二叉树高度计算方法
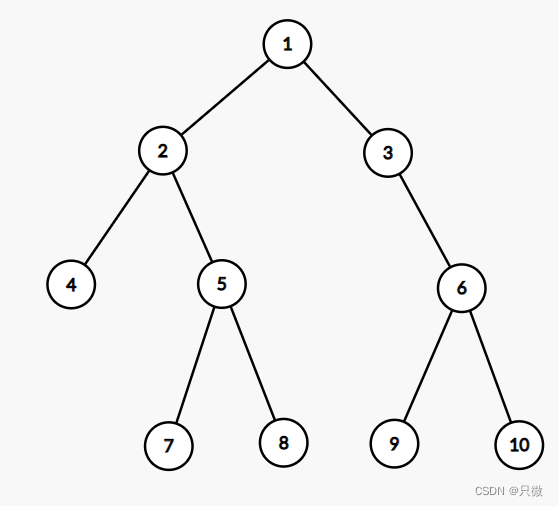
二叉树的高度-递归法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct treeNode {
int a; // 数据成员
struct treeNode *pFather; // 父节点
struct treeNode *pLeft; // 左孩子
struct treeNode *pRight; // 右孩子
};
/**
* 得到一棵树有多少层
* 二叉树的高度
*递归思想 每一个分支都走到叶子节点 看看此时左右子树谁的层更深
* */
int count(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return 0; // 树为空
}
int left = count(root->pLeft);
int right = count(root->pRight);
if (left > right) return left + 1;
else return right + 1;
}
int main() {
struct treeNode t1 = { 1 };
struct treeNode t2 = { 2 };
struct treeNode t3 = { 3 };
struct treeNode t4 = { 4 };
struct treeNode t5 = { 5 };
struct treeNode t6 = { 6 };
struct treeNode t7 = { 7 };
struct treeNode t8 = { 8 };
struct treeNode t9 = { 9 };
struct treeNode t10 = { 10 };
// 链接
t1.pLeft = &t2;
t1.pRight = &t3;
t1.pFather = NULL;
t2.pLeft = &t4;
t2.pRight = &t5;
t2.pFather = &t1;
t3.pRight = &t6;
t3.pLeft = NULL;
t3.pFather = &t1;
t4.pLeft = NULL;
t4.pRight = NULL;
t4.pFather = &t2;
t5.pLeft = &t7;
t5.pRight = &t8;
t5.pFather = &t2;
t6.pLeft = &t9;
t6.pRight = &t10;
t6.pFather = &t3;
t7.pLeft = NULL;
t7.pRight = NULL;
t7.pFather = &t5;
t8.pLeft = NULL;
t8.pRight = NULL;
t8.pFather = &t5;
t9.pLeft = NULL;
t9.pRight = NULL;
t9.pFather = &t6;
t10.pLeft = NULL;
t10.pRight = NULL;
t10.pFather = &t6;
printf("%d\n", count(&t1));
return 0;
}
叶子反根法递归代码
- 非递归思路:叶子节点的特点是左右节点都是NULL,找到叶子节点,通过叶子节点的pFaher指针向上找
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
struct treeNode {
int a; // 数据成员
struct treeNode *pFather; // 父节点
struct treeNode *pLeft; // 左孩子
struct treeNode *pRight; // 右孩子
};
// 链表结构的栈 尾添加尾删除 双向带空头链表
// 栈节点
struct stack {
struct treeNode *node; // 指向树的节点
struct stack *pre; // 指向前一个节点
struct stack *next; // 指向下一个节点
};
struct stack head; // 空头
struct stack *stacktop = &head; // 栈顶指针
// 入栈 链表尾添加
void push(struct treeNode *node) {
// 申请节点 并且成员赋值
struct stack *temp = (struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if (NULL == temp) {
return ;
}
// 赋初值
temp->pre = NULL;
temp->next = NULL;
temp->node = node;
// 尾巴连接
stacktop->next = temp;
temp->pre = stacktop;
// 栈顶指针后移
stacktop = stacktop->next;
}
// 出栈 双向链表尾删除
struct treeNode *pop(void) {
if (stacktop == &head) {
// 栈空
return NULL;
}
struct treeNode *temp = stacktop->node; // 得到栈顶的树节点
stacktop = stacktop->pre; // 节点前移
free(stacktop->next); // 释放节点
stacktop->next = NULL; // 新尾指针指向空
return temp;
}
/**
* 得到一棵树有多少层
* 二叉树的高度
*递归思想 每一个分支都走到叶子节点 看看此时左右子树谁的层更深
* */
int count(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return 0; // 树为空
}
int left = count(root->pLeft);
int right = count(root->pRight);
if (left > right) return left + 1;
