学的是黑马程序员JavaWeb全套基础教程,java web从入门到项目实战(IDEA版javaweb)
反射

获取Class对象的方式:
1.Class.forName


2和3
package cn.ljy;
import cn.domain.Person;
public class ljyhs {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.
Class cls=Class.forName("cn.domain.Person");
System.out.println(cls);
// 2.
Class cls2= Person.class;
System.out.println(cls2);
//3.
Person p=new Person();
Class cls3=p.getClass();
System.out.println(cls3);
}
}
输出:

用==去判断它们是否为同一个Class

Class对象功能:

演示:
1.获取成员变量们
1.
注意:
这里只有a 的修饰符为public,所以只有a输出
那我们如何获取a的值呢?
我们可以用如下方法:
因为我们还没给a赋值,所以a的值为0
我们怎么设置a 的值呢/
2.
这个是不看修饰符的,把所有的成员变量输出
这样我们是不是可以对私有成员变量进行赋值呢?
答案的可以的
让我这个南航第一帅来演示一下:
d.setAccessible(true);//设置访问权限
这个是关键,我们没有这个的话会报错
2.获取构造方法们
3
4
JavaWeb课程介绍

数据库的基本概念

JDBC

快速入门:

mysql数据库软件


图形化界面工具sqlyog
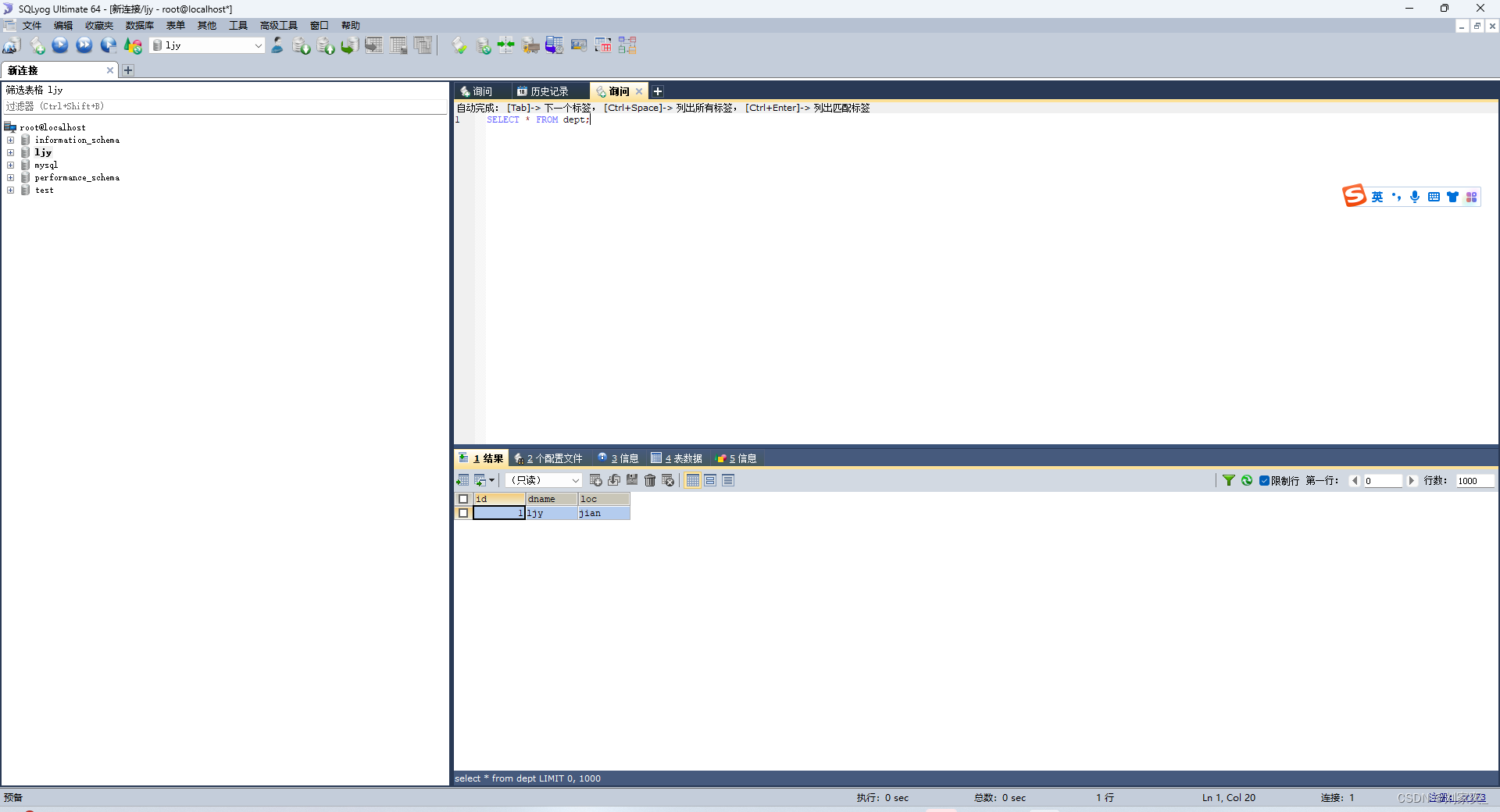
现在我们就可以来学习真正jdbc了
先给一段代码来看看:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ljy","root","root");
String sql="update dept set loc='sc' where id=1";
Statement stmt=conn.createStatement();
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count);
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}数据库的信息被修改了

