目录
一,基本概念
前言
web开发:
web,网页的意思,www.baidu.com·
●静态web
html,css
提供给所有人看的数据始终不会发生变化!
●动态web
淘宝,几乎是所有的网站;
提供给所有人看的数据始终会发生变化,每个人在不同的时间,不同的地点看到的信息各不相同!
技术栈:Servlet/JSP,ASP,PHP
web应用程序
web应用程序:可以提供浏览器访问的程序;
●a.html、b.html.….多个web资源,这些web资源可以被外界访问,对外界提供服务;
●你们能访问到的任何一个页面或者资源,都存在于这个世界的某一个角落的计算机上。
●URL
●这个统一的web资源会被放在同一个文件夹下,web应用程序>Tomcat:服务器
●一个web应用由多部分组成(静态web,动态web)
○html,css,js
○jsp,servlet
○Java程序
○jar包
○配置文件(Properties)
Web应用程序编写完毕后,若想提供给外界访问;需费一个服务器来统一管理
静态web
●*.htm, *.html这些都是网页的后缀、如果服务器上一直存在这些东西,我们就可以直接进行读取、需要网络;

静态web存在的缺点
●Web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看到都是同一个页面
○轮播图,点击特效:伪动态
○JavaScript[实际开发中,它用的最多]
○VBScript
●它无法和数据库交互(数据无法持久化,用户无法交互)
动态web
页面会动态展示,“web页面的展示效果因人而异”

动态web存在的优缺点
●缺点:假如服务器的动态web资源出现了错误,我们需要重新编写我们的后台程序,重新发布;
停机维护
●优点:
Web页面可以动态更新,所有用户看到都不是同一个页面
它可以与数据库交互(数据持久化:注册用户,商品信息,用户信息………)
二,web服务器WebServer
技术讲解
ASP:
○微软:国内最早流行的就是ASP;
○在HTML中嵌入了VB的脚本, ASP + COM;
○在ASP开发中,基本一个页面都有几千行的业务代码,页面极其换乱
<h1>
<h1><h1>
<h1>
<h1>
<h1>
<h1>
<%
System.out.println("hello")
%>
<h1>
<h1>
<h1><h1>
<h1>
○维护成本高!
○C#
○IIS
推荐文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/145430397

IIS是指World Wide Web server服务,IIS是一种Web(网页)服务组件,专业的说,IIS可以赋予一部主机电脑一组以上的IP地址,而且还可以有一个以上的域名作为Web网站。 . 做过服务器配置的都应该知道IIS. . 制作好了网站怎么才能让别人浏览,就是通过网站服务器来实现的。IIS只是网站服务器的一种而已。
Internet Information Service(IIS)是windows开设web网页服务的组件,用来搭载网站运行程序的平台的。还能提供FTP,SMTP等服务。
php:
○PHP开发速度很快,功能很强大,跨平台,代码很简单 (70% , WordPress)
○WordPress是使用PHP语言开发的博客平台,用户可以在支持PHP和MySQL数据库的服务器上架设属于自己的网站。也可以把 WordPress当作一个内容管理系统(CMS)来使用。
○WordPress是一款能让您建立出色网站、博客或应用程序的开源软件:
https://cn.wordpress.org/
○无法承载大访问量的情况(局限性)
JSP/Servlet :
○sun公司主推的B/S架构
B/S:浏览和服务器
C/S: 客户端和服务器
○基于Java语言的 (所有的大公司,或者一些开源的组件,都是用Java写的)
○可以承载三高问题(高并发、高性能、高可用)带来的影响;
○语法像ASP , ASP–>JSP , 加强市场强度;
web服务器
服务器是一种被动的操作,用来处理用户的一些请求和给用户一些响应信息;
●IIS
○微软的; ASP…,Windows中自带的
●Tomcat

面向百度编程
○Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,最新的Servlet 和JSP 规范总是能在Tomcat 中得到体现,因为Tomcat 技术先进、性能稳定,而且免费,因而深受Java 爱好者的喜爱并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,成为目前比较流行的Web 应用服务器。
○Tomcat 服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器,在中小型系统和并发访问用户不是很多的场合下被普遍使用,是开发和调试JSP 程序的首选。对于一个Java初学web的人来说,它是最佳的选择
○Tomcat 实际上运行JSP 页面和Servlet。
○下载tomcat:
安装or解压
了解配置文件及目录结构
这个东西的作用
JDK中dt.jar rt.jar tools.jar的作用
dt.jar和tools.jar位于:{Java_Home}/lib/下,而rt.jar位于:{Java_Home}/jre/lib/下,其中:
rt.jar是JAVA基础类库,也就是你在java doc里面看到的所有的类的class文件
dt.jar是关于运行环境的类库
tools.jar是工具类库,编译和运行需要的都是toos.jar里面的类分别是sun.tools.java.; sun.tols.javac.
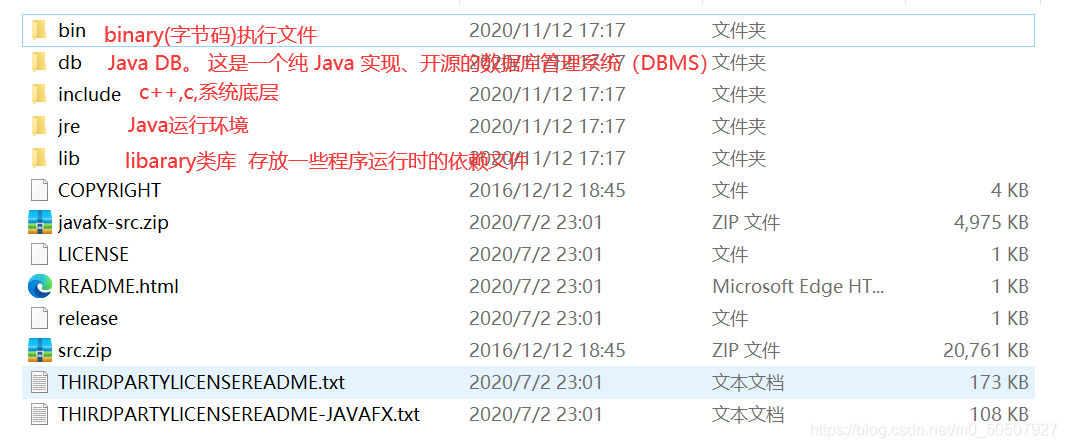
三,Tomcat
3.1安装tomcat tomcat
tomcat官网:http://tomcat.apache.org/

3.2Tomcat启动和配置
文件夹作用::

启动,关闭Tomcat
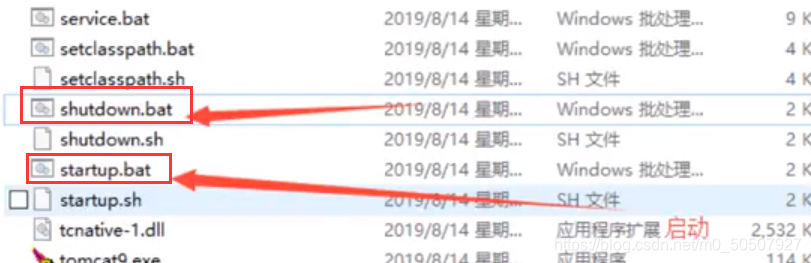
访问测试:http://localhost:8080/
可能遇到的问题:
1,Java环境变量没有配置
2,闪退问题:需要配置兼容性
3,乱码问题:配置文件中设置
3.3配置

可以配置启动的端口号
tomcat的默认端口号为:8080
mysql:3306
http:80
https:443

可以配置主机的名称
●默认的主机名为:localhost->127.0.0.1
●默认网站应用存放的位置为:webapps


请你谈谈网站是如何进行访问的
1,输入一个域名;回车
2,检查本机的C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts配置文件下有没有这个域名映射;
(1)有:直接返回对应的ip地址,这个地址中,有我们需要访问的web程序,可以直接访问

(2)没有:去DNS服务器找,找到的话就返回,找不到就返回找不到;

