1.String类与StringBuffer类
String类
关于 java jDK中内置的一个类:java.Lang. String
1、String表示字符类型,属于引用数据类型,不属于基本数据类型。
2、在java中随便使用双引号括起来的都是String对象。例如:“abc”,“def”," hello world!",这是3个 String对象。
3、java中规定,双引号括起来的字符,是不可变的,也就是说"abc"自出生到最终死亡,不可交,不能变成“abcd",也不能变成”ab“
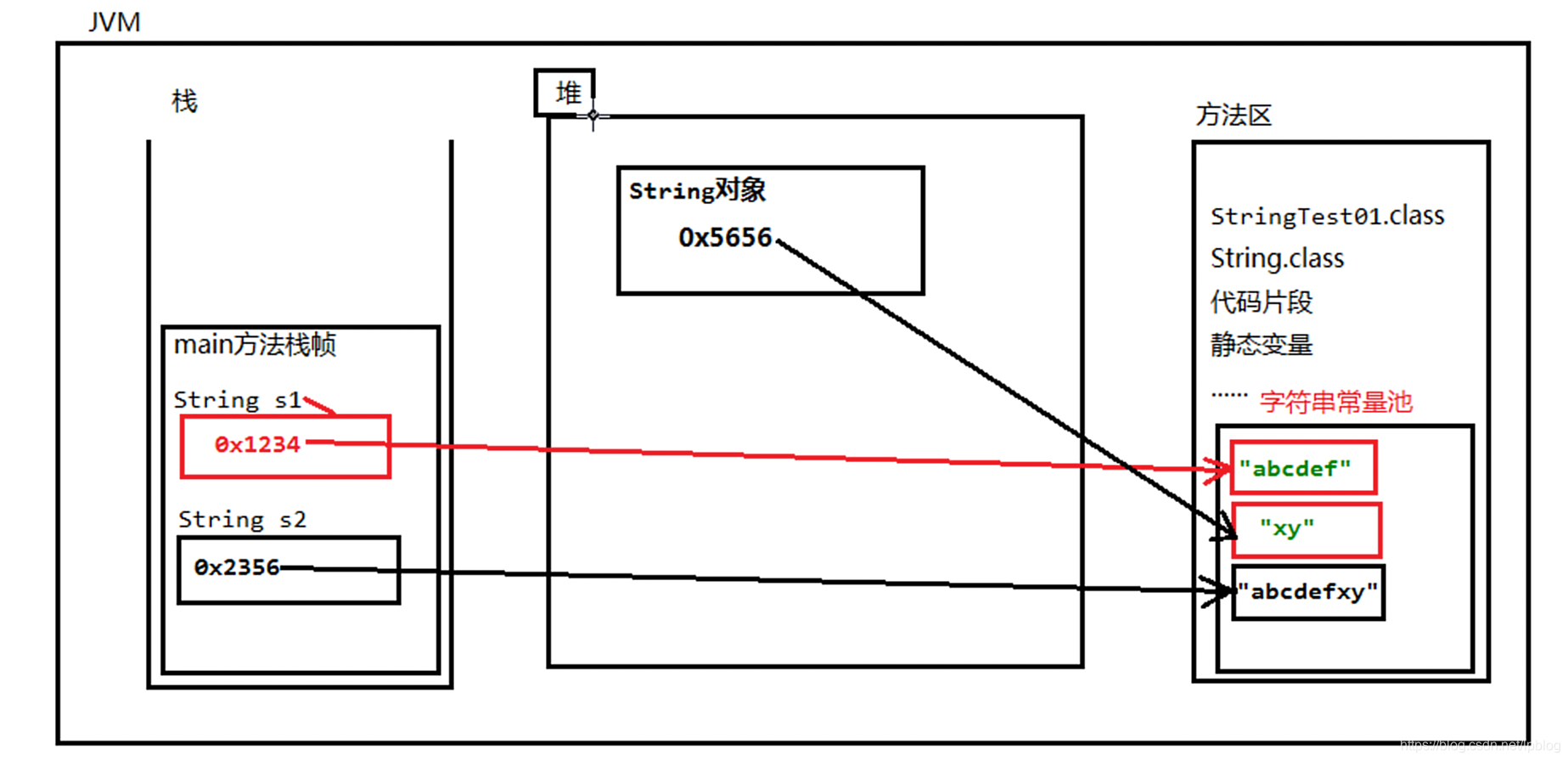
4、在jDK当中双引号括起来的字符串,例如:“abc”"def"都部是直接存在方法的字符串常量池当中的
为什么SUN公司把字符申存倍在一个字符串常量池当中呢。因为字符在实际的开发中使用太频繁。为了执行效率所以把字符放到了方法区的宇符常量池当中。
一.举例(内存图)
case1
public class StringTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="abcdef";
String s2="abcdef"+"xy";
String s3=new String("xy");
}
}
case2
package com.bjpowernode3;
public class User {
int id;
String name;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class UserTest {
User user=new User(110,"张三");
}

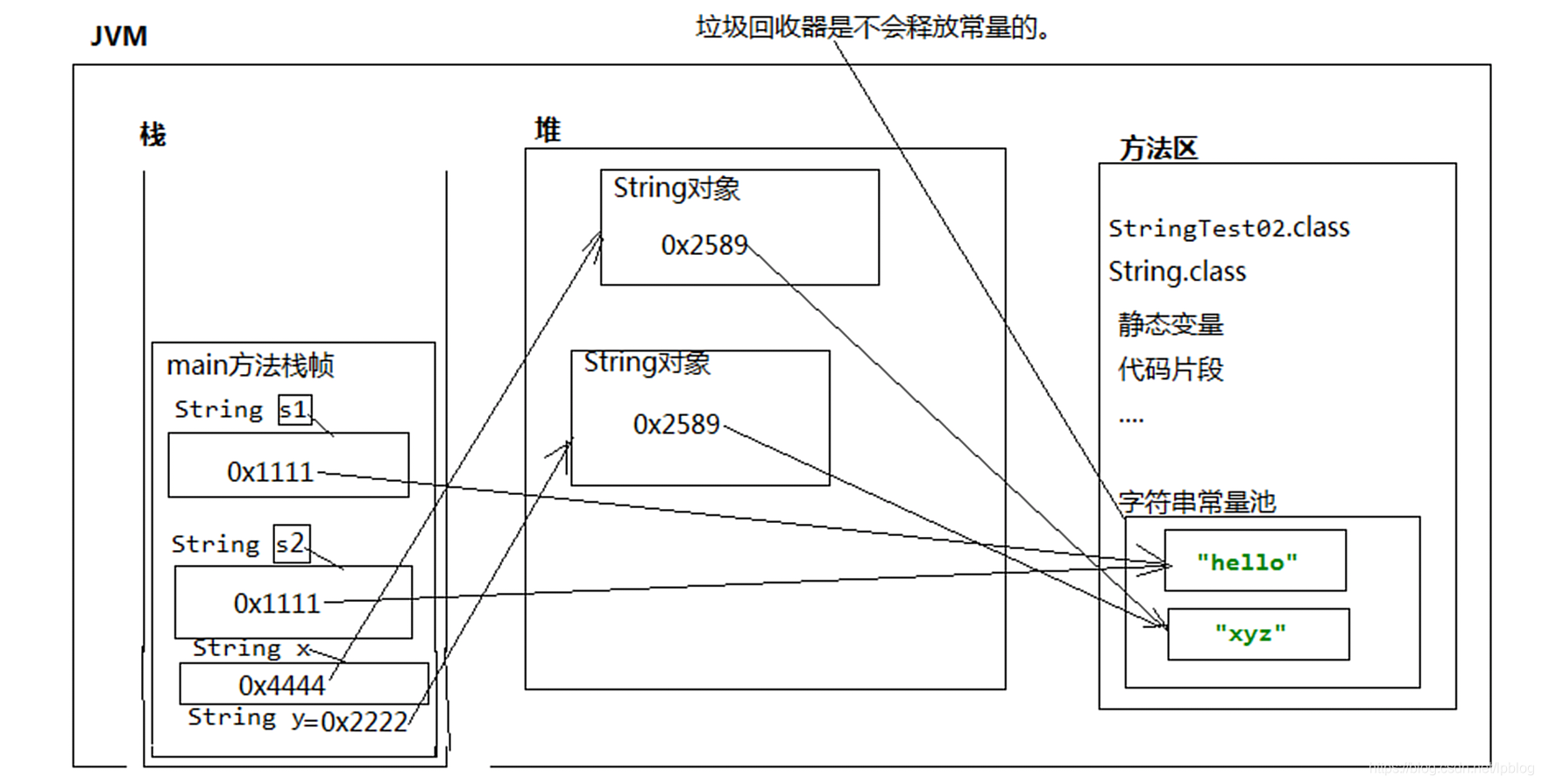
case3
string类new先在堆区创建对象,再由堆区中String类保存的地址指向方法区的字符串常量,所以在s1和s2直接比较时,两x,y在堆区保存的对象地址不一样,但是方法区中字符串常量区地址一样,所以String类equals方法是true
public class StringTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="hello";
String s2="hello";
System.out.println(s1==s2);
String x=new String("xyz");
String y=new String("xyz");
System.out.println(x==y);
System.out.println(x.equals(y));
}
}
true
false
true
StringBuffer类
无论String还是StiringBuffer底层都是一个byte数组(jdk1.8为char[]数组),他们的内存结构是相似的,底层都是char[] 或byte[]数组保存在字符串常量池(方法区),只是前者是final关键字修饰,后者不是final修饰且开辟了数组长度为16的数组.字符串缓冲区在堆区,但是他们都是保存字符串常量池的地址。StringBuffer无参构造时候是长度16,有参则是当前字符串长度+16,如果超过则创建新的字符串。同理数组扩容的原理
string、 StringBuffer、 StringBuilder三者的异同?
string:不可变的字符序列;底层使用char[]存储
StringBuffer:可变的字符序列;线程安全的,效率低;底层使用char[]存储
StringBuilder:可变的字符序列;jdk5.新增的,线程不安全的,效率高;底层使用char[存储
源码分析:
String str =new String (); //char[] value new char[0];
String str1 =new String("abc");//char[] value new char[]{'a','b','c'}
StringBuffer sb1= new StringBuffer();//char[] value= new char[16];底层创建了一个长度为16的数组
sb1 append('a');//value[0]='a'
sb1. append('b');//value[1]='b'
String Buffer sb2 = new StringBuffer ("abc");
