1.Protocol对象生成
1.1 Protocol接口源码
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface Protocol {
int getDefaultPort();
@Adaptive
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
void destroy();
}1.2 对象生成
private static final Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();Dubbo中是通过这行代码生成的Protocol对象,这其实涉及到Dubbo中的SPI机制,通过这里,我们直接看源码吧。
1.3 getExtensionLoader
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(Class<T> type) {
//校验--
if (type == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null");
if (!type.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type + ") is not interface!");
}
if (!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type +
") is not extension, because WITHOUT @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + " Annotation!");
}
//检查是否已经缓存EXTENSION_LOADERS是一个ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>>
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) { //缓存中不存在
//新建并添加到缓存中
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));
//重新从缓存中获取一次
loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
return loader; //返回结果
}这里就是判断ExtensionLoader是否在对应的缓存中,若存在则直接拿来用,否则就创建一个新的。而ExtensionLoader对象的创建过程如下:
/**
* 构建一个ExtensionLoader
*/
private ExtensionLoader(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
/**
* 判断type是否为ExtensionFactory类型
* -是:直接设置objectFactoryweinull
* -否:设置为ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension())
*/
objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension());
}这里如果传入type类型不为ExtensionFactory时,或以同样的方式获取一个ExtensionFactory设置到objectFactory中,这里我们先不关注,看一下获取具体Protocol对象的getAdaptiveExtension方法,这也是获取ExtensionFactory的方法。
1.4 getAdaptiveExtension
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
//先从cachedAdaptiveInstance中获取
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
//未获取到进行以下处理
if (createAdaptiveInstanceError == null) {
//加锁
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {
//再次获取并校验
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
//创建对应实例
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
//设置值到cachedAdaptiveInstance中
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(), createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
}
return (T) instance; //返回实例
}一堆校验,其中重要的方法应该是createAdaptiveExtension,我们看一下这个方法
/**
* 创建一个接口适配器
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
//获取AdaptiveExtensionClass并生成一个实例 后 调用injectExtension方法
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can not create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//获取扩展的class
getExtensionClasses();
//若扩展的class不为null
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass; //直接返回
}
//创建Adaptive扩展的class并赋值到cachedAdaptiveClass后返回
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}接下来就得看看是如何获取扩展得class的getExtensionClasses
/**
* 获取扩展的class
*/
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
//先从cachedClasses中获取
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {//未获取到
synchronized (cachedClasses) {//加锁
classes = cachedClasses.get(); //再次获取
if (classes == null) { //再次判断
classes = loadExtensionClasses();//调用loadExtensionClasses加载扩展的class
cachedClasses.set(classes); //将加载到的class设置到cachedClasses中
}
}
}
return classes;
}同样的关键代码就是loadExtensionClasses,向下看:
/**
* 加载扩展的class
*/
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
//获取SPI注解
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
//注解非空
if (defaultAnnotation != null) {
//获取value
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();
if ((value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
//对value进行匹配
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if (names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
//拿到结果 设置到cachedDefaultName中
if (names.length == 1) cachedDefaultName = names[0];
}
}
//新建extensionClasses
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
//加载这几个目录
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY); // META-INF/dubbo/internal/
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY); // META-INF/dubbo/
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY); // META-INF/services/
return extensionClasses; //返回结果extensionClasses
}这里会加载META-INF/dubbo/internal/与META-INF/dubbo/以及META-INF/services/这三个目录下的文件,观察Dubbo源码包中对应的目录结构如下:
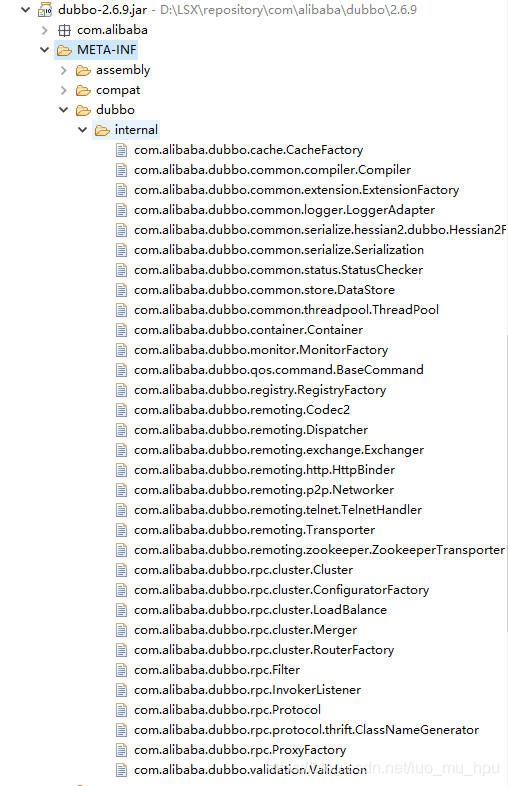
这些就是加载的文件,其中的文件名就是对应的接口的全名,而文件中配置的就是接口对应的实现类,例如/META-INF/dubbo/internal/com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol的配置如下:
filter=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper
listener=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolListenerWrapper
mock=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.support.MockProtocol
dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol
injvm=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol
rmi=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.rmi.RmiProtocol
hessian=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.hessian.HessianProtocol
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.http.HttpProtocol
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.webservice.WebServiceProtocol
thrift=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.thrift.ThriftProtocol
memcached=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.memcached.MemcachedProtocol
redis=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.redis.RedisProtocol
rest=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.rest.RestProtocol
registry=com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol
qos=com.alibaba.dubbo.qos.protocol.QosProtocolWrapper
1.5 加载目录loadDirectory
private void loadDirectory(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, String dir) {
//获取文件名 路径+接口全名
String fileName = dir + type.getName();
try {
Enumeration<java.net.URL> urls;
