JavaWeb
使用Java开发Web服务的技术,统称为JavaWeb。
B/S与C/S模式
B/S:Browser/Server 浏览器/服务器模式
用户只需要一个浏览器即可访问服务器
C/S:Clint/Server 客户端/服务器模式
用户需要下载客户端才能访问服务器
网站
用户通过浏览器访问某个域名或IP地址时,浏览到的综合性页面
实际就是发布在服务器上的一个应用程序,用户通过浏览器访问该程序。
网页
网站中的一个页面
静态页面:所有人看到的数据都一致
动态页面:不同的人看到的页面中的数据不一致
JavaWeb就是B/S模式下的软件开发,开发综合性的服务网站。
网络服务器
部署Web项目的平台。
Tomcat
由Apache、Sun和其他公司及个人共同开发的web服务器。
免费、开源、轻量级,在中小型系统中普遍被使用。
是开发和调试Web项目的首选。
目录结构
目录名称 | 作用 |
bin | 保存一些tomcat相关的可执行文件,如startup.bat等 |
conf | 保存tomcat的配置文件,如server.xml中可以修改默认的端口号 |
lib | 保存tomcat运行时所需的jar文件 |
logs | 保存tomcat运行日志 |
temp | 保存tomcat运行时产生的临时文件 |
webapps | 保存发布在tomcat服务器上的应用程序 |
work | 保存tomcat运行时产生的编译后的文件 |
Maven
用于结构化管理jar文件的工具。
通过在Maven项目中加入某个jar文件的依赖,让其自动从Maven云仓库中下载对应的jar文件。
使用IDEA创建基于Maven的Web项目
1.新建webapp模板
2.设置项目名称和路径
3.设置Maven配置文件
Maven默认的配置文件会从官网下载jar文件,速度较慢,并且下载的jar文件默认会保存在c盘。
这里在D盘的根目录下新建了一个MavenRepository的本地仓库,用于保存下载的jar文件,并且设置国内的镜像下载。
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<!--这个根路径可以更改-->
<localRepository>D:\MavenRepository\maven_jar</localRepository>
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>aliyunmaven</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<name>阿里云公共仓库</name>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<profiles>
</profiles>
</settings>如果IDEA版本没有这个选项,暂时跳过,等待项目创建成功后进入主界面进行设置。
HTTP状态码
用特定数字表示状态。https://http.cat/
常见状态码 | 含义 |
200 | 成功 |
404 | 资源未找到 |
500 | 服务器内部错误 |
405 | 方法不允许 |
Servlet
Server+Applet 运行在服务器上的程序
编写Servlet的步骤
1.在项目中导入Servlet相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>2.在项目的java目录下,创建一个类,继承HttpServlet,重写doGet和doPost方法
通常用户无论发送的是get还是post请求,实际都会执行同一件事情。
为了不将代码重复写两遍,可以在doPost方法中调用doGet方法或在doGet方法中调用doPost方法
package com.hqyj.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
* Servlet是运行在服务器上的应用程序
* 编写一个Servlet的步骤
* 1.创建一个类型,继承HttpServlet
* 2.重写doGet和doPost方法
* 3.在web.xml中设置请求该Servlet的URL地址
* */
public class FirstServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
//只需编写一遍代码
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
//为了不重复编写代码,在这get中调用post或在post中调用get
doPost(req, resp);
}
}3.在web.xml中设置Servlet的请求映射
<!--声明一个Servlet-->
<servlet>
<!--自定义Servlet的名称-->
<servlet-name>firstServlet</servlet-name>
<!--Servlet类所在完整路径(全限定名)-->
<servlet-class>com.hqyj.servlet.FirstServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--设置某个Servlet的请求映射-->
<servlet-mapping>
<!--指定要设置映射的Servlet-->
<servlet-name>firstServlet</servlet-name>
<!--设置请求映射,以/开头-->
<url-pattern>/first</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>4.访问Servlet
至此,重启tomcat,访问"项目上下文地址/first",就表示访问FirstServlet类。
如果是通过浏览器地址栏访问,相当于get请求,执行servlet中的doGet方法
三层架构
通常所说的三层架构中的三层,是指“数据访问层、业务逻辑层和视图表现层”
数据访问层,用于连接数据库,对数据做增删改查的操作
业务逻辑层,用于处理业务逻辑,在适当的情况下调用数据访问层中的方法
视图表现层,用于展示数据和提供用户输入数据的渠道,在适当的情况下调用业务逻辑层中的方法

访问服务器的某个URL
在浏览器的地址栏中输入对应的URL,属于GET提交
使用a标签,在href中输入对应的URL,属于GET提交
使用form表单,在action中输入对应的URL,通过method修改提交方式为GET或POST
页面向服务端提交数据的方式
使用form表单的name属性显示提交
<form action="url地址" method="get">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>提交的数据会暴露在浏览器的地址栏中
使用form表单的name属性隐式提交
<form action="url地址" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>提交的数据不会暴露在浏览器的地址栏中
通过"?参数名=值"方式提交
在地址栏中输入URL的时候,末尾加入这部分
url地址?参数=值&参数=值在a标签的href属性中加入这部分,如果有多个参数,通过&拼接
<a href="地址?参数=值&参数=值">xxx</a>服务器端获取页面传递的数据
以上任何方式提交到服务器的数据,都可以使用以下方式获取。
String str=request.getParameter("name名或?后的参数名");
表单提交数据注意事项
表单通过action提交设置的路径,如果要在路径中传递参数,只能使用post方式提交
<form action="xxxxx?参数=值" method="post">
</form>使用get方式提交,无法识别action路径中的参数,如果要传递参数,使用隐藏域
<form action="xxxxx" method="get">
<input type="hidden" name="参数名" value="参数值">
</form>解决请求和响应的中文乱码
//在servlet的doGet或doPost所有代码之前中加入
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");使用Servlet实现单表的增删改查
数据库脚本文件
/*
Navicat Premium Data Transfer
Source Server : localhost_3306
Source Server Type : MySQL
Source Server Version : 80029
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Schema : gamedb
Target Server Type : MySQL
Target Server Version : 80029
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 03/01/2023 14:46:16
*/
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for hero
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `hero`;
CREATE TABLE `hero` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '编号',
`name` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`position` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '定位',
`sex` char(1) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '男' COMMENT '性别',
`price` int NOT NULL DEFAULT 4800 COMMENT '价格',
`shelf_date` date NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '上架日期',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,
UNIQUE INDEX `name`(`name`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 16 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;实体类entity
实体的属性名保持和表的字段名一致,使用驼峰命名法
package com.hqyj.entity;