1.DriverManager



练习:
向dept里添加数据
package org.example;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class text1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
Statement stat=null;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//定义sql
String str="insert into dept values(2,'cxk','bj')";
//获取Connection对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ljy","root","root");
//获取sql的对象Statement
stat=conn.createStatement();
//执行sql
int count = stat.executeUpdate(str);//受影响的句子个数
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(stat!=null){
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}

Resultset :结果集对象,封装查询结果

例如:
package org.example;
import java.sql.*;
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
Statement stat=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//定义sql
String str="select * from dept";
//获取Connection对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ljy","root","root");
//获取sql的对象Statement
stat=conn.createStatement();
//执行sql
rs=stat.executeQuery(str);
//处理结果
rs.next();//移动游标
int id= rs.getInt(1);
String name= rs.getString(2);
String loc= rs.getString("loc");
System.out.println(id+"---------"+name+"---------"+loc);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(stat!=null){
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}

那如果我们要获取整张表的数据的话,我们应该怎么做呢?
我们没法知道有多少条数据,所以直接手动用next() 不太现实,所以这里我们就要想起循环了。
注:![]()
我们可以这样改进代码:
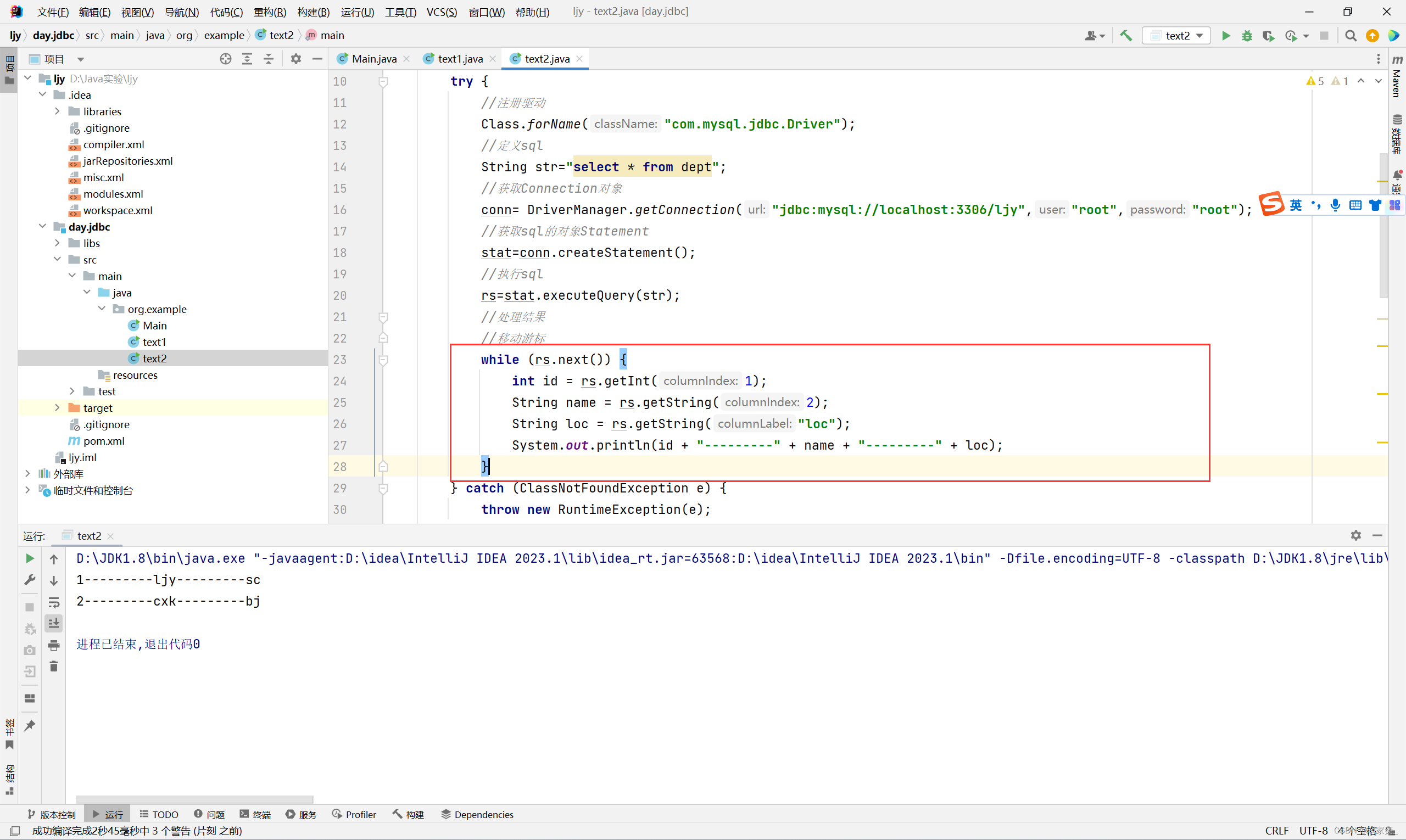
没有问题!!!
例题:

