1.入门
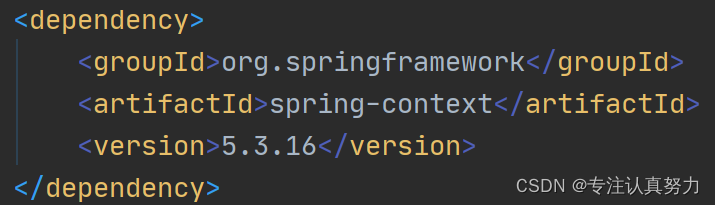
1.创建maven项目,导入spring-context坐标
2.创建UserDao接口和实现该接口的UserDaoImpl类
3.创建Spring配置文件applicationContext.xml
4.在applicationContext.xml中注册UserDaoImpl,指定类的id和全限定名
5.利用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext创建对象管理容器context
6.根据context.getBean(“类id”,类.class)从容器中获得类的实例对象
2.Bean标签
1、作用
用于配置对象让spring来创建的,默认情况下它调用的是类中的无参构造函数,如果没有无参构造函数则不能创建成功。
2、属性
- id:给对象在容器中提供一个唯一标识。用于获取对象。
- class:指定类的全限定类名。用于反射创建对象。默认情况下调用无参构造函数。
- scope:指定对象的作用范围。
singleton:默认值,单例的
prototype:多例的
- init-method:指定类中的初始化方法名称
- destroy-method:指定类中销毁方法名称
3、bean的作用范围和生命周期
单例对象:scope=“singleton”:一个应用只有一个对象的实例。它的作用范围就是整个引用。
生命周期
对象出生:当应用加载,创建容器时,对象就被创建了。
对象活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着。
对象死亡:当应用卸载,销毁容器时,对象就被销毁了。
多例对象:scope=“prototype”:每次访问对象时,都会重新创建对象实例。
生命周期
对象出生:当使用对象时,创建新的对象实例。
对象活着:只要对象在使用中,就一直活着。
对象死亡:当对象长时间不用时,被java的垃圾回收器gc回收了。
4、实例化bean的三种方式
4.1、方式一(无参构造方法实例化)
<!--在默认情况下:它会根据默认无参构造函数来创建类对象。如果bean中没有默认无参构造函数,将会创建失败-->
<bean id="customerService" class="com.hao.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl"/>
4.2、方式二(工厂静态方法实例化)
/**
- 模拟一个静态工厂,创建业务层实现类
*/
public class StaticFactory {
public static ICustomerService createCustomerService(){
return new CustomerServiceImpl();
}
}
<!-- 此种方式是:
使用StaticFactory类中的静态方法createCustomerService创建对象,并存入spring容器
id属性:指定bean的id,用于从容器中获取
class属性:指定静态工厂的全限定类名
factory-method属性:指定生产对象的静态方法
-->
<bean id="customerService"
class="com.hao.factory.StaticFactory"
factory-method="createCustomerService"></bean>
4.3、方式三(工厂实例方法实例化)
/**
- 模拟一个实例工厂,创建业务层实现类
- 此工厂创建对象,必须现有工厂实例对象,再调用方法
*/
public class InstanceFactory {
public ICustomerService createCustomerService(){
return new CustomerServiceImpl();
}
}
<!-- 此种方式是:
先把工厂的创建交给spring来管理。
然后在使用工厂的bean来调用里面的方法
factory-bean属性:用于指定实例工厂bean的id。
factory-method属性:用于指定实例工厂中创建对象的方法。
-->
<bean id="instancFactory" class="com.hao.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="customerService"
factory-bean="instancFactory"
factory-method="createCustomerService"></bean>
3.依赖注入DI
需求描述:容器在创建实例时实现属性值注入
解决方式:set方法注入
<!--引用类型注入-->
<property name="" ref=""></property>
<!--普通类型注入-->
<property name="" value=""></property>
<!--集合类型注入-->
<property name="">
<list>
<value></value>
<value></value>
</list>
</property>
<!--键值对类型注入-->
<property name="">
<map>
<entry key="" value-ref=""></entry>
<entry key="" value-ref=""></entry>
</map>
</property>
4.配置数据源(druid)
步骤:
1.导入数据源和数据库驱动坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
2.创建数据源对象
3.设置数据源的基本连接数据(driver,url,name,password)
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
<!--加载外部properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!--容器创建数据源对象-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
4.获取和归还数据库连接资源
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DruidDataSource dataSource = context.getBean("dataSource", DruidDataSource.class);
DruidPooledConnection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
5.注解
在类前面注解,可以省略全限定类名。


注:在Spring配置文件中添加组件扫描
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hao"/>
6.集成Junit
①导入spring集成Junit的坐标
<!--此处需要注意的是,spring5 及以上版本要求 junit 的版本必须是 4.12 及以上-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.16</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
②使用@Runwith注解替换原来的运行期
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class SpringJunitTest {
}
③使用@ContextConfiguration指定配置文件或配置类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//加载spring核心配置文件
//@ContextConfiguration(value = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
//加载spring核心配置类
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfiguration.class})
public class SpringJunitTest {
}
④使用@Autowired注入需要测试的对象
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfiguration.class})
public class SpringJunitTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
}
⑤创建测试方法进行测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfiguration.class})public class SpringJunitTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testUserService(){
userService.save();
}
}
7.集成Web
1.导入依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.16</version>
</dependency>
2.在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器
<!--全局参数-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--Spring的监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
3.使用WebApplicationContextUtils获得应用上下文对象ApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(request.getServletContext());
Account account = (Account) webApplicationContext.getBean("account");
System.out.println(account);























 3504
3504

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