public class Hero {
private int id;
private String name;
private String position;
private String sex;
private int price;
private String shelfDate;
/*
全参构造方法用于查询
*/
public Hero(int id, String name, String position, String sex, int price, String shelfDate) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.position = position;
this.sex = sex;
this.price = price;
this.shelfDate = shelfDate;
}
/*
不带id的构造方法用于添加
*/
public Hero(String name, String position, String sex, int price, String shelfDate) {
this.name = name;
this.position = position;
this.sex = sex;
this.price = price;
this.shelfDate = shelfDate;
}
//省略get/set/toString
}数据操作类dao
import com.hqyj.entity.Hero;
import com.hqyj.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class HeroDao {
Connection conn;
PreparedStatement pst;
ResultSet rs;
/*
* 查询所有
* */
public List<Hero> queryAll() {
ArrayList<Hero> list = new ArrayList<>();
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement("select * from hero");
rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
String position = rs.getString(3);
String sex = rs.getString(4);
int price = rs.getInt(5);
String shelfDate = rs.getString(6);
Hero hero = new Hero(id, name, position, sex, price, shelfDate);
list.add(hero);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("查询所有异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return list;
}
/*
* 添加
* */
public boolean addHero(Hero hero) {
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
String sql = "insert into hero values(null,?,?,?,?,?)";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1, hero.getName());
pst.setString(2, hero.getPosition());
pst.setString(3, hero.getSex());
pst.setInt(4, hero.getPrice());
pst.setString(5, hero.getShelfDate());
return pst.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("添加异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return false;
}
/*
* 删除
* */
public boolean delete(int id) {
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement("delete from hero where id=?");
pst.setInt(1, id);
return pst.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("删除异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return false;
}
/*
* 根据id查询
* */
public Hero findById(int id) {
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement("select * from hero where id=?");
pst.setInt(1, id);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
String name = rs.getString(2);
String position = rs.getString(3);
String sex = rs.getString(4);
int price = rs.getInt(5);
String shelfDate = rs.getString(6);
Hero hero = new Hero(id, name, position, sex, price, shelfDate);
return hero;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("根据id查询异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return null;
}
/*
* 修改
* */
public boolean update(Hero updateHero) {
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement("update hero set name=?,position=?,sex=?,price=?,shelf_date=? where id=?");
pst.setString(1, updateHero.getName());
pst.setString(2, updateHero.getPosition());
pst.setString(3, updateHero.getSex());
pst.setInt(4, updateHero.getPrice());
pst.setString(5, updateHero.getShelfDate());
pst.setInt(6, updateHero.getId());
return pst.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("修改异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return false;
}
}控制层/表现层servlet
package com.hqyj.servlet;
import com.hqyj.dao.HeroDao;
import com.hqyj.entity.Hero;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.List;
public class HeroServlet extends HttpServlet {
//当前Servlet中需要访问Hero表中的数据,所以加入HeroDao对象
HeroDao heroDao = new HeroDao();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//解决请求和响应的中文乱码
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//获取op,用一个Servlet,判断不同的op值来执行不同的操作
String op = req.getParameter("op");
switch (op) {
case "queryAll":
//调用查询
List<Hero> list = heroDao.queryAll();
//通过resp响应对象调用getWriter()方法,获取字符输出流对象writer,通过writer打印页面
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();
writer.println("<html>");
writer.println("<body>");
writer.println("<table border='1'>");
writer.println("<tr><td>编号</td><td>姓名</td><td>定位</td><td>性别</td><td>价格</td><td>上架时间</td><td colspan=2>操作</td></tr>");
for (Hero hero : list) {
writer.println("<tr>");
writer.println("<td>" + hero.getId() + "</td>");
writer.println("<td>" + hero.getName() + "</td>");
writer.println("<td>" + hero.getPosition() + "</td>");
writer.println("<td>" + hero.getSex() + "</td>");
writer.println("<td>" + hero.getPrice() + "</td>");
writer.println("<td>" + hero.getShelfDate() + "</td>");
//修改的步骤:1.根据id查询,打印详情页 2.在详情页中修改
writer.println("<td><a href='http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=findById&id=" + hero.getId() + "'>修改</a></td>");
//访问某个URL时传递多个参数: URL?参数1=值&参数2=值..