解答如下:
package ljy;
public class domain {
private int id;
private String name;
private String loc;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getLoc() {
return loc;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "domain{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", loc='" + loc + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package org.example;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
import ljy.domain;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<domain> list= new text3().findAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
public List<domain> findAll(){
Connection conn=null;
Statement sta=null;
ResultSet res=null;
List<domain> list=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///ljy","root","root");
String sql="select * from dept";
sta= conn.createStatement();
res=sta.executeQuery(sql);
list=new ArrayList<domain>();
while (res.next()) {
int id = res.getInt(1);
String name = res.getString(2);
String loc = res.getString("loc");
domain d=new domain();
d.setId(id);
d.setLoc(loc);
d.setName(name);
list.add(d);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
{
if(sta!=null){
try {
sta.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(res!=null){
try {
res.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}

jdbc工具类:
为了简化代码,将可以复用的代码封装成一个类:
我们首先写一段这样的代码:
jdbcutils
package jdbcu;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class jdbcutils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;
// 获取连接
//获取静态资源
static {
//加载文件
try {
//读取资源,获取值
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.load(new FileReader("src/jdbc.properties"));
url=pro.getProperty("url");
user =pro.getProperty("user");
password=pro.getProperty("password");
//注册驱动
driver=pro.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName("driver");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
}
public static void close(Statement sta, ResultSet res,Connection conn){
if(sta!=null){
try {
sta.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(res!=null){
try {
res.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
package org.example;
import jdbcu.jdbcutils;
import ljy.domain;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<domain> list= new text3().findAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
public List<domain> findAll(){
Connection conn=null;
Statement sta=null;
ResultSet res=null;
List<domain> list=null;
try {
conn=jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql="select * from dept";
sta= conn.createStatement();
res=sta.executeQuery(sql);
list=new ArrayList<domain>();
while (res.next()) {
int id = res.getInt(1);
String name = res.getString(2);
String loc = res.getString("loc");
domain d=new domain();
d.setId(id);
d.setLoc(loc);
d.setName(name);
list.add(d);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
{
jdbcutils.close(sta,res,conn);
}
}
return list;
}
}
不出意外会报错
所以是路径出现了问题,找不到这个文件

如果用绝对路径是没有问题的。
但是不推荐,因为换一台电脑就没有用了;
所以我们可以用如下的方法:
![]()

