一、进程与线程
1. 进程与线程


2. 并行与并发


并行:同一时间动手做(doing)多件事情的能力
并发:同一时间应对(dealing with)多件事情的能力

3. 应用

同步:
package cn.itcast.n2;
import cn.itcast.Constants;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.FileReader;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Sync")
public class Sync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader.read(Constants.MP4_FULL_PATH); // 同步
log.debug("do other things ...");
}
}
异步:
package cn.itcast.n2;
import cn.itcast.Constants;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.FileReader;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Async")
public class Async {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> FileReader.read(Constants.MP4_FULL_PATH)).start();
log.debug("do other things ...");
}
}

单核和多核环境下,单线程和多线程的性能对比

package com.itcast;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
@Fork(1)
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@Warmup(iterations=3)
@Measurement(iterations=5)
public class MyBenchmark {
static int[] ARRAY = new int[1000_000_00];
static {
Arrays.fill(ARRAY, 1);
}
@Benchmark
public int c() throws Exception {
int[] array = ARRAY;
FutureTask<Integer> t1 = new FutureTask<>(()->{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 250_000_00;i++) {
sum += array[0+i];
}
return sum;
});
FutureTask<Integer> t2 = new FutureTask<>(()->{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 250_000_00;i++) {
sum += array[250_000_00+i];
}
return sum;
});
FutureTask<Integer> t3 = new FutureTask<>(()->{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 250_000_00;i++) {
sum += array[500_000_00+i];
}
return sum;
});
FutureTask<Integer> t4 = new FutureTask<>(()->{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 250_000_00;i++) {
sum += array[750_000_00+i];
}
return sum;
});
new Thread(t1).start();
new Thread(t2).start();
new Thread(t3).start();
new Thread(t4).start();
return t1.get() + t2.get() + t3.get()+ t4.get();
}
@Benchmark
public int d() throws Exception {
int[] array = ARRAY;
FutureTask<Integer> t1 = new FutureTask<>(()->{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 1000_000_00;i++) {
sum += array[0+i];
}
return sum;
});
new Thread(t1).start();
return t1.get();
}
}

二、Java线程
1. 创建和运行线程

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test1")
public class Test1 {
public static void test2() {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{ log.debug("running"); }, "t2");
t.start();
}
public static void test1() {
Thread t = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running");
}
};
t.setName("t1");
t.start();
}
}

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test2")
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running");
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r, "t2");
t.start();
}
}


package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
log.debug("running......");
return 666;
}
});
Thread t = new Thread(task, "t");
t.start();
Integer result = task.get();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
2. 观察多个线程同时运行
package cn.itcast.n3;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestMultiThread")
public class TestMultiThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
while(true) {
log.debug("running");
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while(true) {
log.debug("running");
}
},"t2").start();
}
}

- 线程交替执行
- 谁先谁后,不由我们控制
3. 查看进程线程的方法




4. 原理之线程运行

package cn.itcast.n3;
public class TestFrames {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
method1(20);
}
};
t1.setName("t1");
t1.start();
method1(10);
}
private static void method1(int x) {
int y = x + 1;
Object m = method2();
System.out.println(m);
}
private static Object method2() {
Object n = new Object();
return n;
}
}


5. 常见方法



Thread.interrupted()
- 功能:
Thread.interrupted()是一个静态方法,用于检查当前线程的中断状态。 - 返回值: 如果当前线程已经被中断,返回
true;如果没有被中断,返回false。 - 效果: 调用
Thread.interrupted()会清除当前线程的中断状态,也就是说如果当前线程被中断,调用后它的中断状态将变为false。
Thread.interrupt()
- 功能:
interrupt()是一个实例方法,用于中断特定的线程。 - 效果: 当一个线程调用另一个线程的
interrupt()方法时,被中断的线程会收到一个中断信号。此时,如果被中断的线程正在进行阻塞操作(例如sleep()或wait()),它将抛出InterruptedException。如果线程没有被阻塞,它的中断状态会被设置为true。
总结
Thread.interrupted(): 用于检查当前线程的中断状态,并清除该状态。Thread.interrupt(): 用于中断其他线程,并设置其中断状态。
6. start与run方法详解
run()方法可以被调用多次,而start()方法只可以被调用一次


package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test5")
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running...");
}
};
System.out.println(t1.getState());
t1.start();
System.out.println(t1.getState());
}
}

7. sleep与yield

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test6")
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t1.start();
log.debug("t1 state: {}", t1.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("t1 state: {}", t1.getState());
}
}

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test7")
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("enter sleep...");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.debug("wake up...");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000); // 主线程睡眠
log.debug("interrupt...");
t1.interrupt();
}
}


package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test9")
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable task1 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (;;) {
System.out.println("---->1 " + count++);
}
};
Runnable task2 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (;;) {
// Thread.yield();
System.out.println(" ---->2 " + count++);
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(task1, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(task2, "t2");
t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
8. 案例

9. join方法详解
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test10")
public class Test10 {
static int r = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test1();
}
private static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("开始1");
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("开始2");
sleep(1);
log.debug("结束2");
r = 10;
},"t1");
t1.start();
log.debug("结果为:{}", r);
log.debug("结束1");
}
}


package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test10")
public class Test10 {
static int r = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test1();
}
private static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("开始1");
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("开始2");
sleep(1);
log.debug("结束2");
r = 10;
},"t1");
t1.start();
t1.join(); // 等待t1线程执行结束
// Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("结果为:{}", r);
log.debug("结束1");
}
}


package cn.itcast.n3;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestJoin")
public class TestJoin {
static int r = 0;
static int r1 = 0;
static int r2 = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test1();
}
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
sleep(2);
r1 = 10;
});
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
t1.start();
// 线程执行结束会导致 join 结束
log.debug("join begin");
t1.join(3000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("r1: {} r2: {} cost: {}", r1, r2, end - start);
}
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
sleep(1);
r1 = 10;
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
sleep(2);
r2 = 20;
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("join begin");
t2.join();
log.debug("t2 join end");
t1.join();
log.debug("t1 join end");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("r1: {} r2: {} cost: {}", r1, r2, end - start);
}
private static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("开始");
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("开始");
sleep(1);
log.debug("结束");
r = 10;
});
t1.start();
t1.join();
log.debug("结果为:{}", r);
log.debug("结束");
}
}




