1、创建Thymeleaf入门项目
1.1、创建项目
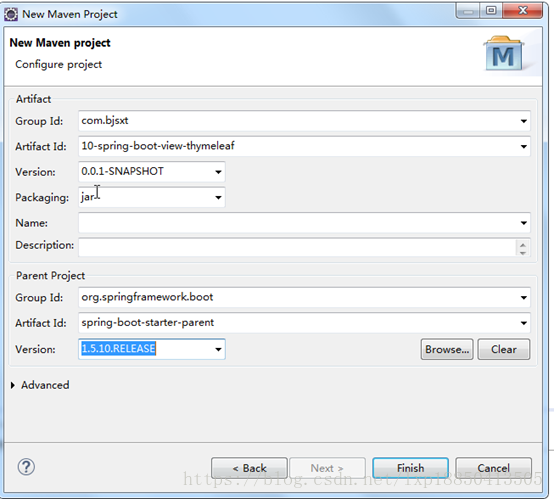
1.2、修改pom文件添加坐标
<!-- thymeleaf -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>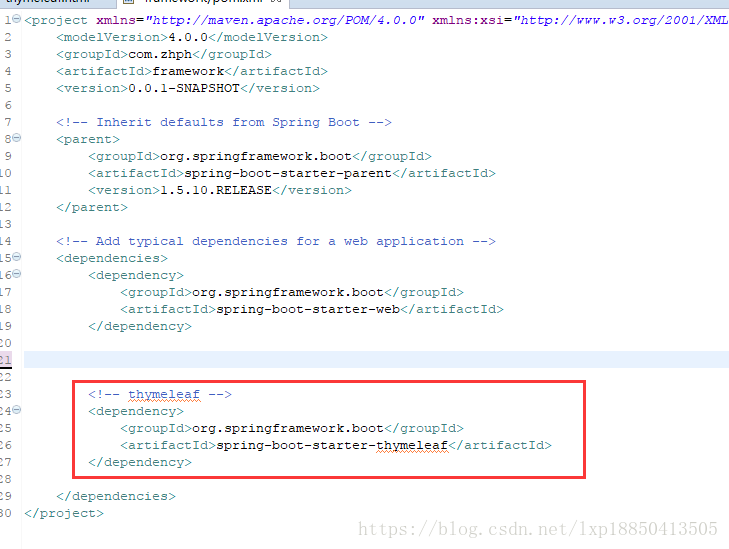
1.3、创建存放视图的目录
目录位置:src/main/resources/templates
templates:该目录是安全的。意味着该目录下的内容是不允许外界直接访问的。
2、 Thymeleaf的基本使用
2.1、Thymeleaf特点:
Thymelaef是通过他特定语法对html的标记做渲染。
2.2、编写Controller
@Controller
publicclassDemoController {
@RequestMapping("/show")
public String showInfo(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg", "Thymeleaf第一个案例");
return"index";
}
}2.3、创建视图 .html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf入门</title>
</head>
<body>
<span th:text="Hello"></span>
<hr/>
<span th:text="${msg}"></span>
</body>
</html>2.4、编写启动类
@SpringBootApplication
publicclass App{
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}2.5、解决异常