//char[] value = new char["abc"Length()+16]
问题1. System. out. println (sb2.Length(); //3
问题2.扩容问题:如果要添加的数据底层数组盛不下了,那就需要扩容底层的数组。
默认情况下,扩容为原来容量的2倍+2,同时将原有数组中的元素复制到新的数组中
举例
public class StringBufferTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer("abc");
stringBuffer.append("abc");
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append('a');
stringBuilder.append("zhangyinying");
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
}
abcabc
azhangyinying
二.String类方法
1.构造方法
String(byte[] bytes)
通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的字节数组构造了一个新的 String。
public String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
String(字节数组,数组元素下标的起始位置,长度)将byte数组中的一部分转换成字符
public String(char[] value)分配一个新的 String,它代表了目前包含在字符数组参数字符序列。字符数组的内容被复制;字符数组的随后的修改不会影响到新创建的字符串。
public String(char[] value,int offset,int count)分配一个包含字符与字符数组数组参数的新 String。的说法是 offset的子阵列的第一个字符的索引和 count参数指定的数组的长度。的子阵列的内容复制的字符数组;随后的修改不影响新创建的字符串。
Parameters:
value阵列是字源
offset -初始偏移
count -长度
public class StringTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] bytes={97,98,99,101};
String s2=new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s2);
String s3=new String(bytes,1,3);
System.out.println(s3);
char []chars={'我','是','一','个','中','国','人'};
//将char数组转换为字符串
String s4=new String(chars);
System.out.println(s4);
//将char数组一部分转换为字符串
String s5=new String(chars,2,3);
System.out.println(s5);
}
}
abce
bce
我是一个中国人
一个中
2.成员方法
charAt方法
public char charAt(int index)返回指定索引的 char价值。指数范围从 0到 length() - 1。第一序列的 char值在指数 0,在指数 1下,等等,作为数组索引。
public class StringTest0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c="中国人".charAt(2);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
人
compareTo方法
Returns:
价值 0如果参数字符串等于这个字符串;值小于 0如果这个字符串是字典序小于字符串参数;和一个值大于 0如果这个字符串的字典序大于字符串参数。
public class StringTest0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c="中国人".charAt(2);
System.out.println(c);
int result="abc".compareTo("abc");
