(仅供个人参考)
摘要:Domain adaptation is an important task to enable learning when labels are scarce. While most works focus only on the image modality , there are many important multi-modal datasets. In order to leverage multi-modality for domain adaptation, we propose cross-modal learning, where we enforce consistency between the predictions of two modalities via mutual mimicking. We constrain our network to make correct predictions on labeled data and consistent predictions across modalities on unlabeled target-domain data.Experiments in unsupervised and semi-supervised domain adaptation settings prove the effectiveness of this novel domain adaptation strategy . Specifically, we evaluate on the task of 3D semantic segmentation from either the 2D image, the 3D point cloud or from both. We leverage recent driving datasets to produce a wide variety of domain adaptation scenarios including changes in scene layout,lighting, sensor setup and weather , as well as the synthetic-to-real setup. Our method significantly improves over previous uni-modal adaptation baselines on all adaption scenarios.
提出一种DA方法,将其用在无监督场景和半监督场景,分别为xMUDA和xMoSSDA
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (xMUDA)
xMUDA通过2D/3D之间的跨模态学习,从源域的监督和目标域的自我监督中学习。
考虑四个数据子集:源2D、目标2D、源3D和目标3D。


其中,Lseg和LxM如下

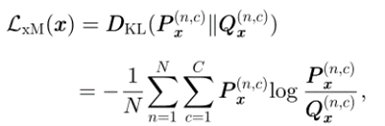
最终目标为源域数据上的损失Lseg和两个域上的跨模态损失LxM的组合:

引入了跨模态的自我训练机制,再次从头开始训练,使用Pseudo-Labels在目标域训练集上进行额外的分割损失,优化如下:
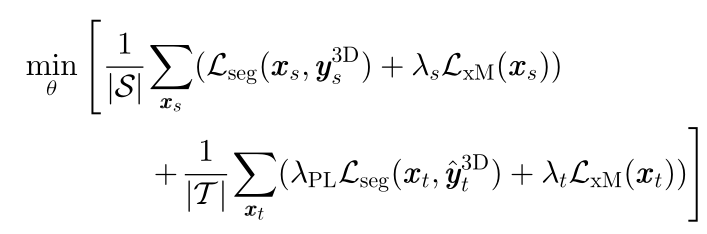
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation (xMoSSDA)
与无监督学习不同:
1目标域集由一个通常很小的标记组成
2 Lseg不仅使用在源域数据集S上,也在标记的目标域数据集上

同理xMUDA,加入Pseudo-Labels

总而言之,相互预测的想法非常不错,未来做多模态的可以参考。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