ClassLoader classloader=jdbcutils.class.getClassLoader();
URL u=classloader.getResource("jdbc.properties");
String path=u.getPath();
现在我们可以来写一个练习:
登录练习
准备数据 建表之类的
package org.example;
import jdbcu.jdbcutils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class text4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键盘录入
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String user=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password=sc.nextLine();
//调用方法
boolean flag=new text4().login(user,password);
//判断
if(flag){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}
else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
public boolean login(String user,String password){
Connection conn=null;
Statement sta=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
if(user==null || password==null){
return false;
}
//获取连接
try {
conn= jdbcutils.getConnection();
//定义sql
String sql=" select * from user where users='"+user+"' and passwords='"+password+"' ";
//获取执行sql的对象
sta= conn.createStatement();
//执行查询
rs= sta.executeQuery(sql);
return rs.next();//又下一行就说明找到了
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
jdbcutils.close(sta,rs,conn);
}
// return false;
}
}
注意sql的写法:

但实际上开发不会用这些,
会有sql注入的风险。
Sql注入

下面我们来改变一下之前的代码:

完整代码:
package org.example;
import jdbcu.jdbcutils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class text4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键盘录入
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String user=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password=sc.nextLine();
//调用方法
boolean flag=new text4().login(user,password);
//判断
if(flag){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}
else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
public boolean login(String user,String password){
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement psta=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
if(user==null || password==null){
return false;
}
//获取连接
try {
conn= jdbcutils.getConnection();
//定义sql
String sql=" select * from user where users= ? and passwords= ? ";
//获取执行sql的对象
psta= conn.prepareStatement(sql);
psta.setString(1,user);
psta.setString(2,password);
//执行查询
rs= psta.executeQuery();
return rs.next();//又下一行就说明找到了
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
jdbcutils.close(psta,rs,conn);
}
// return false;
}
}
jdbc控制事务:

 我们先写个基础的代码:
我们先写个基础的代码:
package org.example;
import jdbcu.jdbcutils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class text5 {
/*事务操作*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement psta1=null;
PreparedStatement psta2=null;
{
try {
// 获取连接
conn = jdbcutils.getConnection();
// 定义sql
String sql1="update account set money=money-? where id=?";
String sql2="update account set money=money+? where id=?";
// 获取sql对象
psta1=conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
psta1.setInt(1,500);
psta1.setInt(2,1);
psta2=conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
psta2.setInt(1,500);
psta2.setInt(2,2);
psta1.executeUpdate();
psta2.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
jdbcutils.close(psta1,null,conn);
jdbcutils.close(psta2,null,null);
}
}
}
}
执行前:

执行后:

现在我们改动下数据:

插入一条代码:

执行:

ljy少了500
而sh没有变
我们怎么可以避免这种错误发生呢?
我们可以这样改进代码:

package org.example;
import jdbcu.jdbcutils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class text5 {
/*事务操作*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement psta1=null;
PreparedStatement psta2=null;
{
try {
// 获取连接
conn = jdbcutils.getConnection();
// 开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 定义sql
String sql1="update account set money=money-? where id=?";
String sql2="update account set money=money+? where id=?";
// 获取sql对象
psta1=conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
psta1.setInt(1,500);
psta1.setInt(2,1);
psta2=conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
psta2.setInt(1,500);
psta2.setInt(2,2);
psta1.executeUpdate();
int a=3/0;
psta2.executeUpdate();
//提交事务
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚
try {
if(conn!=null)
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
jdbcutils.close(psta1,null,conn);
jdbcutils.close(psta2,null,null);
}
}
}
}
执行:
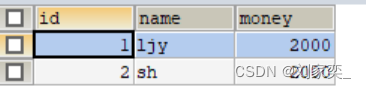
没有变化,成功。
数据库连接池:


基本操作看视频链接https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1qv4y1o79t/?p=104&spm_id_from=pageDriver&vd_source=1bc77496a14dfb26ea6fdea4051246d9








 本文介绍了JavaWeb中的反射机制,包括获取Class对象的三种方式以及其功能,如访问成员变量。接着讲解了JDBC的基础,包括数据库连接、SQL操作、结果集的使用。还涉及到了事务管理,展示了如何在代码中控制事务的提交和回滚,以确保数据一致性。最后提到了数据库连接池的概念。
本文介绍了JavaWeb中的反射机制,包括获取Class对象的三种方式以及其功能,如访问成员变量。接着讲解了JDBC的基础,包括数据库连接、SQL操作、结果集的使用。还涉及到了事务管理,展示了如何在代码中控制事务的提交和回滚,以确保数据一致性。最后提到了数据库连接池的概念。

























 910
910

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