else return right + 1;
}
// 思路类似于前序遍历的 非递归
int Look(struct treeNode *root) {
struct treeNode *t = root;
int max = 0; // 记录最大层
while (1) {
// 左子树入栈并输出
while (t != NULL) {
push(t); // 入栈
t = t->pLeft;
}
if (stacktop == &head) // 栈里面什么都没有
break;
t = pop(); // 出栈
if (NULL == t->pLeft && NULL == t->pLeft) {
// 判断是否是叶子节点
int ce = 0;
struct treeNode *reaf = t;
while (reaf) {
// 向上遍历找到root
ce++;
reaf = reaf->pFather;
}
if (ce > max) {
max = ce;
}
}
t = t->pRight;
}
return max;
}
int max_ce = 0;
void Look2(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return;
}
Look2(root->pLeft); // 左子树入栈
if (NULL == root->pLeft && NULL == root->pRight) {
int cen = 0;
struct treeNode *reaf = root;
while(reaf != NULL) {
cen++;
reaf = reaf->pFather;
}
if (cen > max_ce) {
max_ce = cen;
}
}
Look2(root->pRight); // 右子树入栈
}
int main() {
struct treeNode t1 = { 1 };
struct treeNode t2 = { 2 };
struct treeNode t3 = { 3 };
struct treeNode t4 = { 4 };
struct treeNode t5 = { 5 };
struct treeNode t6 = { 6 };
struct treeNode t7 = { 7 };
struct treeNode t8 = { 8 };
struct treeNode t9 = { 9 };
struct treeNode t10 = { 10 };
// 链接
t1.pLeft = &t2;
t1.pRight = &t3;
t1.pFather = NULL;
t2.pLeft = &t4;
t2.pRight = &t5;
t2.pFather = &t1;
t3.pRight = &t6;
t3.pLeft = NULL;
t3.pFather = &t1;
t4.pLeft = NULL;
t4.pRight = NULL;
t4.pFather = &t2;
t5.pLeft = &t7;
t5.pRight = &t8;
t5.pFather = &t2;
t6.pLeft = &t9;
t6.pRight = &t10;
t6.pFather = &t3;
t7.pLeft = NULL;
t7.pRight = NULL;
t7.pFather = &t5;
t8.pLeft = NULL;
t8.pRight = NULL;
t8.pFather = &t5;
t9.pLeft = NULL;
t9.pRight = NULL;
t9.pFather = &t6;
t10.pLeft = NULL;
t10.pRight = NULL;
t10.pFather = &t6;
printf("%d\n", count(&t1));
Look2(&t1);
printf("叶子反根递归:%d\n", max_ce);
printf("叶子反根非递归:%d\n", Look(&t1));
return 0;
}
叶子反根法非递归代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
struct treeNode {
int a; // 数据成员
struct treeNode *pFather; // 父节点
struct treeNode *pLeft; // 左孩子
struct treeNode *pRight; // 右孩子
};
// 链表结构的栈 尾添加尾删除 双向带空头链表
// 栈节点
struct stack {
struct treeNode *node; // 指向树的节点
struct stack *pre; // 指向前一个节点
struct stack *next; // 指向下一个节点
};
struct stack head; // 空头
struct stack *stacktop = &head; // 栈顶指针
// 入栈 链表尾添加
void push(struct treeNode *node) {
// 申请节点 并且成员赋值
struct stack *temp = (struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if (NULL == temp) {
return ;
}
// 赋初值
temp->pre = NULL;
temp->next = NULL;
temp->node = node;
// 尾巴连接
stacktop->next = temp;
temp->pre = stacktop;
// 栈顶指针后移
stacktop = stacktop->next;
}
// 出栈 双向链表尾删除
struct treeNode *pop(void) {
if (stacktop == &head) {
// 栈空
return NULL;
}
struct treeNode *temp = stacktop->node; // 得到栈顶的树节点
