包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换(jdk1.5前)
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器(通过查询API)
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 .valueOf()
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
①使用对应包装类提供的 xxxValue() 方法。 xxx:代表基本的数据类型
2、自动装箱和自动拆箱(jdk1.5后)3、包装类的缓存
Integer 为我们提供了一个小的缓存吗,该缓存的取值范围为(-128~127之间),若需要装箱的值在该范围内,
则从缓存中取一个实例,若超出该取值范围,则重新new 一个Integer 的实例
(除了float、double 都有缓存)
4、基本数据类型、包装类与String之间的转换
1)基本数据类型、包装类转String
①String str=a+""; 任何基本数据类与String使用连接符‘+’都将自动串接为String 这里是空的字符串
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 toString()
③使用String类的静态方法 valueOf()
2)String 转 基本数据类型、包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 parseXxx() Xxx:表示基本数据类型。注意:没有parseChar()方法 因为字符串就是有字符组成
③使用对应包装类的静态方法 valueOf()
Interger类

package API.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
* */
public class WrapperTest {
@Test
public void test(){
int a=10;
Integer num= new Integer(a);//装箱
System.out.println(num);
}
}
integer重写了object类中的tostring方法


package API.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
* */
public class WrapperTest {
@Test
public void test(){
int a=10;
Integer num= new Integer(a);//装箱
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(a));
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a));
}
}

float:
package API.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器(通过查询API)
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
* */
public class WrapperTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
int a=10;
Integer num= new Integer(a);//装箱
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(a));
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a));
}
@Test
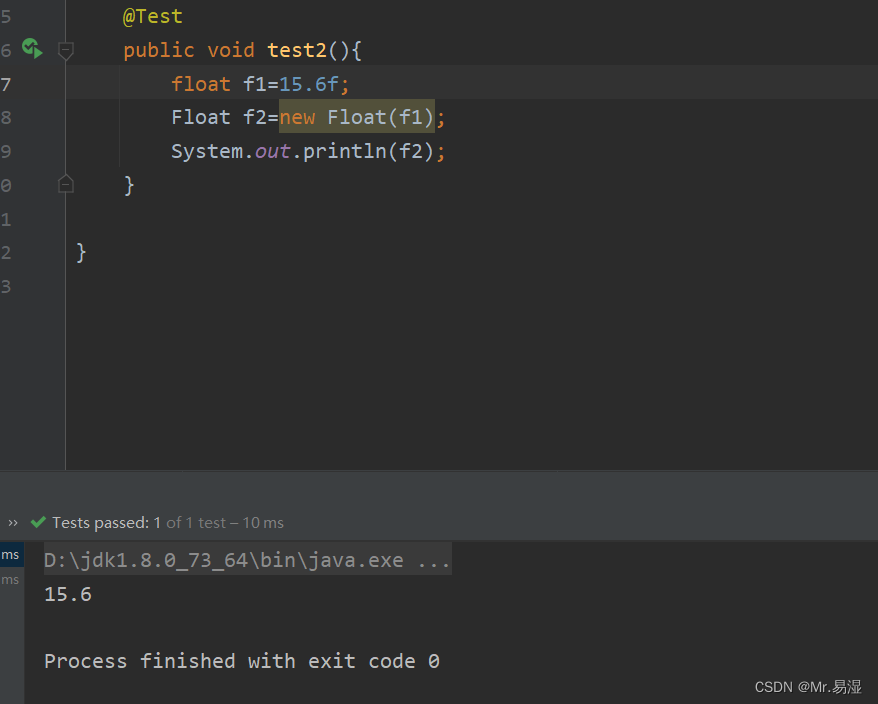
public void test2(){
float f1=15.6f;
Float f2=new Float(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
boolean a=true;
Boolean b=new Boolean(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}


package API.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器(通过查询API)
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 .valueOf()
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
* */
public class WrapperTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
int a=10;
// Integer num= new Integer(a);//装箱
// System.out.println(num);
// System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
// System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
// System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(a));
// System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a));
Integer num=Integer.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(num);
double d1=22.22;
Double d2=Double.valueOf(d1);
System.out.println(d2);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
float f1=15.6f;
Float f2=new Float(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
boolean a=true;
Boolean b=new Boolean(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
拆箱:




package API.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器(通过查询API)
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 .valueOf()
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
①使用对应包装类提供的 xxxValue() 方法。 xxx:代表基本的数据类型
* */
public class WrapperTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
int a=10;
// Integer num= new Integer(a);//装箱
// System.out.println(num);
// System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
// System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
// System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(a));
// System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a));
Integer num=Integer.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(num);
double d1=22.22;
Double d2=Double.valueOf(d1);
System.out.println(d2);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
float f1=15.6f;
Float f2=new Float(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
boolean a=true;
Boolean b=new Boolean(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
@Test
public void test4(){
Integer num=new Integer(10);//装箱
int i=num.intValue();//拆箱
System.out.println(i);
Character character=new Character('A');
char ch=character.charValue();
System.out.println(ch);
}
}
自动装箱与自动拆箱:

3、包装类的缓存 Integer 为我们提供了一个小的缓存吗,该缓存的取值范围为(-128~127之间),若需要装箱的值在该范围内, 则从缓存中取一个实例,若超出该取值范围,则重新new 一个Integer 的实例 (除了float、double 都有缓存)


