六.字符串处理
字符串是字符的序列。
在java中将字符串当作对象来处理。

1.String字符串
(1)String:对象创建
要创建类String的一个对象并进行初始化,需要调用类 String的构造方法。
String s = new String( );
String s = new String(“hello”);
char chars[ ] = { ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ };
String s = new String( chars ) ;
char chars[] = { 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' };
String s = new String ( chars , 2 , 3 );
(2)String:基本方法
length()
String s = "abc";
System.out.println( s.length( ) ); //3
charAt()
System.out.println(“China”.charAt(1)); //输出字符h
substring()
String s1="1234567890" ; System.out.println(s1.substring(5)); //67890public String substring(int beginIndex) 或 public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)beginIndex -- 起始索引(包括), 索引从 0 开始。endIndex -- 结束索引(不包括)。
indexOf()
String s1="user@mail.qq.com";
int i = s1.indexOf(‘@’);
System.out.println(s1.substring(i+1);
+
String s = "He is " + age + " years old.";
假设整数型变量age的值为15,那么,s的值为 “He is 15 years old”。
compareTo()
System.out.println(“this”.compareTo(“that”)); 输出为8(unicode码的差值) System.out.println(“this”.compareTo(“this”)); 输出为0 System.out.println(“abc”.comareTo(“abcd”)); 输出为-1(长度的差值)
equals()
System.out.println(“abc”.equals(”abc”)); 输出为true System.out.println(“abc”.equalsIgnoreCase(”ABC”)); 输出为true System.out.println(“abc”.equals(”efg”)); 输出为false
split()
String s = "I will be back!";
String[] results = s.split(" ");
for(String a : results)
System.out.println(a);
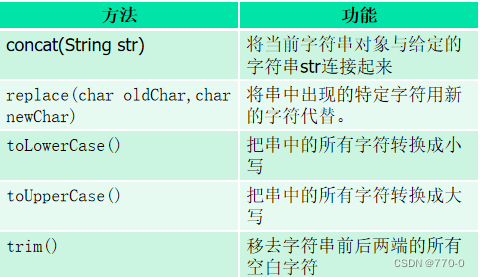
其他方法
2.StringBuffer 字符串

(1)StringBuffer:对象创建
StringBuffer sb1=new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer sb2=new StringBuffer(30);
StringBuffer sb3=new StringBuffer(“StringBuffer”);
(2)StringBuffer:基本方法
除了方法length(),charAt()以外,还有以下几种方法:
Capacity()
append()
insert()
setCharAt()
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“china”);
sb.setCharAt(0,’C’);
System.out.println(sb); 输出China
setLength()
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“china”);
sb.setLength(3);
System.out.println(sb); 输出chi
ensureCapacity()
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“china”);
sb.ensureCapacity(30);
System.out.println(sb.capacity()); 输出44
toString()
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“aabbcc”);
sb.toString();
System.out.println(sb); 输出aabbcc
getChars()
char a[]={‘*’, ‘*’, ‘*’, ‘*’, ‘*’, ‘*’, ‘*’, ‘*’};
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“JAVA”);
sb.getChars(0,4,a,2);
System.out.println(sb); 输出**JAVA**
3.StringTokenizor类