writer.println("<td><a href='http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=delete&id=" + hero.getId() + "'>删除</a></td>");
writer.println("</tr>");
}
writer.println("</table>");
writer.println("</body>");
writer.println("</html>");
writer.close();
break;
case "delete":
int id = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("id"));
if (heroDao.delete(id)) {
//跳转到查询所有
resp.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=queryAll");
}
break;
case "findById":
//获取要修改的id
int findId = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("id"));
//调用查询
Hero byId = heroDao.findById(findId);
//打印详情页
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
pw.println("<html>");
pw.println("<body>");
//如果表单要在action中传递数据,只能使用post方式提交
//pw.println("<form action='http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=update' method='post'> ");
//如果表单使用get方式提交,通过隐藏域提交op
pw.println("<form action='http://localhost:8080/day1/hero'> ");
pw.println("<input type='hidden' name='op' value='update' >");
//使用隐藏域提交id
pw.println("<input type='hidden' name='id' value='" + byId.getId() + "' >");
pw.println("姓名:<input type='text' name='name' value='" + byId.getName() + "'><br>");
pw.println("定位:<input type='text' name='position' value='" + byId.getPosition() + "'><br>");
/*if("男".equals(byId.getSex())){
pw.println("<input type='radio' checked>男");
pw.println("<input type='radio' >女");
}else{
pw.println("<input type='radio' >男");
pw.println("<input type='radio' checked>女");
}*/
pw.println("性别:<input type='radio' name='sex' value='男' " + ("男".equals(byId.getSex()) ? "checked" : "") + ">男");
pw.println("<input type='radio' name='sex' value='女' " + ("女".equals(byId.getSex()) ? "checked" : "") + ">女<br>");
pw.println("价格:<input type='num' name='price' value='" + byId.getPrice() + "'><br>");
pw.println("上架时间:<input type='date' name='shelfDate' value='" + byId.getShelfDate() + "'><br>");
pw.println("<input type='submit' value='修改'><br>");
pw.println("</form>");
pw.println("</body>");
pw.println("</html>");
break;
case "update":
//获取参数
int updateId = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("id"));
String updateName = req.getParameter("name");
String updateSex = req.getParameter("sex");
String updatePosition = req.getParameter("position");
int updatePrice = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("price"));
String updateShelfDate = req.getParameter("shelfDate");
//创建待修改的对象,调用修改,跳转到查询所有页面
Hero updateHero = new Hero(updateId, updateName, updatePosition, updateSex, updatePrice, updateShelfDate);
heroDao.update(updateHero);
//跳转到查询所有
resp.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=queryAll");
break;
case "addHero":
//获取页面提交的数据
//request.getParameter("name名")
String name=req.getParameter("name");
String position=req.getParameter("position");
String sex=req.getParameter("sex");
int price=Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("price"));
String shelfDate=req.getParameter("shelfDate");
//创建添加对象,调用添加方法
Hero hero = new Hero(name, position, sex, price, shelfDate);
if (heroDao.addHero(hero)) {
resp.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=queryAll");
}
break;
}
}
}配置Servlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hero</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.hqyj.servlet.HeroServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hero</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hero</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>添加页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/day1/hero">
<!--通过隐藏域提交op-->
<input type="hidden" name="op" value="addHero">
角色名:<input type="text" name="name" required><br>
定位:<input type="text" name="position" required><br>
性别:<input type="radio" name="sex" value="男" checked>男<input type="radio" name="sex" value="女">女<br>
价格:<input type="number" min="1" name="price" required><br>
上架日期:<input type="date" name="shelfDate" required><br>
<input type="submit" value="添加">
</form>
</body>
</html>主页
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/day1/hero?op=queryAll">查看所有hero</a>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/day1/pages/addHero.html">添加</a>
</body>
</html>web.xml文件中的常用标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--设置项目启动的欢迎页-->
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>login.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<!--设置错误页面-->
<error-page>
<!--错误码-->
<error-code>404</error-code>
<!--页面路径-->
<location>/404.html</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<!--异常类型-->
<exception-type>java.lang.NullPointerException</exception-type>
<location>/error.html</location>
</error-page>
<!--上下文参数-->
<context-param>
<!--参数名-->
<param-name>contentParam</param-name>
<!--参数值-->
<param-value>全局参数</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--servlet标签-->
<!--servlet-mapping标签-->
<!--filter标签-->
<!--filter-mapping标签-->
<!--session-config标签-->
</web-app>Servlet的生命周期
构造方法**-->init()-->service()/doGet()/doPost()-->**destory()
在访问某servlet时
1.执行构造方法一次
2.初始化一次,调用init()方法
