公平模式_TransferQueue(队列实现)
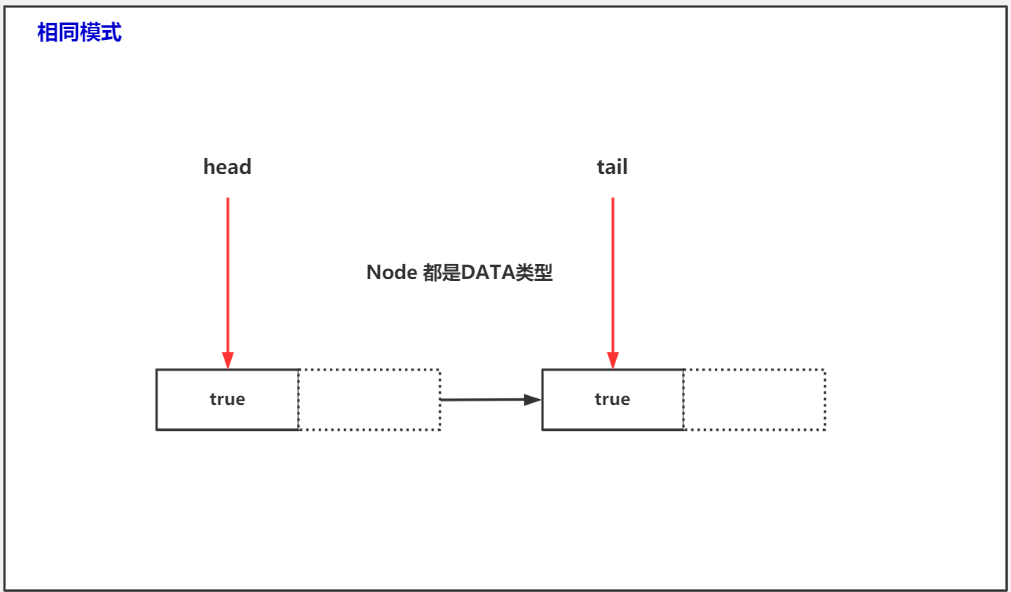
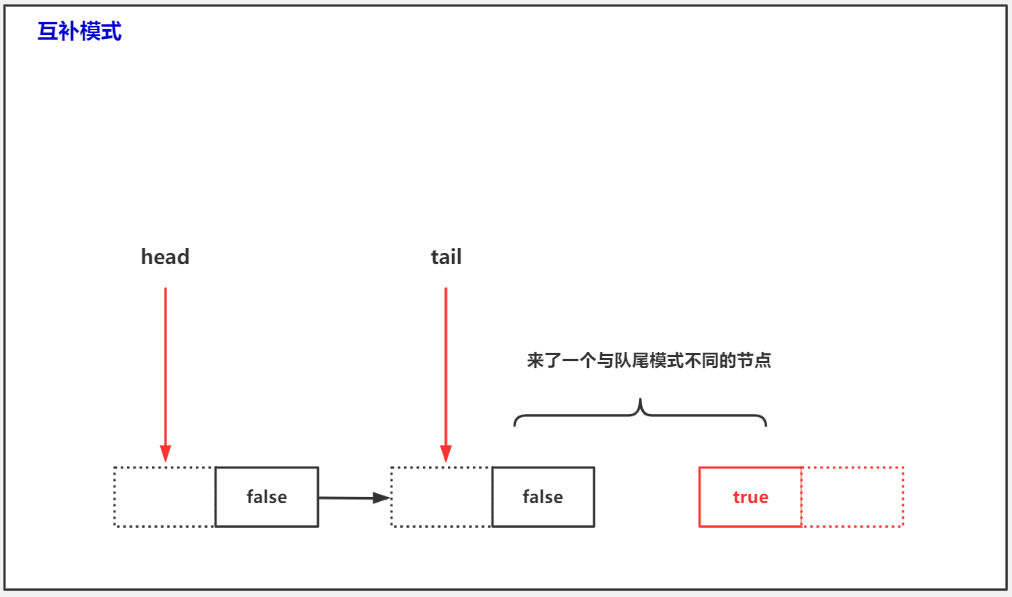
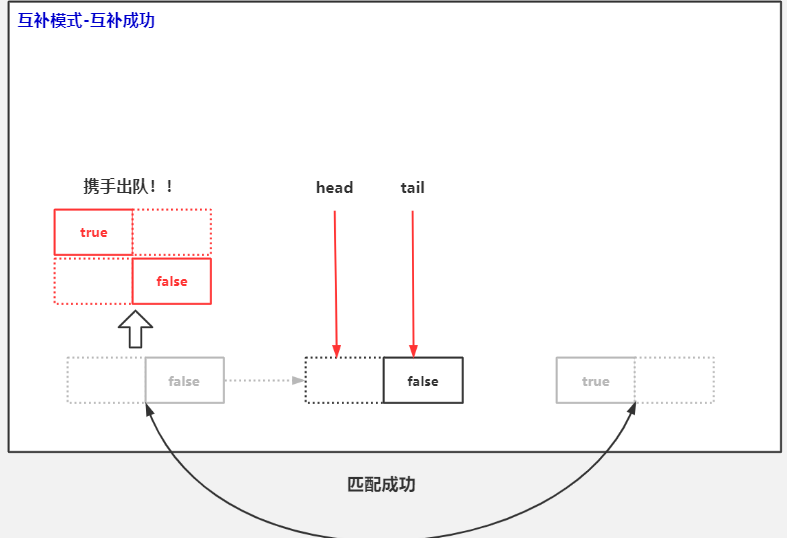
公平模式实现的同步队列
/** Dual Queue */
/**
* 公平模式同步队列
*/
static final class TransferQueue<E> extends Transferer<E> {
static final class QNode {
//指向当前节点的下一个节点,组装链表使用的。
volatile QNode next; // next node in queue
//数据域 Node代表的是DATA类型,item表示数据 否则 Node代表的REQUEST类型,item == null
volatile Object item; // CAS'ed to or from null
//当Node对应的线程 未匹配到节点时,对应的线程 最终会挂起,挂起之前会保留 线程引用到waiter ,
//方法 其它Node匹配当前节点时 唤醒 当前线程..
