目录
什么是MyBatis
MyBatis是当前主流的java持久层框架(对象持久化:是指将对象存储在可持久保存的存储介质上,例如主流的关系数据库中。)之一,与Hibernate一样,都是一种ORM框架(ORM:Object/Relational Mapping,即对象关系映射)。
MyBatis(前身是iBatis)是一个支持普通SQL查询,存储过程和高级映射的持久层框架。
MyBatis优点:性能优异,具有高度的灵活性,可优化性和易维护等特点。
什么是ORM框架
ORM是一种为了解决面向对象与关系型数据库中数据类型不匹配的技术。
ORM的工作原理
通过描述Java对象与数据库表之间的映射关系,自动将Java应用程序中的对象持久化到关系型数据库的表中。工作原理如图:
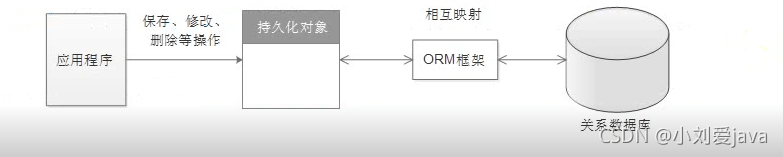
ORM框架中Hibernate和Mybatis区别

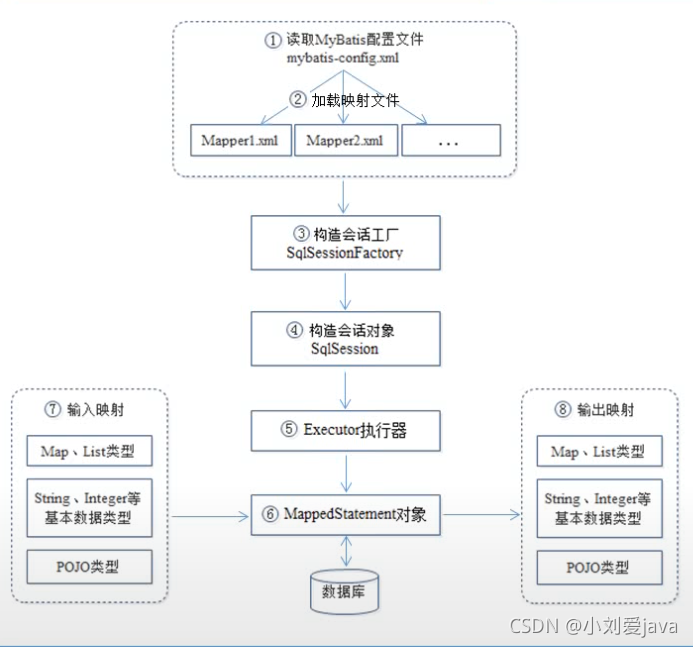
MyBatis工作原理
(可以结合入门程序理解)
(1)配置一个MyBatis全局配置文件,一般命名为sqlMapConfig.xml或者mybatis-config.xml,全局配置文件的作用是,配置MyBatis的运行环境,比如数据库连接,加载映射文件等。后边会介绍。
(2)加载映射文件,一个映射文件对应数据库中的一张表。一边命名为表名+Mapper.xml(如:userMapper.xml,该文件中编写对user表的增删改查语句)。映射文件需要在全局配置文件中加载。
(3)创建SqlSessionFactory会话工厂。
(4)创建SqlSession对象。由SqlSessionFactory会话工厂创建,该对象中包含了执行sql语句的所有方法。
后边的不太好理解,可以先看前四步然后看入门程序,结合入门程序理解。
(5)MyBatis底层定义了一个Executor接口来操作数据库,他会根据SqlSession传递的参数动态的生成需要执行的sql语句,同时负责查询缓存和维护。
(6)在Executor接口的执行方法中,包含一个MappedStatement类型的参数,该参数是对映射信息的封装,用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id,参数等。Mapper.xml文件中一个SQL对应一个MapperedStatement对象,SQL语句的id即是MappedStatement的id。
(7)输入参数映射。
(8)输出参数映射。
MyBatis入门程序
入门程序介绍:客户信息管理。通过该程序实现对数据库中客户的增加修改删除。
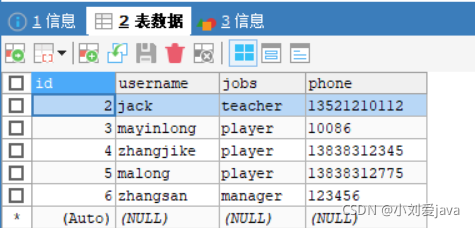
对数据库操作:创建一个mybatis数据库,新建一张名叫customer表,并添加数据。
(1)创建一个web项目,导入MyBatis所需要的jar包以及MySql数据库驱动jar包。
完成程序后web项目的目录结构如图所示:
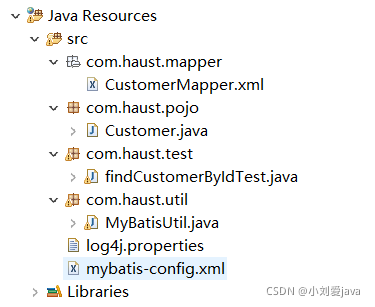
(2)创建全局配置文件myBatis-config.xml和log4j.properties(myBatis默认使用log4j输出日志信息)。
log4j.properties
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, stdout
# MyBatis logging configuration...
log4j.logger.com.haust=DEBUG
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
myBatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 1.配置环境,默认的环境id为mysql -->
<environments default="mysql">
<!-- 1.2 配置id为mysql的数据库环境 -->
<environment id="mysql">
<!-- 使用JDBC的事务管理 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 2.配置映射文件Mapper的位置 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/haust/mapper/CustomerMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>(3)创建Customer实体类
package com.haust.pojo;
/*
* 客户持久化类
*/
public class Customer {
private Integer id ; //主键id
private String username;
private String jobs ;
private String phone ;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getJobs() {
return jobs;
}
public void setJobs(String jobs) {
this.jobs = jobs;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", jobs="
+ jobs + ", phone=" + phone + "]";
}
}
(4)创建CustomerMapper.xml映射文件,并在全局配置文件中添加该映射文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!-- MyBatis的约束配置,约束配置信息位置在mybatis-3.4.2.pdf的Getting started 下的2.1.5小节中 -->
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace表示命名空间 -->
<mapper namespace="com.haust.mapper.CustomerMapper">
<!-- 根据客户编号获取客户信息 -->
<!-- id属性是select元素在映射文件中的唯一标识 -->
<!-- parameterType属性用于指定传入参数的类型,这里表示传递给sql的是一个integer类型的参数 -->
<!-- resultType属性用于指定返回结果的类型,这里表示返回的数据是Customer类型 -->
<select id="findCustomerById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.haust.pojo.Customer">
select * from t_customer where id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- 根据客户名模糊查询客户信息列表 -->
<select id="findCustomerByName" parameterType="String" resultType="com.haust.pojo.Customer">
select * from t_customer where username like concat('%',#{value},'%')
</select>
<select id="addCustomer" parameterType="com.haust.pojo.Customer">
insert into t_customer(username,jobs,phone)
value(#{username},#{jobs},#{phone})
</select>
<update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.haust.pojo.Customer">
update t_customer set
username=#{username},jobs=#{jobs},phone=#{phone}
where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteCustomer" parameterType="com.haust.pojo.Customer">