10. interrupt方法详解

package cn.itcast.n3;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestInterrupt")
public class TestInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test1();
}
// 打断正常运行中的线程
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
boolean interrupted = current.isInterrupted(); // true
if(interrupted) {
log.debug(" 打断状态: {}", interrupted);
break;
}
}
}, "t2");
t2.start();
sleep(0.5);
t2.interrupt();
}
// 打断睡眠中的线程
private static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
sleep(1);
}, "t1");
t1.start();
sleep(0.5);
t1.interrupt();
log.debug(" 打断状态: {}", t1.isInterrupted()); // false
}
}


两阶段终止实现:
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TwoPhaseTermination")
public class Test13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TwoPhaseTermination tpt = new TwoPhaseTermination();
tpt.start();
//tpt.start();
//tpt.start();
Thread.sleep(3500);
log.debug("停止监控");
tpt.stop();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TwoPhaseTermination")
class TwoPhaseTermination {
// 监控线程
private Thread monitorThread;
// 停止标记
private volatile boolean stop = false;
// 判断是否执行过 start 方法
private boolean starting = false;
// 启动监控线程
public void start() {
synchronized (this) {
if (starting) { // false
return;
}
starting = true;
}
monitorThread = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 是否被打断
if (stop) {
log.debug("料理后事");
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("执行监控记录");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 重新设置打断标记
// current.interrupt();
}
}
}, "monitor");
monitorThread.start();
}
// 停止监控线程
public void stop() {
stop = true;
monitorThread.interrupt();
}
}
打断park线程
package cn.itcast.n3;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestInterrupt")
public class TestInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test3();
}
// 打断状态为false时,park生效,当前线程挂起
private static void test4() {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
log.debug("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("打断状态:{}", Thread.interrupted()); // true
}
});
t1.start();
sleep(1);
t1.interrupt();
}
// 打断状态为true时,park失效
private static void test3() {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("unpark...");
log.debug("打断状态:{}", Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); // true
}, "t1");
t1.start();
sleep(0.5);
log.debug("打断");
t1.interrupt();
}
}
11. 不推荐的方法

12. 主线程与守护线程

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test15")
public class Test15 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
break;
}
}
log.debug("结束");
}, "t1");
t1.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("结束");
}
}


12. 线程的状态





package cn.itcast.n3;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestState")
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running...");
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread("t2") {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) { // runnable
}
}
};
t2.start();
Thread t3 = new Thread("t3") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running...");
}
};
t3.start();
Thread t4 = new Thread("t4") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (TestState.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000); // timed_waiting
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
t4.start();
Thread t5 = new Thread("t5") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t2.join(); // waiting
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t5.start();
Thread t6 = new Thread("t6") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (TestState.class) { // blocked
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
t6.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("t1 state {}", t1.getState());
log.debug("t2 state {}", t2.getState());
log.debug("t3 state {}", t3.getState());
log.debug("t4 state {}", t4.getState());
log.debug("t5 state {}", t5.getState());
log.debug("t6 state {}", t6.getState());
System.in.read();
}
}




实现:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test16")
public class Test16 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("洗水壶");
sleep(1);
log.debug("烧开水");
sleep(15);
},"老王");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("洗茶壶");
sleep(1);
log.debug("洗茶杯");
sleep(2);
log.debug("拿茶叶");
sleep(1);
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("泡茶");
},"小王");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}

三、共享模型之管程
1. 共享问题










临界区 Critical Section

竞态条件 Race Condition

2. synchronized

synchronized关键字通过保证线程的互斥性,避免了多个线程并发访问共享资源时出现的竞态条件。- 可以用于实例方法、静态方法和代码块,可以根据需求选择合适的使用方式。
- 使用
synchronized可能会导致线程竞争(造成性能下降),因此应根据具体情况评估是否使用。
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
static int counter = 0;
static Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
synchronized (lock) {
counter++;
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
synchronized (lock) {
counter--;
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println(counter); // 0
}
}


package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test17")
public class Test17 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Room room = new Room();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
room.increment();
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
room.decrement();
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
log.debug("{}", room.getCounter()); // 0
}
}
class Room {
private int counter = 0;
public synchronized void increment() {
counter++;
}
public synchronized void decrement() {
counter--;
}
public synchronized int getCounter() {
return counter;
}
}



线程八锁

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public synchronized void a() {
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
结果:1 2 或 2 1


情况2:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}
结果:2 1 或 1 2


情况3:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.b();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.c();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
public void c() {
log.debug("3");
}
}
结果:3 2 1 或 2 3 1 或 1 3 2 或 3 1 2
情况4:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
Number n2 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n2.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}

情况5:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public static synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}

情况6:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public static synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public static synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}


情况7:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
Number n2 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n2.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public static synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}

情况8:
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Number n1 = new Number();
Number n2 = new Number();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n1.a();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin");
n2.b();
}).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Number")
class Number {
public static synchronized void a() {
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("1");
}
public static synchronized void b() {
log.debug("2");
}
}


