二叉树是子节点小于等于2的树。
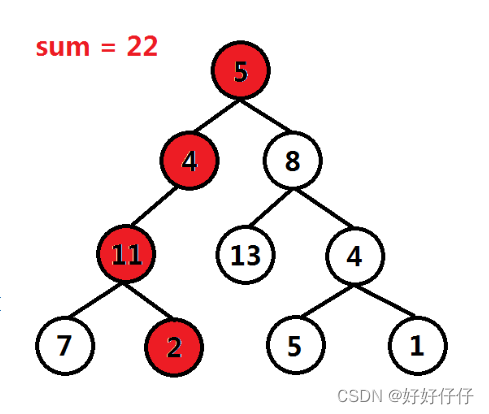
1. 给定一个二叉树于整数sum,找出所有从根节点到叶节点的路径,这些路径上的节点值累加和为sum。
分析:
1. 深度遍历二叉树,需要用一个容器存储节点的值,使用vector容器path,使用path_value累加节点值
2. 遍历到叶节点时,检查path_value,若为sum,加入到result
3. 一条路径的遍历中发现如果不满足要求,清空path_value和path
注:return返回当前函数的结果,不影响外面大函数的运行
#include<vector>
#include<stdio.h>
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode * left;
TreeNode * right;
TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){};
};
class Solution{
public:
std::vector<std::vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root,int sum){
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result;
std::vector<int> path;
int path_value=0;
preorder(root,path_value,sum,path,result);
return result;
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode* node,int &path_value,int sum,std::vector<int> &path,std::vector<std::vector<int>> &result){
if(node==nullptr)
return;
path_value+=node->val;
path.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left==nullptr&&node->right==nullptr&&path_value==sum)
{
result.push_back(path);
}
preorder(node->left,path_value,sum,path,result);
preorder(node->right,path_value,sum,path,result);
path_value-=node->val;
path.pop_back();
}
};
2. 最近的公共祖先
已知二叉树,求二叉树中给定的两个节点的最近公共祖先。
最近公共祖先:树上最低(离根最远)
分析:深度搜索
1. 从根节点遍历,找到后结束搜索
2. 按顺序存储节点
void preorder(TreeNode* node,TreeNode* search,std::vector<TreeNode*> &path,std::vector<TreeNode*> &result,int &finish){
if(node==nullptr||finish==1)
return;
path.push_back(node);
if (node==search)
{
finish=1;
result=path;
}
preorder(node->left,search,path,result,finish);
preorder(node->right,search,path,result,finish);
path.pop_back();
}
1. 求路径的长度n
2. 同时遍历p和q,最后一个的相同节点,即最近公共祖先
3. 给定一个二叉树,将该二叉树按前序遍历的顺序转换成单链表
分析:
按顺序遍历vector,将前面的节点左指针置空,右指针与后面节点相连
#include<stdio.h>
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode * left;
TreeNode * right;
TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){};
};
class Solution{
public:
void flatten(TreeNode * root)
{
std::vector<TreeNode* > node_vec;
preorder(root,node_vec);
for (int i = 1; i < node_vec.size(); i++)
{
node_vec[i-1]->left=nullptr;
node_vec[i-1]->right=node_vec[i];
}
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode* node,std::vector<TreeNode* > node_vec){
if(node==nullptr)
return;
node_vec.push_back(node);
preorder(node->left,node_vec);
preorder(node->right,node_vec);
}
};
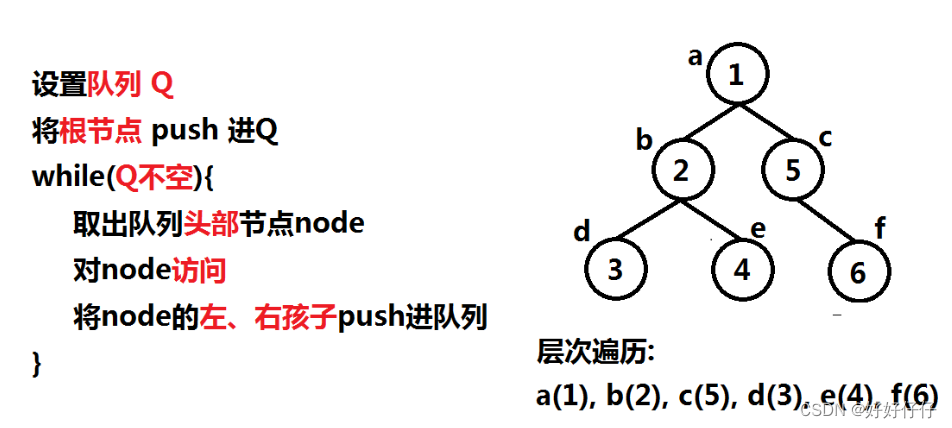
宽度优先遍历
#include<vector>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<queue>
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode * left;
TreeNode * right;
TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){};
};
void BFS_print(TreeNode* root)
{
std::queue<TreeNode *> Q;
Q.push(root);
while (!Q.empty())
{
TreeNode *node=Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("");
if (node->left!=nullptr)
{
Q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right!=nullptr)
{
Q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
深度优先算法
参考:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/weixin_43272781/article/details/82959089
void dfs(int step)
{
判断边界
{
相应操作
}
尝试每一种可能
{
满足check条件
标记
继续下一步dfs(step+1)
恢复初始状态(回溯的时候要用到)
}
}
 二叉树算法解析:路径求和、最近公共祖先与结构转换
二叉树算法解析:路径求和、最近公共祖先与结构转换




















 400
400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