3.调用service()方法,之后每次访问都会调用该方法。有该方法时,doGet和doPost失效。
如果没有该方法,会根据请求方式试图调用doGet或doPost,如果没有相应的方法,会出现405状态码,表示请求方式不允许
4.在当前servlet所在项目从tomcat中停止时,销毁一次,调用destory()方法
使用注解开发Servlet
/*
* 使用注解开发Servlet
* 注解:@特定单词 如@Override
*
* 定义且配置Servlet的注解:@WebServlet("/请求映射")
* */
@WebServlet("/sysAdmin")
public class SysAdminServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
//访问该Servlet时要执行的内容
}
}
//@WebServlet("/sysAdmin")相当于在web.xml中进行配置servlet映射JSP
Java Server Page
使用Java开发、运行在服务器上的页面。
jsp文件的后缀名为".jsp"。
**JSP页面的本质是一个java文件(servlet)**。
在访问某个jsp页面时,会让该页面重新编译为.java文件-->.class文件,所以第一次访问某个JSP页面时会慢一些。
JSP的组成
1.HTML元素
2.脚本(java代码)
<%java代码;%>3.表达式
用于在页面中嵌入变量的值
<%=变量%>4.指令
<%@ 指令名 属性="值" %>page指令 用于设置当前页面的属性
include指令 用于引入其他页面
taglib指令 用于引入其他标签库
5.注释
<%-- jsp注释 --%>在浏览器中可以查看html的注释,无法查看jsp的注释
6.声明
<%! 定义方法 %>在<%%>中无法定义方法,如果非要在jsp页面中定义方法,需要使用声明。不建议在jsp页面中定义方法。
7.动作
jsp中定义了一些标签,可以代替某些java代码
<jsp:动作名></jsp:动作名>跳转
页面与页面之间跳转
//通过超链接跳转
<a href="另一个页面的地址">超链接</a>
//通过表单提交跳转
<form action="另一个页面的地址">
<input type="submit">
</form>
//通过按钮跳转
<button id="btn">跳转</button>
<script>
$("#btn").click(function(){
location.href="另一个页面的地址";
location.assign("另一个页面的地址");
});
</script>页面跳转至Servlet
<a href="servlet映射名">超链接</a>
<form action="servlet映射名">
<input type="submit">
</form>Servlet跳转到页面或另一个Servlet
请求转发(内部跳转)
request.getRequestDispatcher("跳转的地址").forward(request,response);如A同学问B同学问题,B同学自己去问C同学后得到了答案,将答案告诉给A同学。
跳转到目的地时,浏览器的地址栏中的内容是访问时的地址
如果在某个Servlet做完增删改的操作后,不要使用请求转发。因为当重新刷新页面时,会重复提交
如果在request中保存了数据,只能通过请求转发才能读取request中保存的数据
重定向(外部跳转)
response.sendRedirect("跳转的地址");如A同学问B同学问题,B同学告诉A同学去问C同学,A同学重新问C同学后得到答案。
跳转到目的地时,浏览器的地址栏中的内容是最终的目的路径
在做完增删改的操作后,使用重定向,可以保证最终页面与之前页面无关,刷新时不会重新提交
如果在request中保存了数据,使用重定向,保存的数据就会丢失
跳转时传递数据
保存
作用域对象.setAttribute(String str,Object obj);
//将一个名为str的对象obj保存到某个作用域中。request就是一个作用域。
List<泛型> 集合 = dao.查询();
//将查询到的集合保存到请求中,命名为list
request.setAttribute("list",集合);获取
Object obj = 作用域对象.getAttribute(String str);
//获取到的数据是Object类型,通常需要转型
List<泛型> list =(List<泛型>) request.getAttribute("list");MySQL分页查询
原理
select * from 表;
-- 查询前N条记录
select * from 表 limit N;
-- 从第N条记录开始查询M条记录
select * from 表 limit N,M;
-- 如每页显示8条,第一页
select * from 表 limit 0,8
-- 第二页
select * from 表 limit 8,8
-- 公式 size表示每页显示的数量 page表示页数
select * from 表 limit (page-1)*size,sizedao层中分页相关方法
/*
* 查询总记录数
* */
public int getSumCount() {
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
String sql = "select count(book_id) from book_info ";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return rs.getInt(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("查询总记录数异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return 0;
}
/*
* 分页查询
* */
public List<BookInfo> queryByPage(int page, int size) {
ArrayList<BookInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
String sql = "select * from book_info limit ?,?";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, (page - 1) * size);
pst.setInt(2, size);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
int bookId = rs.getInt(1);
int typeId = rs.getInt(2);
String bookName = rs.getString(3);
String bookAuthor = rs.getString(4);
int bookPrice = rs.getInt(5);
int bookNum = rs.getInt(6);
String publisherDate = rs.getString(7);
String bookImg = rs.getString(8);
//参数中所需的主表对象实体,需要通过dao对象查询
BookInfo bookInfo = new BookInfo(bookId, typeId, bookName, bookAuthor, bookPrice, bookNum, publisherDate, bookImg, btDao.findById(typeId));
list.add(bookInfo);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("分页查询异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return list;
}servlet中加入分页请求判断
package com.hqyj.bookShop.servlet;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.dao.BookInfoDao;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.entity.BookInfo;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@WebServlet("/bookInfo")
public class BookInfoServlet extends HttpServlet {
//创建数据访问层对象
BookInfoDao biDao = new BookInfoDao();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String op = req.getParameter("op");
switch (op) {
//分页查询
case "queryByPage":
//得到总记录数
int sumCount = biDao.getSumCount();
//将总记录数保存到请求中
req.setAttribute("sumCount",sumCount);
//初始第一页
int page=1;
int size=8;
//获取要查询的页数
if (req.getParameter("page")!=null) {
page=Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("page"));
}
//调用分页查询
List<BookInfo> list2 = biDao.queryByPage(page,size);
//将查询的结果保存、跳转
req.setAttribute("list", list2);
req.getRequestDispatcher("./pages/bookList.jsp").forward(req, resp);
break;
}
}
}页面
<%@ page import="com.hqyj.bookShop.entity.BookInfo" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<%
List<BookInfo> list = (List<BookInfo>) request.getAttribute("list");
%>
<div class="product_list">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right">
<%for (BookInfo bookInfo : list) {%>
<div>
<img alt="暂无图片" src="./img/<%=bookInfo.getBookImg()%>">
<p class="title"><%=bookInfo.getBookName()%>
</p>
<p class="desc"><%=bookInfo.getBookType().getTypeName()%>|<%=bookInfo.getBookAuthor()%>
</p>
<p class="price">¥<%=bookInfo.getBookPrice()%>