3.4发布一个web网站
将自己写的网站,放到服务器(Tomcat)中指定的web应用的文件夹(webapps)下,就可以访问了

网站应该有的结构
--webapps :Tomcat服务器的web目录
-ROOT
-张三:网站的目录名
- WEB-INF
-classes : java程序
-lib:web应用所依赖的jar包
-web.xml :网站配置文件
- index.html 默认的首页
- static
-css
-style.css
-js
-img
-.....
四,Http
1,什么是HTTP
HTTP(超文本传输协议)是一个简单的请求-响应协议,它通常运行在TCP之上。
●文本:html,字符串,~ ….
●超文本:图片,音乐,视频,定位,地图…….
●80
Https:安全的
●443
2,两个时代
●http1.0
○HTTP/1.0:客户端可以与web服务器连接后,只能获得一个web资源,断开连接
●http2.0
○HTTP/1.1:客户端可以与web服务器连接后,可以获得多个web资源。‘
3,Http请求
●客户端—发请求(Request)—服务器
百度:
Request URL:https://www.baidu.com/ 请求地址
Request Method:GET get方法/post方法
Status Code:200 OK 状态码:200
Remote(远程) Address:14.215.177.39:443
Accept:text/html
Accept-Encoding:gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language:zh-CN,zh;q=0.9 语言
Cache-Control:max-age=0
Connection:keep-alive
请求行
●请求行中的请求方式:GET
●请求方式:Get,Post,HEAD,DELETE,PUT,TRACT…
○get:请求能够携带的参数比较少,大小有限制,会在浏览器的URL地址栏显示数据内容,不安全,但高效
○post:请求能够携带的参数没有限制,大小没有限制,不会在浏览器的URL地址栏显示数据内容,安全,但不高效。
消息头
Accept:告诉浏览器,它所支持的数据类型
Accept-Encoding:支持哪种编码格式 GBK UTF-8 GB2312 ISO8859-1
Accept-Language:告诉浏览器,它的语言环境
Cache-Control:缓存控制
Connection:告诉浏览器,请求完成是断开还是保持连接
HOST:主机..../.
4,Http响应
●服务器—响应-----客户端
百度:
Cache-Control:private 缓存控制
Connection:Keep-Alive 连接
Content-Encoding:gzip 编码
Content-Type:text/html 类型
响应体
Accept:告诉浏览器,它所支持的数据类型
Accept-Encoding:支持哪种编码格式 GBK UTF-8 GB2312 ISO8859-1
Accept-Language:告诉浏览器,它的语言环境
Cache-Control:缓存控制
Connection:告诉浏览器,请求完成是断开还是保持连接
HOST:主机..../.
Refresh:告诉客户端,多久刷新一次;
Location:让网页重新定位;
响应状态码
200:请求响应成功 200
3xx:请求重定向
●重定向:你重新到我给你新位置去;
4xx:找不到资源 404
●资源不存在;
5xx:服务器代码错误 500 502:网关错误
输入url后发生了什么?
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/m0_50507927/article/details/115625069?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
三,输入url后发生了什么?
五,Maven
为什么要学习这个技术?
在Javaweb开发中,需要使用大量的jar包,我们手动去导入;
如何能够让一个东西自动帮我导入和配置这个jar包。
由此,Maven诞生了!
1,Maven项目架构管理工具
我们目前用来就是方便导入jar包的!
Maven的核心思想:约定大于配置
●有约束,不要去违反。
Maven会规定好你该如何去编写我们的Java代码,必须要按照这个规范来;
2,下载安装Maven
官网;https://maven.apache.org/

下载完成后,解压即可;

3,配置环境变量
在我们的系统环境变量中
配置如下配置:
●M2_HOME maven目录下的bin目录
●MAVEN_HOME maven的目录
●在系统的path中配置 %MAVEN_HOME%\bin


测试Maven是否安装成功:

4,阿里云镜像
●镜像:mirrors
●作用:加速我们的下载
maven文件夹下conf/settings.xml
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/repositories/central/</url>
</mirror>

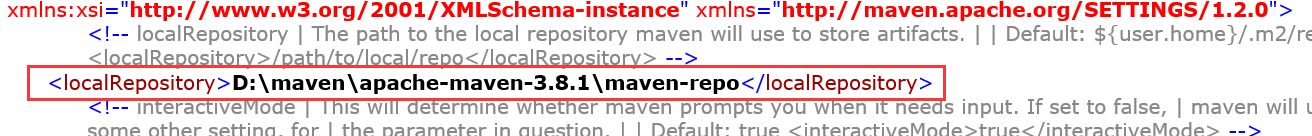
5,本地仓库
maven有本地仓库和远程仓库;
建立一个本地仓库(同样在settings.xml)
<localRepository>D:\maven\apache-maven-3.8.1\maven-repo</localRepository>
6,在IDEA中使用Maven
1,启动IDEA
2,创建一个MavenWeb项目




问题:
Could not transfer artifact org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-clean-plugin:pom:2.5 from/to central (https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2): C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA 2020.1.3\plugins\maven\lib\maven3\maven-repo\org\apache\maven\plugins\maven-clean-plugin\2.5\maven-clean-plugin-2.5.pom.part.lock (系统找不到指定的路径。)
新建maven无法成功运行的原因是,maven仓库放在了C盘,idea没有权限在下面创建文件,把maven仓库放在别的盘可解决
需要修改setting.xml和idea软件内部的两个地方生效。
3,等待项目初始化完毕

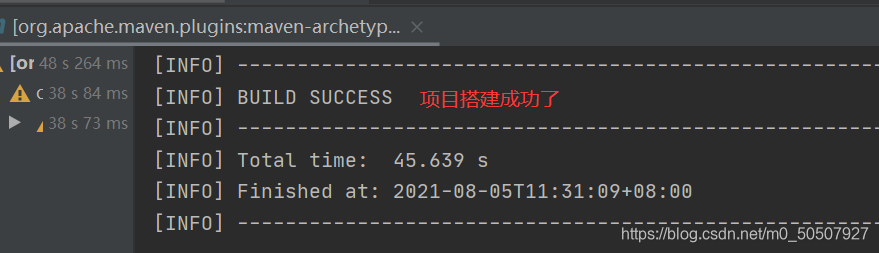
4,观察maven仓库中多了什么东西?

5,IDEA中的Maven设置
注意:IDEA项目创建成功后,看一眼Maven的配置


6,到这里,Maven在IDEA中的配置和使用就OK了!
7,创建一个普通的Maven项目

web应用下:

8,标记文件夹功能




9, 在 IDEA中配置Tomcat

解决警告问题
必须要的配置:为什么会有这个问题:我们访问一个网站,需要指定一个文件夹名字;


