iptables简介:
iptables是采用数据包过滤机制工作的,所以它会对请求的数据包的包头进行分析,并根据我们预先设定的规则进行匹配来决定是否可以进入主机
iptables 四表五链:
四表对应其功能:
filter:过滤,防火墙;
nat:network address translation;用于修改源IP或目标IP,也可以改端口;
mangle:拆解报文,做出修改,并重新封装起来;
raw:关闭nat表上启用的连接追踪机制;
五链
PREROUTING INPUT FORWARD OUTPUT POSTROUTING
功能<--链
raw:PREROUTING, OUTPUT
mangle:PREROUTING,INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
nat:PREROUTING,[INPUT,]OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
filter:INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT
报文流向:
流入本机:PREROUTING --> INPUT
由本机流出:OUTPUT --> POSTROUTING
转发:PREROUTING --> FORWARD --> POSTROUTING
(这里是我画的一个图,比较难看,希望不要介意。)
这里需要注意:iptables规则是写在内核中,关机则没。后面会说怎么保存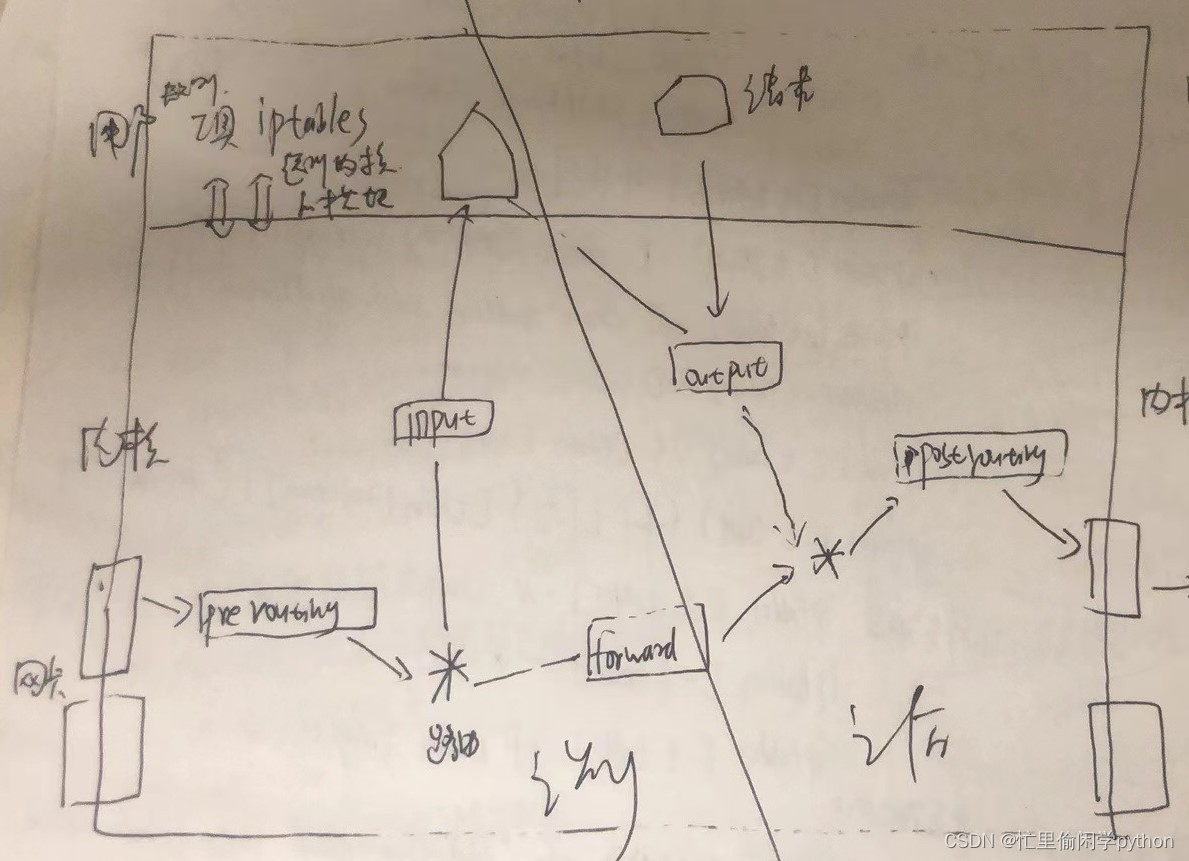
路由功能发生的时刻:
报文进入本机后:
判断目标主机是?
