目录
摘要
本文探讨了传统循环神经网络(RNN)的局限性,包括在处理长序列数据时容易忽略远距离依赖信息,以及在训练过程中可能遇到的梯度消失或梯度爆炸问题。为了解决这些问题,文章介绍了一种改进的RNN模型——长短期记忆网络(LSTM),旨在提高模型对长序列数据的处理能力。文中详细阐述了LSTM的核心思想并对其结构和工作流程做了详细介绍。
Abstract
This article explores the limitations of traditional Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), including their propensity to overlook long-range dependency information when processing long sequence data, as well as the potential issues of vanishing or exploding gradients encountered during training. To address these challenges, the article introduces an improved RNN model—Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs)—that aims to enhance the model's capability to handle long sequence data. The article provides a detailed explanation of the core concepts of LSTMs and offers an in-depth introduction to their structure and workflow.
1. 普通RNN的缺点
对于序列任务,RNN解决了普通神经网络不能共享各个时间步学习到的特征的问题,使每个时间步的输出不仅与当前的输入有关,还与其他时间步的输出信息有关,但普通的RNN在共享信息是也存在问题。

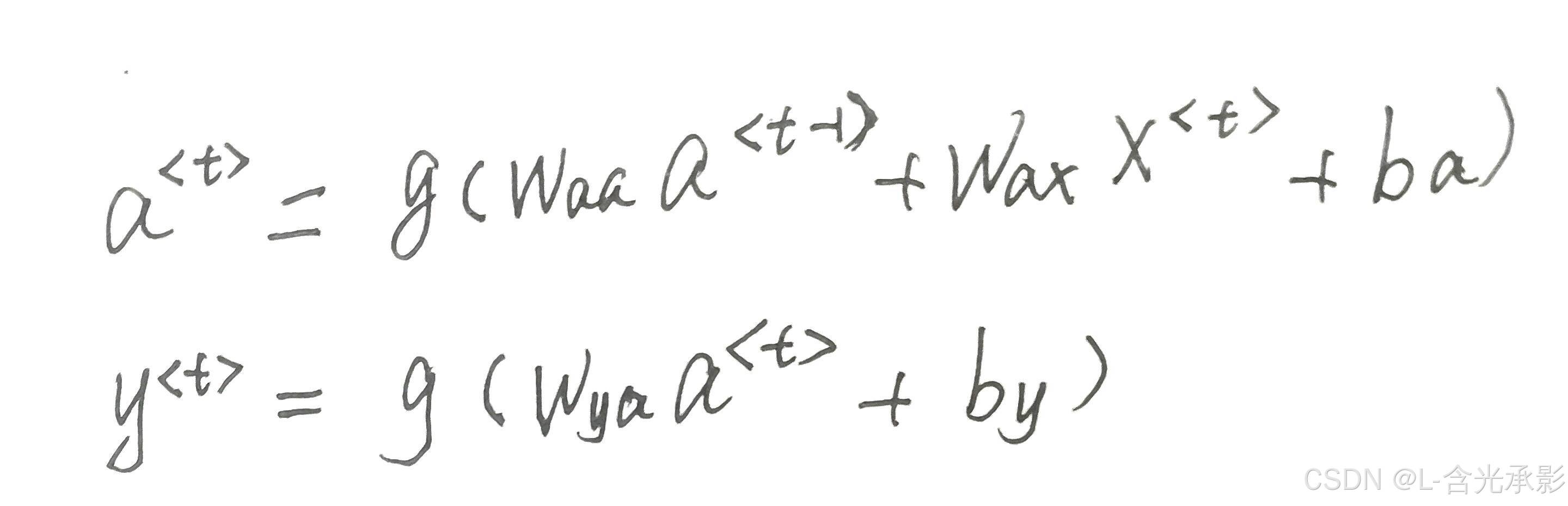
由当前时间步的计算方法可以看出,当考虑到的时间步离当前时间部越远,则它对当前时间步的影响就越小,但实际上距离当前时间步较远的时间步的信息可能也对当前的输出有较大的影响。

因为普通RNN的信息传递是逐层传递的,距离越远,其信息丢失越多,对于距离越远的时间步的输出的影响越小。
举一个例子,预测下面两句英文的下划线处应该是什么单词。








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