4、基本数据类型、包装类与String之间的转换 1)基本数据类型、包装类转String String str=a+""; 任何基本数据类与String使用连接符‘+’都将自动串接为String 这里是空的字符串

另法:
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 toString()


③使用String类的静态方法 valueOf()


2)String 转 基本数据类型、包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器



②使用对应包装类的静态方法 parseXxx() Xxx:表示基本数据类型。注意:没有parseChar()方法 因为字符串就是有字符组成
![]()
③使用对应包装类的静态方法 valueOf()


本文全部代码:
package API.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
包装类(包裹类Wrapper):
java针对八种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
1、基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换(jdk1.5前)
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成对应的包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器(通过查询API)
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 .valueOf()
拆箱:将包装类转换成对应的基本数据类型
①使用对应包装类提供的 xxxValue() 方法。 xxx:代表基本的数据类型
2、自动装箱和自动拆箱(jdk1.5后)
3、包装类的缓存
Integer 为我们提供了一个小的缓存吗,该缓存的取值范围为(-128~127之间),若需要装箱的值在该范围内,
则从缓存中取一个实例,若超出该取值范围,则重新new 一个Integer 的实例
(除了float、double 都有缓存)
4、基本数据类型、包装类与String之间的转换
1)基本数据类型、包装类转String
①String str=a+""; 任何基本数据类与String使用连接符‘+’都将自动串接为String 这里是空的字符串
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 toString()
③使用String类的静态方法 valueOf()
2)String 转 基本数据类型、包装类
①使用对应包装类的构造器
②使用对应包装类的静态方法 parseXxx() Xxx:表示基本数据类型。注意:没有parseChar()方法 因为字符串就是有字符组成
③使用对应包装类的静态方法 valueOf()
* */
public class WrapperTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
int a=10;
// Integer num= new Integer(a);//装箱
// System.out.println(num);
// System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
// System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
// System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(a));
// System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a));
Integer num=Integer.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(num);
double d1=22.22;
Double d2=Double.valueOf(d1);
System.out.println(d2);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
float f1=15.6f;
Float f2=new Float(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
boolean a=true;
Boolean b=new Boolean(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
@Test
public void test4(){
Integer num=new Integer(10);//装箱
int i=num.intValue();//拆箱
System.out.println(i);
Character character=new Character('A');
char ch=character.charValue();
System.out.println(ch);
}
//自动装箱和自动拆箱
@Test
public void test5(){
Integer num=100;//自动装箱
int a=num;//自动拆箱
}
//Integer 为我们提供了一个小的缓存吗,该缓存的取值范围为(-128~127之间),若需要装箱的值在该范围内,
//则从缓存中取一个实例,若超出该取值范围,则重新new 一个Integer 的实例
@Test
public void test6(){
Integer num1=100;
Integer num2=100;
System.out.println(num1==num2);//True
Integer num3=150;
Integer num4=150;
System.out.println(num3==num4);//Flase
}
//1)基本数据类型、包装类转String
@Test
public void test(){
//①任何基本数据类与String使用连接符‘+’都将自动串接为String
int a=10;
String str=a+"";
System.out.println(str);
//②使用对应包装类的静态方法 toString()
String str1= Integer.toString(a);
System.out.println(str1);
float f1=15.6f;
String str2=Float.toString(f1);
System.out.println(str2);
}
//③使用String类的静态方法 valueOf()
@Test
public void test8(){
int a=10;
String str=String.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(str);
}
//2)String 转 基本数据类型、包装类
//①使用对应包装类的构造器
@Test
public void test9(){
String str="123";
Integer num=new Integer(str);
System.out.println(num);
String str1="false";
Boolean b=new Boolean(str1);//转换时,除了true,其余都为false
System.out.println(b);
}
//②使用对应包装类的静态方法 parseXxx() Xxx:表示基本数据类型。注意:没有parseChar()方法 因为字符串就是有字符组成
@Test
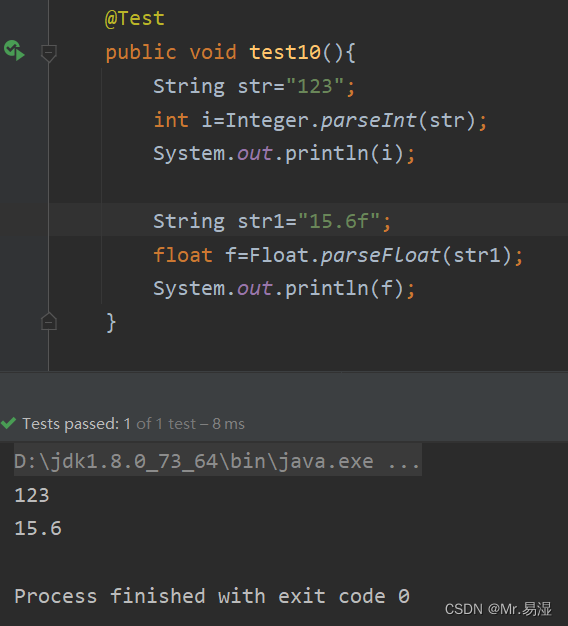
public void test10(){
String str="123";
int i=Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(i);
String str1="15.6f";
float f=Float.parseFloat(str1);
System.out.println(f);
}
//③使用对应包装类的静态方法 valueOf()
@Test
public void test11(){
String str="123";
Integer num =Integer.valueOf(str);
System.out.println(num);
String str1="15.6";
Double d= Double.valueOf(str1);
System.out.println(d);
}
}



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








