1.什么是阻塞队列
阻塞队列是一种特俗的队列,他也满足队列"先进先出"的原则。
阻塞队列还是一种线程安全的数据结构。
阻塞队列有一下几个特征
当队列满时,入队列就会阻塞,直到有其他线程从队列中取走元素。
当队列空时,出队列就会阻塞,直到有其他线程向队列中插入元素。
2.生产者消费者模型
阻塞队列的一大应用就是生产者消费者模型,生产者消费者模型就是通过一个中间媒介来解决生产者消费者之间的强耦合问题。
生产者生产完后不是直接给消费者而是放入阻塞队列中,而消费者也不是找生产者要数据而是从阻塞队列中取元素

不过为什么要有这个阻塞队列呢?
你想想看生产者消费者模型若是没有阻塞队列,生产者中的任务一下来了很多,那也影响不到消费者,因为生产者的任务都被放到阻塞队列中了,而消费者不管任务的多少,还是以一样的速率去工作,从这里就可以体现出阻塞队列的重要性了。
3.标准库中的阻塞队列
在Java的标准库中,也内置了阻塞队列,若在某些场景下需要用到则直接使用标准库中的即可。
BlockingQueue是其接口,LinkedBlockQueue才是类。
put方法为入队列,take方法为出队列。
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
//入队列
queue.put(”abc“);
//出队列
String elem = queue.take();生产者消费者模型
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
Thread customer = new Thread(()->{
while (true){
try {
int value = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费元素"+value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
},"消费者");
customer.start();
Thread producer = new Thread(()->{
Random random = new Random();
while (true){
try {
int num = random.nextInt(1000);
System.out.println("生产元素"+num);
queue.put(num);
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
},"生产者");
producer.start();
customer.join();
producer.join();
}
}4.循环队列实现阻塞队列
import java.util.Random;
public class MyBlockingQueue {
public int[] item = new int[1000];
public volatile int size = 0;
public int head = 0;
public int tail = 0;
public void put(int value) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this){
if(size==item.length){
wait();
}
item[tail] = value;
tail = (tail+1)% item.length;
size++;
notifyAll();
}
}
public int take() throws InterruptedException {
int ret = 0;
synchronized (this){
if(size==0){
wait();
}
ret = item[head];
head = (head+1)%item.length;
size--;
notifyAll();
}
return ret;
}
public synchronized int size(){
return size;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue();
Thread customer = new Thread(()->{
while (true){
try {
int value = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费者"+value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
},"消费者");
customer.start();
Thread producer = new Thread(()->{
Random random = new Random();
while (true){
try {
queue.put(random.nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
},"生产者");
producer.start();
customer.join();
producer.join();
}
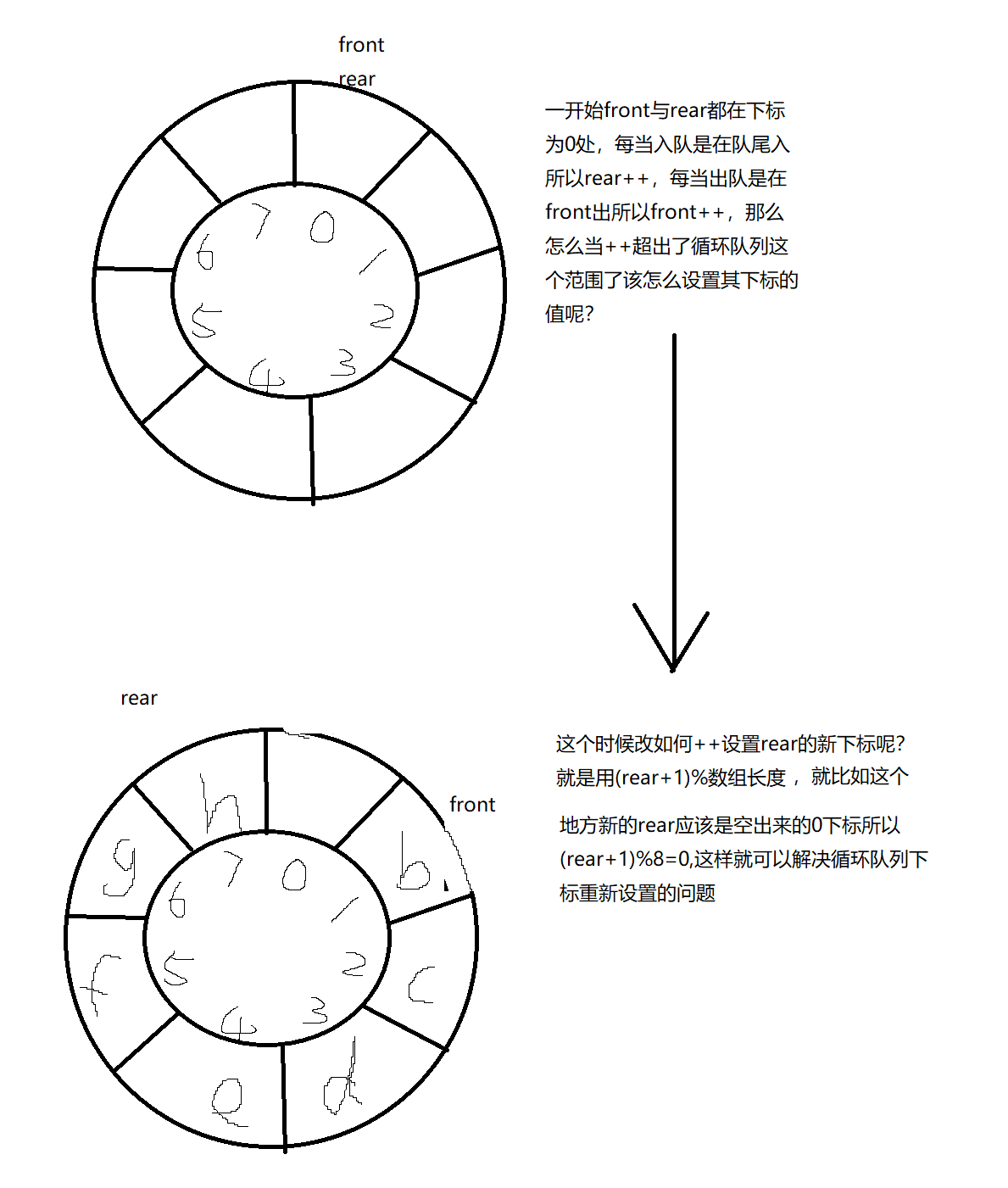
}这里的front与rear下标位置更新使用这个的解释是
tail = (tail+1)% item.length;
head = (head+1)%item.length;








 阻塞队列是一种线程安全的数据结构,遵循FIFO原则,在队列满时入队会阻塞,空时出队会阻塞。它在生产者消费者模型中起到关键作用,允许生产者将任务放入队列,消费者按需取出,降低了两者间的耦合。Java标准库中的BlockingQueue接口及其实现如LinkedBlockingQueue提供了此类功能。示例代码展示了如何使用这些类进行生产和消费操作。
阻塞队列是一种线程安全的数据结构,遵循FIFO原则,在队列满时入队会阻塞,空时出队会阻塞。它在生产者消费者模型中起到关键作用,允许生产者将任务放入队列,消费者按需取出,降低了两者间的耦合。Java标准库中的BlockingQueue接口及其实现如LinkedBlockingQueue提供了此类功能。示例代码展示了如何使用这些类进行生产和消费操作。

















 963
963

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