报文离开本机之前:
判断经由哪个接口送往下一站?


iptables的规则及写法:
iptables/netfilter
规则:
组成部分:根据规则匹配条件来尝试匹配报文,一旦匹配成功,就由规则定义的处理动作作出处理;
匹配条件:
基本匹配条件:内建
扩展匹配条件:由扩展模块定义;
处理动作:
基本处理动作:内建
扩展处理动作:由扩展模块定义;
自定义处理机制:自定义链
iptables的链:内置链和自定义链
内置链:对应于hook function
自定义链接:用于内置链的扩展和补充,可实现更灵活的规则管理机制;
添加规则时的考量点:
(1) 要实现哪种功能:判断添加到哪个表上;
(2) 报文流经的路径:判断添加到哪个链上;
链:链上的规则次序,即为检查的次序;因此,隐含一定的应用法则:
(1) 同类规则(访问同一应用),匹配范围小的放上面;
(2) 不同类的规则(访问不同应用),匹配到报文频率较大的放在上面;
(3) 将那些可由一条规则描述的多个规则合并起来;
(4) 设置默认策略;
iptables命令:
高度模块化,由诸多扩展模块实现其检查条件或处理动作的定义;
/usr/lib64/xtables/
IPv6:libip6t_
IPv4:libipt_, libxt_
iptables [-t table] {-A|-C|-D} chain rule-specification
iptables [-t table] -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification
iptables [-t table] -R chain rulenum rule-specification
iptables [-t table] -D chain rulenum
iptables [-t table] -S [chain [rulenum]]
iptables [-t table] {-F|-L|-Z} [chain [rulenum]] [options...]
iptables [-t table] -N chain
iptables [-t table] -X [chain]
iptables [-t table] -P chain target
iptables [-t table] -E old-chain-name new-chain-name
rule-specification = [matches...] [target]
match = -m matchname [per-match-options]
target = -j targetname [per-target-options]
规则格式:iptables [-t table] COMMAND chain [-m matchname [per-match-options]] -j targetname [per-target-options]
-t table:
raw, mangle, nat, [filter]
COMMAND:
链管理:
-N:new, 自定义一条新的规则链;
-X: delete,删除自定义的规则链;
注意:仅能删除 用户自定义的 引用计数为0的 空的 链;
-P:Policy,设置默认策略;对filter表中的链而言,其默认策略有:
ACCEPT:接受
DROP:丢弃
REJECT:拒绝
-E:重命名自定义链;引用计数不为0的自定义链不能够被重命名,也不能被删除;
规则管理:
-A:append,追加;
-I:insert, 插入,要指明位置,省略时表示第一条;
-D:delete,删除;
(1) 指明规则序号;
(2) 指明规则本身;
-R:replace,替换指定链上的指定规则;
-F:flush,清空指定的规则链;
-Z:zero,置零;
iptables的每条规则都有两个计数器:
(1) 匹配到的报文的个数;
(2) 匹配到的所有报文的大小之和;
查看:
-L:list, 列出指定鏈上的所有规则;
-n:numberic,以数字格式显示地址和端口号;
-v:verbose,详细信息;
-vv, -vvv
-x:exactly,显示计数器结果的精确值;
--line-numbers:显示规则的序号;
chain:
PREROUTING,INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
匹配条件:
基本匹配条件:无需加载任何模块,由iptables/netfilter自行提供;
[!] -s, --source address[/mask][,...]:检查报文中的源IP地址是否符合此处指定的地址或范围;
[!] -d, --destination address[/mask][,...]:检查报文中的目标IP地址是否符合此处指定的地址或范围;
所有地址:0.0.0.0/0
[!] -p, --protocol protocol
protocol: tcp, udp, udplite, icmp, icmpv6,esp, ah, sctp, mh or "all"
{tcp|udp|icmp}
[!] -i, --in-interface name:数据报文流入的接口;只能应用于数据报文流入的环节,只能应用于PREROUTING,INPUT和FORWARD链;
[!] -o, --out-interface name:数据报文流出的接口;只能应用于数据报文流出的环节,只能应用于FORWARD、OUTPUT和POSTROUTING链;
处理动作:
-j targetname [per-target-options]