3. 变量的线程安全分析




package cn.itcast.n4;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestThreadSafe {
static final int THREAD_NUMBER = 2;
static final int LOOP_NUMBER = 200;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ThreadSafeSubClass test = new ThreadSafeSubClass();
ThreadUnsafe test = new ThreadUnsafe();
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
test.method1(LOOP_NUMBER);
}, "Thread" + (i+1)).start();
}
}
}
class ThreadUnsafe {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
public void method1(int loopNumber) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
method2();
method3();
}
}
private void method2() {
list.add("1");
}
private void method3() {
list.remove(0);
}
}其中一种情况是,如果 线程2 还没add,线程1 remove就会报错:

将list修改位局部变量就不会有上面的问题了。



package cn.itcast.n4;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestThreadSafe {
static final int THREAD_NUMBER = 2;
static final int LOOP_NUMBER = 200;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadSafeSubClass test = new ThreadSafeSubClass();
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
test.method1(LOOP_NUMBER);
}, "Thread" + (i+1)).start();
}
}
}
class ThreadSafe {
public final void method1(int loopNumber) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
method2(list);
method3(list);
}
}
public void method2(ArrayList<String> list) {
list.add("1");
}
public void method3(ArrayList<String> list) {
System.out.println(1);
list.remove(0);
}
}
class ThreadSafeSubClass extends ThreadSafe{
@Override
public void method3(ArrayList<String> list) {
System.out.println(2);
new Thread(() -> {
list.remove(0);
}).start();
}
}![]()
4. 常见的线程安全类
- String
- Integer等包装类
- StringBuffer
- Random
- Vector
- Hashtable
- java.util.cocurrent包下的类
这里说它们是线程安全的是指,多个线程调用它们同一个实例的某个方法时,是线程安全的。也可以理解为:
- 它们的每个方法是原子的
- 但注意它们多个方法的组合不是原子的
每个方法都是线程安全的,但他们的组合使用不能保证线程安全性。

不可变类线程安全性

String的substring、replace方法会返回一个新对象






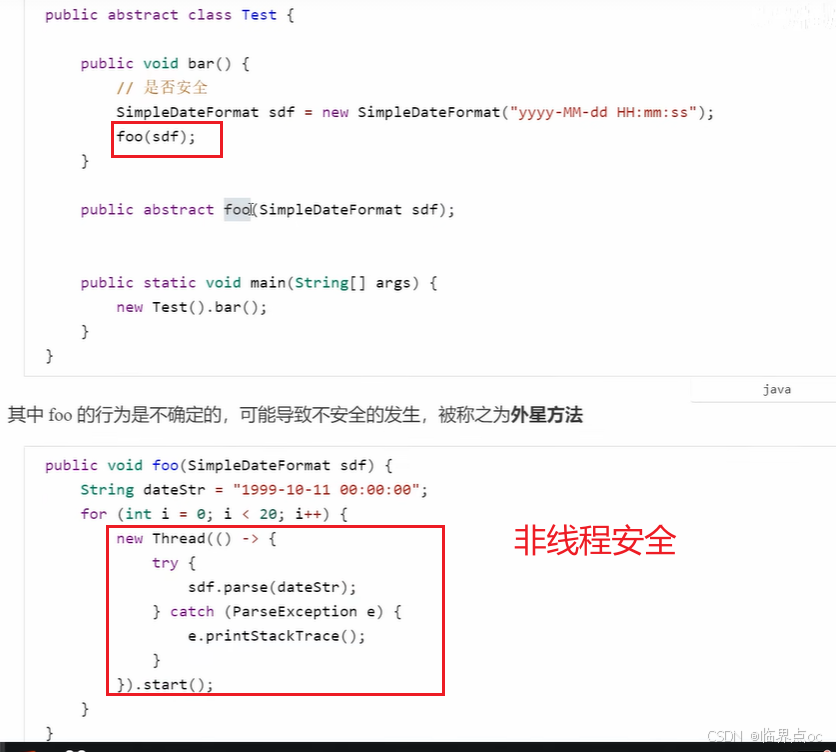
卖票练习:
package cn.itcast.n4.exercise;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ExerciseSell")
public class ExerciseSell {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟多人买票
TicketWindow window = new TicketWindow(1000);
// 所有线程的集合
List<Thread> threadList = new ArrayList<>();
// 卖出的票数统计
List<Integer> amountList = new Vector<>(); // 线程安全
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 买票
int amount = window.sell(random(5));
// 统计买票数
amountList.add(amount);
});
threadList.add(thread);
thread.start();
}
// 确保所有线程执行完毕,再执行下面统计的代码
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
thread.join();
}
// 统计卖出的票数和剩余票数
log.debug("余票:{}",window.getCount());
log.debug("卖出的票数:{}", amountList.stream().mapToInt(i-> i).sum());
}
// Random 为线程安全
static Random random = new Random();
// 随机 1~5
public static int random(int amount) {
return random.nextInt(amount) + 1;
}
}
// 售票窗口
class TicketWindow {
private int count;
public TicketWindow(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
// 获取余票数量
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 售票
public synchronized int sell(int amount) { // 保证线程安全
if (this.count >= amount) {
this.count -= amount;
return amount;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}转账练习:
package cn.itcast.n4.exercise;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Random;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ExerciseTransfer")
public class ExerciseTransfer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Account a = new Account(1000);
Account b = new Account(1000);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
a.transfer(b, randomAmount());
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
b.transfer(a, randomAmount());
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
// 查看转账2000次后的总金额
log.debug("total:{}", (a.getMoney() + b.getMoney()));
}
// Random 为线程安全
static Random random = new Random();
// 随机 1~100
public static int randomAmount() {
return random.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
}
// 账户
class Account {
private int money;
public Account(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
// 转账
public void transfer(Account target, int amount) {
synchronized(Account.class) { // 性能差
if (this.money >= amount) {
this.setMoney(this.getMoney() - amount);
target.setMoney(target.getMoney() + amount);
}
}
}
}
5. Monitor