//获取ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
//加载所有的classpath下面的同名文件(包含项目本地classpath和依赖jar包)
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
if (urls != null) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
java.net.URL resourceURL = urls.nextElement();
//加载资源
loadResource(extensionClasses, classLoader, resourceURL);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", description file: " + fileName + ").", t);
}
}继续看加载资源的loadResource
private void loadResource(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, ClassLoader classLoader, java.net.URL resourceURL) {
try {
//获取文件输入流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(resourceURL.openStream(), "utf-8"));
try {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
//以#开头的不进行处理
final int ci = line.indexOf('#');
//若#存在 则获取#之前的内容
if (ci >= 0) line = line.substring(0, ci);
line = line.trim();//去空格
//判断是否有数据
if (line.length() > 0) {
try {
String name = null;
//是否有等号=
int i = line.indexOf('=');
if (i > 0) {
//有等号 获取=前的内容
name = line.substring(0, i).trim();
//获取=后的内容
line = line.substring(i + 1).trim();
}
if (line.length() > 0) {
//加载class
loadClass(extensionClasses, resourceURL, Class.forName(line, true, classLoader), name);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("Failed to load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class line: " + line + ") in " + resourceURL + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
exceptions.put(line, e);
}
}
}
} finally {
reader.close();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class file: " + resourceURL + ") in " + resourceURL, t);
}
}加载class的loadClass
private void loadClass(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, java.net.URL resourceURL, Class<?> clazz, String name) throws NoSuchMethodException {
//判断class是否为目标接口的实现
if (!type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class "
+ clazz.getName() + "is not subtype of interface.");
}
//判断class是否被@Adaptive注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
if (cachedAdaptiveClass == null) {
cachedAdaptiveClass = clazz;//设置cachedAdaptiveClass
} else if (!cachedAdaptiveClass.equals(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("More than 1 adaptive class found: "
+ cachedAdaptiveClass.getClass().getName()
+ ", " + clazz.getClass().getName());
}
} else if (isWrapperClass(clazz)) { //判断是否为包装类
Set<Class<?>> wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses; //包装类可能有多个 用set进行去重
if (wrappers == null) {
cachedWrapperClasses = new ConcurrentHashSet<Class<?>>();
wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
}
wrappers.add(clazz); //添加到wrappers中
} else {
clazz.getConstructor();
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
//若name为空 获取注解上名字
name = findAnnotationName(clazz);
if (name.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + resourceURL);
}
}
//将配置的key名字根据逗号来分割
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name);
if (names != null && names.length > 0) {
//获取class上的Activate注解
Activate activate = clazz.getAnnotation(Activate.class);
//若Activate非null
if (activate != null) {
//存储注解值
cachedActivates.put(names[0], activate);
}
//遍历names
for (String n : names) {
if (!cachedNames.containsKey(clazz)) {
//cachedNames存储 clazz-n
cachedNames.put(clazz, n);
}
Class<?> c = extensionClasses.get(n);
if (c == null) {
//extensionClasses存储n-class
extensionClasses.put(n, clazz);
} else if (c != clazz) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate extension " + type.getName() + " name " + n + " on " + c.getName() + " and " + clazz.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 判断class是否为包装类
*/
private boolean isWrapperClass(Class<?> clazz) {
try {
//判断有没有拷贝构造函数,如果有的话说明该类是实现的包装类,进行缓存。一个接口可能有多个对应的包装类实现
clazz.getConstructor(type);
return true;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
return false;
}
}
到此,加载文件的操就完成了。
1.6 injectExtension适配
看了上面加载的过程,让我们回到这段代码处
/**
* 创建一个接口适配器
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
//获取AdaptiveExtensionClass并生成一个实例 后 调用injectExtension方法
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can not create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}刚才的一堆操作其实是在getAdaptiveExtensionClass方法中完成的,返回一个class对象,这里会根据这个class生成一个实例,然后调用injectExtension方法,那就继续吧:
/**
* 通过反射自动调用instance的set方法把自身的属性注入进去
* 解决的扩展类依赖问题,也就是说解决扩展类依赖扩展类的问题
*/
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
try {
if (objectFactory != null) {
//遍历所有方法
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
if (method.getName().startsWith("set")//如果该扩展点实例有Set开头的公共方法
&& method.getParameterTypes().length == 1
&& Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
/**
* Check {@link DisableInject} to see if we need auto injection for this property
*/
//判断方法上是否加了DisableInject注解
if (method.getAnnotation(DisableInject.class) != null) {
continue;
}
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];//得到set方法的参数类型
try {
//得到属性名称,比如setName方法就得到name属性名称
String property = method.getName().length() > 3 ? method.getName().substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + method.getName().substring(4) : "";
//获得属性值
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property);
if (object != null) {
// 如果不为空,说明set方法的参数是扩展点类型,那么进行注入,意思也就是说扩展点里面还有依赖其他扩展点
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("fail to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;
}







 本文深入剖析Dubbo SPI机制,详细介绍了如何通过SPI机制生成Protocol对象,包括ExtensionLoader的使用,加载扩展类的过程,以及AdaptiveExtension的创建。通过源码解读,揭示了Dubbo SPI机制的工作原理。
本文深入剖析Dubbo SPI机制,详细介绍了如何通过SPI机制生成Protocol对象,包括ExtensionLoader的使用,加载扩展类的过程,以及AdaptiveExtension的创建。通过源码解读,揭示了Dubbo SPI机制的工作原理。
















 6540
6540

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