这里访问到的Hello World!就是默认的index.jsp中的内容

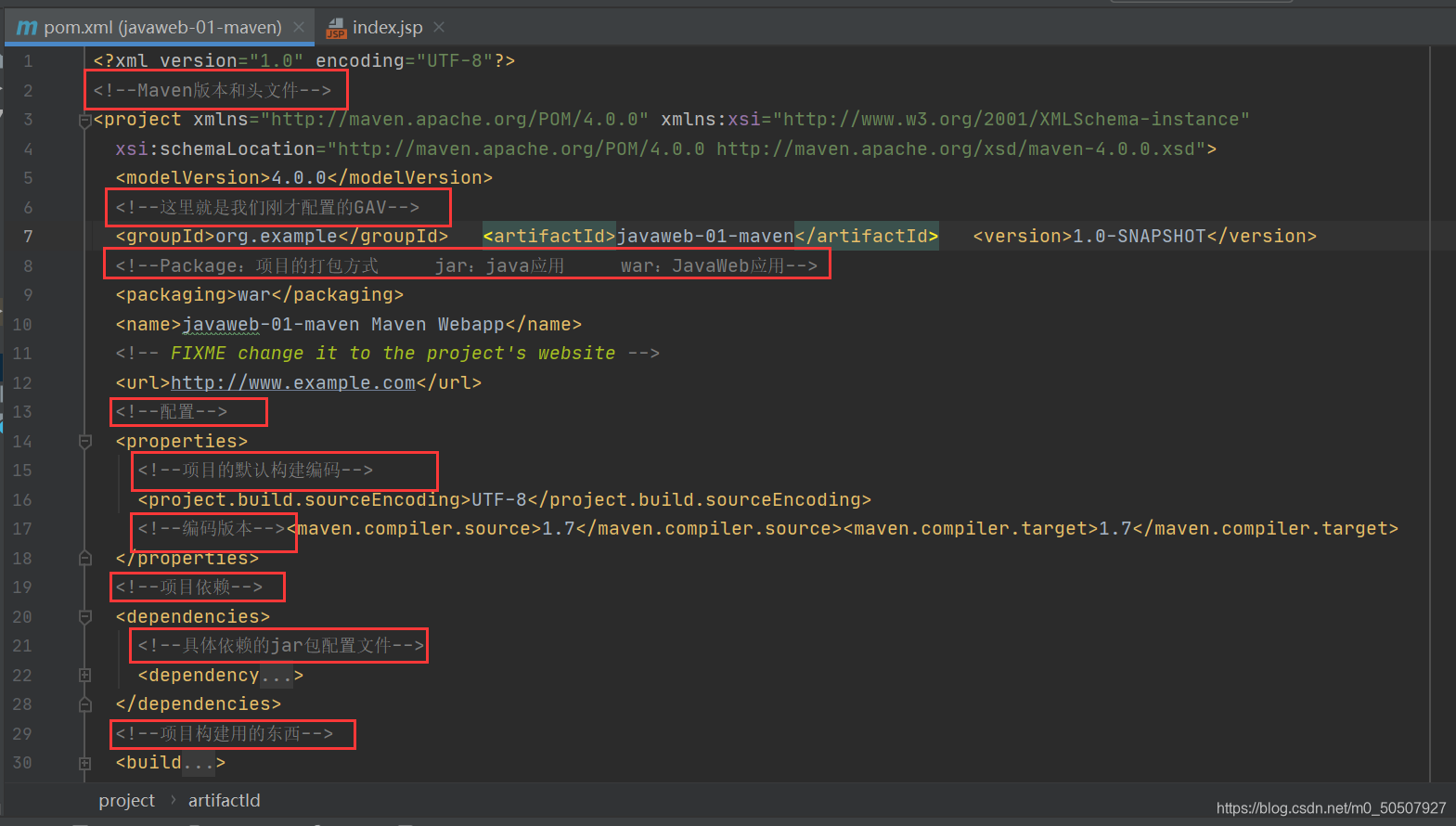
10,pom文件
pom.xml 是Maven的核心配置文件

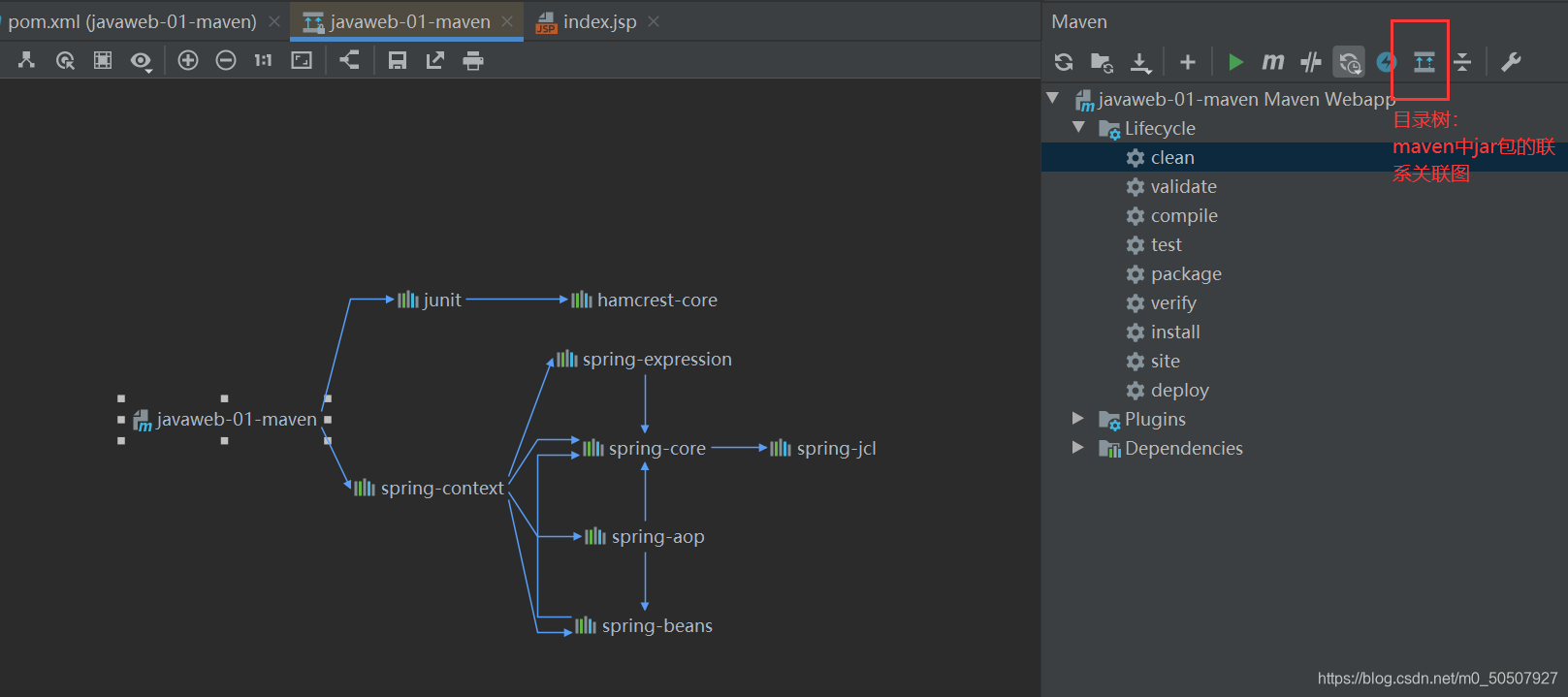
maven仓库:https://mvnrepository.com/

maven由于他的约定大于配置,我们之后可以能遇到我们写的配置文件,无法被导出或者生效的问题,解决方案:
<!--在build中配置resources,来防止我们资源导出失败的问题-->
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
11,IDEA操作
12,解决遇到的问题
1,Maven 3.6.2


解决方法:降级为3.6.1
2,Tomcat闪退
3,IDEA中每次都要重复配置Maven
在IDEA中的全局默认配置中去配置


4,Maven项目中Tomcat无法配置
5,maven默认web项目中的web.xml版本问题

6,替换为webapp4.0版本和tomcat一致
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1"
metadata-complete="true">
</web-app>
7,Maven仓库的使用
地址:https://mvnrepository.com/
8,Servlet

静态资源
header.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h1{
background-color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>了解Servlet</h1>
</body>
</html>

动态web资源jsp/Servlet
HelloServlet
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
//响应的类型html
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//获取响应的输出流
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Hello World!</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<h1>Hello World!</h1>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
doGet(request, response);
}
}
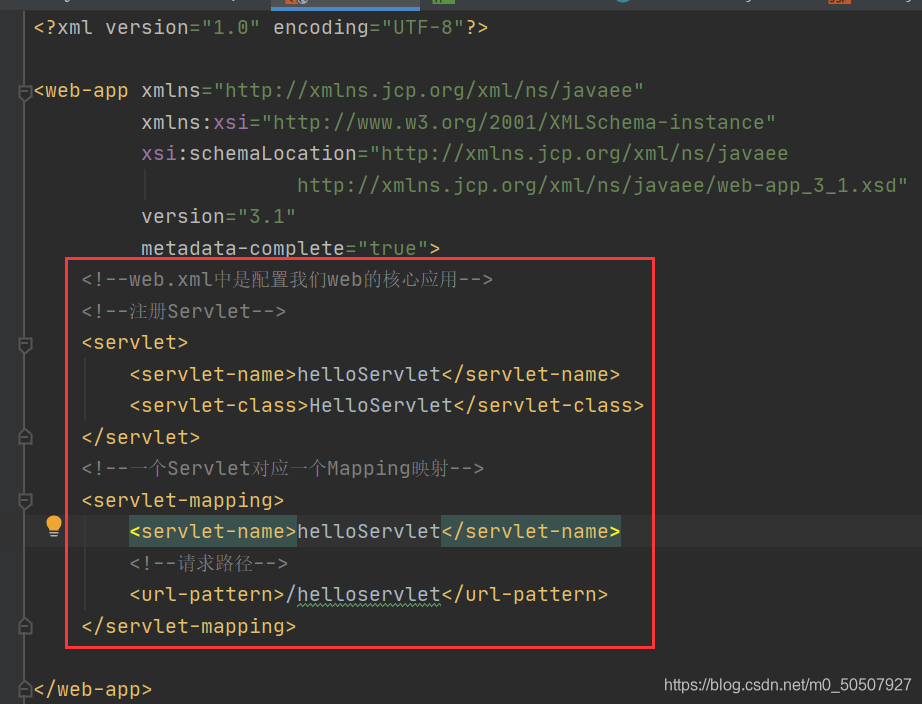
web.xml

六,Servlet
1,Servlet简介
●Servlet是sun公司开发的动态web的一项技术
●Sun在API中提供一个接口叫做:Servlet,开发一个Servlet程序需要完成两个小步骤:
○编写一个类,实现servlet接口;
○把开发好的Java类部署到web服务器上。
把实现了Servlet接口的Java程序叫做,Servlet
2,编写HelloServlet
Serlvet接口Sun公司有两个默认的实现类:HttpServlet,GenericServlet
(1)构建一个普通的Maven项目,删掉里面的src目录,在这个项目里面建立Moudel(模块),这个空的工程就是Maven主工程;
(2)在Maven父子工程中
●父项目的pom.xml中自动生成
<modules>
<module>servlet-01</module>
</modules>
//告诉编译器,在读取主pom时,去找子pom
●子项目(测试中没有自动生成)
<parent>
<artifactId>javaweb-servlet</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
//使子项目继承父项目的设置,避免重复导入依赖
父项目中的java,子项目可以直接使用 (son extends father)
(3)Maven环境优化
1,.修改web.xml为最新(去tomca文件夹下的webapps下去取);
2,将maven结构搭建完整,,main下建java文件夹,resources文件夹
(4)编写一个Servlet程序

1.编写一个普通类
2.实现Servlet接口,这里我们直接继承HttpServlet(HttpServlet实现了Servlet接口)
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
//由于get或者post只是请求实现的不同的方式,可以相互调用,业务逻辑都一样;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream();
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter(); //响应流
writer.print("Hello,Serlvet");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
(5)编写Servlet的映射
为什么需要映射:我们写的是JAVA程序,但是要通过浏览器访问,而浏览器需要连接web服务器,所以我们需要在web服务中注册我们写的Servlet,还需给他一个浏览器能够访问的路径;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1"
metadata-complete="true">
<!--web.xml中是配置我们web的核心应用-->
<!--注册Servlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--一个Servlet对应一个Mapping映射-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<!--请求路径-->
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
(6)配置Tomca
注意:配置项目发布路径即可。
(7)启动项目
启动后通过请求路径访问程序。
域名/发布路径/请求路径