synchronized原理





轻量级锁





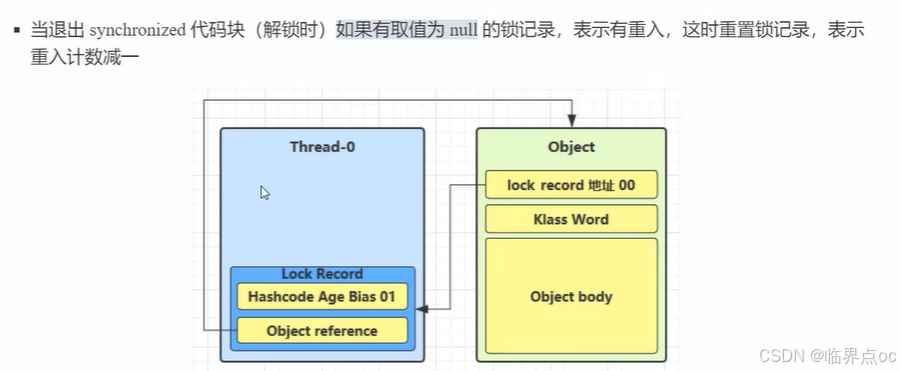

锁膨胀


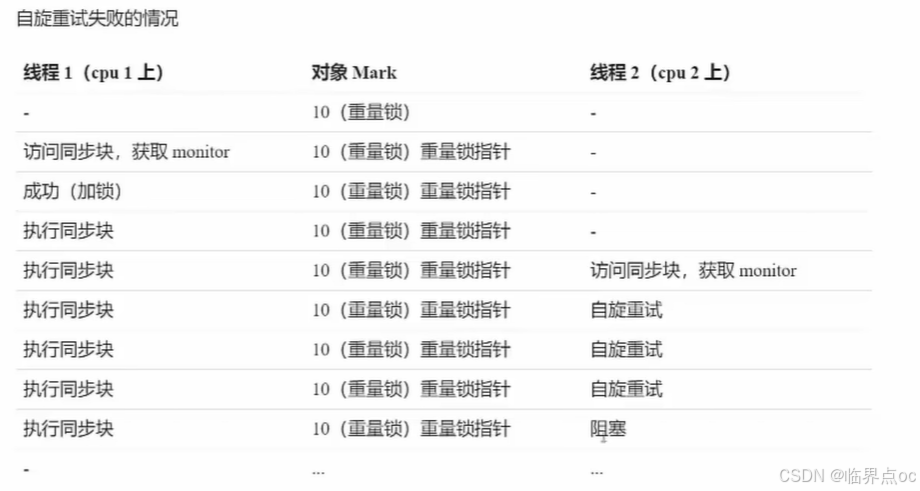
自旋优化


偏向锁




![]()


// 测试撤销偏向锁
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
Dog d = new Dog();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
synchronized (TestBiased.class) {
TestBiased.class.notify();
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (TestBiased.class) {
try {
TestBiased.class.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug(ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
log.debug(ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}, "t2");
t2.start();
}
class Dog {
}
private static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
Vector<Dog> list = new Vector<>();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
Dog d = new Dog();
list.add(d);
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
}
synchronized (list) {
list.notify();
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (list) {
try {
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("===============> ");
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
Dog d = list.get(i);
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
}, "t2");
t2.start();
}批量重偏向
在 Java 中,批量重偏向(Bulk Re-biasing)是 HotSpot 虚拟机在偏向锁(Biased Locking)机制中的一个优化特性。偏向锁是为了提高线程竞争不频繁的情况下的性能,特别是在某个线程多次访问同一对象时,通过偏向锁避免了重复的同步开销。
偏向锁的工作机制
1. 偏向锁的获取:
- 当一个线程第一次获得一个对象的锁时,虚拟机会将这个对象的锁状态设置为偏向锁,并把这个锁的偏向线程ID记录在对象头中。此后,这个线程在没有其他线程竞争的情况下,可以无需进行同步操作(如进入 `synchronized` 块),直接访问对象。
2. 偏向锁的升级:
- 如果另一个线程尝试获取同一个对象的锁,偏向锁会被撤销,锁会升级为轻量级锁(Lightweight Locking)。在这种情况下,偏向线程会被强制进行 CAS(比较并交换)操作来验证锁的状态。
3. 批量重偏向:
- 当许多线程竞争同一个对象的锁时,偏向锁可能会频繁撤销和重新偏向。当这种情况发生得很频繁时,虚拟机可能会进行一项优化,即批量重偏向。
- 批量重偏向的过程是,虚拟机会检查一段时间内的锁操作,找到最频繁获取锁的线程,并将锁的偏向状态再重新偏向到这个线程。这可以减少频繁的偏向撤销和开销,从而提高性能。
批量重偏向的目的
- 性能优化: 批量重偏向的目的是为了提高多线程环境下的性能,避免频繁的偏向锁撤销和重新获取的开销。
- 减少竞争: 在一些低竞争场景下,单一线程对某个对象的访问比较频繁,而其他线程的访问相对较少时,批量重偏向可以保持偏向锁的状态,从而提高这种情况下的执行效率。
注意事项
- 批量重偏向的触发是自动的,开发者通常不用直接控制。
- 虽然偏向锁能提高单线程访问的性能,但在高竞争场景下,它可能会导致性能下降。这时可能需要考虑使用轻量级锁或者更重的重量级锁(如 `Lock` 类)来管理线程间的竞争。
结论
批量重偏向是 Java 虚拟机中偏向锁机制的一个重要优化特征,旨在通过有效管理线程的锁状态来提升性能,特别是在多线程竞争情况下。它在许多情况下都可以显著减少锁的竞争和提高程序的执行效率。
批量撤销