</p>
</div>
<% }%>
</div>
</div>
<%
/*pno默认1*/
int pno = 1;
/*从请求中获取当前页数*/
if (request.getParameter("page") != null) {
pno = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("page"));
}
/*获取总记录数*/
int sumCount = (Integer) request.getAttribute("sumCount");
//计算最大页数
int maxPage=(int)Math.ceil(sumCount/8.0);
%>
<div class="pageTool">
<%--在请求分页的servlet时,传递page参数表示当前页--%>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/Web03/bookInfo?op=queryByPage&page=<%=(pno-1==0)?1:pno-1%>">上一页</a>
<span>第<%=pno%>页</span>
<span>共<%=maxPage%>页</span>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/Web03/bookInfo?op=queryByPage&page=<%=pno+1>maxPage?maxPage:pno+1%>">下一页</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>条件分页(关键字搜索)
原理
select * from 表 where 字段 like concat('%',keyword,'%') limit (page-1)*size,size dao
package com.hqyj.bookShop.dao;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.entity.BookInfo;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.entity.BookType;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BookInfoDao {
BookTypeDao btDao = new BookTypeDao();
/*
* 查询所有类型
* */
Connection conn;
PreparedStatement pst;
ResultSet rs;
/*
* 根据关键字查询总记录数
* */
public int getSumCount(String keyword) {
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
String sql = "select count(book_id) from book_info where book_name like concat('%',?,'%')";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1,keyword);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return rs.getInt(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("查询总记录数异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return 0;
}
/*
* 条件查询(关键字分页)
* */
public List<BookInfo> queryByCondition(int page,int size,String keyword){
ArrayList<BookInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
conn = DBUtil.getConn();
String sql = "select * from book_info where book_name like concat('%',?,'%') limit ?,?";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1, keyword);
pst.setInt(2, (page-1)*size);
pst.setInt(3, size);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
int bookId = rs.getInt(1);
int typeId = rs.getInt(2);
String bookName = rs.getString(3);
String bookAuthor = rs.getString(4);
int bookPrice = rs.getInt(5);
int bookNum = rs.getInt(6);
String publisherDate = rs.getString(7);
String bookImg = rs.getString(8);
//参数中所需的主表对象实体,需要通过dao对象查询
BookInfo bookInfo = new BookInfo(bookId, typeId, bookName, bookAuthor, bookPrice, bookNum, publisherDate, bookImg, btDao.findById(typeId));
list.add(bookInfo);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("关键字分页查询异常" + e);
} finally {
DBUtil.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
return list;
}
}servlet
package com.hqyj.bookShop.servlet;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.dao.BookInfoDao;
import com.hqyj.bookShop.entity.BookInfo;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@WebServlet("/bookInfo")
public class BookInfoServlet extends HttpServlet {
//创建数据访问层对象
BookInfoDao biDao = new BookInfoDao();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String op = req.getParameter("op");
switch (op) {
case "search":
//获取搜索关键字,第一次访问时没有关键字,使用""查询
String keyword = req.getParameter("keyword")==null?"":req.getParameter("keyword");
//得到总记录数
int sumCount = biDao.getSumCount(keyword);
//将总记录数保存到请求中
req.setAttribute("sumCount", sumCount);
//初始第一页
int page = 1;
int size = 8;
//获取要查询的页数
if (req.getParameter("page") != null) {
page = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("page"));
}
//调用条件查询,保存集合,跳转页面
List<BookInfo> list = biDao.queryByCondition(page, size, keyword);
req.setAttribute("list",list);
req.getRequestDispatcher("./pages/bookList.jsp").forward(req, resp);
break;
}
}
}页面
<%@ page import="com.hqyj.bookShop.entity.BookInfo" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.product_list {
width: 1240px;
height: 614px;
margin: 0px auto;
}
.product_list > div {
float: left;
}
.left {
width: 234px;
height: 614px;
background-image: url(./img/left.jpg);
background-size: 100%;
}
.right {
width: 992px;
height: 614px;
}
.right > div {
width: 234px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #fff;
float: left;
margin-left: 14px;
margin-bottom: 14px;
position: relative;
transition-duration: 0.2s;
}
.right > div img {
width: 160px;
height: 160px;
display: block;
margin: 20px auto;
}
.right .title {
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 400;
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.right .desc {
width: 214px;
height: 18px;
margin: 2px auto 10px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #b0b0b0;
overflow: hidden;
text-align: center;
}
.right .price {
text-align: center;
color: #ff6700;
font-size: 14px;
}
.right > div:hover {
/* 向上平移2px */
transform: translate(0, -3px);
box-shadow: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2) 0 0 20px;
}
.header {
width: 100%;
height: 80px;
border-bottom: 2px solid #eee;
background-color: #fff;
}
.header .logo {
width: 240px;
height: 80px;
float: left;
margin-left: 100px;