3,Servlet原理
Servlet是由Web服务器调用的,web服务器收到浏览器请求后:
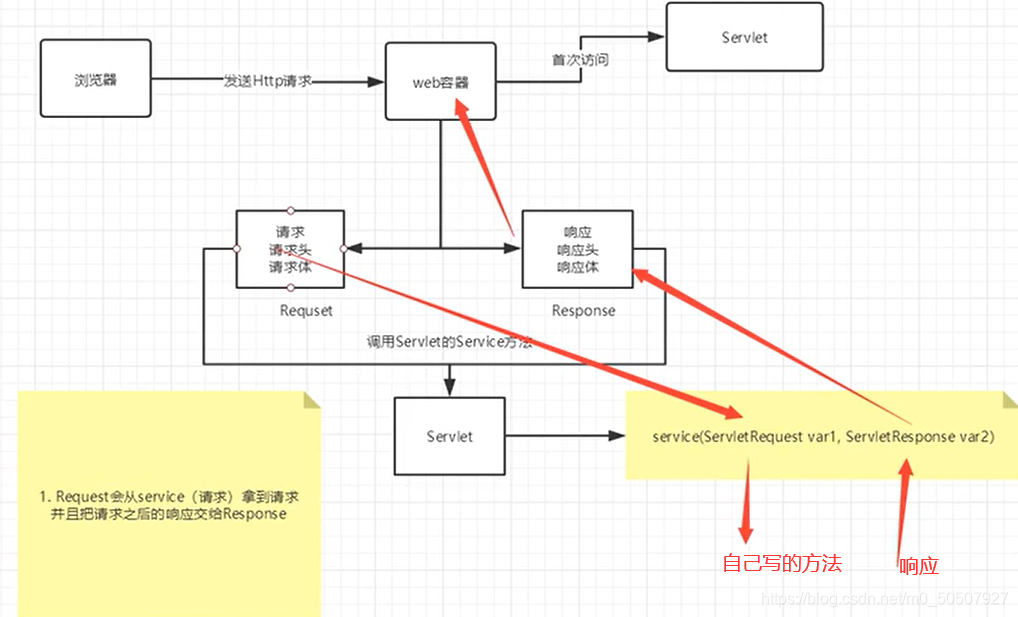
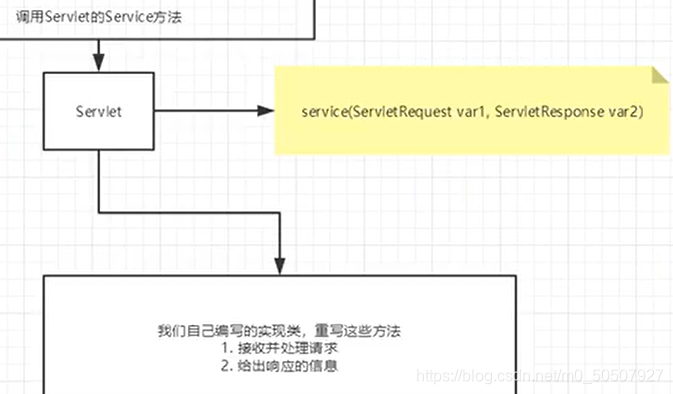
4,Mapping
1,一个Servlet可以指定一个映射路径
<!--一个Servlet对应一个Mapping映射-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<!--请求路径-->
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
2,一个Servlet可以指定多个映射路径
<!--一个Servlet对应一个Mapping映射-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<!--请求路径-->
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello3</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
3,一个Servlet可以指定通用映射路径
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<!--请求路径-->
<url-pattern>/hello/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
4,默认请求路径
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<!--请求路径-->
<url-pattern>/* </url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>

5,指定一些后缀或者前缀等等….
<!--可以自定义后缀实现请求映射
注意:*前面不能加项目映射的路径-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<!--请求路径-->
<url-pattern>*.zhangsan</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>


6,优先级问题
指定了固有的映射路径优先级最高,如果找不到就会走默认的处理请求;

5,ServletContext

web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用;
1,共享数据
我在这个Servlet中保存的数据,可以在另外一个servlet中拿到;

将一个数据保存到了ServletContext中 :
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
String username="张三";//数据
//将一个数据保存在了ServletContext中,名字:username(键) 值:username
servletContext.setAttribute("username",username);
}
}
在另外一个servlet中拿到该数据
public class GetServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext=this.getServletContext();
String username = (String)servletContext.getAttribute("username");
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.getWriter().print("名字:"+username);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
web.xml
<!--web.xml中是配置我们web的核心应用-->
<!--注册servlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>getDate</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.GetServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>getDate</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/getDate</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>

2,获取初始化参数
web.xml中
<!--配置一些web应用初始化参数-->
<context-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis</param-value>
</context-param>
获取
public class GetInitializationParameters extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
String url = servletContext.getInitParameter("url");
resp.getWriter().print(url);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}

3,请求转发
web.xml中
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Forward</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.Forward</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Forward</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/forward</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
请求转发
public class Forward extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
System.out.println("进入了Forward");
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = servletContext.getRequestDispatcher("/getParameter");//转发的请求路径
requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);//调用forward实现请求路径
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
请求转发路径不变,重定向路径变化


4,读取资源文件
Properties
●在java目录下新建properties
●在resources目录下新建properties
发现:都被打包到了同一个路径下:classes,我们俗称这个路径为classpath:类路径

web.xml中
<servlet>
<servlet-name>readResource</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.ReadResource</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>readResource</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/readResource</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
读取资源文件
public class ReadResource extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
InputStream is = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties");
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String username=properties.getProperty("username");
String password=properties.getProperty("password");
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.getWriter().print(username+"密码为:"+password);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}

6,HttpServletResponse
web服务器接收到客户端的http请求,针对这个请求,分别创建一个代表请求的HttpServletRequest对象,代表响应的一个HttpServletResponse;
●如果要获取客户端请求过来的参数:找HttpServletRequest
●如果要给客户端响应一些信息:找HttpServletResponse
1,简单分类
负责向浏览器发送数据的方法
ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException;
PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException;
负责向浏览器发送响应头的方法
void setCharacterEncoding(String var1);
void setContentLength(int var1);
void setContentLengthLong(long var1);
void setContentType(String var1);
void setDateHeader(String var1, long var2);
void addDateHeader(String var1, long var2);
void setHeader(String var1, String var2);
void addHeader(String var1, String var2);
void setIntHeader(String var1, int var2);
void addIntHeader(String var1, int var2);
响应的状态码
int SC_CONTINUE = 100;
int SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
int SC_OK = 200;
int SC_CREATED = 201;
int SC_ACCEPTED = 202;
int SC_NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
int SC_NO_CONTENT = 204;
int SC_RESET_CONTENT = 205;
int SC_PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
int SC_MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
int SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
int SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
int SC_FOUND = 302;
int SC_SEE_OTHER = 303;
int SC_NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
int SC_USE_PROXY = 305;
int SC_TEMPORARY_REDIRECT = 307;
int SC_BAD_REQUEST = 400;
int SC_UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
int SC_PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
int SC_FORBIDDEN = 403;
int SC_NOT_FOUND = 404;
int SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
int SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
int SC_PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
int SC_REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
int SC_CONFLICT = 409;
int SC_GONE = 410;
int SC_LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
int SC_PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
int SC_REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
int SC_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG = 414;
int SC_UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
int SC_REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
int SC_EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
int SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
int SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
int SC_BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
int SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
int SC_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
int SC_HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
2,下载文件
(1)向浏览器输出消息
(2)下载文件
○要获取下载文件的路径
○下载的文件名是啥?
○设置想办法让浏览器能够支持下载我们需要的东西
○获取下载文件的输入流
○创建缓冲区
○获取OutputStream对象
○将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区
○使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端!
public class FileServlet extends HttpServlet {
/*
下载文件
*/
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//○要获取下载文件的路径
String realPath="C:\\gitcode\\maven\\maven测试\\javaweb-servlet\\HttpServletResponse\\target\\classes\\辉夜大小姐.png";
System.out.println("下载文件的路径"+realPath);
//○下载的文件名是啥?
String fileName = realPath.substring(realPath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1);
//○设置想办法让浏览器能够支持(Content-Disposition)下载我们需要的东西,中文文件名URLEncoder.encode编码,否则有可能乱码
resp.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename"+ URLEncoder.encode(fileName,"UTF-8") );
//○获取下载文件的输入流
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//○创建缓冲区
int len=0;
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
//○获取OutputStream对象
ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream();
//○将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区,使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端!
while((len=inputStream.read(buffer))>0){
outputStream.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//关闭输入输出流
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}

3,验证码功能
验证怎么来的?
●前端js实现
●后端实现,需要用到 Java 的图片类,生产一个图片
public class ImageServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//如何让浏览器3秒自动刷新一次
resp.setHeader("refresh","3");
//在内存中创建一个图片
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(80, 20, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
//得到图片
Graphics2D graphics = (Graphics2D)image.getGraphics();//笔
//设置图片的背景颜色
graphics.setColor(Color.white);
graphics.fillRect(0,0,80,20);
//给图片写数据
graphics.setColor(Color.green);
graphics.setFont(new Font(null,Font.BOLD,20));
graphics.drawString(makeRandom(),0,20);
//告诉浏览器,这个请求用图片的方式打开
resp.setContentType("image/jpeg");
//网站存在缓存,不让浏览器缓存
resp.setDateHeader("expires",-1);
resp.setHeader("Cache-Control","no-cache");
resp.setHeader("Pragma","no-cache");
//把图片写给浏览器
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",resp.getOutputStream());
}
//生成随机数
private String makeRandom(){
Random random=new Random();
String num=random.nextInt(9999999)+"";
StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 7-num.length(); i++) {
stringBuffer.append("0");
}
num=stringBuffer.toString()+num;
return num;
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
4,实现重定向
B一个web资源收到客户端A请求后,B他会通知A客户端去访问另外一个web资源C,这个过程叫重定向