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("bcd".compareTo("bce"));
System.out.println("fdc".compareTo("fdb"));
System.out.println("afc".compareTo("efc"));
//endWith方法
//判断当前字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
System.out.println("dfsafdf".endsWith("f"));
System.out.println("dfsafdf".endsWith("ea"));
System.out.println("dsafdf".endsWith("fdf"));
System.out.println("abc".equals("aBc"));
System.out.println("abc".equalsIgnoreCase("abC"));
/* equals只能看出相等不相等。
compareto方法可以看出是否相等,并且同时还可以看出谁木谁小。*/
}
}
人
0
-1
1
-4
true
false
true
false
true
剩下方法自查表只演功能
public class StringTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//两种写法都可以
String s1 = new String("abcd");
String s3 = "abcdef";
byte[] bytes1 = s3.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes1[i]);
}
int a = s3.indexOf("def");
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println("************************");
//将字符串对象转换成字符数组
byte[] bytes = s1.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
String s2 = new String("cd");
System.out.println("************************");
// 返回指数在这个字符串指定的子字符串中第一个出现的
int a1 = s1.indexOf(s2);
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println("************************");
//判断字符串是否为空字符串
String s = "";
System.out.println(s.isEmpty());
//判断数组长度是length属性,而字符串是length()方法
String s4 = "abc";
System.out.println(s4.length());
//11(掌握).int lastIndexOf(String str)
//判断某个子字符串在当前字符中最后一次出现的索引(下标)
System.out.println("lupengpeng".lastIndexOf("pen"));
// 掌握 String replace( CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
//替换。
// String的父接口就是: Charsequence
String newString = "lupenglupeng".replace("ng", "ying");
System.out.println(newString);
String[] strs = "2001-07-30".split("-");//"2001-07-30”以”-"分符进行拆分。
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strs[i]);
}
System.out.println("************************");
//14(掌握) boolean startswith( String prefix)
//判断某个字符是否以某个子字符开始。