background-image: url("./img/logo.png");
background-size: cover;
}
.header .customer {
float: right;
width: 300px;
height: 80px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 80px;
color: deepskyblue;
font-size: 14px;
margin-right: 100px;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: deepskyblue;
}
.search {
width: 600px;
height: 80px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.search input[type="text"] {
width: 300px;
height: 40px;
margin-top: 20px;
margin-left: 100px;
font-size: 20px;
outline: none;
border: none;
border: 1px solid skyblue;
}
.search input[type="submit"] {
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
border: none;
background-color: #fff;
color: deepskyblue;
font-size: 20px;
}
.pageTool {
width: 200px;
margin: 0 auto 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<%
List<BookInfo> list = (List<BookInfo>) request.getAttribute("list");
%>
<div class="header">
<div class="logo"></div>
<div class="customer">
当前客户:xxx
<a href="#">我的购物车</a>
<a href="#">安全退出</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="search">
<form action="./bookInfo">
<input type="hidden" name="op" value="search">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字查询" value="<%=request.getParameter("keyword")==null?"": request.getParameter("keyword")%>" name="keyword">
<input type="submit" value="搜索">
</form>
</div>
<div class="product_list">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right">
<%for (BookInfo bookInfo : list) {%>
<div>
<img alt="暂无图片" src="./img/<%=bookInfo.getBookImg()%>">
<p class="title"><%=bookInfo.getBookName()%>
</p>
<p class="desc"><%=bookInfo.getBookType().getTypeName()%>|<%=bookInfo.getBookAuthor()%>
</p>
<p class="price">¥<%=bookInfo.getBookPrice()%>
</p>
</div>
<% }%>
</div>
</div>
<%
/*pno默认1*/
int pno = 1;
/*从请求中获取当前页数*/
if (request.getParameter("page") != null) {
pno = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("page"));
}
/*获取总记录数*/
int sumCount = (Integer) request.getAttribute("sumCount");
//计算最大页数
int maxPage=(int)Math.ceil(sumCount/8.0);
//获取请求中的关键字,如果没有搜索过,使用空白字符串
String keyword= request.getParameter("keyword")==null?"": request.getParameter("keyword");
%>
<div class="pageTool">
<%--在请求分页的servlet时,传递page参数表示当前页--%>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/Web03/bookInfo?op=search&keyword=<%=keyword%>&page=<%=(pno-1==0)?1:pno-1%>">上一页</a>
<span>第<%=pno%>页</span>
<span>共<%=maxPage%>页</span>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/Web03/bookInfo?op=search&keyword=<%=keyword%>&page=<%=pno+1>maxPage?maxPage:pno+1%>">下一页</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>绝对路径
<a href="地址">跳转</a>相对路径问题
/
表示从根目录(域名+ip)出发
./
表示从当前位置出发
../
表示跳向上一层
如有index页面所在路径为
localhost:8080/system/pages/index.html
<a href="/hello.html">跳转</a>
这种方式,从根目录(localhost:8080)出发,会跳转到localhost:8080/hello.html
<a href="./hello.html">跳转</a>
这种方式,从当前位置(localhost:8080/system/pages)出发,会跳转到localhost:8080/system/pages/hello.html
<a href="../hello.html">跳转</a>
这种方式,从当前位置跳向上一层,会跳转到localhost:8080/system/hello.html在jsp页面中,可以使用**${pageContex.request.contextPath}**表示页面上下文路径。
如项目默认上下文访问路径为localhost:8080/system
<a href="${pageContex.request.contextPath}/pages/hello.html">跳转</a>以上路径相当于/system/pages/hello.html,即从根目录出发localhost:8080/system/pages/hello.html
如果在jsp页面中无法识别${},在<%@ page%>中加入isELIgnored="false"
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isELIgnored="false" %>四大作用域对象
作用域:共享数据的区域
pageContext
当前页面对象。共享数据区域范围为当前页面。
如果不在同一个页面,数据无法读取。
request
请求对象。共享数据区域范围为一次请求。
如果跳转中途使用了重定向,数据无法读取。
session
会话对象。会话是用户访问服务器时的某个时间段。
共享数据区域范围在这个时间段内,默认30分钟。
如果在指定时间内没有操作或销毁会话时,数据无法读取。
application
项目对象。共享数据区域范围为整个项目。
作用域范围
application > session > request > pageContext
以上四个作用域对象,都有这几个方法
//将某个对象obj保存到作用域中,命名为str
作用域对象.setAttribute(String str,Object obj);
//从某个作用域中获取保存的某个对象
Object obj = 作用域对象.getAttribute(String str);
//从某个作用域中移除某个保存的对象
作用域对象.removeAttribute(String str);作用域对象的使用
在JSP页面中
作用域对象也称为内置对象,直接通过对应的单词使用
p1.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
//在jsp中使用pageContext页面上下文对象,跳转到p2时不能使用
pageContext.setAttribute("str","保存在pageContext作用域中的字符串");
//在jsp中使用request请求对象,请求转发到p2时可以使用,重定向到p2时不能使用
request.setAttribute("str","保存在request中的字符串");
//在jsp中使用session会话对象,在默认的30分钟内,没有销毁,哪种跳转都能在p2中使用
session.setAttribute("str","保存在session中的字符串");
//在jsp中使用application应用程序对象,整个项目中任何页面都能使用
application.setAttribute("str","保存在application中的字符串");
//以上四个作用域对象,也是jsp中的内置对象,无需定义
//销毁会话
//session.invalidate();
//使用请求转发跳转到p2.jsp
//request.getRequestDispatcher("p2.jsp").forward(request,response);
//使用重定向跳转到p2.jsp
response.sendRedirect("p2.jsp");
%>
<h1><%=pageContext.getAttribute("str")%></h1>
</body>
</html>p2.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3><%=pageContext.getAttribute("str")%></h3>
<h3><%=request.getAttribute("str")%></h3>
<h3><%=session.getAttribute("str")%></h3>
<h3><%=application.getAttribute("str")%></h3>
</body>
</html>在servlet中使用
pageContext
servlet本身就是一个java类,在类中定义成员变量,就能在当前类中使用。
所以在servlet中不会使用pageContext对象
request
使用doGet/doPost/service方法中的HttpServletRequest参数req
session