常见场景:用户登录
void sendRedirect(String var1) throws IOException;
测试:
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
/**
* resp.setHeader("Location","/HttpServletResponse_war/image");
* resp.setStatus(302);
*/
resp.sendRedirect("/HttpServletResponse_war/image");
}
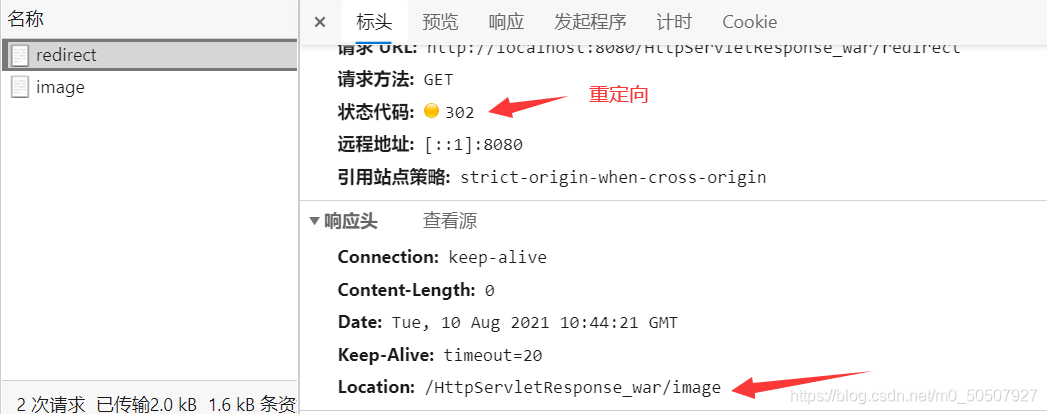
重定向和转发的区别
相同点
●页面都会实现跳转
不同点
●请求转发的时候,url不会产生变化307
●重定向时候,url地址栏会发生变化;302

5,简单实现登录重定向
index.jsp
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello World!</h2>
<%--这里提交的路径,需要寻找到项目的路径--%>
<%--${pageContext.request.contextPath代表当前的项目--%>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Login" method="get">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Success</h1>
</body>
</html>
RequestTest
public class RequestTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//处理请求
String username=req.getParameter("username");
String password=req.getParameter("password");
System.out.println(username+":"+password);
//重定向时候一定要注意,路径问题,否则404;
resp.sendRedirect("/HttpServletResponse_war/success.jsp");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Login</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.RequestTest</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Login</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/Login</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>

7,HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest代表客户端的请求,用户通过Http协议访问服务器,HTTP请求中的所有信息会被封装到HttpServletRequest,通过这个HttpServletRequest的方法,获得客户端的所有信息;


1,获取前端传递的参数,并请求转发

index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>登录</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录</h1>
<div style="text-align: center">
<%--以post方式提交表单,提交到我们的Login请求--%>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"> <br>
爱好:
<input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="篮球">篮球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="乒乓球">乒乓球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="羽毛球">羽毛球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="排球">排球
<br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1"
metadata-complete="true">
<!--web.xml中是配置我们web的核心应用-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.LoginServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/login</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
LoginServlet
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String username=req.getParameter("username");
String password=req.getParameter("password");
String[] hobbys=req.getParameterValues("hobbys");
System.out.println("--------------------");
//后台解决中文乱码问题
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbys));
System.out.println("--------------------");
//通过请求转发
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//这里的 / 代表当前的web应用
req.getRequestDispatcher("/success.jsp").forward(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
七,web.xml(常用)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1"
metadata-complete="true">
<!--web.xml中是配置我们web的核心应用-->
</web-app>
八,Cookie、Session
会话
会话:用户打开一个浏览器,点击了很多超链接,访问多个web资源,关闭浏览器,这个过程可以称之为会话;
无状态会话:打开,关闭
有状态会话:一个同学来过教室,下次再来教室,我们会知道这个同学,曾经来过,称之为有状态会话;
你能怎么证明你是某高校的学生?
你 某高校
●发票 某高校给你发票
●学校登记 某高校标记你来过了
一个网站,怎么证明你来过?
客户端 服务端
●服务端给客户端一个 信件,客户端下次访问服务端带上信件就可以了; cookie
●服务器登记你来过了,下次你来的时候我来匹配你; seesion
保存会话的两种技术
cookie
●客户端技术
响应:在服务器把cookie发送给客户端
请求:客户端把cookie带到服务器
session
●服务器技术,利用这个技术,可以保存用户的会话信息?可将信息或数据放在 session 中
常见场景:网站登录之后,你下次不用再登录了,第二次访问直接就上去了!
Cookie

1,从请求中拿到cookie信息
2,服务器响应给客户端cookie
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies(); //获得Cookie
cookie.getName(); //获得cookie中的key
cookie.getValue(); //获得cookie中的vlaue
new Cookie("lastLoginTime", System.currentTimeMillis()+""); //新建一个cookie
cookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60); //设置cookie的有效期
resp.addCookie(cookie); //响应给客户端一个cookie
代码:
public class CookieDemo extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//服务器,告诉你,你来的时候,把这个时间封装成为一个信件,你下次带来,我就知道你来了
//解决中文乱码
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
//Cookie,服务器从客户端获取
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();//这里返回数组,说明Cookie可能存在多个
//判断Cookie是否存在
if(cookies!=null){
//如果存在
out.print("你上一次访问的时间是:");
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
Cookie cookie=cookies[i];
//获取cookie的名字
if(cookie.getName().equals("lastLoginTime")){
//获取cookie中的值
long lastLoginTime = Long.parseLong(cookie.getValue());
Date date = new Date(lastLoginTime);
out.write(date.toLocaleString());
}
}
}else{
out.print("这是你第一次访问本站");
}
//服务端给客户端响应一个Cookie
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("lastLoginTime",System.currentTimeMillis()+"");
//cookie有效期为1天
cookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60);
resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}


cookie:一般会保存在本地的 用户目录下 appdata;

一个网站cookie是否存在上限!
●一个Cookie只能保存一个信息;
●一个web站点可以给浏览器发送多个cookie,最多存放20个cookie;
●Cookie大小有限制4kb;
●300个cookie浏览器上限
删除Cookie
●不设置有效期,关闭浏览器,自动失效;
●设置有效期时间为 0 ;cookie.setMaxAge(0); //设置cookie的有效期
编码解码:
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("name","张三");
resp.addCookie(cookie);

URLEncoder.encode("张三","utf-8")
URLDecoder.decode(cookie.getValue(),"UTF-8")
public class CookieDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//解决中文乱码
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//Cookie,服务器端从客户端获取
Cookie[] cookies=req.getCookies();
PrintWriter out=resp.getWriter();
//判断cookie是否存在
if(cookies!=null){
//如果存在
out.write("你上一次访问的时间是:");
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
Cookie cookie=cookies[i];
//获取Cookie的名字
if(cookie.getName().equals("name")){
out.write(URLDecoder.decode(cookie.getValue(),"UTF-8"));
}
}
}else {
out.write("这是你第一次访问本站");
}
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("name", URLEncoder.encode("张三","utf-8"));
resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
Session

什么是 Session ?
●服务器会给每一个用户(浏览器)创建一个 Session 对象;
●一个 Session 独占一个浏览器,只要浏览器没有关闭,这个 Session 就存在;
●用户登录之后,整个网站它都可以访问!-> 保存用户的信息;保存购物车的信息…

给session存东西代码:
public class SessionDemo extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//解决乱码问题
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//得到Session
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
//给Session中存东西
session.setAttribute("name","张三");
//获得session的ID
String sessionId=session.getId();
//判断session是不是新创建的
if(session.isNew()){
resp.getWriter().write("session创建成功,ID:"+sessionId);
}else {
resp.getWriter().write("session已经在服务器中存在了,ID:"+sessionId);
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}

session取东西代码:
取出一个字符串
public class SessionDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//解决乱码问题
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//得到Session
HttpSession session=req.getSession();
String name =(String) session.getAttribute("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}

取出一个对象
public class SessionDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//解决乱码问题
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//得到Session
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
Person person = (Person) session.getAttribute("name");
System.out.println(person);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
//给Session中存东西
session.setAttribute("name",new Person("张三",18));

注销session
//手动注销Session
session.invalidate();
web.xml
<!--设置Session默认的失效时间-->
<session-config>
<!--15分钟后Session自动失效,以分钟为单位-->
<session-timeout>15</session-timeout>
</session-config>
Session创建的时候做了什么事情;

Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID",sessionId);
resp.addCookie(cookie);
Session 使用场景:
●保存一个登录用户的信息;
●购物车信息;
●在整个网站中经常会使用的数据,我们将它保存在 Session 中;
Session 和 Cookie 的区别:
●Cookie是把用户的数据写给用户的浏览器,浏览器保存 (可以保存多个)
●Session把用户的数据写到用户独占Session中,服务器端保存 (保存重要的信息,减少服务器资源的浪费)
1,session 在服务器端,cookie 在客户端(浏览器)
2,session会在一定时间内保存在服务器上。当访问增多,会比较占用你服务器的性能,如果主要考虑到减轻服务器性能方面,应当使用COOKIE
3,session 的运行依赖 session id,而 session id 是存在 cookie 中的,也就是说,如果浏览器禁用了 cookie ,同时 session 也会失效(但是可以通过其它方式实现,比如在 url 中传递 session_id)
4,session 可以放在 文件、数据库、或内存中都可以。
5,cookie不是很安全,别人可以分析存放在本地的COOKIE并进行COOKIE欺骗,如果主要考虑到安全应当使用session,用户验证这种场合一般会用 session
6,单个cookie在客户端的限制是4K

九,JSP
1,什么是JSP
Java Server Pages : Java服务器端页面,也和Servlet一样,用于动态Web技术
最大的特点: 写JSP就像在写HTML
区别:
~ HTML只给用户提供静态的数据
~ JSP页面中可以嵌入JAVA代码,为用户提供动态数据;
2,JSP原理
思路:JSP到底怎么执行的
代码层面没有任何问题
服务器内部工作:
tomcat中有一个work目录;
IDEA中使用Tomcat的会在IDEA的tomcat中生产一个work目录

电脑的地址:
C:\Users\Administrator.IntelliJIdea2018.1\system\tomcat\Unnamed_javaweb-session-cookie\work\Catalina\localhost\ROOT\org\apache\jsp
发现页面转变成了Java程序!

浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet!
JSP最终也会被转换成为一个Java类!
JSP 本质上就是一个Servlet
//初始化
public void _jspInit() {
}
//销毁
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
//JSPService
public void _jspService(.HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
jsp做了:
1,判断请求
2,内置一些对象
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; //页面上下文
javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; //session
final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; //applicationContext
final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; //config
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; //out
final java.lang.Object page = this; //page:当前
HttpServletRequest request //请求
HttpServletResponse response //响应
3,输出页面前增加的代码<这些个对象我们可以在JSP页面中直接使用>
response.setContentType(“text/html”); //设置响应的页面类型
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
4,输出页面

流程:
Tomcat简单的说就是一个运行JAVA的网络服务器,底层是Socket的一个程序,它也是JSP和Serlvet的一个容器。


在JSP页面中,只要是 JAVA代码就会原封不动的输出
如果是HTML代码,就会被转换为:
out.write("<html>\r\n");
这样的格式,输出到前端

3,JSP基础语法
任何语言都有自己的语法,Java中有,JSP作为java技术的一种应用,它拥有自己扩充的一些语法,Java所有语法都支持
jsp表达式
<%--jsp表达式
作用:用来将程序的结果输出到客户端
<%= 变量或者表达式%>
--%>
<%= new java.util.Date()%>
jsp脚本片段
<%--jsp脚本片段--%>
<%
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <=100 ; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
out.println("<h1>Sum="+sum+"</h1>");
%>
在代码嵌入HTML元素
<%--在代码嵌入HTML元素--%>
<%
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
%>
<h1>Hello,World <%=i%> </h1>
<%
}
%>
EL表达式${i}简化在代码嵌入HTML元素
<%--在代码嵌入HTML元素--%>
<%for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {%>
<h1>Hello,World ${i} </h1>
<%}%>
JSP声明
<%!
static {
System.out.println("Loading Servlet!");
}
private int globalVar = 0;
public void exit(){
System.out.println("进入了方法!");
}
%>
JSP声明:会被编译到JSP生成Java的类中!其他的,就会被生成到_jspService方法中!在JSP,嵌入Java代码即可!
总结:JSP的注释,不会在客户端显示,HTML会
<%%> 片段
<%=%> 表达式输出一个值
<%!%> 全局方法
<%--注释--%>
4,JSP指令
Idea部署javaweb项目jsp无法加载图片
推荐文章:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_43445553/article/details/107400543
定制错误页面
<%@page args.... %>
<%--定制错误页面--%>
<%@ page errorPage="error/500.jsp" %>

网站公共页面
@include会将两个页面合二为一
<%@include file="common/header.jsp"%>
<h1>网页主体</h1>
<%@include file="common/footer.jsp"%>

jSP标签
jsp:include:拼接页面,本质还是三个
<jsp:include page="/common/header.jsp"/>
<h1>网页主体</h1>
<jsp:include page="/common/footer.jsp"/>
5,JSP内置对象及作用域
PageContext 存东西
Request 存东西
Response
Session 存东西
Application 【SerlvetContext】 存东西
config 【SerlvetConfig】
out
page
exception
内置对象及作用域:
<%--内置对象--%>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("name1","张三1号"); //保存的数据只在一个页面中有效
request.setAttribute("name2","张三2号"); //保存的数据只在一次请求中有效,请求转发会携带这个数据
session.setAttribute("name3","张三3号"); //保存的数据只在一次会话中有效,从打开浏览器到关闭浏览器
application.setAttribute("name4","张三4号"); //保存的数据只在服务器中有效,从打开服务器到关闭服务器
%>
脚本片段中的代码,会被原封不动的生成到JSP.java
要求:这里面的代码必须要验证java语法的正确性
<%
//从pageContext取出,我们通过寻找的方式
//作用域:从底层到高层{page->request->session->application}
//JVM:双亲委派机制
String name1 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("name1");
String name2 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("name2");
String name3 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("name3");
String name4 = (String)pageContext.findAttribute("name4");
%>
<%--使用EL表达式输出${} --%>
<h1>取出的名字为:</h1>
<h2>${name1}</h2>
<h2>${name2}</h2>
<h2>${name3}</h2>
<h2>${name4}</h2>

request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如:新闻,用户看完没用的!
session:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户用完一会还有用,比如:购物车;
application:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如:聊天数据;

<%pageContext.setAttribute("hello","张三",pageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
%>
6,JSP标签、JSTL标签、EL表达式
导包:
<!-- JSTL表达式的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- standard标签库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
(1)EL表达式 ${ }
获取数据
执行运算
获取web开发的常用对象
(2)JSP标签
<%–jsp:include–%>
<%–http://localhost:8080/jspTag.jsp?name=zhangsan&age=18–%>
<jsp:forward page="index.jsp">
<jsp:param name="name" value="zhangsan"></jsp:param>
<jsp:param name="age" value="18"></jsp:param>
</jsp:forward>
index.jsp
<body>
hello
<%--取出参数--%>
名字:<%=request.getParameter("name")%>
年龄:<%=request.getParameter("age")%>
</body>
(3)JSTL,JSP 标准标签库表达式
jstl菜鸟教程:https://www.runoob.com/jsp/jsp-jstl.html
JSP标准标签库(JSTL)是一个JSP标签集合,它封装了JSP应用的通用核心功能。
JSTL标签库的使用就是为了弥补HTML标签的不足;它自定义许多标签,可以供我们使用,标签的功能和Java代码一样!
引用标签库
格式化标签
JSTL格式化标签用来格式化并输出文本、日期、时间、数字。引用格式化标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt"
uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
SQL标签
JSTL SQL标签库提供了与关系型数据库(Oracle,MySQL,SQL Server等等)进行交互的标签。引用SQL标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib prefix="sql"
uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/sql" %>
XML 标签
JSTL XML标签库提供了创建和操作XML文档的标签。引用XML标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib prefix="x"
uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/xml" %>
引用核心标签
核心标签是最常用的 JSTL标签。引用核心标签库的语法如下:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
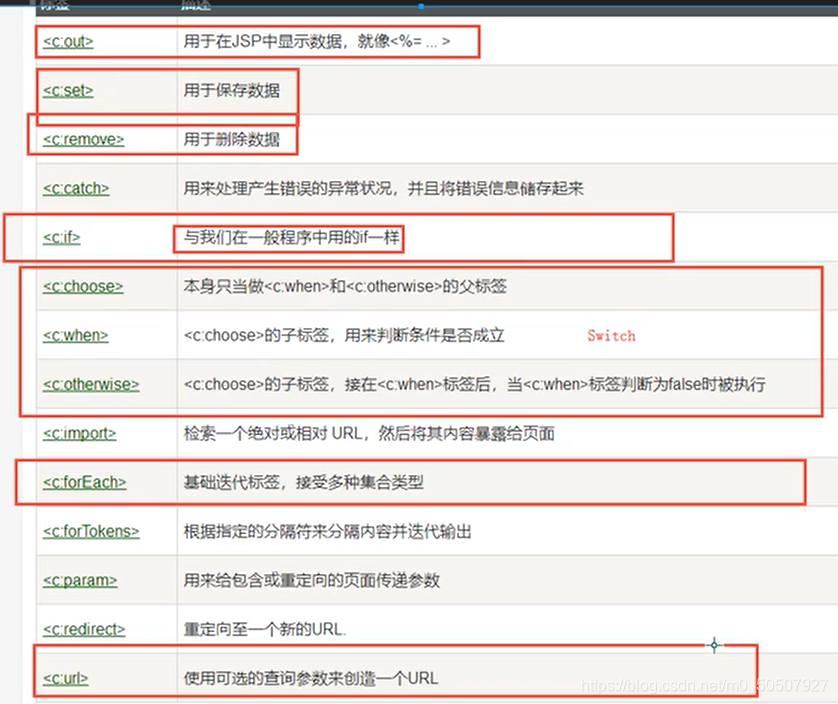
JSTL标签库使用步骤
引入对应的 taglib
使用其中的方法
在Tomcat 也需要引入 jstl的包,否则会报错:JSTL解析错误
c:if
<%--引用核心标签库--%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h4>if测试</h4>
<hr>
<form action="coreif.jsp" method="get">
<%--
EL表达式获取表单中的数据
${param.参数名}--%>
<input type="text" name="username" value="${param.username}">
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
<%--判断如果提交的用户名是管理员,则登录成功--%>
<c:if test="${param.username=='admin'}" var="isAdmin">
<c:out value="管理员欢迎您!"/>
</c:if>
<%--自闭合标签--%>
<c:out value="${isAdmin}"/>
</body>
</html>