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".startsWith("http"));
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".startsWith("https"));
//15(掌握) String substring(int beginIndex)参数是起始下标。
//截取字符串
System.out.println("zhangyinying".substring(5));
//16(掌握)、 String substring( int beginIndex, int endIndex)
// beginIndex起始位(包括)
// endIndex结束位置
//返回一个字符串,这个字符串的子串。
// 子字符串从指定的 beginIndex延伸在指数 endIndex - 1特征。这样子串的长度是 endIndex-beginIndex。
System.out.println("zhangyinying".substring(5, 11));
System.out.println("************************");
//17(掌握)、 char[] toCharArray()
// /将字符串转换成char数组
char[] chars = "I am Chinese".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i]);
}
//18(掌握) String toLowerCase()
System.out.println("************************");
//转换为小写
System.out.println();
System.out.println("luPEng".toLowerCase());
//转换为大写
System.out.println("luPEng".toUpperCase());
System.out.println("************************");
String s7 = String.valueOf(true);
//21(掌握). String中只有一个方法是静态的,不需要new对象
// /这个方法叫做 valueof
// 作用:将"非字符串"转换成"字符串"
System.out.println(s1);
String s6 = String.valueOf(new Customer());
System.out.println(s6);
}
}
class Customer{
}
97
98
99
100
101
102
3
97
98
99
100
2
true
3
6
lupeyinglupeying
2001
07
30
true
false
yinying
yinyin
I am Chinese************************
lupeng
LUPENG
abcd
com.override.Customer@10f87f48
三.String类已重写equals和toString方法
2.System类与Runtime类
一.System类
在下文时间类提到
二.Runtime类
3.Math类与Random类
一.随机类和高精度
import java.math.BigDecimal;//仅针对高精度数字
import java.util.Random; //产生随机数
public class BigDecimalTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal a1=new BigDecimal(100);
BigDecimal a2=new BigDecimal(200);
System.out.println(a1.add(a2));
Random a3=new Random();
int x=a3.nextInt();
System.out.println(x);
//产生[0-100]间的随机数。不能产生101
//nextInt翻译为:下一个int类型的数据是101,表示只能取到100
int y=a3.nextInt(101);
System.out.println(y);
}
}
61
80
2
99
37
二.枚举类
总结:
1、枚举是一种引用数据类型
2、枚举类型怎么定义,语法是?