stacktop = stacktop->pre; // 节点前移
free(stacktop->next); // 释放节点
stacktop->next = NULL; // 新尾指针指向空
return temp;
}
/**
* 得到一棵树有多少层
* 二叉树的高度
*递归思想 每一个分支都走到叶子节点 看看此时左右子树谁的层更深
* */
int count(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return 0; // 树为空
}
int left = count(root->pLeft);
int right = count(root->pRight);
if (left > right) return left + 1;
else return right + 1;
}
// 思路类似于前序遍历的 非递归
int Look(struct treeNode *root) {
struct treeNode *t = root;
int max = 0; // 记录最大层
while (1) {
// 左子树入栈并输出
while (t != NULL) {
push(t); // 入栈
t = t->pLeft;
}
if (stacktop == &head) // 栈里面什么都没有
break;
t = pop(); // 出栈
if (NULL == t->pLeft && NULL == t->pLeft) {
// 判断是否是叶子节点
int ce = 0;
struct treeNode *reaf = t;
while (reaf) {
// 向上遍历找到root
ce++;
reaf = reaf->pFather;
}
if (ce > max) {
max = ce;
}
}
t = t->pRight;
}
return max;
}
int max_ce = 0;
void Look2(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return;
}
Look2(root->pLeft); // 左子树入栈
if (NULL == root->pLeft && NULL == root->pRight) {
int cen = 0;
struct treeNode *reaf = root;
while(reaf != NULL) {
cen++;
reaf = reaf->pFather;
}
if (cen > max_ce) {
max_ce = cen;
}
}
Look2(root->pRight); // 右子树入栈
}
int main() {
struct treeNode t1 = { 1 };
struct treeNode t2 = { 2 };
struct treeNode t3 = { 3 };
struct treeNode t4 = { 4 };
struct treeNode t5 = { 5 };
struct treeNode t6 = { 6 };
struct treeNode t7 = { 7 };
struct treeNode t8 = { 8 };
struct treeNode t9 = { 9 };
struct treeNode t10 = { 10 };
// 链接
t1.pLeft = &t2;
t1.pRight = &t3;
t1.pFather = NULL;
t2.pLeft = &t4;
t2.pRight = &t5;
t2.pFather = &t1;
t3.pRight = &t6;
t3.pLeft = NULL;
t3.pFather = &t1;
t4.pLeft = NULL;
t4.pRight = NULL;
t4.pFather = &t2;
t5.pLeft = &t7;
t5.pRight = &t8;
t5.pFather = &t2;
t6.pLeft = &t9;
t6.pRight = &t10;
t6.pFather = &t3;
t7.pLeft = NULL;
t7.pRight = NULL;
t7.pFather = &t5;
t8.pLeft = NULL;
t8.pRight = NULL;
t8.pFather = &t5;
t9.pLeft = NULL;
t9.pRight = NULL;
t9.pFather = &t6;
t10.pLeft = NULL;
t10.pRight = NULL;
t10.pFather = &t6;
printf("%d\n", count(&t1));
Look2(&t1);
printf("叶子反根递归:%d\n", max_ce);
printf("叶子反根非递归:%d\n", Look(&t1));
return 0;
}
最大栈法-数组
- 可以根据之前的前中后序遍历的过程,发现栈内的元素根层数是有关系的,后序遍历是最大的栈内元素
//
// Created by Cauchyshy on 2023/5/25.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
#define TREE_DEEP 15
struct treeNode {
int a; // 数据成员
struct treeNode *pFather; // 父节点
struct treeNode *pLeft; // 左孩子
struct treeNode *pRight; // 右孩子
};
// 数组栈
// 由于不需要前后指针 直接用树叶指针类型即可 装树几点地址即可
struct treeNode *stack[TREE_DEEP] = {0};
// 用下标最栈顶指示符即可 栈顶
int stacktop = -1; // -1表示空栈 因为下标从0开始 0元素就是一个栈内元素了
// 入栈
void push(struct treeNode *node) {
if (NULL == node)
return ;
stacktop++; // 栈顶标记先自加1