volatile Thread waiter; // to control park/unpark
//true 当前Node是一个DATA类型 false表示当前Node是一个REQUEST类型。
final boolean isData;
QNode(Object item, boolean isData) {
this.item = item;
this.isData = isData;
}
//修改当前节点next引用
boolean casNext(QNode cmp, QNode val) {
return next == cmp &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
//修改当前节点数据域item
boolean casItem(Object cmp, Object val) {
return item == cmp &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* Tries to cancel by CAS'ing ref to this as item.
* 尝试取消当前node
* 取消状态的Node,它的item域,指向自己Node。
*/
void tryCancel(Object cmp) {
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, this);
}
//判断当前Node是否为取消状态
boolean isCancelled() {
return item == this;
}
/**
* Returns true if this node is known to be off the queue
* because its next pointer has been forgotten due to
* an advanceHead operation.
*
* 判断当前节点是否 “不在” 队列内,当next指向自己时,说明节点已经出队。
*/
boolean isOffList() {
return next == this;
}
//指向队列的dummy节点
transient volatile QNode head;
/** Tail of queue */
//指向队列的尾节点。
transient volatile QNode tail;
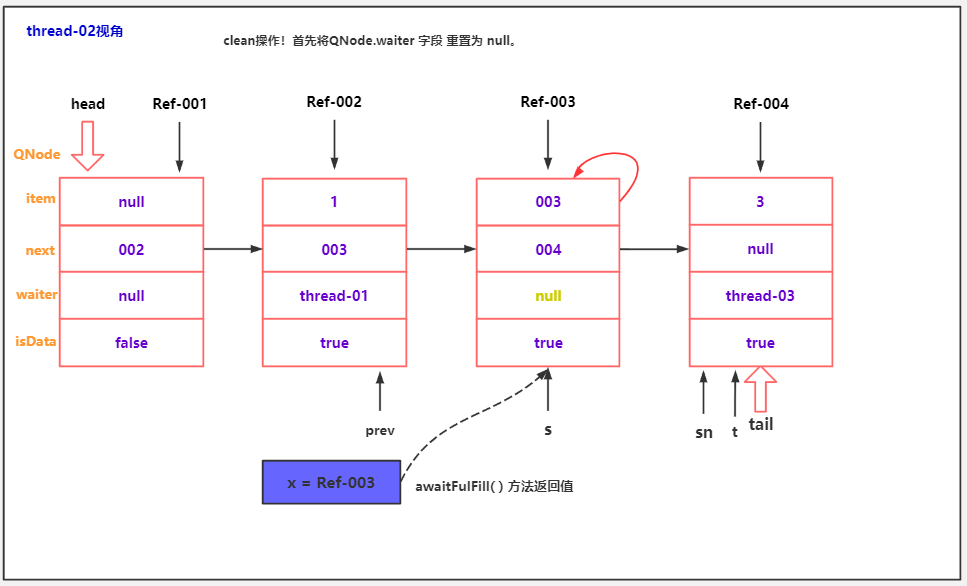
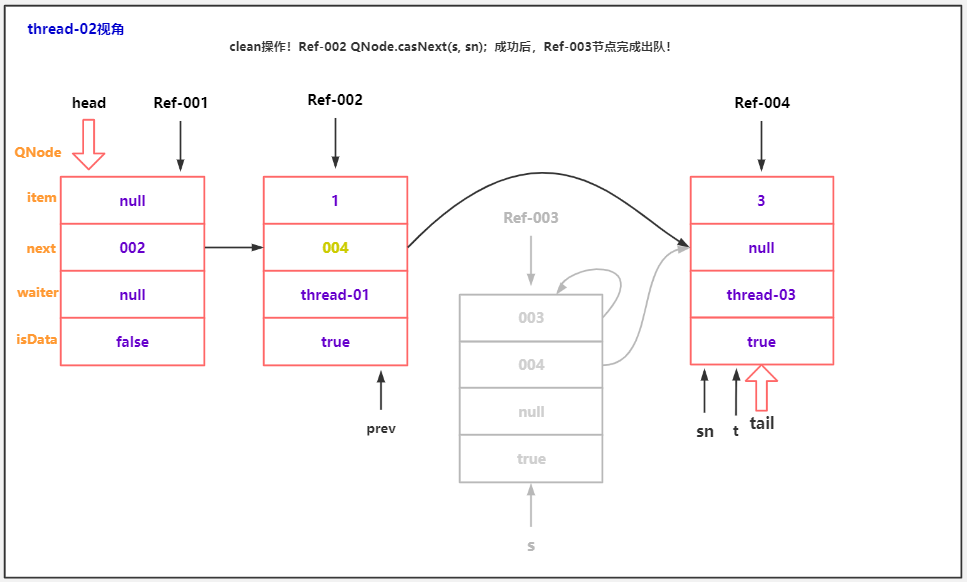
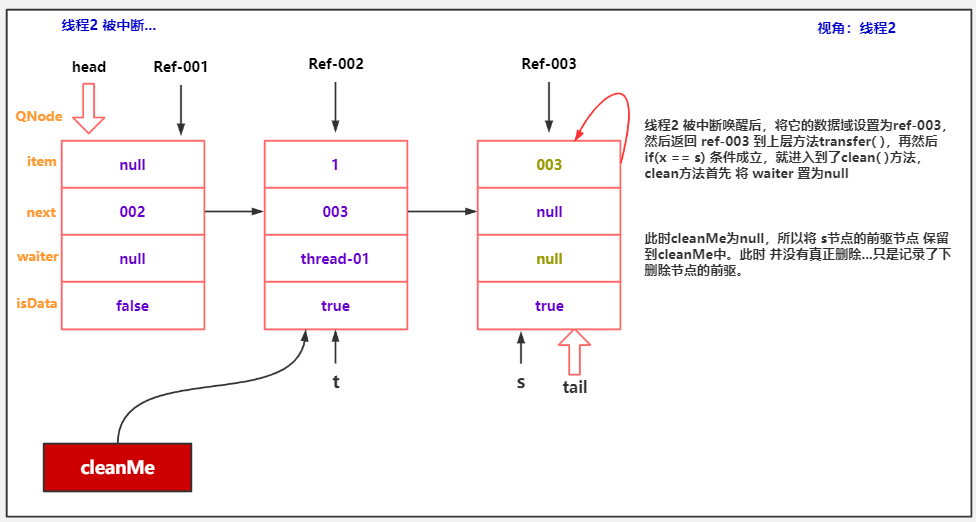
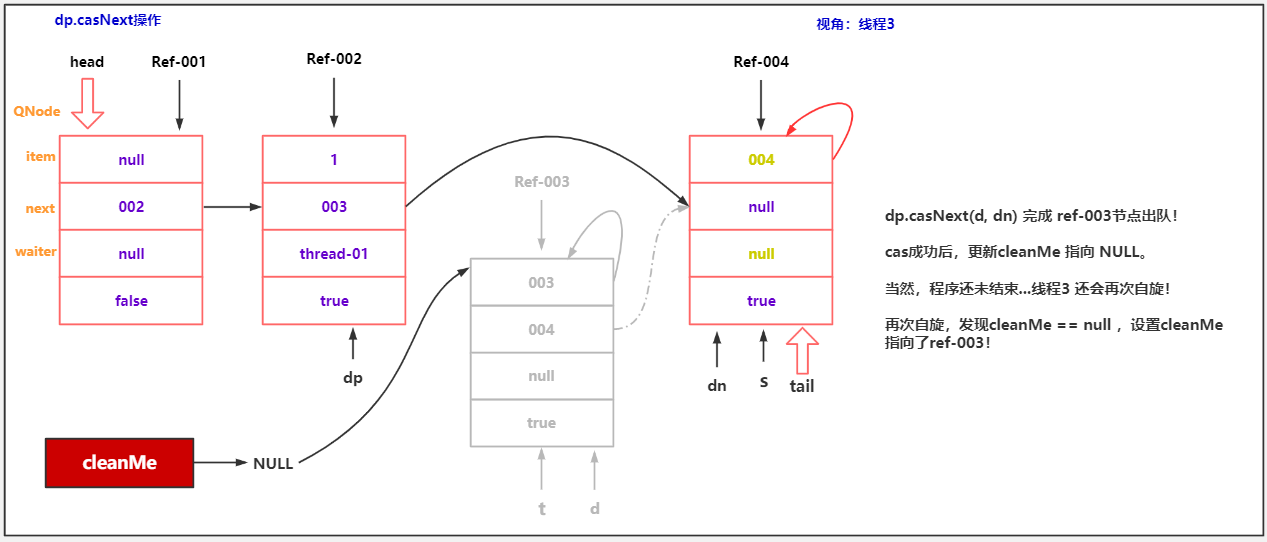
/* 表示被清理节点的前驱节点。因为入队操作是 两步完成的,
* 第一步:t.next = newNode
* 第二步:tail = newNode
* 所以,队尾节点出队,是一种非常特殊的情况,需要特殊处理,回头讲!
*/
transient volatile QNode cleanMe;
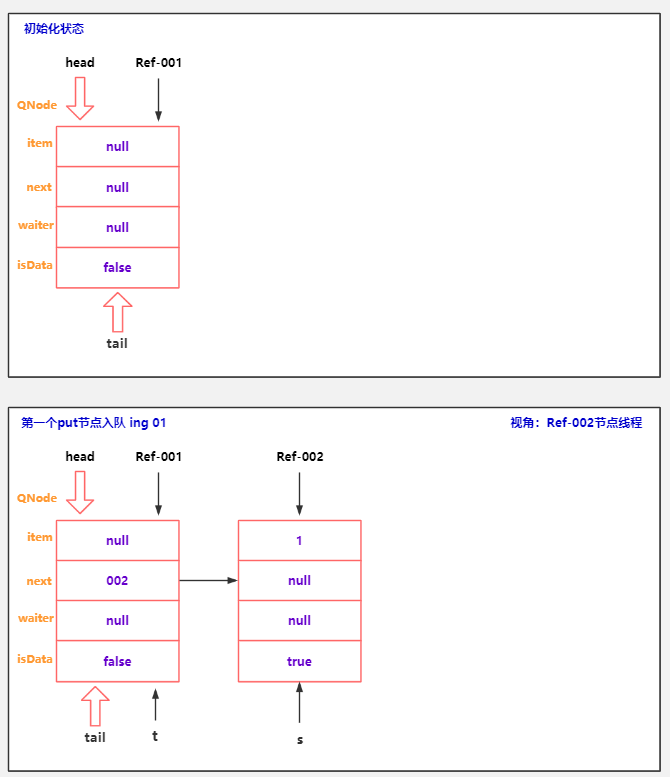
TransferQueue() {
QNode h = new QNode(null, false); // initialize to dummy node.
head = h;
tail = h;
}
/**
* Tries to cas nh as new head; if successful, unlink
* old head's next node to avoid garbage retention.
* 设置头指针指向新的节点,蕴含操作:老的头节点出队。
*/
void advanceHead(QNode h, QNode nh) {
if (h == head &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, h, nh))
h.next = h; // forget old next
}
/**
* Tries to cas nt as new tail.