//在servlet中使用session,需要通过请求对象request调用getSession()方法
HttpSession session= req.getSession();application
//通过getServletContext()方法获取的ServletContext类型对象,就是当前项目对象
ServletContext application = getServletContext();总结
在jsp页面中使用pageContext保存的数据,只能共享于当前页面
通常在servlet中查询后的数据保存在request中,使用请求转发跳转到其他页面,在对应的页面中数据数据
通常在登录后,将登录的用户保存在session中,无论用哪种方式跳转,都能从session中获取当时登录的用户。
在application中保存一些共享于整个项目中的数据
EL
Expression Language 表达式语言
是为了使JSP写起来更加简便,替换JSP中的<%=%>,简化了JSP页面中输出数据的操作。
主要输出保存在某个作用域中的数据。
特点
如果通过"某个作用域对象.setAttribute("cus",customer)"方法保存的对象,
在JSP页面中如果用表达式,使用<%=cus%>,如果用EL,使用**${cus}**输出。
会依次从pageContext-->reqeust-->session-->application中获取指定对象,
如果一旦从某个作用域中获取到了指定对象,就不再判断后续作用域。
也可以输出指定作用域中的对象。
只能输出保存在作用域中的对象
减少代码(省去了获取对象、转换的过程)
免去非空判断
如果某个要输出的对象不存在,不会输出null,而是输出空字符串""。
使用
在页面中输出保存在作用域中的对象
从作用域中依次查询并输出对象
${对象名}从指定作用域中输出对象
作用域 | 对应作用域 | 代码 |
pageScope | 当前页pageContex | ${pageScope.对象} |
requestScope | 请求request | ${requestScope.对象} |
sessionScope | 会话session | ${sessionScope.对象} |
applicationScope | 项目application | ${applicationScope.对象} |
输出对象的属性
${对象名.属性名}
${对象名["属性名"]}输出对象的方法返回值
${对象名.方法名()}如在servlet中
Person p = new Person("admin","男",20);
request.setAttribute("p",p);跳转到某个页面中
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<%-- 如果不用EL,先获取对象,向下转型 --%>
<% Person p =(Person) request.getAttribute("p");%>
<%-- 如果p为null,会报错,如果name没有赋值,会输出null --%>
<h3>
<%=p.getName()%>;
</h3>
<%--如果使用EL,无需获取对象,无需转型,直接通过保存的对象名.属性名即可--%>
<h3>
${p.name}
</h3>
<%--使用EL输出对象的属性时,该对象必须要有getXX()方法--%>
<%--如果没有在任何作用域中获取到对象p,或对象p没有name属性,不会保存,输出空字符串--%>
<h3>
${p["name"]}
</h3>
</body>
</html>在页面中获取请求中的参数
用于获取表单提交的数据或超链接?后传递的数据。
使用${param.参数名}替换request.getParameter("参数")。
如有表单或超链接
<form action="page.jsp">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>
<a href="page.jsp?username=admin">跳转</a>在page.jsp中获取
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<%-- 传统写法--%>
<% String username = request.getParameter("username");%>
<h3>
<%=username%>;
</h3>
<%--如果使用EL--%>
<h3>
${param.username}
</h3>
</body>
</html>用于获取当前项目上下文(根目录+项目名)路径
如http://localhost:8080/Web03/就是一个项目上下文路径,
在JSP中使用**${pageContext.request.contextPath}**获取项目上下文路径
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/servlet映射">
</form>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/页面路径">超链接</a>注意
web.xml版本在4.0之后,在JSP中使用EL时,默认可以识别。
如果JSP无法识别EL,在指令(<%@ %>)中加入 isELIgnored="false"表示不忽略EL。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isELIgnored="false"%>如果在使用EL过程中,出现PropertyNotFoundException异常,表示未发现指定属性,原因有
缺少指定属性
指定属性没有对应的get方法
JSTL
Java Server Page Standarded Tag Library JSP标准标签库
可以使用JSTL中的特定标签,来替换JSP中常见的Java代码。如循环判断等,减少Java代码,提高页面的可读性。
使用
1.导入JSTL对应的依赖
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/jstl/1.2
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>2.在JSP页面中,加入标签库指令
<%--在当前页面中使用jstl,加入以下指令--%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>这句话可以不写,在使用循环遍历时会自动生成。
3.具体用法
定义变量或给变量赋值
<c:set var="变量名" value="值"></c:set>如
<c:set var="num" value="123123"></c:set>if判断
<c:if test="判断条件">
满足条件时的内容
</c:if>如在servlet中
request.setAttribute("person",new Person("ez","男"));在Jsp中
<c:if test="${person.sex=='男'}">
<input type="raido" name="sex" checked>男
<input type="raido" name="sex" >女
</c:if>遍历List集合
<c:forEach items="要遍历的集合" var="遍历出的对象名"></c:forEach>如servlet中保存了集合
List<BookInfo> list = dao.queryAll();
request.setAttribute("list",list);在jsp页面中
<%--判断集合为空--%>
<c:if test="${empty list}">
无数据
</c:if>
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="bi">
<tr>
<td>${bi.bookName}</td>
<td>${bi.bookAuthor}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>遍历Map集合
<c:forEach items="要遍历的集合名" var="遍历出的键值对的名称">
${键值对名.key.属性}
${键值对名.value.属性}
</c:forEach>如
<%
HashMap<String,String> hm=new HashMap();
hm.put("yyds","永远单身");
hm.put("xswl","吓死我了");
hm.put("pyq","朋友圈");
session.setAttribute("hm",hm);
%>
<c:forEach items="${hm}" var="kv">
<!--遍历键-->
<h3>${kv.key}</h3>
<!--遍历值-->
<h3>${kv.value}</h3>
</c:forEach>Ajax
Asynchronous Javascript And XML
异步JavaScript和XML
一种数据交互方式,请求和响应是异步的。
使用ajax能实现在整个页面不重新加载的情况下,更新局部内容。
使用
浏览器都是支持异步提交,原生的JavaScript就能实现ajax,但使用极不方便,所以都是使用jquery封装后的**$.ajax()**或$.get() $.post()等函数。
1.在页面中导入jquery文件
<!--使用Ajax,需要导入jquery-->
<script src="jquery文件路径"></script>2.在script标签中写ajax
<script>
某个节点.事件(function(){
//使用ajax异步提交数据
$.ajax({
//访问的URL地址
url:"servlet映射或具体url",
//提交的数据
data:{
//键:值
"形参":值,
"形参":值
},
//提交方式
type:"get/post/put/delete",
//成功访问URL后的回调函数
success:function(res){//res表示访问URL后返回的数据
},
//访问URL失败时的回调函数
error:function(){
}
});
});
</script>JSP内置对象
在jsp页面中有一些对象是已经定义好了可以直接使用的,称为内置对象。
一共有9个内置对象。
"rrppsoace"
request
请求作用域对象
response
响应对象
pageContext
当前页作用域对象
session
会话作用域对象
page
当前jsp页面对象
out
输出对象
application
项目作用域对象
config
配置对象
exception
异常对象
Session和Cookie
这两个都是用于保存数据的对象。
session是一个作用域对象,在servlet中通过request.getSession()获取,在JSP中直接使用内置对象session获取。
cookie是一个对象,也是一个文件,保存在本地。
Cookie
cookie通常用于更长时间地保存一些信息,即便关闭浏览器,也能保存。
cookie的创建
//创建cookie
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("username", "保存在cookie中的用户名");
//设置有效时长,单位为秒,这里表示7天有效
cookie.setMaxAge(60*60*24*7);
