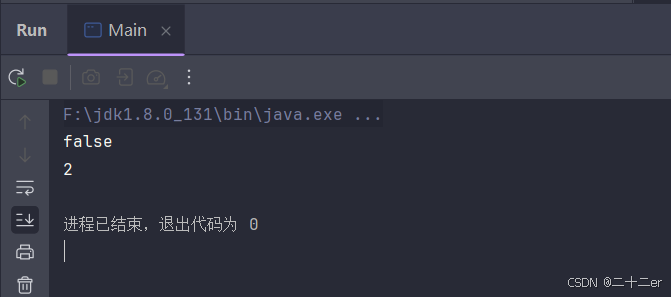
这里我建了一个Person类只写了构造方法,没有重写hashcode和equals方法,显然hashmap没有把两个john当作同一个人
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) obj;
return age == person.age && name.equals(person.name);
}
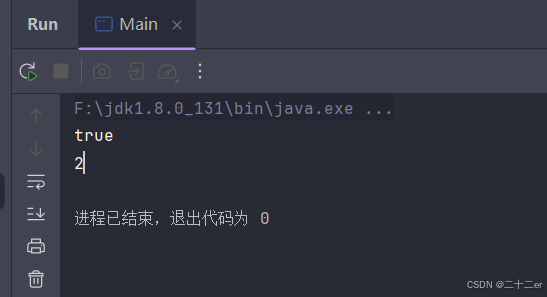
重写equals后,hashmap还是没有把john当作一个人
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) obj;
return age == person.age && name.equals(person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
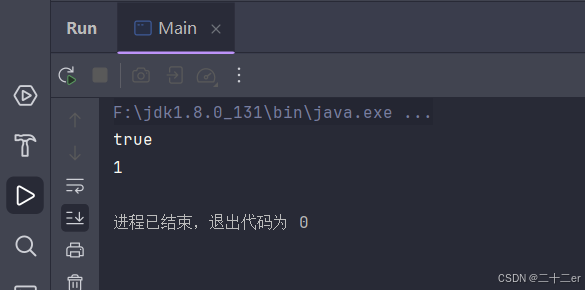
重写了hashcode和equals后,hashmap终于认为john是一个人。
总结:
hashmap首先判断hashcode是否相同,因为存在哈希碰撞的问题,所以还得通过equals来确认是否是同一个key。




















 6668
6668

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