enum 枚举类型名{
枚举值1,教举值2
}
public class EnumTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result revalue=divide(10,0);
System.out.println(revalue==Result.SUCCESS?"success":"done");
}
public static Result divide(int a, int b){
try{
int c=a/b;
return Result.SUCCESS;
}
catch (Exception e){
return Result.FAIL;
}
}
}
//枚举:一枚一故可以列举出来的,才建议使用枚举类型。
//枚举也举编译之后也是生成Lass文件。
//枚举是一种引用数据类型。
//枚举中的每一个值可以看做是常量。
enum Result{
SUCCESS,FAIL
}
done
4.包装类
一.概述
虽然Java是面向对象的编程语言,但它所包含的8种基本数据类型却不支持面向对象的编程机制(无属性和方法),Java提供8种基本数据类型是为了常规数据的处理。在Java中,很多方法需要接收引用类型的对象,无法将一个基本类型的值传入,为解决这个问题jdk提供一系列包装类,通过这些包装类可以将基本数据类型的值包装为引用数据类型到底对象.
二.包装类型的描述性实现
public class IntegerTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myint myint=new Myint(100);
IntegerTest01.fuck(myint);
}
public static void fuck(Object obj){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
public class Myint {
int value;
public Myint(){
}
public Myint(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public String toString(){
return String.valueOf(value);
}
}
100
基本数据类型
包装类型
| byte | java. Lang Byte |
|---|---|
| short | java. Lang Short |
| int | java. Lang Integer |
| Long | java. lang Long |
| float | java. Lang FLoat |
| double | java. Lang Double |
| boolean | java. Lang Boolean |
| char | java. Lang Character |
三.装箱和拆箱的概念
public class IntergeTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//123这个基本数据类型,进行构造方法的包装达到了:基本数据类型向引用数据类型的转换。
//基本数据类型-(转换为)->引用数据类型(装箱)
//手动装箱
Integer a=new Integer(123);
Integer a3=new Integer("123");
//Integer a1=new Integer("中文");
//不是一个数中可以包装成 Integer吗?不能。运行时出现异常
// java.Lang.NumberFormatException
//数字格式化异常
//将引用数据类型-(转换为)->基本数据类型(拆箱)
//手动拆箱
float f=a.floatValue();
System.out.println(f);
int b=a.intValue();