static Thread t1, t2, t3;
private static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
Vector<Dog> list = new Vector<>();
int loopNumber = 39;
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
Dog d = new Dog();
list.add(d);
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
}
LockSupport.unpark(t2);
}, "t1");
t1.start();
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("===============> ");
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
Dog d = list.get(i);
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
LockSupport.unpark(t3);
}, "t2");
t2.start();
t3 = new Thread(() -> {
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("===============> ");
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
Dog d = list.get(i);
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
synchronized (d) {
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
log.debug(i + "\t" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(d).toPrintableSimple(true));
}
}, "t3");
t3.start();
t3.join();
log.debug(ClassLayout.parseInstance(new Dog()).toPrintableSimple(true));
}锁消除


6. wait / notify




package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test18")
public class Test18 {
static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
synchronized (lock) { // 先获得锁,才能进入waiting状态
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestWaitNotify")
public class TestWaitNotify {
final static Object obj = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
log.debug("执行....");
try {
obj.wait(); // 让线程在obj上一直等待下去
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("其它代码....");
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
log.debug("执行....");
try {
obj.wait(); // 让线程在obj上一直等待下去
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("其它代码....");
}
},"t2").start();
// 主线程两秒后执行
sleep(0.5);
log.debug("唤醒 obj 上其它线程");
synchronized (obj) {
// obj.notify(); // 唤醒obj上一个线程
obj.notifyAll(); // 唤醒obj上所有等待线程
}
}
}

在 Java 中,wait() 和 notify() 方法被定义在 Object 类中,而不是 Thread 类中,这主要是由以下几个原因:
1. 对象锁的机制
- 在 Java 中,所有的对象都有一个内置的监视器(monitor),它是用来实现同步的机制。当一个线程调用
synchronized方法或代码块时,它锁定了一个对象(即获取了这个对象的监视器),其他线程就无法再获得这个锁。 wait()和notify()与对象的监视器管理密切相关。它们都是与该对象的锁状态直接交互的。具体来说,调用wait()方法的线程会释放该对象的锁并进入等待状态,直到其他线程调用notify()或notifyAll()来唤醒它。这种设计需要在对象层面进行管理,因此它们适合定义在Object类中。
2. 多线程和共享资源的概念
- 在多线程编程中,通常需要协作和通信。如果
wait()和notify()方法放在Thread类中,意味着它们只适用于单个线程而不是与具体的对象相关联。这样就失去了对象锁的意义。 - 线程可能需要在不同的对象上等待或唤醒,而这些操作都需要与对象的状态相关联。因此,将这些方法定义在
Object类中能更好地支持基于对象的等待和通知机制。
3. 灵活性与通用性
- 将
wait()和notify()方法放在Object类中,使得所有 Java 对象都可以使用这些方法。这增加了灵活性和通用性,因为任何对象都可以作为锁,而不是仅仅依赖于线程实现。 - 这种设计使得 Java 的同步机制更加一致。程序员可以根据需要在任何对象上调用
wait()和notify(),允许在不同的上下文中处理线程间的协调。
sleep(long n)和wait(long n)的区别

package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test19")
public class Test19 {
static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
log.debug("获得锁");
try {
// Thread.sleep(2000); // 不会释放锁
lock.wait(2000); // 会释放锁
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t1").start();
Sleeper.sleep(1);
synchronized (lock) {
log.debug("获得锁");
}
}
}


Step 1:
package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCorrectPosture")
public class TestCorrectPostureStep1 {
static final Object room = new Object();
static boolean hasCigarette = false; // 有没有烟
static boolean hasTakeout = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (!hasCigarette) {
log.debug("没烟,先歇会!");
sleep(2);
}
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (hasCigarette) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
}
}
}, "小南").start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
}
}, "其它人").start();
}
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
// 这里能不能加 synchronized (room)?
// synchronized (room) {
hasCigarette = true;
log.debug("烟到了噢!");
// }
}, "送烟的").start();
}
}

Step 2:
package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCorrectPosture")
public class TestCorrectPostureStep2 {
static final Object room = new Object();
static boolean hasCigarette = false;
static boolean hasTakeout = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (!hasCigarette) {
log.debug("没烟,先歇会!");
try {
room.wait(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (hasCigarette) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
}
}
}, "小南").start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
}
}, "其它人").start();
}
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
hasCigarette = true;
log.debug("烟到了噢!");
room.notify();
}
}, "送烟的").start();
}
}

Step 3:wait / notifyAll
package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCorrectPosture")
public class TestCorrectPostureStep3 {
static final Object room = new Object();
static boolean hasCigarette = false;
static boolean hasTakeout = false;
// 虚假唤醒
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (!hasCigarette) {
log.debug("没烟,先歇会!");
try {
room.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (hasCigarette) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
} else {
log.debug("没干成活...");
}
}
}, "小南").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
log.debug("外卖送到没?[{}]", hasTakeout);
if (!hasTakeout) {
log.debug("没外卖,先歇会!");
try {
room.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("外卖送到没?[{}]", hasTakeout);
if (hasTakeout) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
} else {
log.debug("没干成活...");
}
}
}, "小女").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
hasTakeout = true;
log.debug("外卖到了噢!");
room.notifyAll();
}
}, "送外卖的").start();
}
}