* 更新队尾节点 为新的队尾。
* @param t 老的队尾
* @param nt 新的队尾
*/
void advanceTail(QNode t, QNode nt) {
if (tail == t)
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, t, nt);
}
/**
* Puts or takes an item.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E transfer(E e, boolean timed, long nanos) {
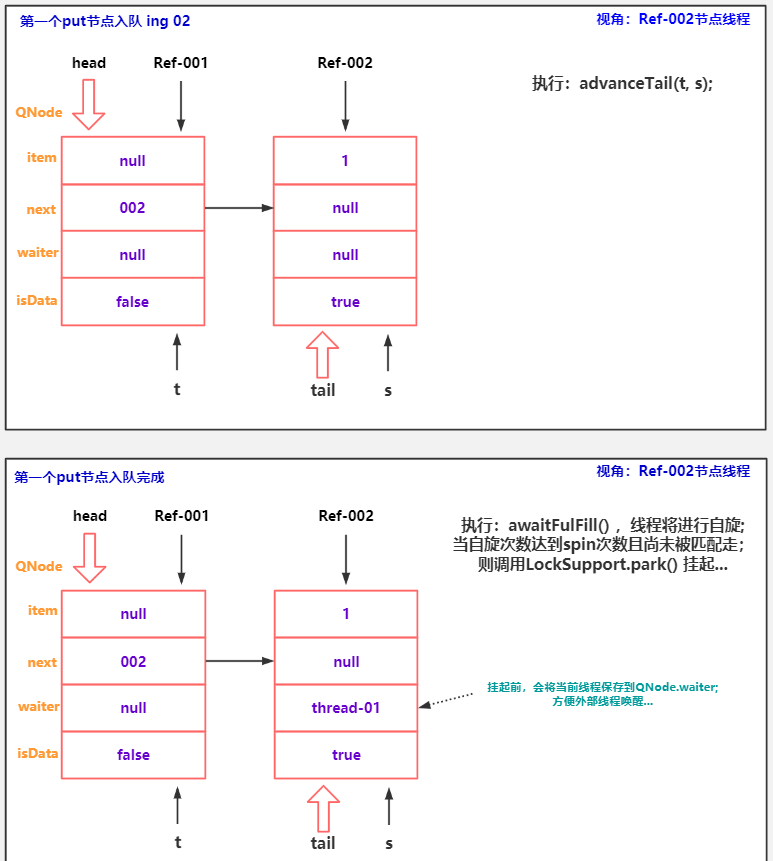
//s 指向当前请求 对应Node
QNode s = null; // constructed/reused as needed
//isData == true 表示 当前请求是一个写数据操作(DATA) 否则isData == false 表示当前请求是一个 REQUEST操作。
boolean isData = (e != null);
//自旋..
for (;;) {
QNode t = tail;
QNode h = head;
if (t == null || h == null) // saw uninitialized value
continue; // spin
//CASE1:入队
//条件一:成立,说明head和tail同时指向dummy节点,当前队列实际情况 就是 空队列。此时当前请求需要做入队操作,因为没有任何节点 可以去匹配。
//条件二:队列不是空,队尾节点与当前请求类型是一致的情况。说明也是无法完成匹配操作的情况,此时当前节点只能入队...
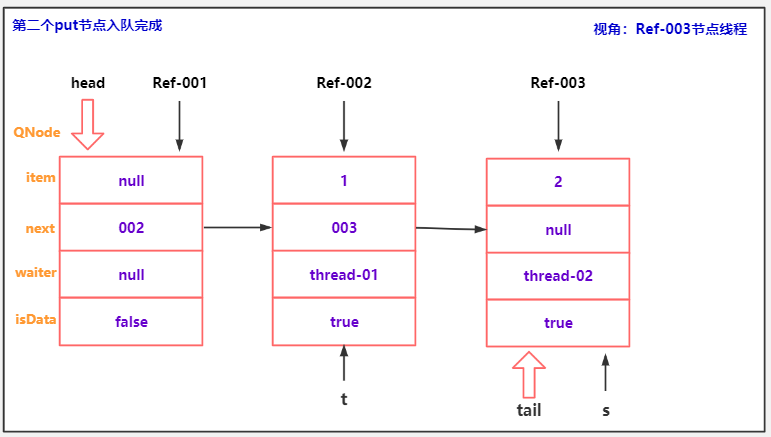
if (h == t || t.isData == isData) { // empty or same-mode
//获取当前队尾t 的next节点 tn - t.next
QNode tn = t.next;
//因为多线程环境,当前线程在入队之前,其它线程有可能已经入队过了..改变了 tail 引用。
if (t != tail) // inconsistent read
//线程回到自旋...再选择路径执行。
continue;
//条件成立:说明已经有线程 入队了,且只完成了 入队的 第一步:设置t.next = newNode, 第二步可能尚未完成..
if (tn != null) { // lagging tail
//协助更新tail 指向新的 尾结点。
advanceTail(t, tn);
//线程回到自旋...再选择路径执行。
continue;
}
//条件成立:说明当前调用transfer方法的 上层方法 可能是 offer() 无参的这种方法进来的,这种方法不支持 阻塞等待...
if (timed && nanos <= 0) // can't wait
//检查未匹配到,直接返回null。
return null;
//条件成立:说明当前请求尚未 创建对应的node
if (s == null)
//创建node过程...
s = new QNode(e, isData);
//条件 不成立:!t.casNext(null, s) 说明当前t仍然是tail,当前线程对应的Node入队的第一步 完成!
if (!t.casNext(null, s)) // failed to link in
continue;
//更新队尾 为咱们请求节点。
advanceTail(t, s); // swing tail and wait
//当前节点 等待匹配....