System.out.println(b);
//重点方法
// static int parseInt (String s)
//静态方法,传参 String,返回int
//网页上文本框中输入的100实际上是"100"字符串。
// 后台数据库中要求存100数字,此时java程序需要"100"转换成100数字
int reValue=Integer.parseInt("123123");
//int reValue=Integer.parseInt("123123");String 转换为 int
System.out.println(reValue);
// static String toBinaryString (int i)
//静态的:将十进制转换成二进制字符牢。
String binaryString=Integer.toBinaryString(10);
System.out.println(binaryString);
// static String toHexString int i)
//静态的:将十进制转换成十六进制字符串。
///十六进制:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
String hexString=Integer.toHexString(10);
System.out.println(hexString);
//static String toOctalString(int i)
//静态的:捋十进制转换成八进制字符串
String octalString=Integer.toOctalString(10);
System.out.println(octalString);
//valueOf方法作为了解
//static Integer valueOf(int i)
//静态的:int--> Integer
Integer i1=Integer.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(i1);
// static Integer valueOf(String s)
//静态的: String-->Integer
Integer i2=Integer.valueOf("100");
System.out.println(i2);
//int --->String
int i=200;
String s=200+"";
System.out.println(s);
}
}
123.0
123
123123
1010
a
12
100
100
200
四.Integer构造方法
构造方法 Constructor and Description
Integer(int value) 构建了一个新分配的 Integer表示指定的 int价值。
Integer(String s) 构建了一个新分配的 Integer表示 int值表示的 String参数。
public class IntegerTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将数字100转换成Integer包装类型(int--> Integer)
Integer integer=new Integer(100);
//将 String类型的数字,转换成Integer包装类型。( String-> Integer)
Integer integer1=new Integer("123");
}
}
123.0
123
五.通过常量获取最大值和最小值
public class IntegerTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//静态常量
System.out.println("int的最大值"+Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//通过访问包装类的常量,来获取最大值和最小值