Step 4:while循环
package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCorrectPosture")
public class TestCorrectPostureStep5 {
static final Object room = new Object();
static boolean hasCigarette = false;
static boolean hasTakeout = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
while (!hasCigarette) {
log.debug("没烟,先歇会!");
try {
room.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
if (hasCigarette) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
} else {
log.debug("没干成活...");
}
}
}, "小南").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
log.debug("外卖送到没?[{}]", hasTakeout);
while (!hasTakeout) {
log.debug("没外卖,先歇会!");
try {
room.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("外卖送到没?[{}]", hasTakeout);
if (hasTakeout) {
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
} else {
log.debug("没干成活...");
}
}
}, "小女").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (room) {
hasTakeout = true;
log.debug("外卖到了噢!");
room.notifyAll();
}
}, "送外卖的").start();
}
}

同步模式之保护性暂停


package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test20")
public class Test20 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new People().start(); // 等待收信
}
Sleeper.sleep(1);
for (Integer id : Mailboxes.getIds()) {
new Postman(id, "内容" + id).start();
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.People")
class People extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
// 收信
GuardedObject guardedObject = Mailboxes.createGuardedObject();
log.debug("开始收信 id:{}", guardedObject.getId());
Object mail = guardedObject.get(5000);
log.debug("收到信 id:{}, 内容:{}", guardedObject.getId(), mail);
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Postman")
class Postman extends Thread {
private int id;
private String mail;
public Postman(int id, String mail) {
this.id = id;
this.mail = mail;
}
@Override
public void run() {
GuardedObject guardedObject = Mailboxes.getGuardedObject(id);
log.debug("送信 id:{}, 内容:{}", id, mail);
guardedObject.complete(mail);
}
}
class Mailboxes {
private static Map<Integer, GuardedObject> boxes = new Hashtable<>();
private static int id = 1;
// 产生唯一 id
private static synchronized int generateId() {
return id++;
}
public static GuardedObject getGuardedObject(int id) {
return boxes.remove(id);
}
public static GuardedObject createGuardedObject() {
GuardedObject go = new GuardedObject(generateId());
boxes.put(go.getId(), go);
return go;
}
public static Set<Integer> getIds() {
return boxes.keySet();
}
}
// 增加超时效果
class GuardedObject {
// 标识 Guarded Object
private int id;
public GuardedObject(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
// 结果
private Object response;
// 获取结果
// timeout 表示要等待多久 2000
public Object get(long timeout) {
synchronized (this) {
// 开始时间 15:00:00
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 经历的时间
long passedTime = 0;
while (response == null) {
// 这一轮循环应该等待的时间
long waitTime = timeout - passedTime;
// 经历的时间超过了最大等待时间时,退出循环
if (waitTime <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
this.wait(waitTime); // 虚假唤醒 15:00:01
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 求得经历时间
passedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin; // 15:00:02 1s
}
return response;
}
}
// 产生结果
public void complete(Object response) {
synchronized (this) {
// 给结果成员变量赋值
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}

异步模式之生产者/消费者

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test21")
public class Test21 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageQueue queue = new MessageQueue(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int id = i;
new Thread(() -> {
queue.put(new Message(id , "值"+id));
}, "生产者" + i).start();
}
new Thread(() -> {
while(true) {
sleep(1);
Message message = queue.take();
}
}, "消费者").start();
}
}
// 消息队列类 , java 线程之间通信
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MessageQueue")
class MessageQueue {
// 消息的队列集合
private LinkedList<Message> list = new LinkedList<>();
// 队列容量
private int capcity;
public MessageQueue(int capcity) {
this.capcity = capcity;
}
// 获取消息
public Message take() {
// 检查队列是否为空
synchronized (list) {
while(list.isEmpty()) {
try {
log.debug("队列为空, 消费者线程等待");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 从队列头部获取消息并返回
Message message = list.removeFirst();
log.debug("已消费消息 {}", message);
list.notifyAll();
return message;
}
}
// 存入消息
public void put(Message message) {
synchronized (list) {
// 检查对象是否已满
while(list.size() == capcity) {
try {
log.debug("队列已满, 生产者线程等待");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 将消息加入队列尾部
list.addLast(message);
log.debug("已生产消息 {}", message);
list.notifyAll();
}
}
}
final class Message {
private int id;
private Object value;
public Message(int id, Object value) {
this.id = id;
this.value = value;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Message{" +
"id=" + id +
", value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
7. Park & Unpark



package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestParkUnpark")
public class TestParkUnpark {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("start...");
sleep(2);
log.debug("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("resume...");
}, "t1");
t1.start();
sleep(1);
log.debug("unpark...");
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
}







8. 线程状态转换



package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestWaitNotify")
public class TestWaitNotify {
final static Object obj = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
log.debug("执行....");
try {
obj.wait(); // 让线程在obj上一直等待下去
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("其它代码....");
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
log.debug("执行....");
try {
obj.wait(); // 让线程在obj上一直等待下去
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("其它代码....");
}
},"t2").start();
// 主线程两秒后执行
sleep(0.5);
log.debug("唤醒 obj 上其它线程");
synchronized (obj) {
// obj.notify(); // 唤醒obj上一个线程
obj.notifyAll(); // 唤醒obj上所有等待线程
}
}
}





9. 多把锁

package cn.itcast.n4;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
public class TestMultiLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigRoom bigRoom = new BigRoom();
new Thread(() -> {
bigRoom.study();
},"小南").start();
new Thread(() -> {
bigRoom.sleep();
},"小女").start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BigRoom")
class BigRoom {
private final Object studyRoom = new Object();
private final Object bedRoom = new Object();
public void sleep() {
synchronized (bedRoom) {
log.debug("sleeping 2 小时");
Sleeper.sleep(2);
}
}
public void study() {
synchronized (studyRoom) {
log.debug("study 1 小时");
Sleeper.sleep(1);
}
}
}