//当前请求为DATA模式时:e 请求带来的数据
//x == this 当前SNode对应的线程 取消状态
//x == null 表示已经有匹配节点了,并且匹配节点拿走了item数据。
//当前请求为REQUEST模式时:e == null
//x == this 当前SNode对应的线程 取消状态
//x != null 且 item != this 表示当前REQUEST类型的Node已经匹配到一个DATA类型的Node了。
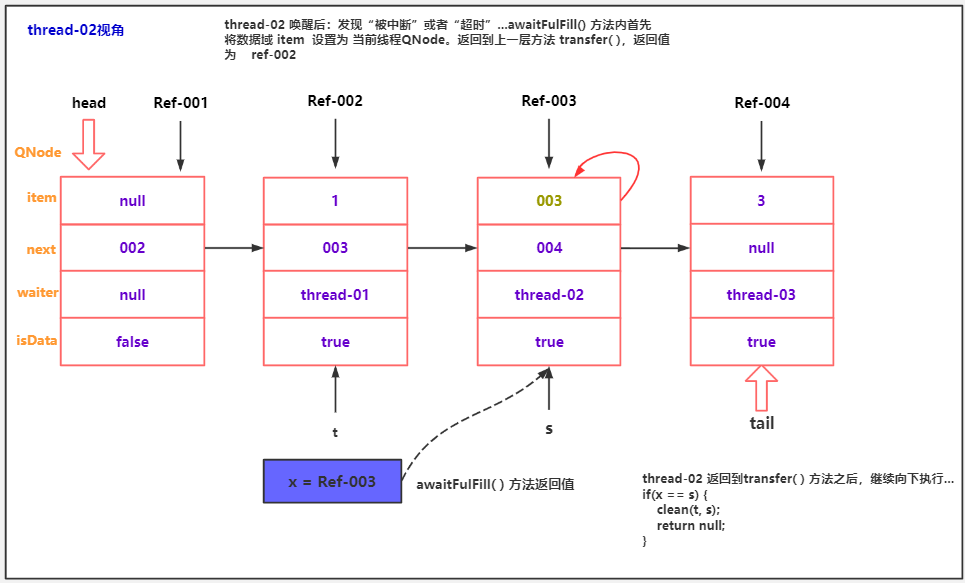
Object x = awaitFulfill(s, e, timed, nanos);
//说明当前Node状态为 取消状态,需要做 出队逻辑。
if (x == s) { // wait was cancelled
//清理出队逻辑,最后讲。
clean(t, s);
return null;
}
//执行到这里说明 当前Node 匹配成功了...
//1.当前线程在awaitFulfill方法内,已经挂起了...此时运行到这里时是被 匹配节点的线程使用LockSupport.unpark() 唤醒的..
//被唤醒:当前请求对应的节点,肯定已经出队了,因为匹配者线程 是先让当前Node出队的,再唤醒当前Node对应线程的。
//2.当前线程在awaitFulfill方法内,处于自旋状态...此时匹配节点 匹配后,它检查发现了,然后返回到上层transfer方法的。
//自旋状态返回时:当前请求对应的节点,不一定就出队了...
//被唤醒时:s.isOffList() 条件会成立。 !s.isOffList() 不会成立。
//条件成立:说明当前Node仍然在队列内,需要做 匹配成功后 出队逻辑。
if (!s.isOffList()) { // not already unlinked
//其实这里面做的事情,就是防止当前Node是自旋检查状态时发现 被匹配了,然后当前线程 需要将
//当前线程对应的Node做出队逻辑.
//t 当前s节点的前驱节点,更新dummy节点为 s节点。表示head.next节点已经出队了...
advanceHead(t, s); // unlink if head
//x != null 且 item != this 表示当前REQUEST类型的Node已经匹配到一个DATA类型的Node了。
//因为s节点已经出队了,所以需要把它的item域 给设置为它自己,表示它是个取消出队状态。
if (x != null) // and forget fields
s.item = s;
//因为s已经出队,所以waiter一定要保证是null。
s.waiter = null;
}
//x != null 成立,说明当前请求是REQUEST类型,返回匹配到的数据x
//x != null 不成立,说明当前请求是DATA类型,返回DATA请求时的e。
return (x != null) ? (E)x : e;
}
//CASE2:队尾节点 与 当前请求节点 互补 (队尾->DATA,请求类型->REQUEST) (队尾->REQUEST, 请求类型->DATA)
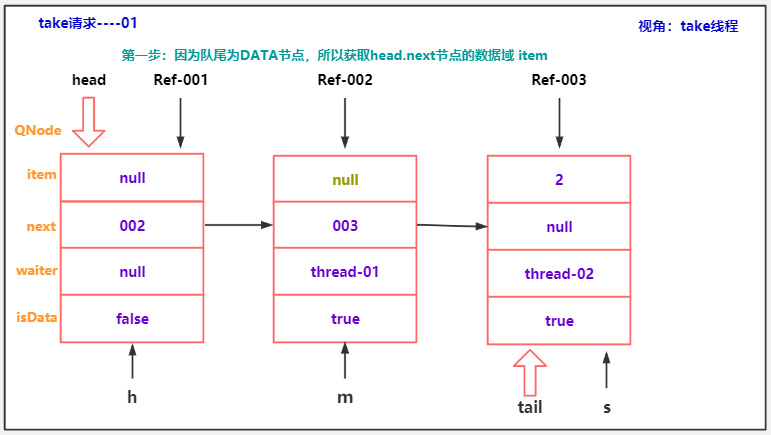
else { // complementary-mode
//h.next节点 其实是真正的队头,请求节点 与队尾模式不同,需要与队头 发生匹配。因为TransferQueue是一个 公平模式
QNode m = h.next; // node to fulfill
//条件一:t != tail 什么时候成立呢? 肯定是并发导致的,其它线程已经修改过tail了,有其它线程入队过了..当前线程看到的是过期数据,需要重新循环
//条件二:m == null 什么时候成立呢? 肯定是其它请求先当前请求一步,匹配走了head.next节点。
//条件三:条件成立,说明已经有其它请求匹配走head.next了。。。当前线程看到的是过期数据。。。重新循环...
if (t != tail || m == null || h != head)
continue; // inconsistent read
//执行到这里,说明t m h 不是过期数据,是准确数据。目前来看是准确的!