System.out.println("int的最小值"+ Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("byte的最大值"+Byte.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("byte的最小值"+Byte.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
int的最大值2147483647
int的最小值-2147483648
byte的最大值127
byte的最小值-128
六.自动拆箱和装箱
在java5之后才支持的新特性
public class IntegerTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//900是基本数据类型
// x1是包装类型
//基本数据类型--(自动转换)-)包装类型:自动装箱
Integer x1=900;
System.out.println(x1);
//x是包装类型
//y是基本数据类型
//包装类型--(自动转换)->基本数据类型:自动拆箱
int y1=x1;
System.out.println(y1);
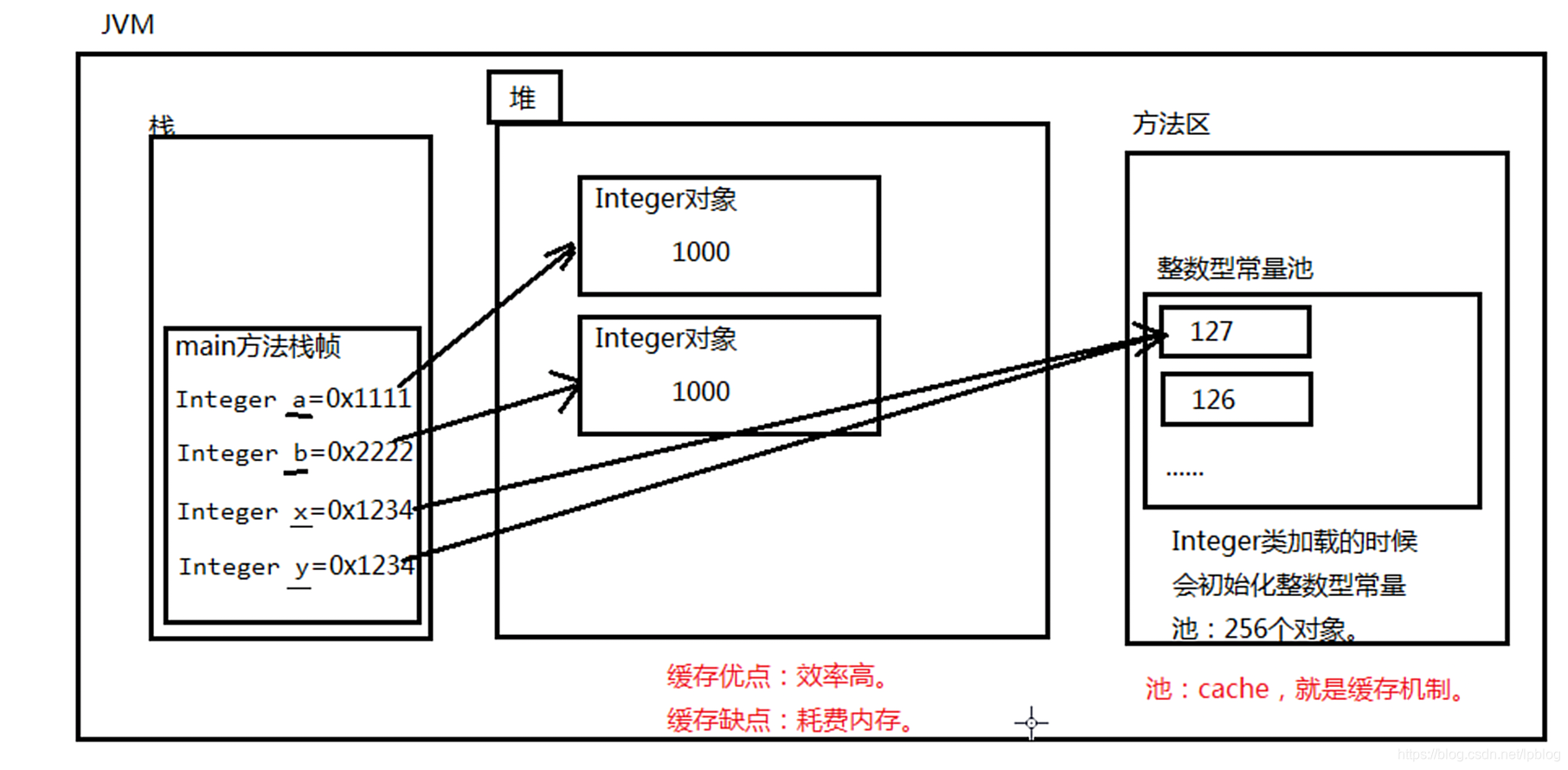
Integer a=1000;//Integer a= new Integer(1000);a是个引用,保存内存地址指向对象。
Integer b=1000;//Integer b= new Integer(1000);b是个引用,保存内存地址指向对象。
Integer x=127;
Integer y=127;
Integer a1=128;
Integer b1=128;
//==比较的是对条的内存地址,a和b两个引用中保存的对内存地址不同。
//==这个运算符不会触发自动拆箱机制(只有+-*/等运算的时候才会。)
System.out.println(a1==b1);
/* java中为了提高程序的执行效率,将-128到127之间所有的包装对是前创建好
放到了一个方法区的整数型常量池当中了,目的是只要用这个区间的数据不需要
new了,直接从整数型常量池当中取出来。
原理:x交量中保存的对的内存地址和变量中保存的对的内存地址是一样的。*/
System.out.println(x==y);
}
}
900
900
false
true
//图中ab分别代表a1和b1
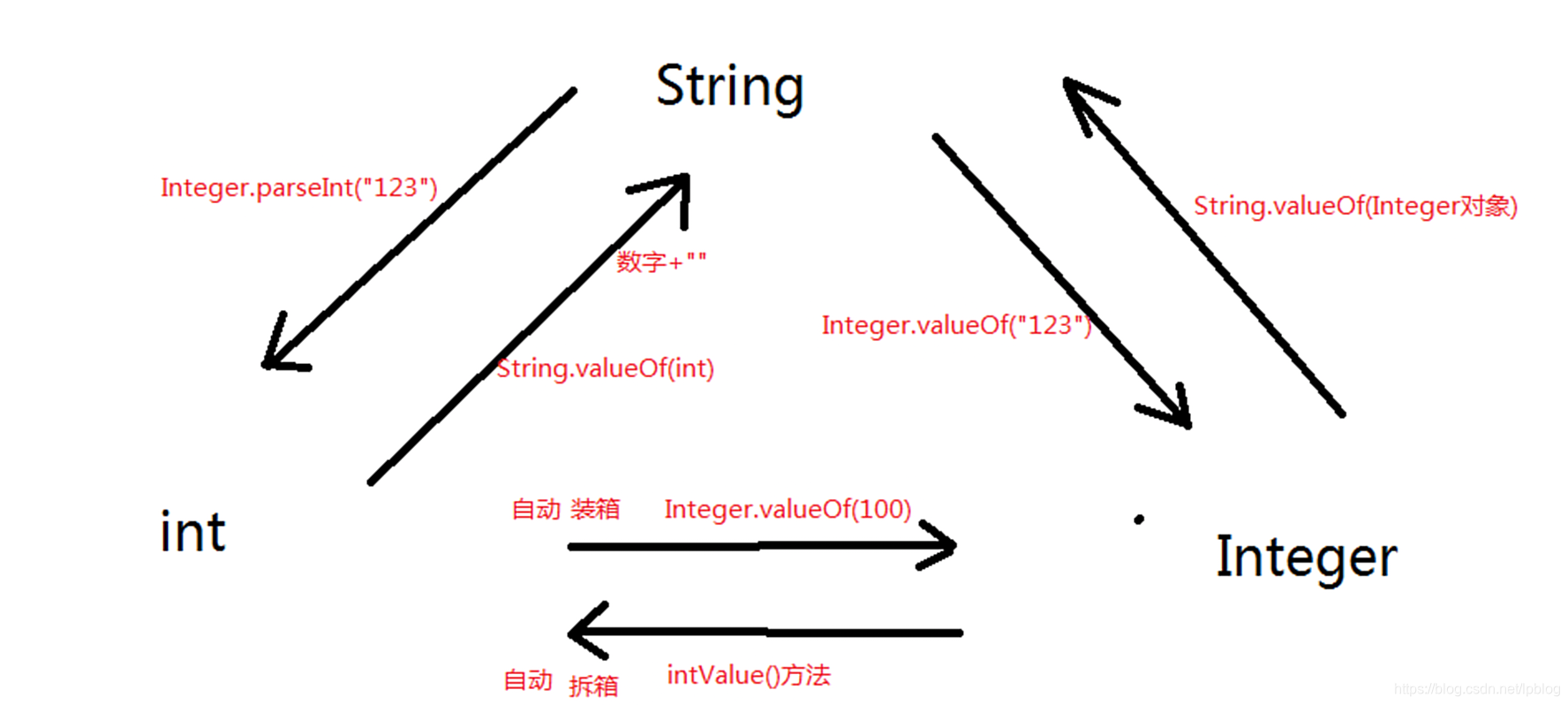
String int Integer类型互换
P142代码实现暂省略17:39
5.日期和时间类
public class DateTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取系绕当前时间(精确到毫秒的系统当前时间)
//接调用无参数构造方法就行。
Date nowTime=new Date();
//java.utiL.Date类的 tostring()方法已经被重写了。
//输出的应该不是一个对的内存地址,应该是一个日期字符串。
//System.out.println(now Time);//Thu Mar 05 10: 51: 06 CST 2020
//日期可以格式化吗?
//将日期类型bate,按照指定的格式进行转换:Date-转换成具有一定格式的日字符- String
// SimpleDateFormat是java,text包下的。专门负责日薊格式化的。
/* yyyy年(年是4位)
MM月(月是2位)
dd 日
HH 时
mm 分
ss 秒
SSS毫秒(毫秒3位,最高999。1000秒代表秒)
注意:在日期格式中,除了y M d H m S S这些字符不能随便写之外,剩下的符号格式白己随意组织。*/
System.out.println(nowTime);
