1 spring介绍
Spring框架是一个开源的Java平台,广泛用于构建各种类型的应用程序。自2003年首次发布以来,Spring已经成为了Java企业级开发的事实标准之一。它提供了一个全面的编程和配置模型,旨在简化现代Java应用开发,特别是企业级应用。
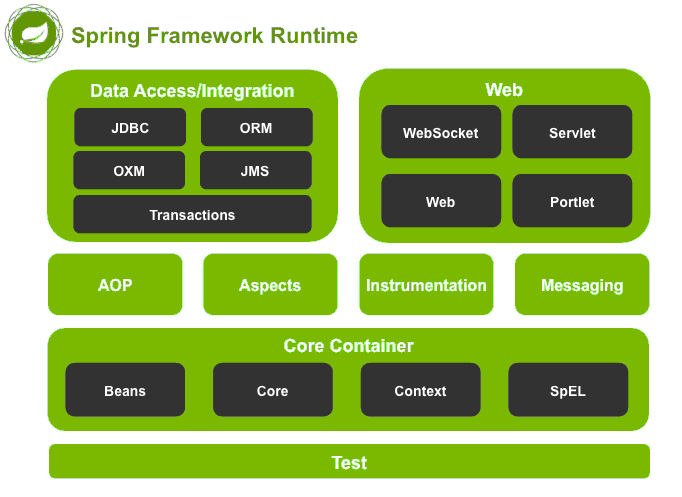
Spring框架已经成为Java企业级应用开发的基石。它以其强大的功能、灵活性和模块化而著称,为开发现代Java应用程序提供了一个坚实的基础。随着不断的更新和社区的发展,Spring继续保持其在企业级Java开发中的领导地位,不断推动Java生态系统的发展。
1.1 核心特性
-
轻量级和最小侵入性: Spring是轻量级的,不会强迫使用特定的编程模型,旨在尽可能减少对应用代码的侵入。
-
依赖注入(DI): Spring的核心是依赖注入容器,它管理应用中的组件(称为beans),并通过构造器、工厂方法或属性来组装它们的依赖关系。
-
面向切面编程(AOP): 支持面向切面编程,将如事务管理、日志记录等横切关注点与业务逻辑分离。
-
模块化: Spring具有模块化结构,允许开发者根据需求选择和使用不同的模块。
-
事务管理: 提供了一致的事务管理接口,支持声明式事务管理。
-
MVC框架: Spring MVC提供了一个丰富的模型-视图-控制器(MVC)框架,用于构建Web应用程序。
-
数据访问与集成: 提供了对JDBC、Hibernate、JPA等数据访问技术的支持,简化了数据库操作。
1.2 架构和组件
-
核心容器: 包含依赖注入(DI)容器,是Spring框架的基础部分。
-
数据访问/集成层: 包括JDBC、ORM、OXM、JMS和事务模块,用于简化数据库交互。
-
Web和MVC层: 提供了构建Web应用程序的基础,包括Spring MVC和Spring WebFlux。
-
AOP和设备支持: 提供了面向切面编程的实现,以及对消息传递、邮件、任务调度、JMX的支持。
-
测试模块: 提供了测试Spring组件的工具,支持JUnit和TestNG。
1.3 使用Spring框架
-
应用程序开发: 开发者可以使用Spring来构建从简单的独立应用程序到复杂的企业级应用程序。
-
配置: Spring提供了基于XML、注解和Java的配置选项。
-
集成: Spring可以与许多其他技术和框架集成,包括Web服务、消息传递服务和持久化技术。
1.4 性能优化
-
轻量级设计: Spring的轻量级设计意味着对内存和其他资源的消耗相对较小。
-
单例Beans: 默认情况下,Spring中的Beans是单例的,这减少了对象创建的开销。
-
代理和索引: 在AOP和DI中使用代理和索引技术,优化了性能。
1.5 安全性和事务管理
-
Spring Security: 提供了一个全面的安全解决方案,用于认证和授权。
-
声明式事务管理: 支持声明式事务管理,简化了事务管理代码。
1.6 社区和生态系统
-
强大的社区: 拥有活跃的开发者社区,提供支持、文档和大量的资源。
-
扩展和插件: 社区贡献了大量的扩展和插件,进一步丰富了Spring的功能。
-
与其他框架的集成: 与如Hibernate、Quartz、Kafka等其他流行框架的集成,扩展了其在不同领域的应用。
2 Spring自定义注解加载和使用
在工作中经常使用Spring的相关框架,免不了去看一下Spring的实现方法,了解一下Spring内部的处理逻辑。特别是开发Web应用时,我们会频繁的定义@Controller,@Service等JavaBean组件,通过注解,Spring自动扫描加载了这些组件,并提供相关的服务。
Spring是如何读取注解信息,并注入到bean容器中的,本文就是通过嵌入Spring的Bean加载,来描述Spring的实现方法。
2.1 自定义注解
先看一个最简单的例子,在使用SpringWeb应用中的过程中,大家免不了会使用@Controller,@Service,@Repository等注解来定义JavaBean。那么怎么自己定义一个注解,Spring可以自动加载呢。所以就有了第一个例子。
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface MyComponent {
String value() default "";
}
@Configuration
public class ComponentAnnotationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(ComponentAnnotationTest.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
InjectClass injectClass = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(InjectClass.class);
injectClass.print();
}
@MyComponent
public static class InjectClass {
public void print() {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
}
运行这个例子,就会发现,@MyComponent 注解的类,也被Spring加载进来了,而且可以当成普通的JavaBean正常的使用。查看Spring的源码会发现,Spring是使用ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider扫描package,这个类有这样的注释
A component provider that scans the classpath from a base package.
It then applies exclude and include filters to the resulting classes to find candidates.
这个类的 registerDefaultFilters 方法有这样几行代码
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
这里就会发现Spring在扫描类信息的使用只会判断被@Component注解的类,所以任何自定义的注解只要带上@Component(当然还要有String value() default "";的方法,因为Spring的Bean都是有beanName唯一标示的),都可以被Spring扫描到,并注入容器内。
2.2 定制功能
但上面的方法太局限了,没办法定制,而且也没有实际的意义。如何用特殊的注解来实现定制的功能呢,一般有两种方式:
- 还是用上面的方法,在注入Spring的容器后,再取出来做自己定制的功能,Spring-MVC就是使用这样的方法。AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping 中的detectHandlers方法,这个方法取出了所有的bean,然后循环查找带有Controller的bean,并提取其中的RequestMapping信息
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for.
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
// URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler.
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified");
}
}
}
}
- 不依赖@Component,自定义扫描。所以就有了第二个例子。
2.3 自定义扫描
结构比较复杂,这里是关键的几个类
- 还是定义一个注解,只不过不再需要@Component了
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CustomizeComponent {
String value() default "";
}
- 注解修饰的类
@CustomizeComponent
public class ScanClass1 {
public void print() {
System.out.println("scanClass1");
}
}
- BeanScannerConfigurer用于嵌入到Spring的加载过程的中,这里用到了BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和ApplicationContextAware。