StringTokenizor类的构造方法

StringTokenizor类的常用方法

4.题目
(1)单选题
1.1 有如下程序代码, 程序运行的结果是( )。
String s1 = "sdut";
String s2 = "I love " + s1;
String s3 = "I love " + s1;
System.out.print(s2 == s3);
Sytem.out.println(" "+s2.equals(s3));
A.true false
B.true true
C.false false
D.false true
1.2 关于字符串的构造方法,如下代码执行结果是( )。
String str="ABCDEFG";
char[] chars=str.toCharArray();
System.out.println(new String(chars,1,3));
A.ABC
B.BCD
C.AB
D.BC
1.3 关于字符串的相关使用,如下代码执行结果是( )。
String str1 = "110";
int i=Integer.parseInt(str1,2);
int i1=i+2;
System.out.println(i1);
A.112 *
B.8
C.110
D.10
public static int parseInt(String s,int radix)
将字符串s按照radix进制转换成整数。
1.4 关于字符串的方法,如下代码执行结果是( )。
String str1 = "abcd";
String str2="sdut";
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)>0);
A.true
B.false
C.1
D.-1
1.5 String类的equals方法,其作用是:( )
A.比较2个字符串对象是否为同一个对象
B.比较2个字符串对象的字符长度是否相同
C.比较2个字符串对象的首地址是否相同
D.比较2个字符串对象的字符序列是否相同
1.6 下列关于字符串对象的叙述中,错误的是( )。
A.字符串常量是对象
B.String 对象存储字符串的效率比 StringBuilder 高
C.字符串对象具有不变性
D.String类提供了许多用来操作字符串的方法:连接、提取、查询等,一旦返回的结果与原字符串不同,就生成一个新对象,而不是在原字符串进行修改
1.7 已知: String s="abcdedcba”; 则 s.substring(3,4) 返回的字符串是哪个?( )
A.cd
B.de
C.d
D.dedc
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
beginIndex -- 起始索引(包括), 索引从 0 开始。endIndex -- 结束索引(不包括)。
1.8 关于字符串对象的比较,==用于比较字符串对象的( )是否相同;equals()方法用于比较字符串对象的( )是否相同。
A.存储地址 字符序列
B.存储地址 存储地址
C.字符序列 存储地址
D.字符序列 字符序列
1.9 执行如下两行代码之后,则内存中存在几个字符串对象?( )
String str="abc";
str+="def";
A.1
B.2 *
C.3
D.4
1.10 StringBuffer类维护字符的容量和长度的概念。有该类的对象buf1,其容量与长度的关系是:( )。
A.buf1.capacity()>=buf1.length()
B.buf1.capacity()<=buf1.length()
C.buf1.size()>buf1.=length()
D.buf1.size()<buf1.=length()
1.11 关于StringBuffer对象的操作,有如下程序代码,程序运行的结果是( )。
StringBuffer buf1=new StringBuffer("abcd");
StringBuffer buf2=buf1.append("def");
System.out.print(buf1+" ");
System.out.print(buf2+" ");
System.out.println(buf1==buf2);
A.abcd abcddef false
B.abcddef abcddef true
C.abcd abcddef true
D.abcddef abcddef false
1.12 对String类型的字符串String str="abcd",调用str对象的( )方法,得到char类型的数组['a','b','c','d'] ?
A.toCharArray()
B.toChars()
C.getChars()
D.getBytes()
(2)程序填空题
2.1 实现字符串大小写的转换并倒序输出。
实现字符串大小写的转换并倒序输出。
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine() /;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String s1 = null;
for (int i = str.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char curChar = str.charAt(i) ;
if (curChar >= 'a' && curChar <= 'z')
s1 = String.valueOf(curChar).toUpperCase() ;
else if (curChar >= 'A' && curChar <= 'Z')
s1 = String.valueOf(curChar).toLowerCase() ;
else s1 = String.valueOf(curChar);
sb.append(s1) ;
}
System.out.println( sb.toString() );
}
}
2.2 输入一行字符,统计字符个数
输入一行字符,请分别统计出英文字母、数字、空格和其他字符个数。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
char x[]= str.toCharArray() ;
int a=0;
int b=0;
int c=0;
int d=0;
for(int i=0; i<x.length ;i++){
char ch=x[i];
if( (ch >= 'A' && ch<= 'Z')||(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') )
a++;
else if( ch >='0'&& ch<='9' )
b++;
else if(ch==' ')
c++ ;
else
d++;
}
System.out.println("letters="+a);//输出英文字母个数 System.out.println("digits="+b);//输出数字个数
System.out.println("spaces="+c);//输出空格个数
System.out.println("others="+d);//输出其他字符个数
}
}
2.3 统计一个子串在整串中出现的次数
本程序的功能是统计一个子串在整串中出现的次数,例如子串“nba”在整串“nbaabcdefnbaxyzmba”中出现的次数为2。
import java.util.* ;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner( System.in );
String s, sub; // s为整串,sub为子串
int count = 0; //子串在整串中出现的次数
s = sc.next(); //从键盘输入一个整串
sub = sc.next() ; //从键盘输入一个子串
int i = 0;
while( i<=s.length()-sub.length() ) {
int index = s.indexOf(sub); //sub在s中第一次出现处的索引
if ( index < 0 ) //sub在s中没出现
break;
else { //sub在s中出现了
count++;
s = s.substring(index + sub.length()); //将后面的字符串当作新的整串,方便继续判断
i = 0;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
sc.close();
}
}
(3)编程题
3.1 sdut-String--判定Java源文件名称
输入若干行字符串,判断每行字符串是否可以作为Java的源文件名称。其中:
Java源文件的命名规则:合法的 Java标识符+“.java”;
Java标识符的命名规则:可包含字母、数字、下划线、$,但是数字不能作为首字母。
输入格式:
输入有多行,每行一个字符串。
输出格式:
若该行字符串可做为Java的源文件名称,则输出“true”;否则,输出“false”。
输入样例:
abc.java
_test
$test.java
$12.java
a 1.java
a+b+c.java
a’b.java
123.java
变量.java
Main.java.java
ab abc.java
输出样例:
true
false
true
true
false
false
false
false
true
false
false代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner in = new Scanner ( System.in );
while( in.hasNext() ){
String s = in.nextLine();
String []s1 = s.split("\\.");
boolean t = true;
if( s1.length==2 ){
if( !legal(s1[0]) || !s1[1].equals("java") ){
t = false;
}
}
else
t = false;
System.out.println(t);
}
in.close();
}
public static boolean legal( String str ){
boolean t = true;