ACCEPT
DROP
REJECT
练习:本机地址172.16.0.67
1、开放本机的所有tcp服务给所有主机;
# iptables -I INPUT -d 172.16.0.67 -p tcp -j ACCEPT
# iptables -I OUTPUT -s 172.16.0.67 -p tcp -j ACCEPT
2、开放本机的所有udp服务给172.16.0.0/16网络中的主机,但不包含172.16.0.200;
# iptables -I INPUT 2 -d 172.16.0.67 -s 172.16.0.200 -p udp -j REJECT
# iptables -I INPUT 3 -d 172.16.0.67 -s 172.16.0.0/16 -p udp -j ACCEPT
# iptables -I OUTPUT 2 -s 172.16.0.67 -d 172.16.0.0/16 -p udp -j ACCEPT
3、默认策略为REJECT;
iptables规则2
iptables [-t table] COMMAND [chain] [PARAMETERS] [-m matchname [per-match-options]] [-j targetname [per-target-options]]
匹配条件:
基本匹配条件:PARAMETERS
扩展匹配条件:
隐式扩展:在使用-p选项指明了特定的协议时,无需再同时使用-m选项指明扩展模块的扩展机制;
显式扩展:必须使用-m选项指明要调用的扩展模块的扩展机制;
隐式扩展:不需要手动加载扩展模块;因为它们是对协议的扩展,所以,但凡使用-p指明了协议,就表示已经指明了要扩展的模块;
tcp:
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文的源端口;可以是端口范围;
[!] --destination-port,--dport port[:port]:匹配报文的目标端口;可以是端口范围;
[!] --tcp-flags mask comp
mask is the flags which we should examine, written as a comma-separated list,例如 SYN,ACK,FIN,RST
comp is a comma-separated list of flags which must be set,例如SYN
例如:“--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN”表示,要检查的标志位为SYN,ACK,FIN,RST四个,其中SYN必须为1,余下的必须为0;
[!] --syn:用于匹配第一次握手,相当于”--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN“;
udp
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文的源端口;可以是端口范围;
[!] --destination-port,--dport port[:port]:匹配报文的目标端口;可以是端口范围;
icmp
[!] --icmp-type {type[/code]|typename}
echo-request:8
echo-reply:0
显式扩展:必须要手动加载扩展模块, [-m matchname [per-match-options]];
显式扩展:必须使用-m选项指明要调用的扩展模块的扩展机制;
1、multiport
This module matches a set of source or destination ports. Up to 15 ports can be specified. A port range (port:port) counts as two ports. It can only be used in conjunction with one of the following protocols: tcp, udp, udplite, dccp and sctp.
以离散或连续的 方式定义多端口匹配条件,最多15个;
[!] --source-ports,--sports port[,port|,port:port]...:指定多个源端口;
[!] --destination-ports,--dports port[,port|,port:port]...:指定多个目标端口;
# iptables -I INPUT -d 172.16.0.7 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80,139,445,3306 -j ACCEPT
2、iprange
以连续地址块的方式来指明多IP地址匹配条件;
[!] --src-range from[-to]
[!] --dst-range from[-to]
# iptables -I INPUT -d 172.16.0.7 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80,139,445,3306 -m iprange --src-range 172.16.0.61-172.16.0.70 -j REJECT
3、time
This matches if the packet arrival time/date is within a given range.
