一、什么是shell?
shell是linux的一外壳,它包在linux内核的外面,为用户和内核之间的交互提供了一个接口;当用户下达指令给操作系统的时候,实际上是把指令告诉shell,经过shell解释,处理后让内核做出相应的动作;系统的回应和输出的信息也在由shell处理,然后显示在用户的屏幕上。
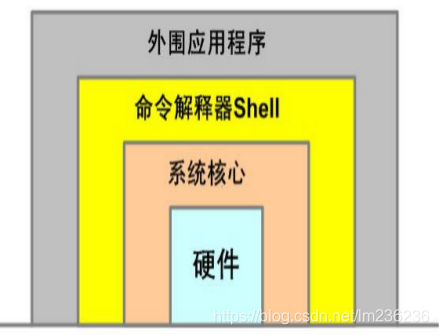
二、什么是shell脚本?
简单的说,当命令或者程序不在命令行执行,而是通过一个程序文件来执行,这个程序就被成为shell脚本。shell脚本里内置了多条命令,语句,循环控制,然后将这些命令一次性执行完毕,这种通过文件执行命令的方式称为非交互式
三、为什么使用shell脚本?
1.适合处理操作系统底层的业务,有众多的系统命令为其做支撑(还有文本处理三兄弟grep,sed,awk)
2.适合处理纯文本文件,linux中许多服务配置文件,启动脚本,都是纯文本(httpd,nfs,mysql,nginx,lvs)
3.linux系统脚本用shell开发更简单
四、如何查看系统默认shell?(企业面试题)
方法1:
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
方法2:
[root@foundation8 mnt]# grep root /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
五、shell脚本的建立
1.第一行:#!/bin/bash
指定解释器:由哪个程序来执行脚本内容
#!:幻数
注意:#!/bin/bash必须写在第一行,否则会被认为是注释
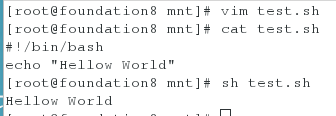
vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello World"
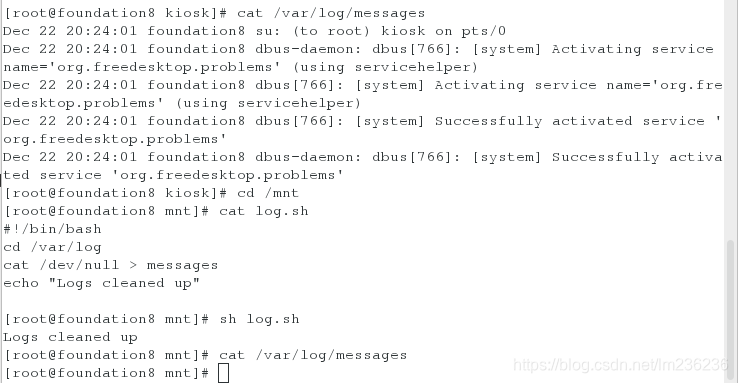
示例:清空/var/log/messages文件
vim log.sh
#!/bin/bash
cd /var/log
cat /dev/null > messages
echo "Logs cleaned up..."
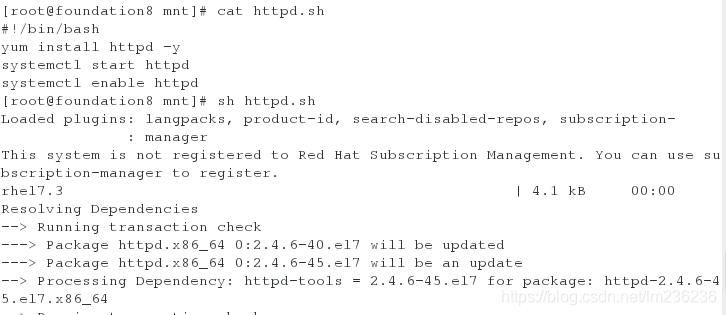
•练习:写一个安装,启动并开机自启动httpd的脚本
vim httpd.sh
#!/bin/bash
yum install httpd -y
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
但是,这个脚本有一些很明显的缺陷
1.没有用户判断,任何用户都可以执行这个脚本
2.没有流程判断,只是把简单的命令进行顺序操作,没有成功与否的判断
六、脚本的执行过程
1.先加载系统环境变量,怎么查看系统环境变量:env
2.一条一条命令执行,遇到子脚本,先执行子脚本,然后返回父脚本继续执行
七、脚本的执行方法
- bash script.sh或者 sh script.sh(当脚本没有执行权限时)
- path/script.sh或者 ./script.sh(绝对路径,或当前目录下,脚本需要有执行权限)
- source script.sh 或者 . script.sh(需要传递变量或函数时使用)
前两种方法执行 shell 脚本时都是在当前 shell 环境下又开了一个子 shell 环境,当脚本执行完后,子 shell 环境立刻就会关闭,而方法三是在当前 shell 环境下执行的。
举例:
[root@desktop8 脚本]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
username=`whoami`
[root@desktop8 脚本]# ll test.sh
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 30 12月 24 06:32 test.sh
[root@desktop8 脚本]# /root/Desktop/脚本/test.sh
-bash: /root/Desktop/脚本/test.sh: Permission denied
[root@desktop8 脚本]# sh test.sh
[root@desktop8 脚本]# echo $username
[root@desktop8 脚本]# source test.sh
[root@desktop8 脚本]# echo $username
root
八、脚本开发规范
1.注释:可以命令后,也可以自成一行
2.脚本信息:
#!/bin/bash
#Date:2018-12-14
#Author:westos-wsp
#Connect:wsp439@sina.com
#Desc:This script is for…
#Version:1.0
3.脚本名:最好以.sh结尾
九、定义变量
[root@foundation8 mnt]# a=hellow
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $a
hellow
[root@foundation8 mnt]# a=redhat-$a
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $a
redhat-hellow
[root@foundation8 mnt]# b='redhat-$a'
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $b
redhat-$a
[root@foundation8 mnt]# c="redhat-$a"
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $c
redhat-redhat-hellow
[root@foundation8 mnt]# a=redhat hellow
bash: hellow: command not found...