//SimpleDateFormat是格式和语言环境敏感的方式解析一个类的具体日期。
// 可以格式化(日期→文本),分析(文本→日期),和归一化。
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
/* public StringBuffer format(Date date,
StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldPosition pos)
给定的 Date进入日期/时间线和附加的结果给出的 StringBuffer格式。 */
/*String nowTimestr=sdf.format(nowTime);
System.out.println(nowTimestr);*/
System.out.println(sdf.format(nowTime));
}
}
Mon Feb 15 16:05:52 CST 2021
2021-02–15 16:05:52 852
Sat Jan 13 08:08:08 CST 2001
/*简单总结一下 System类的相关属性和方法
System.out [out是 System类的静态变量。]
System.out.println() [println()方法不是System类的,是 Printstream类的方法。
System.gc()建议启动垃级回收器
System. currentTimeMillis()获取自1970年月1日到系统当前时间的总毫秒数。
System.exi(0) 退出JVM*/
public class DateTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取自1970年1月1日00:00:000到当前系统时间的总毫秒数。
long nowTimeMillis=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(nowTimeMillis);
//统计一个方法
//在调用目标方法之前纪录一个毫秒数
long begin=System.currentTimeMillis();
print();
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}
public static void print(){
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
}
1628822551302
i=1
…
=996
i=997
i=998
i=999
耗费时间15ms
6.格式化类
一.日期格式化
上文提到
二.数字格式化
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class DecimalFormatTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//千分位形式即从个位数起,每三位之间加一个逗号,例如,将7654321输出成7,654,321。
DecimalFormat df= new DecimalFormat("###,###.##");
String s=df.format(1234.5678);
System.out.println(s);
DecimalFormat df2=new DecimalFormat("###,###,0000");
String s2=df.format(1234.56);
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
1,234.57
1,234.56























 326
326

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








