目录
1 ReentrantLock
可重入的独占锁,允许同一线程多次获取同一锁而不会被阻塞;功能类似于synchronized,是一种互斥锁
ReentrantLock具备如下特点:
可中断 interrupt()
可以设置超时时间
公平 非公平
支持多个条件变量
与sychronized一样,支持可重入
1.1 常用API

在使用时要注意 4 个问题:
默认情况下 ReentrantLock 为非公平锁而非公平锁
加锁次数和释放锁次数一定要保持一致,否则会导致线程阻塞或程序异常
加锁操作一定要放在 try 代码之前,这样可以避免未加锁成功又释放锁的异常
释放锁一定要放在 finally 中,否则会导致线程阻塞
1.2 公平锁和非公平锁
公平锁:线程在获取锁时,按照等待的先后顺序获取锁
非公平锁:线程在获取锁时,不按照等待的先后顺序获取锁,而是随机获取锁
1.3 可重入锁
可重入锁又名递归锁,锁对象得是同一个对象,不会因为之前已经获取过还没释放而阻塞
1.4 实战
1.4.1 抢票场景
public class ReetrantLockDemo {
private static final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static int tickets = 8; //总票数为8
public static void buyTicks() {
lock.lock();
try {
if (tickets > 0) {
Thread.sleep(20);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "购买了第" + tickets-- + "张票");
} else {
System.out.println("票已经卖完了," + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "抢票失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
ReetrantLockDemo.buyTicks();
}, "线程:" + i);
thread.start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
} 
1.4.2 生产者消费者
public class ReentrantLockDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue(5);
new Thread(new Producer(queue)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(queue)).start();
}
}
class Queue {
private Object[] items;
int size = 0;
int takeIndex;
int putIndex;
private ReentrantLock lock;
public Condition notEmpty;
public Condition notFull;
public Queue(int capacity) {
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock();
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
public void put(Object value) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (size == items.length)
//队列满了让生产者等待
notFull.await();
items[putIndex] = value;
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
size++;
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public Object take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (size == 0)
notEmpty.await();
Object value = items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
size--;
notFull.signal();
return value;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable {
private Queue queue;
public Producer(Queue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue.put(new Random().nextInt());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Queue queue;
public Consumer(Queue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("consumer消费:" + queue.take());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2 Semaphore
用于多线程编程的同步工具,用于控制同时访问某个资源的线程数量
2.1 常用API
acquire() 表示阻塞并获取许可
tryAcquire() 方法在没有许可的情况下会立即返回 false,要获取许可的线程不会阻塞
release() 表示释放许可
2.2 使用
2.2.1 接口限流
public class SemaphoreDemo {
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2);
private static Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static String getProInfo() {
if (!semaphore.tryAcquire()) {
System.out.println("请求被限流");
return "请求被限流了!";
}
//业务代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在执行代码...");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
return "商品信息";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executor.execute(() -> getProInfo());
}
}
}
2.2.2 Semaphore实现数据库连接池
semaphore.acquire():如果拿不到资源则一直阻塞,直到获取
2.3 应用场景总结
限流:限制并发的访问数量
资源池:维护有限的资源
3 CountDownLatch
3.1 常用API
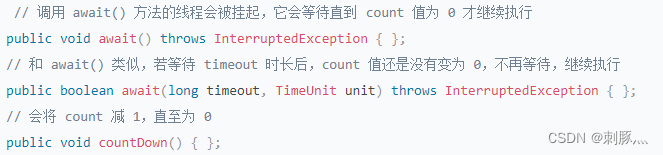
3.2 使用
3.2.1 百米赛跑
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
//裁判
private static CountDownLatch referee = new CountDownLatch(1);
//玩家
private static CountDownLatch player = new CountDownLatch(3);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("参赛者:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经准备好了!");
//等待裁判开哨
referee.await();
System.out.println("参赛者:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始跑步!");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("参赛者:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达终点!");
player.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
//裁判开哨
referee.countDown();
//等待选手跑完
player.await();
System.out.println("比赛结束");
}
}
3.2.2 多任务完成后汇总
3.3 应用场景总结
并行任务同步
多任务汇总
资源初始化
4 CyclicBarrier
让一组线程等待到某一状态之后再全部同时执行,可以被重用


4.1 常用API

4.2 使用
4.2.1 人满发车
public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(5,
() -> System.out.println("人齐了,准备发车"));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int id = i + 1;
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(id + "号马上就到");
int sleepMills = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(2000);
Thread.sleep(sleepMills);
System.out.println(id + "号到了,上车");
cyclicBarrier.await();
}
});
}
}
}
4.2.2 多线程批量处理任务
4.3 应用场景总结
多线程任务
数据处理
5 Exchanger
5.1 使用
5.1.1 模拟交易
public class ExchangerDemo {
private static Exchanger exchanger = new Exchanger();
private static String goods = "电脑";
private static String money = "1000";
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("卖家已经准备好货...");
String money = (String) exchanger.exchange(goods);
System.out.println("卖家已经收到钱:" + money);
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("买家已就位");
String goods = (String)exchanger.exchange(money);
System.out.println("买家收到商品:" + goods);
}
}).start();
}
}
5.1.2 模拟对账
6 Phaser

6.1 常用API

6.2 使用
6.3 应用场景总结
多线程任务分配
多级任务流程
模拟并行计算
阶段性任务


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