2.5.1、解决异常方式1
让html的标记按照严禁的语法去编写。

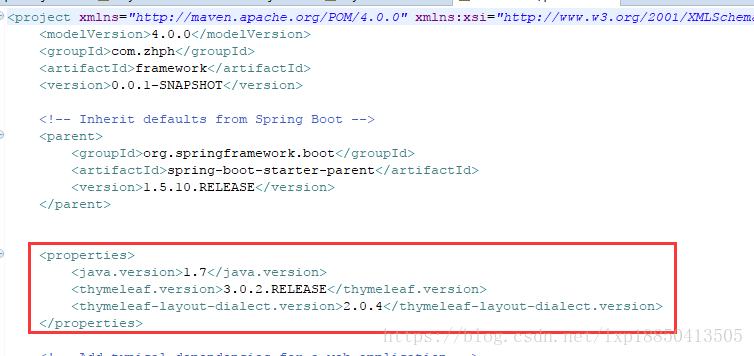
2.5.2、解决异常方式2
Thymeleaf.jar:更新为3.0以上的版本
thymeleaf-layout-dialect.jar:更新为2.0以上的版本
3、 Thymeleaf语法详解
3.1变量输出与字符串操作
3.1.1th:text
th:text |
在页面中输出值 |
3.1.2th:value
th:value |
可以将一个值放入到input标签的value中 |
3.1.3判断字符串是否为空
Thymeleaf内置对象
注意语法:
1,调用内置对象一定要用#
2,大部分的内置对象都以s结尾 strings、numbers、dates
${#strings.isEmpty(key)} |
判断字符串是否为空,如果为空返回true,否则返回false |
|
${#strings.contains(msg,'T')} |
判断字符串是否包含指定的子串,如果包含返回true,否则返回false |
|
${#strings.startsWith(msg,'a')} |
判断当前字符串是否以子串开头,如果是返回true,否则返回false |
|
${#strings.endsWith(msg,'a')} |
判断当前字符串是否以子串结尾,如果是返回true,否则返回false |
|
${#strings.length(msg)} |
返回字符串的长度 |
|
${#strings.indexOf(msg,'h')} |
查找子串的位置,并返回该子串的下标,如果没找到则返回-1 |
|
${#strings.substring(msg,13)} ${#strings.substring(msg,13,15)} |
截取子串,用户与jdk String类下SubString方法相同 |
|
${#strings.toUpperCase(msg)} ${#strings.toLowerCase(msg)} |
字符串转大小写。 |
|
3.2日期格式化处理
${#dates.format(key)} |
格式化日期,默认的以浏览器默认语言为格式化标准 |
|
${#dates.format(key,'yyy/MM/dd')} |
按照自定义的格式做日期转换 |
|
${#dates.year(key)} ${#dates.month(key)} ${#dates.day(key)} |
year:取年 Month:取月 Day:取日 |
3.3条件判断
3.3.1th:if
<span th:if="${sex} == '男'"> 性别:男 </span> <span th:if="${sex} == '女'"> 性别:女 </span> |
3.3.2th:switch
<div th:switch="${id}"> <span th:case="1">ID为1</span> <span th:case="2">ID为2</span> <span th:case="3">ID为3</span> </div> |
3.4迭代遍历
3.4.1th:each
@RequestMapping("/show3") public String showInfo3(Model model){ List<Users> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Users(1,"张三",20)); list.add(new Users(2,"李四",22)); list.add(new Users(3,"王五",24)); model.addAttribute("list", list); return"index3"; } |
<table border="1"> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="u : ${list}"> <td th:text="${u.userid}"></td> <td th:text="${u.username}"></td> <td th:text="${u.userage}"></td> </tr> </table> |
3.4.2ht:each 状态变量
@RequestMapping("/show3") public String showInfo3(Model model){ List<Users> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Users(1,"张三",20)); list.add(new Users(2,"李四",22)); list.add(new Users(3,"王五",24)); model.addAttribute("list", list); return"index3"; } |
<table border="1"> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> <th>Index</th> <th>Count</th> <th>Size</th> <th>Even</th> <th>Odd</th> <th>First</th> <th>lase</th> </tr> <tr th:each="u,var : ${list}"> <td th:text="${u.userid}"></td> <td th:text="${u.username}"></td> <td th:text="${u.userage}"></td> <td th:text="${var.index}"></td> <td th:text="${var.count}"></td> <td th:text="${var.size}"></td> <td th:text="${var.even}"></td> <td th:text="${var.odd}"></td> <td th:text="${var.first}"></td> <td th:text="${var.last}"></td> </tr> </table> |
状态变量属性
1,index:当前迭代器的索引 从0开始
2,count:当前迭代对象的计数 从1开始
3,size:被迭代对象的长度
4,even/odd:布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数 从0开始
5,first:布尔值,当前循环的是否是第一条,如果是返回true否则返回false
6,last:布尔值,当前循环的是否是最后一条,如果是则返回true否则返回false
3.4.3th:each迭代Map
@RequestMapping("/show4") public String showInfo4(Model model){ Map<String, Users> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("u1", new Users(1,"张三",20)); map.put("u2", new Users(2,"李四",22)); map.put("u3", new Users(3,"王五",24)); model.addAttribute("map", map); return"index4"; } |
<table border="1"> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="maps : ${map}"> <td th:text="${maps}"></td> </tr> </table> <th/> <table border="1"> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="maps : ${map}"> <td th:each="entry:${maps}" th:text="${entry.value.userid}" ></td> <td th:each="entry:${maps}" th:text="${entry.value.username}"></td> <td th:each="entry:${maps}" th:text="${entry.value.userage}"></td> </tr> </table> |
3.5域对象操作
3.5.1HttpServletRequest
request.setAttribute("req", "HttpServletRequest"); |
Request:<span th:text="${#httpServletRequest.getAttribute('req')}"></span><br/> |
3.5.2HttpSession
request.getSession().setAttribute("sess", "HttpSession"); |
Session:<span th:text="${session.sess}"></span><br/> |
3.5.3ServletContext
request.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("app", "Application"); |
Application:<span th:text="${application.app}"></span> |
3.6 URL表达式
th:href
th:src
3.6.1url表达式语法
基本语法:@{}
3.6.2URL类型
3.6.2.1绝对路径
<a th:href="@{http://www.baidu.com}">绝对路径</a><br/> |
3.6.2.2 相对路径
1)相对于当前项目的根
相对于项目的上下文的相对路径
<a th:href="@{/show}">相对路径</a> |
2) 相对于服务器路径的根
<a th:href="@{~/project2/resourcename}">相对于服务器的根</a> |
3.6.3在url中实现参数传递
<a th:href="@{/show(id=1,name=zhagnsan)}">相对路径-传参</a> |
3.6.4在url中通过restful风格进行参数传递
<a th:href="@{/path/{id}/show(id=1,name=zhagnsan)}">相对路径-传参-restful</a> |









 本文介绍如何创建Thymeleaf入门项目,包括配置依赖、编写控制器与视图等步骤,并深入讲解Thymeleaf的基本语法,如变量输出、字符串操作、日期格式化、条件判断、迭代遍历及URL表达式等。
本文介绍如何创建Thymeleaf入门项目,包括配置依赖、编写控制器与视图等步骤,并深入讲解Thymeleaf的基本语法,如变量输出、字符串操作、日期格式化、条件判断、迭代遍历及URL表达式等。
















 910
910

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