c:choosec:when
<body>
<%--定义一个变量score,值为85--%>
<c:set var="score" value="55"/>
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${score>=90}">
你的成绩为优秀
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score>=80}">
你的成绩为一般
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score>=70}">
你的成绩为良好
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score<=60}">
你的成绩为不及格
</c:when>
</c:choose>
</body>
c:forEach
<%
ArrayList<String> people = new ArrayList<>();
people.add(0,"张三");
people.add(1,"李四");
people.add(2,"王五");
people.add(3,"赵六");
people.add(4,"田七");
request.setAttribute("list",people);
%>
<%--
var , 每一次遍历出来的变量
items, 要遍历的对象
begin, 哪里开始
end, 到哪里
step, 步长
--%>
<c:forEach var="people" items="${list}">
<c:out value="${people}"/> <br>
</c:forEach>
<hr>
<c:forEach var="people" items="${list}" begin="1" end="3" step="1" >
<c:out value="${people}"/> <br>
</c:forEach>
7,JavaBean
实体类
JavaBean有特定的写法:
必须要有一个无参构造
属性必须私有化
必须有对应的get/set方法;
一般用来和数据库的字段做映射 ORM;
ORM :对象关系映射
表—>类
字段–>属性
行记录---->对象
people表
| id | name | age | address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 18 | 法院 |
| 2 | 李四 | 18 | 派出所 |
| 3 | 王五 | 18 | 李四隔壁 |
//实体类一般都是跟数据库中的表结构一一对应
class People{
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String address;
}
class A{
new People(1,"张三",18,"法院");
new People(2,"李四",18,"派出所");
new People(3,"王五",18,"李四隔壁");
}
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page import="com.wang.pojo.People" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
People people=new People();
people.setName("李四");
people.setId(2);
people.setAge(18);
people.setAddress("派出所");
%>
<jsp:useBean id="people" class="com.wang.pojo.People" scope="page"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="people" property="name" value="张三"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="people" property="id" value="1"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="people" property="age" value="18"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="people" property="address" value="法院"/>
id:<% people.getId(); %>
name:<%people.getName(); %>
age:<%people.getAge(); %>
地址:<%people.getAddress(); %>
姓名:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="name"/>
id:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="id"/>
年龄:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="age"/>
地址:<jsp:getProperty name="people" property="address"/>
</body>
</html>
十,MVC三层架构
1,以前的架构
●什么是MVC: Model view Controller 模型、视图、控制器
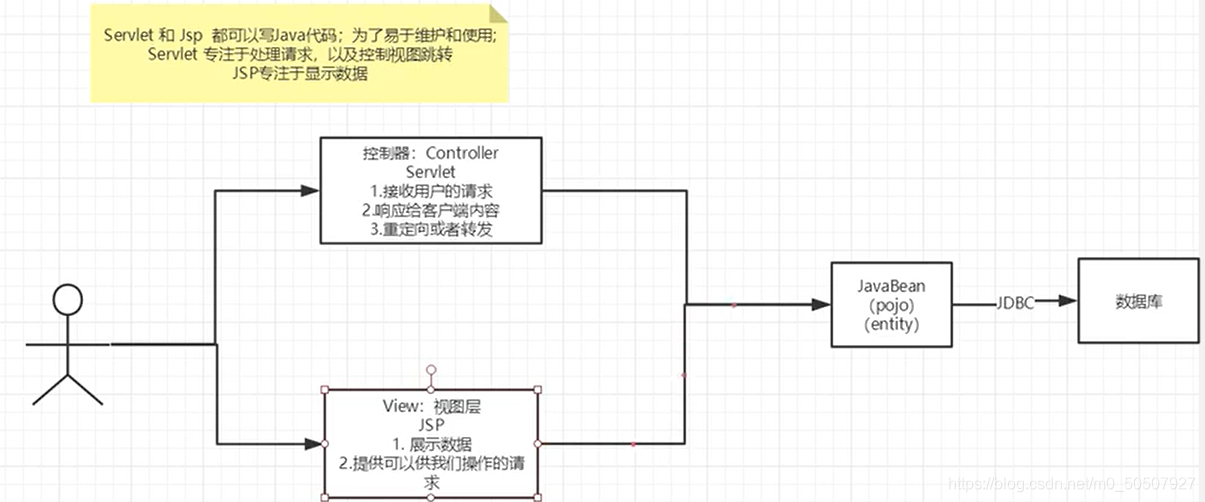
用户直接访问控制层,控制层就可以直接操作数据库;
servlet--CRUD-->数据库
弊端:程序十分臃肿,不利于维护
servlet的代码中:处理请求、响应、视图跳转、处理JDBC、处理业务代码、处理逻辑代码
架构:没有什么是加一层解决不了的!
程序猿调用
↑
JDBC (实现该接口)
↑
Mysql Oracle SqlServer ....(不同厂商)
2,MVC 三层架构

Model
●业务处理:业务逻辑(Service)
●数据持久层:CRUD
View
●展示数据
●提供链接发起 Servlet 请求(a,form,img…)
Controller (Servlet)
●接收用户的请求:(req:请求参数、Session 信息…)
●交给业务层处理对应的代码
●控制视图的跳转
登录--->接收用户的登录请求
--->处理用户的请求(获取用户登录的参数,username,password)
---->交给业务层处理登录业务(判断用户名密码是否正确:事务)
--->Dao层查询用户名和密码是否正确
-->数据库
十一,Filter
Filter:过滤器 ,用来过滤网站的数据;
●处理中文乱码
●登录验证….

Filter开发步骤:
1,导包
2,编写过滤器


Chain : 链
1. 过滤中的所有代码,在过滤特定请求的时候都会执行
2. 必须要让过滤器继续通行
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//让我们的请求继续走,如果不写,程序到这里就被拦截停止
public class CharacterEncodingFilter implements Filter {
//初始化:web服务器启动,就已经初始化了,随时等待过滤对象出现
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter初始化");
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
servletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
servletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
servletResponse.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter执行前~~~~~~");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//让我们的请求继续走,如果不写,程序到这里就被拦截停止
System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter执行后~~~~~~");
}
//销毁:web服务器关闭的时候,过滤会销毁
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter销毁");
}
}
3,在web.xml中配置 Filter
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.wang.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<!--只要是 /servlet的任何请求,会经过这个过滤器-->
<url-pattern>/servlet/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
过滤器常见应用
用户登录之后才能进入主页!用户注销后就不能进入主页了!
登录,提交到这个请求 login.jsp
<body>
<h1>登录</h1>
<form action="/servlet/login" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
找到这个请求对应的Servlet web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.LoginServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet/login</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
LoginServlet
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取前端请求的参数
String username=req.getParameter("username");
if(username.equals("admin")){
//登陆成功
req.getSession().setAttribute("USER_SESSION",req.getSession().getId());
resp.sendRedirect("/sys/success.jsp");
}else{
//登陆失败
resp.sendRedirect("/sys/error.jsp");
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}

问题:没有登陆也能进入成功页面
jsp实现:success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
Object user_session = request.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION");
if(user_session==null){
response.sendRedirect("/login.jsp");
}
%>
<h1>主页</h1>
<p><a href="/servlet/logout">注销</a></p>
</body>
</html>
解决:进入成功页面的时候要判断用户是否已经登录;要求:在过滤器中实现!
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<%--<%--%>
<%-- Object user_session = request.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION");--%>
<%-- if(user_session == null){--%>
<%-- pageContext.forward("/login.jsp");--%>
<%-- }--%>
<%--%>--%>
<h1>主页</h1>
<p><a href="/servlet/logout">注销</a> </p>
</body>
</html>
web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LogoutServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.wang.servlet.LogoutServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LogoutServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet/logout</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--注册过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>SysFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.wang.Listener.SysFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>SysFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/sys/success.jsp</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
LogoutServlet
public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Object user_session = req.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION");
if(user_session!=null){
req.getSession().removeAttribute(Constant.USER_SESSION);
resp.sendRedirect("/login.jsp");
}else {
resp.sendRedirect("/login.jsp");
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
SysFilter
public class SysFilter implements Filter {
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) resp;
Object user_session = request.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION");
if(user_session == null){
response.sendRedirect("/sys/error.jsp");
}
chain.doFilter(request,response);
}
public void destroy() {
}
}

伪代码

十二,监听器
实现一个监听器;
1,编写一个监听器,实现监听器的接口…
//统计网站在线人数:统计session
public class OnlineCountListener implements HttpSessionListener {
//创建session监听:看你的一举一动
//一旦创建session就会触发一次这个事件
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {
ServletContext context = se.getSession().getServletContext();
Integer onlineCount=(Integer)context.getAttribute("OnlineCount");
if(onlineCount==null){
onlineCount=new Integer(1);
}else{
int count=onlineCount.intValue();
onlineCount=new Integer(count+1);
}
context.setAttribute("OnlineCount",onlineCount);
}
//销毁session
//一旦销毁session就会触发一次这个事件
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {
ServletContext context = se.getSession().getServletContext();
Integer onlineCount=(Integer)context.getAttribute("OnlineCount");
if(onlineCount==null){
onlineCount=new Integer(0);
}else{
int count=onlineCount.intValue();
onlineCount=new Integer(count-1);
}
context.setAttribute("OnlineCount",onlineCount);
}
}
Session销毁:
1. 手动销毁 getSession().invalidate();
2. 自动销毁 在web.xml中配置
<session-config>
<session-timeout>1</session-timeout>
</session-config>
2,在 web.xml 中注册监听器
<!--注册监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>com.wang.Listener.OnlineCountListener</listener-class>
</listener>
3,看情况是否使用!
index.jsp
<body>
<h1>当前有<span style="color: greenyellow"><%=this.getServletConfig().getServletContext().getAttribute("OnlineCount")%></span>人在线</h1>
</body>
监听器常见应用
监听器:GUI编程中经常使用;
public class PanelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("张三牛逼");//新建一个窗体
Panel panel = new Panel(null);//面板
frame.setLayout(null);//设置窗体的布局
frame.setBounds(888,888,888,888);
frame.setBackground(new Color(97, 203, 40));//设置背景颜色
panel.setBounds(500,500,666,666);
panel.setBackground(new Color(201, 46, 206));
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowListener() {
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("打开");
}
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("关闭ing");
System.exit(0);
}
public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("关闭ed");
}
public void windowIconified(WindowEvent e) {
}
public void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e) {
}
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("激活");
}
public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("未激活");
}
});
// //监听事件,监听关闭事件
// frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
// @Override
// public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
// System.out.println("关闭ing");
// System.exit(0);
// }
// });
}
}
十三,JDBC
1,什么是JDBC :Java连接数据库!