stack[stacktop] = node; // 然后对栈顶赋值
}
//出栈
struct treeNode * pop(void) {
if (stacktop == -1)
return NULL;
int pre = stacktop;
stacktop--;
return stack[pre];
}
/**
* 得到一棵树有多少层
* 二叉树的高度
*递归思想 每一个分支都走到叶子节点 看看此时左右子树谁的层更深
* */
int count(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return 0; // 树为空
}
int left = count(root->pLeft);
int right = count(root->pRight);
if (left > right) return left + 1;
else return right + 1;
}
int maxCe;
void Look2(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return ;
}
struct treeNode *pre = NULL;
while (1) {
// 左子树入栈
while (root != NULL) {
push(root);
root = root->pLeft;
}
// 这里判断栈内元素最大个数
if (maxCe < stacktop) {
maxCe = stacktop;
}
if (-1 == stacktop)
break;
if (NULL == stack[stacktop]->pRight || stack[stacktop]->pRight == pre) {
pre = pop();
// printf("%d")
} else {
root = stack[stacktop]->pRight;
}
}
}
int main() {
struct treeNode t1 = { 1 };
struct treeNode t2 = { 2 };
struct treeNode t3 = { 3 };
struct treeNode t4 = { 4 };
struct treeNode t5 = { 5 };
struct treeNode t6 = { 6 };
struct treeNode t7 = { 7 };
struct treeNode t8 = { 8 };
struct treeNode t9 = { 9 };
struct treeNode t10 = { 10 };
// 链接
t1.pLeft = &t2;
t1.pRight = &t3;
t1.pFather = NULL;
t2.pLeft = &t4;
t2.pRight = &t5;
t2.pFather = &t1;
t3.pRight = &t6;
t3.pLeft = NULL;
t3.pFather = &t1;
t4.pLeft = NULL;
t4.pRight = NULL;
t4.pFather = &t2;
t5.pLeft = &t7;
t5.pRight = &t8;
t5.pFather = &t2;
t6.pLeft = &t9;
t6.pRight = &t10;
t6.pFather = &t3;
t7.pLeft = NULL;
t7.pRight = NULL;
t7.pFather = &t5;
t8.pLeft = NULL;
t8.pRight = NULL;
t8.pFather = &t5;
t9.pLeft = NULL;
t9.pRight = NULL;
t9.pFather = &t6;
t10.pLeft = NULL;
t10.pRight = NULL;
t10.pFather = &t6;
printf("%d\n", count(&t1));
Look2(&t1);
printf("最大栈法-数组:%d\n", maxCe + 1);
return 0;
}
最大栈法-链表栈
//
// Created by Cauchyshy on 2023/5/25.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
struct treeNode {
int a; // 数据成员
struct treeNode *pFather; // 父节点
struct treeNode *pLeft; // 左孩子
struct treeNode *pRight; // 右孩子
};
// 链表结构的栈 尾添加尾删除 双向带空头链表
// 栈节点
struct stack {
struct treeNode *node; // 指向树的节点
struct stack *pre; // 指向前一个节点
struct stack *next; // 指向下一个节点
};
struct stack head; // 空头
struct stack *stacktop = &head; // 栈顶指针
// 入栈 链表尾添加
void push(struct treeNode *node) {
// 申请节点 并且成员赋值
struct stack *temp = (struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if (NULL == temp) {
return ;
}
// 赋初值
temp->pre = NULL;
temp->next = NULL;
temp->node = node;
// 尾巴连接
stacktop->next = temp;
temp->pre = stacktop;
// 栈顶指针后移
stacktop = stacktop->next;
}
// 出栈 双向链表尾删除
struct treeNode *pop(void) {
if (stacktop == &head) {
// 栈空
return NULL;
}