8. 死锁

package cn.itcast.n4.deadlock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestDeadLock")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
}
private static void test1() {
Object A = new Object();
Object B = new Object();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (A) {
log.debug("lock A");
sleep(1);
synchronized (B) {
log.debug("lock B");
log.debug("操作...");
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (B) {
log.debug("lock B");
sleep(0.5);
synchronized (A) {
log.debug("lock A");
log.debug("操作...");
}
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
定位死锁

哲学家就餐问题

package cn.itcast.n4.deadlock.v1;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Random;
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1");
Chopstick c2 = new Chopstick("2");
Chopstick c3 = new Chopstick("3");
Chopstick c4 = new Chopstick("4");
Chopstick c5 = new Chopstick("5");
new Philosopher("苏格拉底", c1, c2).start();
new Philosopher("柏拉图", c2, c3).start();
new Philosopher("亚里士多德", c3, c4).start();
new Philosopher("赫拉克利特", c4, c5).start();
new Philosopher("阿基米德", c5, c1).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Philosopher")
class Philosopher extends Thread {
Chopstick left;
Chopstick right;
public Philosopher(String name, Chopstick left, Chopstick right) {
super(name);
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 尝试获得左手筷子
synchronized (left) {
// 尝试获得右手筷子
synchronized (right) {
eat();
}
}
}
}
Random random = new Random();
private void eat() {
log.debug("eating...");
Sleeper.sleep(0.5);
}
}
class Chopstick {
String name;
public Chopstick(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "筷子{" + name + '}';
}
}
9. 活锁
活锁出现在两个线程互相改变对方的结束条件,最后谁也无法结束
解决:随机的睡眠时间
package cn.itcast.n4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestLiveLock")
public class TestLiveLock {
static volatile int count = 10;
static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
// 期望减到 0 退出循环
while (count > 0) {
sleep(0.2);
count--;
log.debug("count: {}", count);
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
// 期望超过 20 退出循环
while (count < 20) {
sleep(0.2);
count++;
log.debug("count: {}", count);
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
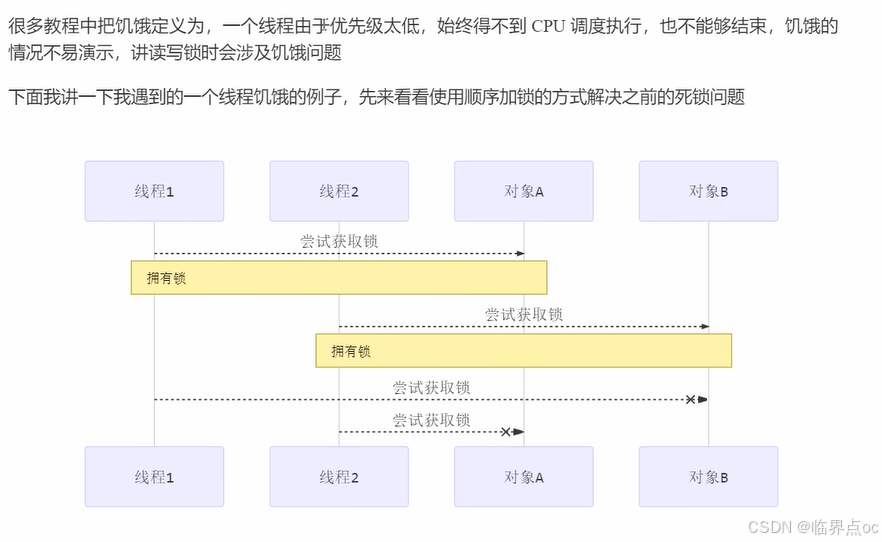
10. 饥饿

package cn.itcast.n4.deadlock.v1;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Random;
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1");
Chopstick c2 = new Chopstick("2");
Chopstick c3 = new Chopstick("3");
Chopstick c4 = new Chopstick("4");
Chopstick c5 = new Chopstick("5");
new Philosopher("苏格拉底", c1, c2).start();
new Philosopher("柏拉图", c2, c3).start();
new Philosopher("亚里士多德", c3, c4).start();
new Philosopher("赫拉克利特", c4, c5).start();
new Philosopher("阿基米德", c1, c5).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Philosopher")
class Philosopher extends Thread {
Chopstick left;
Chopstick right;
public Philosopher(String name, Chopstick left, Chopstick right) {
super(name);
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 尝试获得左手筷子
synchronized (left) {
// 尝试获得右手筷子
synchronized (right) {
eat();
}
}
}
}
Random random = new Random();
private void eat() {
log.debug("eating...");
Sleeper.sleep(0.5);
}
}
class Chopstick {
String name;
public Chopstick(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "筷子{" + name + '}';
}
}11. ReentrantLock

可重入

package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args){
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("enter main");
m1();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void m1() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("enter m1");
m2();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void m2() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("enter m2");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
可打断
防止无限制等待,避免死锁
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 如果没有竞争那么此方法就会获取lock对象锁
// 如果有竞争就进入阻塞队列,可以被其他线程用interrupt方法打断
log.debug("尝试获得锁");
lock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("没有获取到锁,返回");
return;
}
try {
log.debug("获取到锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
t1.start();
Sleeper.sleep(1);
log.debug("打断t1");
t1.interrupt();
}
}
锁超时
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test22")
public class Test22 {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("尝试获得锁");
try {
if (!lock.tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
log.debug("获取不到锁");
return;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("获取不到锁");
return;
}
try {
log.debug("获得到锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
log.debug("获得到锁");
t1.start();
sleep(1);
log.debug("释放了锁");
lock.unlock();
}
}