//获取匹配节点的数据域 保存到x
Object x = m.item;
//条件一:isData == (x != null)
//isData 表示当前请求是什么类型 isData == true:当前请求是DATA类型 isData == false:当前请求是REQUEST类型。
//1.假设isData == true DATA类型
//m其实表示的是 REQUEST 类型的NODE,它的数据域是 null => x==null
//true == (null != null) => true == false => false
//2.假设isData == false REQUEST类型
//m其实表示的是 DATA 类型的NODE,它的数据域是 提交是的e ,并且e != null。
//false == (obj != null) => false == true => false
//总结:正常情况下,条件一不会成立。
//条件二:条件成立,说明m节点已经是 取消状态了...不能完成匹配,当前请求需要continue,再重新选择路径执行了..
//条件三:!m.casItem(x, e),前提条件 m 非取消状态。
//1.假设当前请求为REQUEST类型 e == null
//m 是 DATA类型了...
//相当于将匹配的DATA Node的数据域清空了,相当于REQUEST 拿走了 它的数据。
//2.假设当前请求为DATA类型 e != null
//m 是 REQUEST类型了...
//相当于将匹配的REQUEST Node的数据域 填充了,填充了 当前DATA 的 数据。相当于传递给REQUEST请求数据了...
if (isData == (x != null) || // m already fulfilled
x == m || // m cancelled
!m.casItem(x, e)) { // lost CAS
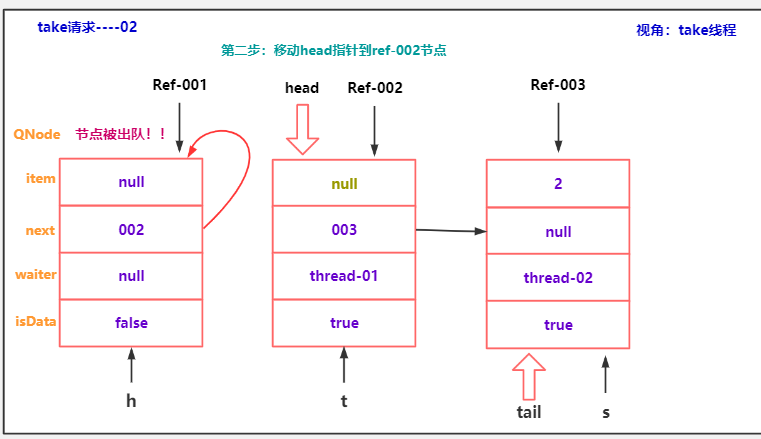
advanceHead(h, m); // dequeue and retry
continue;
}
//执行到这里,说明匹配已经完成了,匹配完成后,需要做什么?
//1.将真正的头节点 出队。让这个真正的头结点成为dummy节点
advanceHead(h, m); // successfully fulfilled
//2.唤醒匹配节点的线程..
LockSupport.unpark(m.waiter);
//x != null 成立,说明当前请求是REQUEST类型,返回匹配到的数据x
//x != null 不成立,说明当前请求是DATA类型,返回DATA请求时的e。
return (x != null) ? (E)x : e;
}
}
}
SuppressWarnings -》 awaitFulfill
Object awaitFulfill(QNode s, E e, boolean timed, long nanos) {
/* Same idea as TransferStack.awaitFulfill */
//deadline 表示等待截止时间...
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
//当前请求节点的线程..
Thread w = Thread.currentThread();
//允许自旋检查的次数..
int spins = ((head.next == s) ?
(timed ? maxTimedSpins : maxUntimedSpins) : 0);
//自旋:1.检查状态等待匹配 2.挂起线程 3.检查状态 是否被中断 或者 超时..
for (;;) {
//条件成立:说明线程等待过程中,收到了中断信号,属于中断唤醒..
if (w.isInterrupted())
//更新线程对应的Node状态为 取消状态..
//数据域item 指向当前Node自身,表示取消状态.
s.tryCancel(e);
//获取当前Node数据域
Object x = s.item;
//item有几种情况呢?
//当SNode模式为DATA模式时:
//1.item != null 且 item != this 表示请求要传递的数据 put(E e)
//2.item == this 当前SNode对应的线程 取消状态
//3.item == null 表示已经有匹配节点了,并且匹配节点拿走了item数据。
//当SNode模式为REQUEST模式时:
//1.item == null 时,正常状态,当前请求仍然未匹配到对应的DATA请求。
//2.item == this 当前SNode对应的线程 取消状态
//3.item != null 且 item != this 表示当前REQUEST类型的Node已经匹配到一个DATA类型的Node了。
//条件成立:
//当前请求为DATA模式时:e 请求带来的数据
//item == this 当前SNode对应的线程 取消状态
//item == null 表示已经有匹配节点了,并且匹配节点拿走了item数据。
//当前请求为REQUEST模式时:e == null
//item == this 当前SNode对应的线程 取消状态
//item != null 且 item != this 表示当前REQUEST类型的Node已经匹配到一个DATA类型的Node了。
if (x != e)
return x;
//条件成立:说明请求指定了超时限制..
if (timed) {
//nanos表示距离截止时间的长度..
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
//条件成立:说明当前Node对应的线程 已经等待超时了,需要取消了.
if (nanos <= 0L) {
s.tryCancel(e);
continue;
}
}
//条件成立:说明当前线程 还可以进行自旋检查..
if (spins > 0)
//递减..