struct treeNode *temp = stacktop->node; // 得到栈顶的树节点
stacktop = stacktop->pre; // 节点前移
free(stacktop->next); // 释放节点
stacktop->next = NULL; // 新尾指针指向空
return temp;
}
/**
* 得到一棵树有多少层
* 二叉树的高度
*递归思想 每一个分支都走到叶子节点 看看此时左右子树谁的层更深
* */
int count(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return 0; // 树为空
}
int left = count(root->pLeft);
int right = count(root->pRight);
if (left > right) return left + 1;
else return right + 1;
}
int getMaxNode() {
int ans = 0;
// 因为是空头 下一个就是数据了 如果没有就是0
if (head.next == NULL)
return 0;
struct stack *tp = head.next;
while(tp != NULL) {
ans++;
tp = tp->next;
}
return ans;
};
int maxCe;
void Look2(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return ;
}
struct treeNode *pre = NULL;
while (1) {
// 左子树入栈
while (root != NULL) {
push(root);
root = root->pLeft;
}
// if (maxCe < stacktop) {
// maxCe = stacktop;
// }
if (&head == stacktop)
break;
// 统计栈内元素个数
if (maxCe < getMaxNode()) {
maxCe = getMaxNode();
}
if (NULL == stacktop->node->pRight || stacktop->node->pRight == pre) {
pre = pop();
// printf("%d")
} else {
root = stacktop->node->pRight;
}
}
}
int main() {
struct treeNode t1 = { 1 };
struct treeNode t2 = { 2 };
struct treeNode t3 = { 3 };
struct treeNode t4 = { 4 };
struct treeNode t5 = { 5 };
struct treeNode t6 = { 6 };
struct treeNode t7 = { 7 };
struct treeNode t8 = { 8 };
struct treeNode t9 = { 9 };
struct treeNode t10 = { 10 };
// 链接
t1.pLeft = &t2;
t1.pRight = &t3;
t1.pFather = NULL;
t2.pLeft = &t4;
t2.pRight = &t5;
t2.pFather = &t1;
t3.pRight = &t6;
t3.pLeft = NULL;
t3.pFather = &t1;
t4.pLeft = NULL;
t4.pRight = NULL;
t4.pFather = &t2;
t5.pLeft = &t7;
t5.pRight = &t8;
t5.pFather = &t2;
t6.pLeft = &t9;
t6.pRight = &t10;
t6.pFather = &t3;
t7.pLeft = NULL;
t7.pRight = NULL;
t7.pFather = &t5;
t8.pLeft = NULL;
t8.pRight = NULL;
t8.pFather = &t5;
t9.pLeft = NULL;
t9.pRight = NULL;
t9.pFather = &t6;
t10.pLeft = NULL;
t10.pRight = NULL;
t10.pFather = &t6;
printf("%d\n", count(&t1));
Look2(&t1);
printf("最大栈法-链表栈:%d\n", maxCe); // 这个不用加一 刚才数组记录的下标 所以要+1
return 0;
}
进出栈统计法
//
// Created by Cauchyshy on 2023/5/25.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
int cnt = 0;
struct treeNode {
int a; // 数据成员
struct treeNode *pFather; // 父节点
struct treeNode *pLeft; // 左孩子
struct treeNode *pRight; // 右孩子
};
// 链表结构的栈 尾添加尾删除 双向带空头链表
// 栈节点
struct stack {
struct treeNode *node; // 指向树的节点
struct stack *pre; // 指向前一个节点
struct stack *next; // 指向下一个节点
};
struct stack head; // 空头
struct stack *stacktop = &head; // 栈顶指针
// 入栈 链表尾添加
void push(struct treeNode *node) {
// 申请节点 并且成员赋值
struct stack *temp = (struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if (NULL == temp) {
return ;
}