Spring提供了一些的接口使程序可以嵌入Spring的加载过程。这个类中的继承ApplicationContextAware接口,Spring会读取ApplicationContextAware类型的的JavaBean,并调用setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)传入Spring的applicationContext。
同样继承BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,Spring会在BeanFactory的相关处理完成后调用postProcessBeanFactory方法,进行定制的功能。
@Component
public static class BeanScannerConfigurer implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.scan("org.wcong.test.spring.scan");
}
}
- Scanner继承的ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner是Spring内置的Bean定义的扫描器。
includeFilter里定义了类的过滤器,newAnnotationTypeFilter(CustomizeComponent.class)表示只取被CustomizeComponent修饰的类。
doScan里扫面了包底下的读取道德BeanDefinitionHolder,自定义GenericBeanDefinition相关功能。
public final static class Scanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner {
public Scanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
public void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(CustomizeComponent.class));
}
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
definition.getPropertyValues().add("innerClassName", definition.getBeanClassName());
definition.setBeanClass(FactoryBeanTest.class);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
public boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
return super.isCandidateComponent(beanDefinition) && beanDefinition.getMetadata()
.hasAnnotation(CustomizeComponent.class.getName());
}
}
- FactoryBean是Spring中比较重要的一个类。它的描述如下
Interface to be implemented by objects used within a BeanFactory which are themselves factories.
If a bean implements this interface, it is used as a factory for an object to expose, not directly as a bean* instance that will be exposed itself
普通的JavaBean是直接使用类的实例,但是如果一个Bean继承了这个借口,就可以通过getObject()方法来自定义实例的内容,在FactoryBeanTest的getObject()就通过代理了原始类的方法,自定义类的方法。
public static class FactoryBeanTest<T> implements InitializingBean, FactoryBean<T> {
private String innerClassName;
public void setInnerClassName(String innerClassName) {
this.innerClassName = innerClassName;
}
public T getObject() throws Exception {
Class innerClass = Class.forName(innerClassName);
if (innerClass.isInterface()) {
return (T) InterfaceProxy.newInstance(innerClass);
} else {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(innerClass);
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptorImpl());
return (T) enhancer.create();
}
}
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
try {
return Class.forName(innerClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
}
}
public static class InterfaceProxy implements InvocationHandler {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("ObjectProxy execute:" + method.getName());
return method.invoke(proxy, args);
}
public static <T> T newInstance(Class<T> innerInterface) {
ClassLoader classLoader = innerInterface.getClassLoader();
Class[] interfaces = new Class[] { innerInterface };
InterfaceProxy proxy = new InterfaceProxy();
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, proxy);
}
}
public static class MethodInterceptorImpl implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("MethodInterceptorImpl:" + method.getName());
return methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
}
}
- main函数
@Configuration
public class CustomizeScanTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(CustomizeScanTest.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
ScanClass1 injectClass = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(ScanClass1.class);
injectClass.print();
}
}
至此一个完整的例子就完成了,这里主要用到了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,ApplicationContextAware,FactoryBean等Spring内置的接口,来嵌入Spring的加载和使用过程,这样就实现了自定义注解,和自定义代理了。







 本文介绍Spring框架中自定义注解的加载方法及其实现原理。通过具体示例展示了如何定义并使用自定义注解,同时深入探讨了Spring内部处理逻辑。
本文介绍Spring框架中自定义注解的加载方法及其实现原理。通过具体示例展示了如何定义并使用自定义注解,同时深入探讨了Spring内部处理逻辑。

















 872
872

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