--spins;
//执行到这里,说明spins == 0;
//条件成立:当前Node尚未设置waiter字段..
else if (s.waiter == null)
//保存当前Node对应的线程,方便后面挂起线程后,外部线程使用s.waiter字段唤醒 当前Node对应的线程。
s.waiter = w;
//条件成立:说明当前请求未指定超时限制。挂起采用 不指定超时的挂起方法..
else if (!timed)
LockSupport.park(this);
//执行到这里,说明 timed==true
//条件 不成立:nanos 太小了,没有必要挂起线程了,还不如自旋 实在。
else if (nanos > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
//nanos > 1000.
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
}
案例分析
public class TransferQueueDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue<Integer> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>(true);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread3.start();
}
}
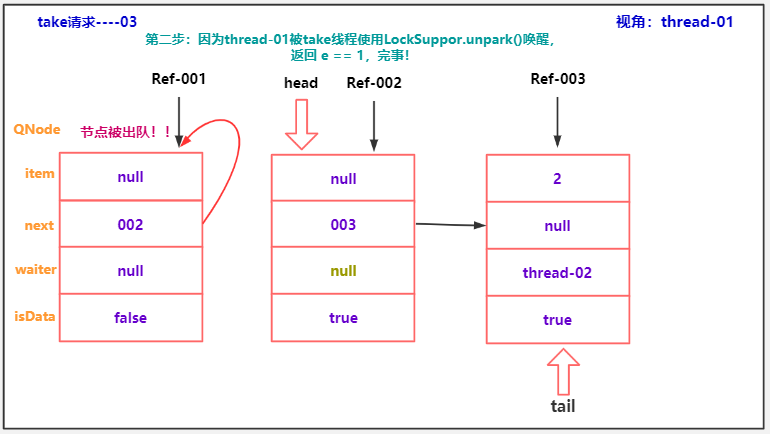
队首节点取消出队分析
public class TransferQueueCancelDemo01 {
/**
* head.next节点取消....案例
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue<Integer> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>(true);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
thread1.interrupt();
}
}
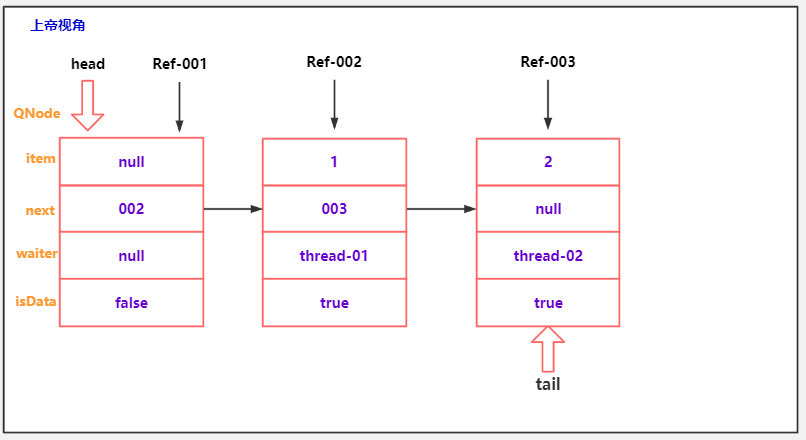
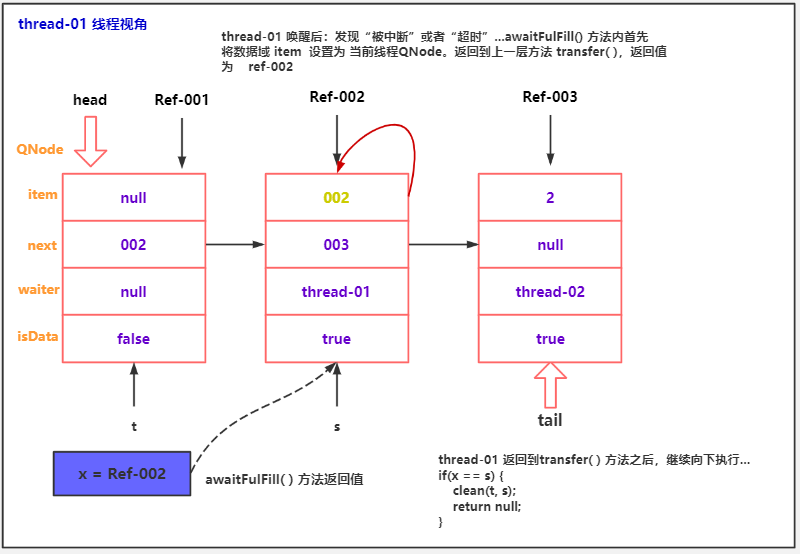
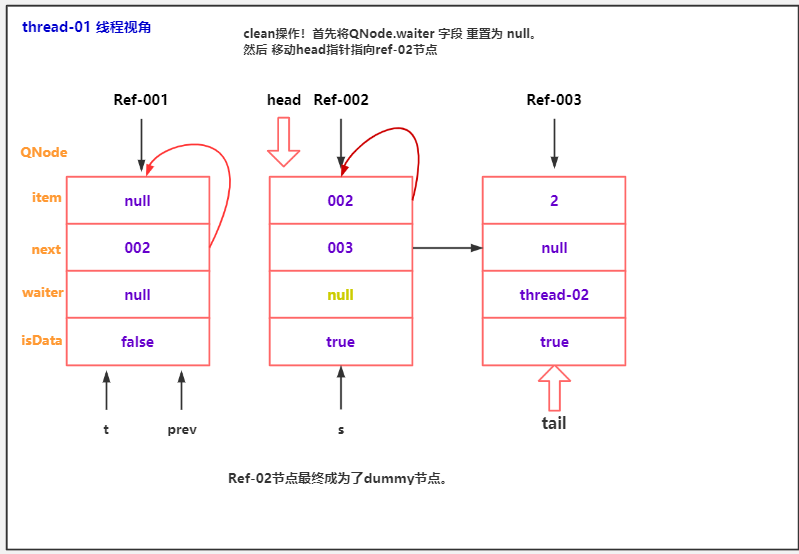