delete from t_customer where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>(5)创建工具类MyBatisUtil,在工具类中实现sqlSessionFactory会话工厂的创建和sqlSession对象。
package com.haust.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.Reader;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
/*
* 使用工具类创建sqlSession
*/
public class MyBatisUtil {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null ;
//初始化sqlSessionFactory对象
static{
try {
//使用mybatis提供的Resourcrs类加载MyBatis的配置文件
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
//构建SqlSessionFactory工厂
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取SqlSession对象的静态方法
public static SqlSession getSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
(6)添加测试类(对客户的查询添加操作没有用工具类,而是在每个测试方法中创建了会话工厂和sqlSession对象,所以会有很多重复的代码和注释)。
package com.haust.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.haust.pojo.Customer;
import com.haust.util.MyBatisUtil;
public class findCustomerByIdTest {
//通过id查询客户信息
@Test
public void findCustomerByIdTest() throws Exception{
//1.通过输入流读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回映射结果
//sqlSession.selectOne()的第一个参数表示映射SQL的标识字符串,他由映射文件中<mapper>元素的namespace属性值+<select>元素的id属性值组成
//第二个参数表示查询所需要的参数,这里查询的是客户表中id为1的客户
Customer customer = sqlSession.selectOne("com.haust.mapper"+".CustomerMapper.findCustomerById",1);
//打印输出结果
System.out.println(customer.toString());
//5.关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
//查询全部客户信息
@Test
public void findCustomerByName() throws Exception{
//通过输入流读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//sqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回映射结果
List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.haust.mapper"+".CustomerMapper.findCustomerByName","j");
//打印输出结果集
for (Customer customer : customers) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
//添加客户
@Test
public void addCustomerTest() throws Exception{
//通过输入流读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//根据SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//sqlSession执行添加操作
//4.1创建Customer对象,并向对象中添加数据
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("malong");
customer.setJobs("player");
customer.setPhone("13838312775");
//4.2执行sqlSession的插入方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数
int rows = sqlSession.insert("com.haust.mapper.CustomerMapper.addCustomer",customer);
//4.3通过返回结果判断插入操作是否执行成功
if(rows>0){
System.out.println("成功插入了"+rows+"条数据");
}else{
System.out.println("执行插入操作失败!!");
}
//4.4提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭sqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
//更新用户信息
@Test
public void updateCustomerTest() throws Exception{
//获取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//SqlSession执行更新操作
//创建Customer对象
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("mayinlong");
customer.setJobs("player");
customer.setPhone("10086");
customer.setId(3);
//执行sqlSession的更新操作,返回的是受sql语句影响的行数
int rows = sqlSession.update("com.haust.mapper.CustomerMapper.updateCustomer", customer);
if(rows>0){
System.out.println("成功修改了"+rows+"条语句");
}
else{
System.out.println("修改失败!!!");
}
//提交更新操作
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭sqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
//删除用户信息
@Test
public void deleteCustomer(){
MyBatisUtil myBatisUtil = new MyBatisUtil();
SqlSession sqlSession = myBatisUtil.getSession();
//执行Sql语句
int rows = sqlSession.delete("com.haust.mapper.CustomerMapper.deleteCustomer", 1);
if(rows>0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else{
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
映射文件中${}和#{}
关于映射文件中sql语句中${}和#{}的区别在sql注入文章中有所说明
思考题:请简述MyBatis的工作执行流程?







 没有检索到摘要
没有检索到摘要
















 363
363

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