哲学家就餐问题
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test23")
public class Test23 {public static void main(String[] args) {
Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1");
Chopstick c2 = new Chopstick("2");
Chopstick c3 = new Chopstick("3");
Chopstick c4 = new Chopstick("4");
Chopstick c5 = new Chopstick("5");
new Philosopher("苏格拉底", c1, c2).start();
new Philosopher("柏拉图", c2, c3).start();
new Philosopher("亚里士多德", c3, c4).start();
new Philosopher("赫拉克利特", c4, c5).start();
new Philosopher("阿基米德", c5, c1).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Philosopher")
class Philosopher extends Thread {
Chopstick left;
Chopstick right;
public Philosopher(String name, Chopstick left, Chopstick right) {
super(name);
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 尝试获得左手筷子
if(left.tryLock()) {
try {
// 尝试获得右手筷子
if(right.tryLock()) {
try {
eat();
} finally {
right.unlock();
}
}
} finally {
left.unlock(); // 释放自己手里的筷子
}
}
}
}
Random random = new Random();
private void eat() {
log.debug("eating...");
Sleeper.sleep(0.5);
}
}
class Chopstick extends ReentrantLock {
String name;
public Chopstick(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "筷子{" + name + '}';
}
}
公平锁
ReentrantLock默认是不公平的

条件变量

package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import static cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper.sleep;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test24")
public class Test24 {
static final Object room = new Object();
static boolean hasCigarette = false;
static boolean hasTakeout = false;
static ReentrantLock ROOM = new ReentrantLock();
// 等待烟的休息室
static Condition waitCigaretteSet = ROOM.newCondition();
// 等外卖的休息室
static Condition waitTakeoutSet = ROOM.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
ROOM.lock();
try {
log.debug("有烟没?[{}]", hasCigarette);
while (!hasCigarette) {
log.debug("没烟,先歇会!");
try {
waitCigaretteSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
} finally {
ROOM.unlock();
}
}, "小南").start();
new Thread(() -> {
ROOM.lock();
try {
log.debug("外卖送到没?[{}]", hasTakeout);
while (!hasTakeout) {
log.debug("没外卖,先歇会!");
try {
waitTakeoutSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("可以开始干活了");
} finally {
ROOM.unlock();
}
}, "小女").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
ROOM.lock();
try {
hasTakeout = true;
log.debug("外卖送到了");
waitTakeoutSet.signal();
} finally {
ROOM.unlock();
}
}, "送外卖的").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
ROOM.lock();
try {
hasCigarette = true;
log.debug("烟送到了");
waitCigaretteSet.signal();
} finally {
ROOM.unlock();
}
}, "送烟的").start();
}
}

12. 同步模式之顺序控制
固定运行顺序
wait / notify
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test25")
public class Test25 {
static final Object lock = new Object();
// 表示 t2 是否运行过
static boolean t2runned = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
while (!t2runned) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("1");
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
log.debug("2");
t2runned = true;
lock.notify();
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}

await / signal
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.n2.util.Sleeper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test")
public class Test {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 等待t2执行的休息室
static Condition waitT2Set = lock.newCondition();
static boolean t2runned = false;
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
while (!t2runned) {
try {
waitT2Set.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
log.debug("1");
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("2");
t2runned = true;
waitT2Set.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
park / unpark
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test26")
public class Test26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("1");
}, "t1");
t1.start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("2");
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
},"t2").start();
}
}
交替输出

wiat / notify版
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test27")
public class Test27 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WaitNotify wn = new WaitNotify(1, 5);
new Thread(() -> {
wn.print("a", 1, 2);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
wn.print("b", 2, 3);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
wn.print("c", 3, 1);
}).start();
}
}
/*
输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记
a 1 2
b 2 3
c 3 1
*/
class WaitNotify {
// 打印 a 1 2
public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFlag) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
while(flag != waitFlag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print(str);
flag = nextFlag;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
// 等待标记
private int flag; // 2
// 循环次数
private int loopNumber;
public WaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber) {
this.flag = flag;
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
}await / signal
package cn.itcast.test;
import sun.rmi.runtime.Log;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Test30 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AwaitSignal awaitSignal = new AwaitSignal(5);
Condition a = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition b = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition c = awaitSignal.newCondition();
new Thread(() -> {
awaitSignal.print("a", a, b);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
awaitSignal.print("b", b, c);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
awaitSignal.print("c", c, a);
}).start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
awaitSignal.lock();
try {
System.out.println("开始...");
a.signal();
} finally {
awaitSignal.unlock();
}
}
}
class AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock{
private int loopNumber;
public AwaitSignal(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
// 参数1 打印内容, 参数2 进入哪一间休息室, 参数3 下一间休息室
public void print(String str, Condition current, Condition next) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
lock();
try {
current.await();
System.out.print(str);
next.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}
}
park / unpark
package cn.itcast.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test31")
public class Test31 {
static Thread t1;
static Thread t2;
static Thread t3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParkUnpark pu = new ParkUnpark(5);
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
pu.print("a", t2);
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
pu.print("b", t3);
});
t3 = new Thread(() -> {
pu.print("c", t1);
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
// 唤醒第一个线程
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
}
class ParkUnpark {
public void print(String str, Thread next) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
// 阻塞
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print(str);
// 唤醒下一个线程
LockSupport.unpark(next);
}
}
private int loopNumber;
public ParkUnpark(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