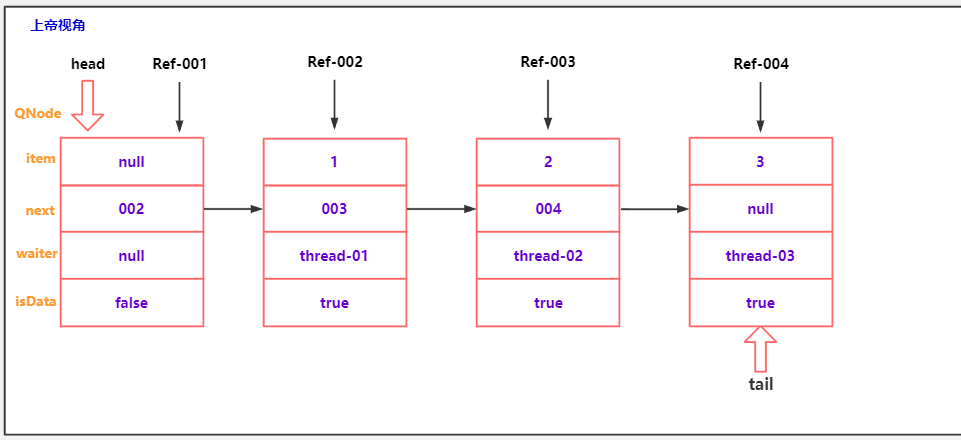
队中节点取消出队分析
public class TransferQueueCancelDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue<Integer> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>(true);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread3.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
thread2.interrupt();
}
}
队尾节点取消出队分析
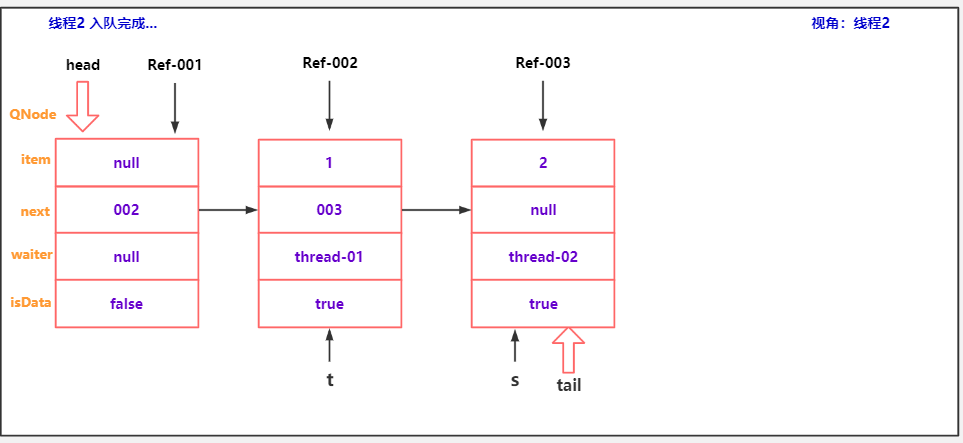
public class TransferQueueCancelDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue<Integer> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>(true);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
thread2.interrupt();
Thread.sleep(200);
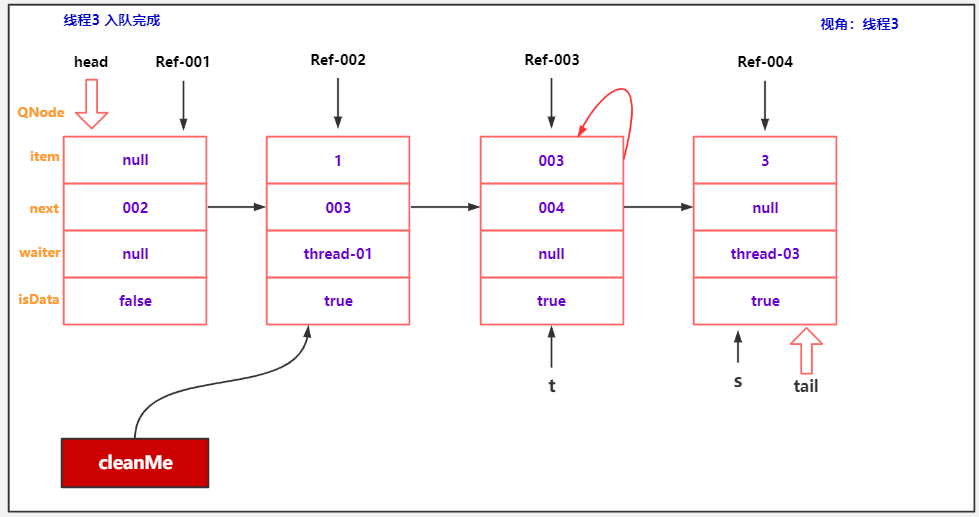
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread3.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
thread3.interrupt();
}
}





 这篇博客详细解析了公平模式下同步队列`TransferQueue`的实现,包括节点结构`QNode`、队列操作如入队、出队、取消等逻辑,并通过案例分析了不同场景下的行为。主要涉及线程安全、并发控制和队列操作的优化。
这篇博客详细解析了公平模式下同步队列`TransferQueue`的实现,包括节点结构`QNode`、队列操作如入队、出队、取消等逻辑,并通过案例分析了不同场景下的行为。主要涉及线程安全、并发控制和队列操作的优化。
















 2597
2597

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