cnt++;
// 赋初值
temp->pre = NULL;
temp->next = NULL;
temp->node = node;
// 尾巴连接
stacktop->next = temp;
temp->pre = stacktop;
// 栈顶指针后移
stacktop = stacktop->next;
}
// 出栈 双向链表尾删除
struct treeNode *pop(void) {
if (stacktop == &head) {
// 栈空
return NULL;
}
cnt--;
struct treeNode *temp = stacktop->node; // 得到栈顶的树节点
stacktop = stacktop->pre; // 节点前移
free(stacktop->next); // 释放节点
stacktop->next = NULL; // 新尾指针指向空
return temp;
}
/**
* 得到一棵树有多少层
* 二叉树的高度
*递归思想 每一个分支都走到叶子节点 看看此时左右子树谁的层更深
* */
int count(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return 0; // 树为空
}
int left = count(root->pLeft);
int right = count(root->pRight);
if (left > right) return left + 1;
else return right + 1;
}
int getMaxNode() {
int ans = 0;
// 因为是空头 下一个就是数据了 如果没有就是0
if (head.next == NULL)
return 0;
struct stack *tp = head.next;
while(tp != NULL) {
ans++;
tp = tp->next;
}
return ans;
};
// 直接在后序遍历里面加减
int maxCe = 0;
void Look2(struct treeNode *root) {
if (NULL == root) {
return ;
}
struct treeNode *pre = NULL;
while (1) {
// 左子树入栈
while (root != NULL) {
push(root);
root = root->pLeft;
}
// if (maxCe < stacktop) {
// maxCe = stacktop;
// }
if (&head == stacktop)
break;
// 统计栈内元素个数
if (maxCe < cnt) {
maxCe = cnt;
}
if (NULL == stacktop->node->pRight || stacktop->node->pRight == pre) {
pre = pop();
// printf("%d")
} else {
root = stacktop->node->pRight;
}
}
}
int main() {
struct treeNode t1 = { 1 };
struct treeNode t2 = { 2 };
struct treeNode t3 = { 3 };
struct treeNode t4 = { 4 };
struct treeNode t5 = { 5 };
struct treeNode t6 = { 6 };
struct treeNode t7 = { 7 };
struct treeNode t8 = { 8 };
struct treeNode t9 = { 9 };
struct treeNode t10 = { 10 };
// 链接
t1.pLeft = &t2;
t1.pRight = &t3;
t1.pFather = NULL;
t2.pLeft = &t4;
t2.pRight = &t5;
t2.pFather = &t1;
t3.pRight = &t6;
t3.pLeft = NULL;
t3.pFather = &t1;
t4.pLeft = NULL;
t4.pRight = NULL;
t4.pFather = &t2;
t5.pLeft = &t7;
t5.pRight = &t8;
t5.pFather = &t2;
t6.pLeft = &t9;
t6.pRight = &t10;
t6.pFather = &t3;
t7.pLeft = NULL;
t7.pRight = NULL;
t7.pFather = &t5;
t8.pLeft = NULL;
t8.pRight = NULL;
t8.pFather = &t5;
t9.pLeft = NULL;
t9.pRight = NULL;
t9.pFather = &t6;
t10.pLeft = NULL;
t10.pRight = NULL;
t10.pFather = &t6;
printf("%d\n", count(&t1));
Look2(&t1);
printf("进出栈统计法:%d\n", maxCe); // 这个不用加一 刚才数组记录的下标 所以要+1
return 0;
}









 文章介绍了计算二叉树高度的三种方法:递归法、叶子反根法(递归和非递归)以及最大栈法(数组和链表栈)。每种方法都通过示例代码详细解释了其工作原理,如递归法通过比较左右子树的高度,叶子反根法从叶子节点向上找到根节点计数,最大栈法通过维护栈内元素个数来确定树的最大深度。
文章介绍了计算二叉树高度的三种方法:递归法、叶子反根法(递归和非递归)以及最大栈法(数组和链表栈)。每种方法都通过示例代码详细解释了其工作原理,如递归法通过比较左右子树的高度,叶子反根法从叶子节点向上找到根节点计数,最大栈法通过维护栈内元素个数来确定树的最大深度。

















 589
589

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