--timestart hh:mm[:ss]
--timestop hh:mm[:ss]
[!] --weekdays day[,day...]
[!] --monthdays day[,day...]
--datestart YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]]
--datestop YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]]
--kerneltz:使用内核配置的时区而非默认的UTC;
4、string
This modules matches a given string by using some pattern matching strategy.
--algo {bm|kmp}
[!] --string pattern
[!] --hex-string pattern
--from offset
--to offset
~]# iptables -I OUTPUT -m string --algo bm --string "gay" -j REJECT
5、connlimit
Allows you to restrict the number of parallel connections to a server per client IP address (or client address block).
--connlimit-upto n
--connlimit-above n
~]# iptables -I INPUT -d 172.16.0.7 -p tcp --syn --dport 22 -m connlimit --connlimit-above 2 -j REJECT
6、limit
This module matches at a limited rate using a token bucket filter.
--limit rate[/second|/minute|/hour|/day]
--limit-burst number
~]# iptables -I OUTPUT -s 172.16.0.7 -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT
限制本机某tcp服务接收新请求的速率:--syn, -m limit
7、state
The "state" extension is a subset of the "conntrack" module. "state" allows access to the connection tracking state for this packet.
[!] --state state
INVALID, ESTABLISHED, NEW, RELATED or UNTRACKED.
NEW: 新连接请求;
ESTABLISHED:已建立的连接;
INVALID:无法识别的连接;
RELATED:相关联的连接,当前连接是一个新请求,但附属于某个已存在的连接;
UNTRACKED:未追踪的连接;
state扩展:
内核模块装载:
nf_conntrack
nf_conntrack_ipv4
手动装载:
nf_conntrack_ftp
追踪到的连接:
/proc/net/nf_conntrack
调整可记录的连接数量最大值:
/proc/sys/net/nf_conntrack_max
超时时长:
/proc/sys/net/netfilter/*timeout*
处理动作(跳转目标):
-j targetname [per-target-options]
简单target:
ACCEPT, DROP
扩展target:
REJECT
This is used to send back an error packet in response to the matched packet: otherwise it is equivalent to DROP so it is a terminating TARGET, ending rule traversal.
--reject-with type
The type given can be icmp-net-unreachable, icmp-host-unreachable, icmp-port-unreachable, icmp-proto-unreach‐ able, icmp-net-prohibited, icmp-host-prohibited, or icmp-admin-prohibited (*), which return the appropriate ICMP error message (icmp-port-unreachable is the default).
LOG
Turn on kernel logging of matching packets.
--log-level
--log-prefix
默认日志保存于/var/log/messages
RETURN:
返回调用者;
自定义链做为target:
保存和载入规则:
保存:iptables-save > /PATH/TO/SOME_RULE_FILE
重载:iptabls-restore < /PATH/FROM/SOME_RULE_FILE
-n, --noflush:不清除原有规则
-t, --test:仅分析生成规则集,但不提交
CentOS 6:
保存规则:
service iptables save
保存规则于/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件,覆盖保存;
重载规则:
service iptables restart
默认重载/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件中的规则
配置文件:/etc/sysconfig/iptables-config
CentOS 7:
(1) 自定义Unit File,进行iptables-restore;
(2) firewalld服务;
(3) 自定义脚本;
规则优化的思路:
使用自定义链管理特定应用的相关规则,模块化管理规则;
(1) 优先放行双方向状态为ESTABLISHED的报文;
(2) 服务于不同类别的功能的规则,匹配到报文可能性更大的放前面;
(3) 服务于同一类别的功能的规则,匹配条件较严格的放在前面;
(4) 设置默认策略:白名单机制
(a) iptables -P,不建议;
(b) 建议在规则的最后定义规则做为默认策略;
























 276
276

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