[root@foundation8 mnt]# a="redhat hellow"
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $a
redhat hellow
注意:建议没有特别要求时,字符串都加双引号,需要原样输出就加单引号
十、特殊变量
$0:获取脚本文件名,如果执行时包含路径,则输出脚本路径
$n: 传递给脚本的第n个参数值(n为1~9)
$#:传递给脚本的参数个数
$*:传递给脚本的所有参数
@
:
与
@:与
@:与*功能类似
$?:显示最后命令的退出状态(0表示没有错误,其他任何值表明有错误)
$$:当前脚本运行的进程ID号
$0:
[root@desktop8 脚本]# cat test1.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $0
[root@desktop8 脚本]# sh test1.sh
test1.sh
$n:
[root@desktop8 脚本]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $1 $2
[root@desktop8 脚本]# sh test.sh aa bb
aa bb
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo echo \${1..10} > test.sh $需要转义符\
[root@foundation8 mnt]# cat test.sh
echo $1 $2 $3 $4 $5 $6 $7 $8 $9 $10
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {1..10}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 此时看似正确,实际上输出的不是1-10,而文件中的$10也并非$10,而是$1和0,所以看到的效果是正确的效果,可以在下面的例子体现出来。
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {a..z}
a b c d e f g h i a0
$#:
[root@foundation8 mnt]# cat test.sh
echo $#
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {a..z}
26
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {1..10}
10
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {1..100}
100
$*
[root@foundation8 mnt]# cat test.sh
echo $*
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {1..10}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {a..z}
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
$@
[root@foundation8 mnt]# cat test.sh
echo $@
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {a..z}
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh {1..10}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
$?
[root@foundation8 mnt]# date
2018年 12月 24日 星期一 20:27:10 CST
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $?
0
[root@foundation8 mnt]# data
bash: data: command not found...
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $?
127
$$
[root@foundation8 mnt]# cat test.sh
echo $$
[root@foundation8 mnt]# sh test.sh
10957
十一、read用法
[root@foundation8 mnt]# read aa
hello
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $aa
hello
[root@foundation8 mnt]# read -p "请输入一个数:" i
请输入一个数:8
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $i
8
十二、将命令的结果赋值给变量
[root@foundation8 mnt]# a=`date`
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $a
2018年 12月 24日 星期一 20:42:08 CST
[root@foundation8 mnt]# b=$(uptime)
[root@foundation8 mnt]# echo $b
20:42:54 up 6:45, 3 users, load average: 0.12, 0.20, 0.24
练习:将每天的日志打包并以当天的时间命名,时间的格式为 年:月:日
[root@foundation8 mnt]# tar -zcf log_`date +%F`.tar.gz /var/log/
tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
[root@foundation8 mnt]# ls
httpd.sh log_2018-12-24.tar.gz test1.sh test.sh







 本文介绍Linux shell的基础概念,包括shell的定义、shell脚本的作用及其创建与执行方式。讲解了如何利用shell脚本处理操作系统底层业务及纯文本文件,演示了如何通过脚本执行常见系统任务,如清空日志文件和自动化服务安装与启动。
本文介绍Linux shell的基础概念,包括shell的定义、shell脚本的作用及其创建与执行方式。讲解了如何利用shell脚本处理操作系统底层业务及纯文本文件,演示了如何通过脚本执行常见系统任务,如清空日志文件和自动化服务安装与启动。
















 32万+
32万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