需要jar包的支持:
●java.sql
●javax.sql
●mysql-connector-java-5.1.46 连接驱动(必须要导入)
实验环境搭建
CREATE TABLE users(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
`NAME` VARCHAR(40),
`PASSWORD` VARCHAR(40),
emai lVARCHAR(60),
birthdayDATE
);
INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,email,birthday)
VALUES(1,'六一','123456','zs@sina.com','1980-12-04');
INSERT INTO users(id,`name`,`password`,email,birthday)
VALUES(2,'lisi','123456','lisi@sina.com','1981-12-04');
INSERT INTO users(id,`name`,`password`,email,birthday)
VALUES(3,'wangwu','123888','wangwu@sina.com','1979-12-04');
INSERT INTO users(id,`name`,`password`,email,birthday)
VALUES(3,'小四','12323838','123456789@qq.com','2021-07-25');
SELECT * FROM users;

导入数据库依赖
<!--mysql的驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.32</version>
</dependency>
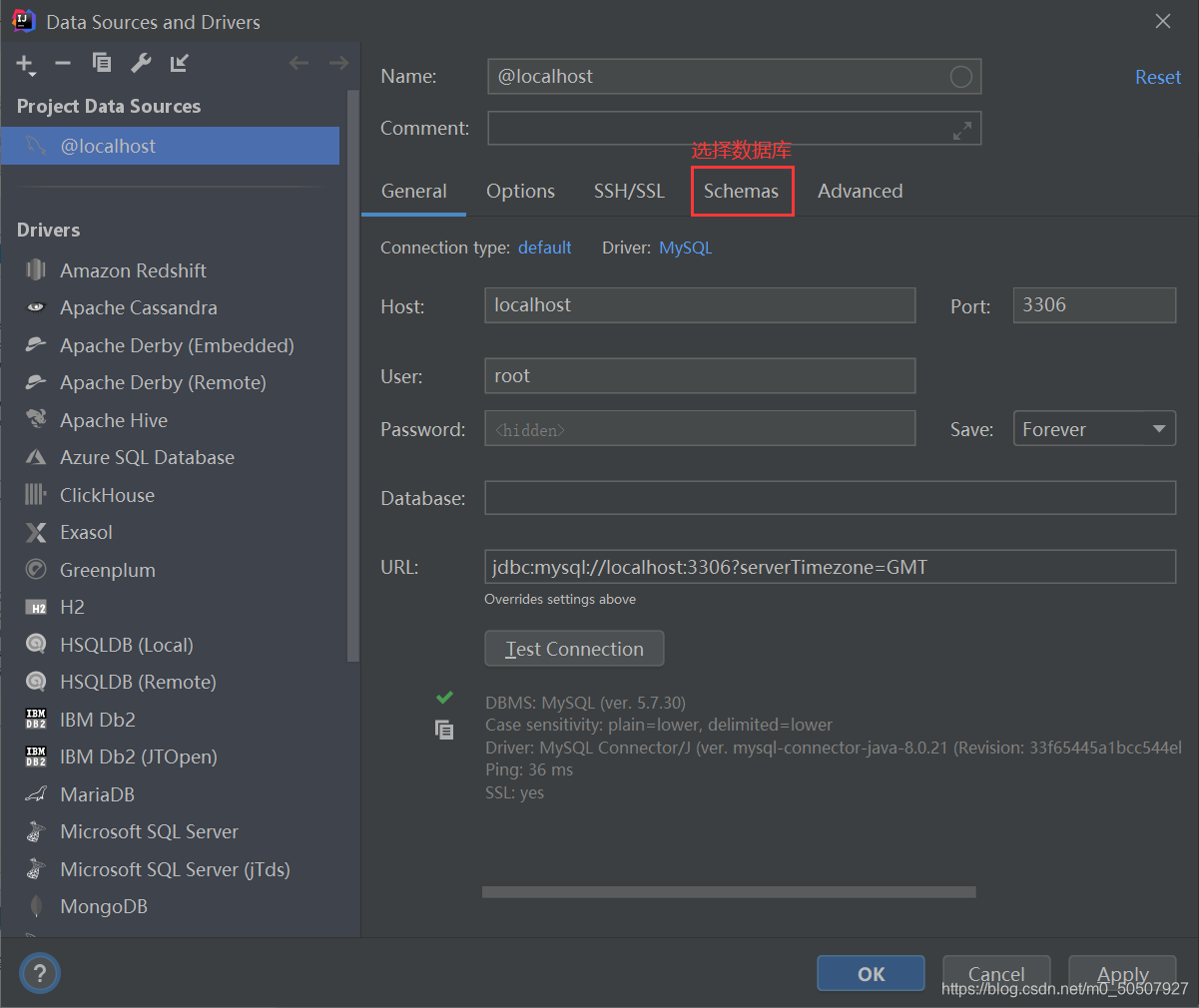
IDEA中连接数据库
2,JDBC 固定步骤
1,加载驱动
2,连接数据库,代表数据库
3,向数据库发送SQL的对象Statement : CRUD
4,编写SQL (根据业务,不同的SQL)
5,执行SQL
6,关闭连接(先开的后关)
public class JDBCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1,加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//固定写法,加载驱动
//2,用户信息和url useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=true
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//3,连接成功,数据库对象,connection代表数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4,执行sql的对象,statement执行sql的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5,执行sql的对象 去 执行sql,可能存在结果,查看返回结果
String sql="select * from users";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//返回的结果集,结果集中封装了我们全部的查询出来的结果
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("id="+resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("NAME="+resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println("PASSWORD="+resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("email="+resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birthday="+resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
}
//6,释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
预编译SQL
public class JDBCTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1,加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//固定写法,加载驱动
//2,用户信息和url useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=true
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//3,连接成功,数据库对象,connection代表数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4.编写SQL
String sql = "insert into jdbcstudy.users(id, NAME, PASSWORD, email, birthday) values (?,?,?,?,?);";
//5.预编译
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,5);//给第一个占位符? 的值赋值为1;
preparedStatement.setString(2,"张三");//给第二个占位符? 的值赋值为狂神说Java;
preparedStatement.setString(3,"123456");//给第三个占位符? 的值赋值为123456;
preparedStatement.setString(4,"24736743@qq.com");//给第四个占位符? 的值赋值为1;
preparedStatement.setDate(5,new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));//给第五个占位符? 的值赋值为new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime());
//6.执行SQL
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
//6,释放连接
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Junit单元测试
依赖
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
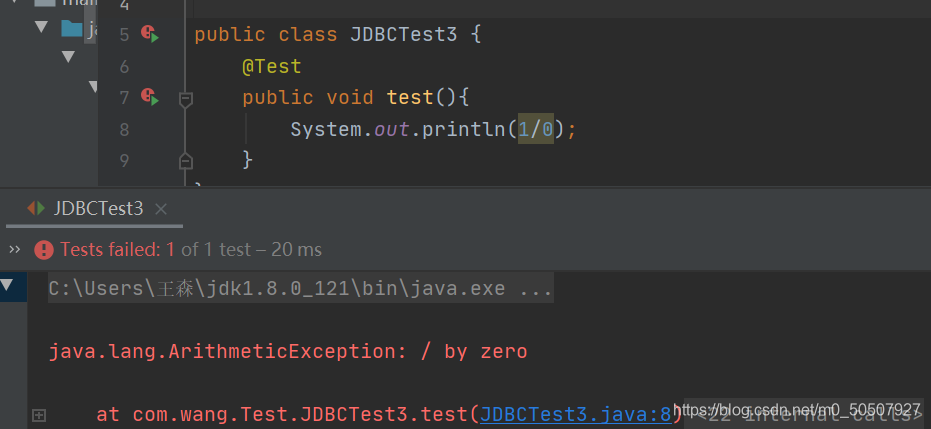
简单使用
@Test注解只有在方法上有效,只要加了这个注解的方法,就可以直接运行!

失败的时候是红色:
3,事务
要么都成功,要么都失败!
ACID原则:保证数据的安全。
开启事务
事务提交 commit()
事务回滚 rollback()
关闭事务
转账:
A:1000
B:1000
A(900) --100--> B(1100)
搭建一个环境
CREATE TABLE account(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(40),
money FLOAT
);
INSERT INTO account(`name`,money) VALUES('A',1000);
INSERT INTO account(`name`,money) VALUES('B',1000);
INSERT INTO account(`name`,money) VALUES('C',1000);

测试事务
1,开启事务conn.setAutoCommit(false);
2,一组业务执行完毕,提交事务
3,可以在catch语句中显示的定义回滚,但是默认失败会回滚
代码:
public class JDBCTest3 {
@Test
public void test() {
//用户信息和url useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=true
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
Connection connection = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.连接数据库,代表数据库
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.通知数据库开启事务,false 开启
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "update jdbcstudy.account set money = money-100 where name = 'A'";
connection.prepareStatement(sql).executeUpdate();
//制造错误
//int i=1/0;
String sql2 = "update jdbcstudy.account set money = money+100 where name = 'B'";
connection.prepareStatement(sql2).executeUpdate();
connection.commit();//以上两条SQL都执行成功了,就提交事务!
System.out.println("success");
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
//如果出现异常,就通知数据库回滚事务
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








