530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
思路,二叉搜索树是有序的,所以我们可以有序遍历树dfs中序遍历,记录当前节点的值及其前一个节点的值进行比较,我们使用了pre指针和当前指针root指针的技巧
class Solution {
TreeNode pre=null;//记录上一个遍历的节点
int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){return 0;}
dfs(root);
return result;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
//终止条件
if(root==null){return;}
//左
dfs(root.left);
//中
if(pre!=null){
result=Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
}
pre=root;//更新pre节点,,开始的pre节点一定是最底层的左叶子节点
//右
dfs(root.right);
}
}501.二叉搜索树中的众数
思路:二叉树搜索树(BST)是有序的,题目要寻找的众数可能不是唯一的,因此我们需要遍历二叉树把符合要求的数值放入结果列表resList,最后将结果列表转换成数组
遍历BST思路:
中序遍历递归法
1.当前节点root为null,直接return
2.单层递归逻辑:
遍历左子树
处理中间节点逻辑:比较当前节点值和当前节点的前一个节点值是否相等,如果相等计数器count++,同时我们将count与记录最大频数的maxCount比较,确定是否需要更新maxCount
遍历右子树
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> resList;
int maxCount;//记录最大频数
int count;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resList=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root);
//结果数组
int[] res=new int[resList.size()];
for(int i=0;i<resList.size();i++){
res[i]=resList.get(i);//ArrayList get(int index)方法用于从列表中获取元素。我们需要在调用get方法时指定索引,并返回指定索引处的值。
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
//终止条件
if(root==null){return;}
//单层递归逻辑
dfs(root.left);
int rootValue=root.val;
//计数
if(pre==null||rootValue!=pre.val){
count=1;
}
else{count++;}
//更新结果以及maxCount
if(count>maxCount){
resList.clear();//发现更大的频数,需要清空原来的结果列表
resList.add(rootValue);
maxCount=count;
}
else if(count==maxCount){//说明发现了又一个众数,添加到结果集中
resList.add(rootValue);
}
pre=root;
dfs(root.right);//处理右子树
}
}236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 (二刷)
思路
没有任何思路把,只知道应该是递归
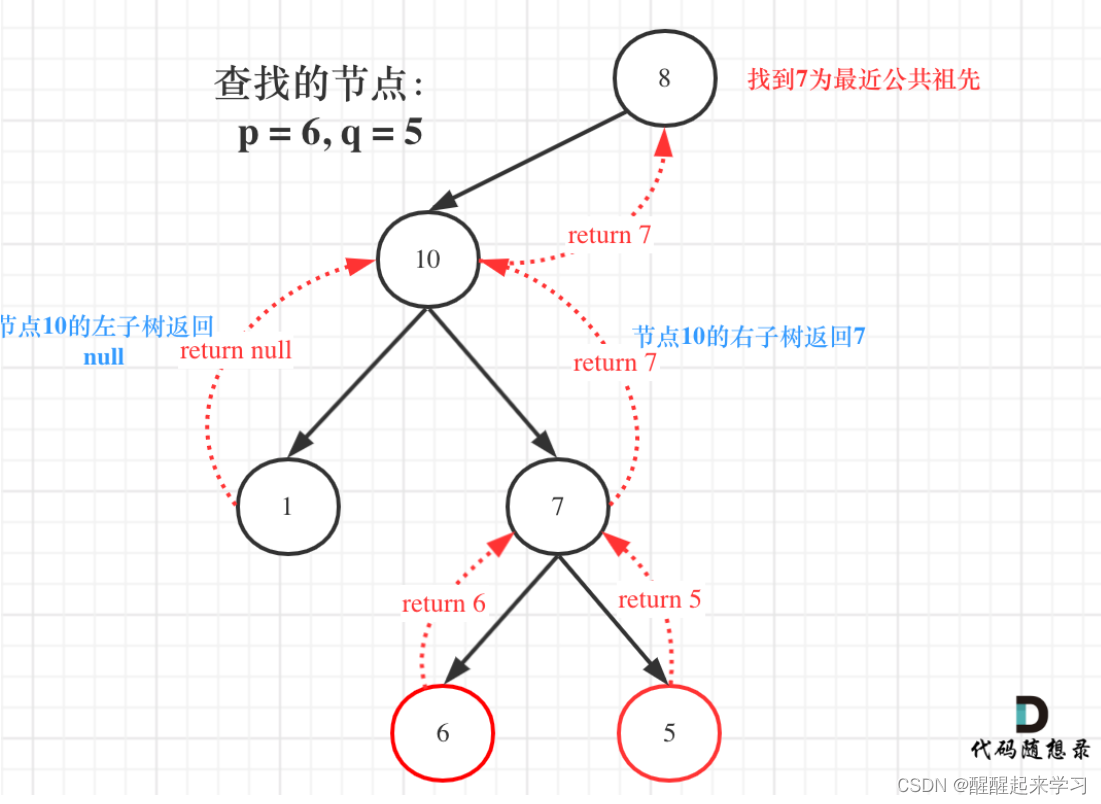
代码实现
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//递归后序遍历
if(root==q||root==p||root==null){return root;}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
//处理中间节点
if(left!=null&&right!=null){return root;}
if(left==null&&right!=null){return right;}
if(left!=null&&right==null){return left;}
else{//left==null和right==null
return null;
}
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