//通过响应对象response保存cookie对象到本地
response.addCookie(cookie);cookie的获取
//读取cookie时是获取当前站点的所有cookie数组
Cookie[] cks = request.getCookies();
//遍历
for(Cookie ck :cks){
System.out.println( ck.getName()+"--"+ck.getValue());
}Session
session是一个作用域对象,在访问任意jsp页面时,默认就会创建一个session对象(可以通过设置取消自动创建)。
通常使用session保存一些信息,用于在同一站点的各个页面之间共享数据。
原理:
1.当访问的jsp页面或servlet中使用了session,会创建一个JSESSIONID(session编号),这是一个字符串,保存在一个cookie中。
默认访问某个jsp页面时,该页面中没有使用session,也会自动创建session,因为
<%--默认每个jsp页面都有这句话,表示访问该页面时,自动使用session--%>
<%@ page session="true"%>如果将其设置为false,访问该jsp时则不会自动创建session。
2.再次访问该页面时,会查询该JSESSIONID是否存在,如果存在,直接使用,如果不存在,创建新的JSESSIONID
3.保存该JSESSIONID的cookie会随着浏览器的关闭自动销毁,所以关闭浏览器,session就会失效。
session对象的常用方法
常用方法 | 作用 |
session.setAttribute(String str,Object obj) | 将obj对象保存在session中,命名为str |
session.getAttribute(String str) | 获取保存在session中的对象 |
session.removeAttribute(String str) | 移除保存在session中的对象 |
session.invalidate() | 销毁session |
session.getCreationTime() | 获取session创建时间对应的毫秒数 |
session.getId() | 获取JSESSIONID |
session.getMaxInactiveInterval() | 获取session有效时长(默认1800秒) |
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(int seconds) | 设置session有效时长,参数为秒 |
ServletContext app = session.getServletContext(); | 获取当前application对象 |
设置全局session有效时长
在指定时间内,打开浏览器但对session无操作,就会自动销毁session。
通过session.setMaxInactiveInterval(int seconds)设置有效秒数
在web.xml中配置
<!--设置全局session配置-->
<session-config>
<!--session有效时长,单位为分钟-->
<session-timeout>15</session-timeout>
</session-config>Session和Cookie对比
session中保存的是对象Object,cookie中保存的是字符串String,都以键值对的形式保存
session保存在浏览器和服务器端,cookie保存在浏览器
session保存的数据没有大小限制,cookie保存的数据有大小限制,不超过3KB
session在30分钟内没有访问或随着浏览器的关闭而销毁,cookie可以设置销毁时间
监听器Listener
对于项目的某个操作进行监听,这个操作可以是创建或销毁application、session,发送请求、得到响应。
用于在执行某个操作时,通过监听器同时再执行其他操作,如记录日志、统计站点人数等。
常用的三个监听器接口
ServletContextListener application监听器
HttpSessionListener session监听器
ServletRequestListener request监听器 实现一个监听器
1.创建一个类,实现某个监听器接口
2.重写某个监听器接口中方法
初始化的方法
销毁的方法
3.在web.xml中配置监听器或通过注解配置
如果在web.xml中配置
<!--配置监听器-->
<listener>
<!--设置监听器的全限定名-->
<listener-class>com.hqyj.bookShop.listener.MyListener</listener-class>
</listener>如果通过注解配置,在自定义的监听器类上,加入@Web
package com.hqyj.bookShop.listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequestEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
/*
* 监听器
* 1.创建一个类,实现某个或多个监听器接口
* 2.重写方法
* 3.在该类上加入@WebListener注解或在web.xml中配置监听器
* */
@WebListener
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener,HttpSessionListener, ServletRequestListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("监听到项目初始化");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("监听到项目销毁");
}
@Override
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("监听到请求销毁");
}
@Override
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("监听到发送请求");
}
@Override
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {
System.out.println("监听到session创建");
}
@Override
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {
System.out.println("监听到session销毁");
}
}过滤器Filter
使用
1.创建一个类,继承HttpFilter
2.重写其中受保护的doFilter的方法
3.在web.xml中配置过滤器或使用注解配置
在web.xml中配置的话
<!--声明过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.hqyj.filter.MyFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--设置什么请求要经过该过滤器,通常过滤所有请求-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<!--/*表示过滤所有请求-->
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>使用@WebFilter("/*")注解配置的话
package com.hqyj.filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
* 自定义一个过滤器
* 1.继承HttpFilter
* 2.重写受保护的doFilter方法
* 3.web.xml中配置该过滤器
* */
//@WebFilter("/*")
public class MyFilter extends HttpFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilter(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//由于设置了过滤所有请求,所以在这里设置请求的编码格式
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//获取请求的地址后,决定是否放行
String uri = req.getRequestURI();
System.out.println(uri+"试图访问");
//判断地址中是否包含登录页或登录页相关的servlet映射或资源路径
if (uri.contains("login")|| uri.contains("customer")||uri.contains("jquery")) {
//允许放行
chain.doFilter(req,res);
return;
}
//如果登录成功,会在session中保存customer,所以在这里判断session中是否存在customer,如果存在,放行一切请求
if(req.getSession().getAttribute("customer")==null){
res.sendRedirect("http://localhost:8080/Web03/pages/login.html");
}else{
//允许放行
chain.doFilter(req,res);
}
}
}Web项目开发模式
Model1
JSP+JavaBean模式。
JSP负责渲染数据和处理页面。
JavaBean是一个满足以下条件的类
被public修饰
其中的属性进行封装
用private修饰属性
提供get/set方法
有无参数的构造方法
这种模式,不适合复杂项目的开发。
jsp既要显示内容,又要处理数据,后期维护扩展不方便。

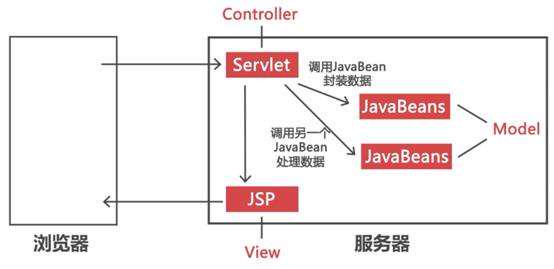
Model2(MVC)
MVC模式:模型-视图-控制器模式。
M:Model模型 用于封装数据处理数据,对应业务逻辑类、数据访问类、实体类
V:View视图 用于渲染数据,对应页面(jsp或html)
C:Controller控制器 用户调度用户请求,对应servlet
这种模式适合复杂项目的开发。
每个模块各司其职,耦合性低。
对于后期维护和扩展较为方便。




 这篇博客详细梳理了JavaWeb后端开发中的关键概念和技术,包括B/S与C/S模式、网络服务器、Tomcat的目录结构、Maven的使用、Servlet的编写步骤、HTTP状态码、JSP的组成和跳转、数据分页查询、作用域对象的使用、EL表达式和JSTL。还涵盖了数据提交、会话管理、监听器、过滤器以及Web开发模式的介绍。
这篇博客详细梳理了JavaWeb后端开发中的关键概念和技术,包括B/S与C/S模式、网络服务器、Tomcat的目录结构、Maven的使用、Servlet的编写步骤、HTTP状态码、JSP的组成和跳转、数据分页查询、作用域对象的使用、EL表达式和JSTL。还涵盖了数据提交、会话管理、监听器、过滤器以及Web开发模式的介绍。
















 855
855

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