if( Character.isJavaIdentifierStart( str.charAt(0) ) ){
for( int i=1; i<str.length(); i++ ){
if( !Character.isJavaIdentifierPart(str.charAt(i))){
t = false;
break;
}
}
}
else
t = false;
return t;
}
}3.2 字符串加密
输入一个原始字符串(长度小于80),然后输入一个5位的数字字符串作为加密密钥,对原始字符串中的每个字符根据其位置(对5取模)变换为加上数字字符串中的数字的字符。如输入原始字符串student,然后输入5位的加密数字12345,因此:
原始字符 加密数字 变换后的字符
s 1 t
t 2 v
u 3 x
d 4 h
e 5 j
n 1 o
t 2 v
加密后的字符串位:tvxhjov
输入格式:
第一个输入一个原始字符串
第二行输入一个5位用来加密的数字字符串
输出格式:
加密后的字符串
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
student
12345
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
tvxhjov
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
Welcome to Java!
10932
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Xeufqne)wq!Jjyc"代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String a =sc.nextLine();
char[] s=a.toCharArray();//读入待加密字符串
StringBuffer ss= new StringBuffer();
String num1=sc.nextLine();//读入加密数字(类型是字符串)
int[] num=new int[num1.length()];//创造一个加密数字数组(9-12行)
for (int i = 0; i < num1.length(); i++) {
num[i]=Integer.parseInt(num1.substring(i, i+1));
}
int k=0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
char aa;
aa=(char)((int)s[i]+num[k]);
ss.append(aa);
k++;
if(k>num.length-1) {
k=0;
}
}
System.out.println(ss.toString());
sc.close();
}
}或
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String []args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
String num = sc.nextLine();
StringBuffer fin = new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++){
int addr = i%5;
fin.append((char)(s.charAt(i)+(num.charAt(addr)-48)));
}
System.out.println(fin);
}
}3.3 群发邮件
作为一个职业HR,要给某个项目组的所有职员群发邮件,已经知道HR有所有人的姓名、电话以及邮箱,请编写程序,取出所有人的邮箱,合并为一个邮箱列表,邮箱之间以“;”隔开,使其可以群发邮件。
输入格式:
在一行中给出所有人的姓名、电话以及邮箱,例如:丽丽/13539870198/lili@qq.com,天梯/13408791122/tiant@qq.com
输出格式:
一行中邮箱列表,以分号隔开。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
丽丽/13539870198/lili@qq.com,天梯/13408791122/tiant@qq.com,楠楠/13112034567/nn@qq.com
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
lili@qq.com;tiant@qq.com;nn@qq.com;代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.next();
String s[]=str.split(",");
String m[];
for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++)
{
String sg[]=s[i].split("/");
System.out.print(sg[2]+";");
}
}
}或
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String []args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
String []a = s.split(",");
for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++){
int j = a[i].lastIndexOf("/");
System.out.print(a[i].substring(j+1)+";");
}
}
}
3.4 通过键盘输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其它字符的个数。
统计一行字符串中的英文字母个数、空格个数、数字个数、其他字符个数
输入格式:
通过键盘输入一行字符(任意字符)
输出格式:
统计一行字符串中的英文字母个数、空格个数、数字个数、其他字符个数
输入样例:
rwrwewre2345asdJSJQI%^&(& *&sdf YY( 2342-k'
输出样例:
字母个数:22
数字个数:8
空格个数:5
其他字符个数:10代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
sc.close();
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int letter=0,num=0,blank=0,other=0;
for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++) {
if((chars[i]>='A' && chars[i]<='Z') || (chars[i]>='a' && chars[i]<='z')){
letter++;
}else if(chars[i]>=47 && chars[i]<=57) {
num++;
}else if(chars[i]==32) {
blank++;
}else {
other++;
}
}
System.out.println("字母个数:"+letter);
System.out.println("数字个数:"+num);
System.out.println("空格个数:"+blank);
System.out.println("其他字符个数:"+other);
}
}3.5 单词替换
设计一个对字符串中的单词查找替换方法,实现对英文字符串中所有待替换单词的查找与替换。
输入格式:
首行输入母字符串,第二行输入查询的单词,第三行输入替换后的单词。
输出格式:
完成查找替换后的完整字符串
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
Although I am without you, I will always be ou you
ou
with
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Although I am without you, I will always be with you代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
String str1 = sc.nextLine();
String str2 = sc.nextLine();
String[] s = str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if (s[i].equals(str1)){
s[i] = str2;
}
}
String s1 = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
s1 += s[i] + " ";
}
System.out.println(s1.trim());
}
}或
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String []args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
String []a = s.split(" ");
String s1 = sc.nextLine();
String s2 = sc.nextLine();
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++){
if(a[i].equals(s1)){
System.out.print(s2);
}
else{
System.out.print(a[i]);
}
if(i == a.length-1)System.out.println();
else System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}



































 6600
6600

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








