异步通知概念
当设备就绪的时候,主动通知应用程序。
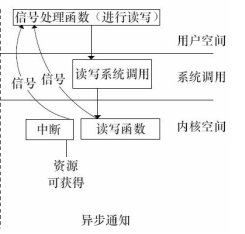
设备驱动支持异步通知代码
index 452df8f..b0a1038 100644
@@ -40,6 +40,7 @@ struct globalfifo_dev
struct mutex mutex;
wait_queue_head_t r_wait;
wait_queue_head_t w_wait;
+ struct fasync_struct *async_queue;
};
static struct globalfifo_dev *globalfifo_devp = NULL;
@@ -270,6 +271,11 @@ static ssize_t globalfifo_write (struct file *filep, const char __user *buf, siz
#ifdef globalfifo_debug
printk(KERN_DEBUG "globalfifo_write = %s\n", dev->mem);
#endif
+ if (dev->async_queue) // post readable signal when async
+ {
+ kill_fasync(&dev->async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
+ printk("%s kill SIGIO\n", __func__);
+ }
}
out:
@@ -347,8 +353,16 @@ static int globalfifo_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filep)
return 0;
}
+static int globalfifo_fasync (int fd, struct file *filep, int mode)
+{
+ struct globalfifo_dev *dev = filep->private_data;
+ return fasync_helper(fd, filep, mode, &dev->async_queue);
+}
+
static int globalfifo_release (struct inode *inode, struct file *filep)
{
+ // remove async function form the async queue
+ globalfifo_fasync(-1, filep, 0);
return 0;
}
@@ -362,6 +376,7 @@ static struct file_operations chrdev_file_operations =
.open = globalfifo_open,
.release = globalfifo_release,
.poll = globalfifo_poll,
+ .fasync = globalfifo_fasync, // binging the interface @fasync
};
/**
增加异步IO应用层编码
/**
** This file is part of the LinuxTrainningCompany project.
** Copyright (C) duanzhonghuan Co., Ltd.
** All Rights Reserved.
** Unauthorized copying of this file, via any medium is strictly prohibited
** Proprietary and confidential
**
** Written by duanzhonghuan <15818411038@163.com>, 2019/5/18
**/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "unistd.h"
void signal_handle(int signo)
{
printf("Have caught the Signal: %d\n", signo);
exit(0);
}
int main(void)
{
int fd, oflags;
fd = open("/dev/globalfifo", O_RDWR);
if (fd != -1)
{
// if the signal @SIGIO is captured,
// the function of @signal_handle is called
signal(SIGIO, signal_handle);
// set one of the @fd owners as the process
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
// receive the asynchronous sinals
oflags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, oflags | O_ASYNC);
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
}
}
else
{
printf("open /dev/globalfifo failed \n");
}
#if 0
signal(SIGINT, signal_handle);
signal(SIGTERM, signal_handle);
while(1) {}
#endif
return 0;
}
由此可见,为了能在用户空间中处理一个设备释放的信号,它必须完成3项工作。
1)通过F_SETOWN IO控制命令设置设备文件的拥有者为本进程,这样从设备驱动发出的信号才能被本进程接收到。
2)通过F_SETFL IO控制命令设置设备文件以支持FASYNC,即异步通知模式。
3)通过signal()函数连接信号和信号处理函数。
AIO
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
有关AIO的介绍可参考Asynchronous I/O and vectored operations
总结
- 使用信号可以实现设备驱动与用户程序之间的异步通知。我们利用这个特性与设备驱动进行通信。
- 关于AIO,drivers/char/mem.c里实现的null、zero驱动是通过AIO机制实现的。








 博客介绍了设备驱动的异步通知,即设备就绪时主动通知应用程序。为在用户空间处理设备信号,需完成设置设备文件拥有者、支持异步通知模式、连接信号和处理函数3项工作。还提及AIO,null、zero驱动通过AIO机制实现,可利用信号特性与设备驱动通信。
博客介绍了设备驱动的异步通知,即设备就绪时主动通知应用程序。为在用户空间处理设备信号,需完成设置设备文件拥有者、支持异步通知模式、连接信号和处理函数3项工作。还提及AIO,null、zero驱动通过AIO机制实现,可利用信号特性与设备驱动通信。
















 383
383

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








